Electric cars, as revealed by research, are generally more environmentally friendly than conventional petrol or diesel vehicles. They produce fewer greenhouse gases and air pollutants, taking into account their entire lifecycle, including production and the electricity used for charging.
This makes electric vehicles a popular and sustainable choice for transportation, offering the potential to reduce emissions and decrease reliance on fossil fuels—electric cars use motors powered by rechargeable batteries, distinguishing them from traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
The continued growth in electric vehicle adoption is expected, with the number of electric vehicle users predicted to triple by 2030 compared to 2011. This anticipated increase is primarily attributed to advancements in battery technology, enhancing vehicle range and performance.
In this article, we will go into the economic and environmental benefits of Electric Vehicles. Let’s delve into them
Environmental Benefits of Electric Vehicles

Energy Efficiency
Electric vehicles (EVs) offer an efficiency rate of 85-90%, substantially improving over conventional internal combustion engines, generally achieving a mere 17-21% efficiency.
This enhanced efficiency reduces energy consumption during journeys and mitigates CO2 emissions, especially considering non-renewable energy sources and the broader energy supply chain.
An in-depth examination of electric vehicle efficiency reveals that Advanced Electric Vehicles (AEVs) like those from Tesla convert 59 to 62 percent of energy into vehicle movement, starkly contrasting to gas-powered cars that struggle to achieve just 17 to 21 percent efficiency. Charging an AEV’s battery emerges as a far more efficient and environmentally friendly means of powering your vehicle compared to filling the gas tank of a traditional car.
Urban Serenity through Noise Reduction
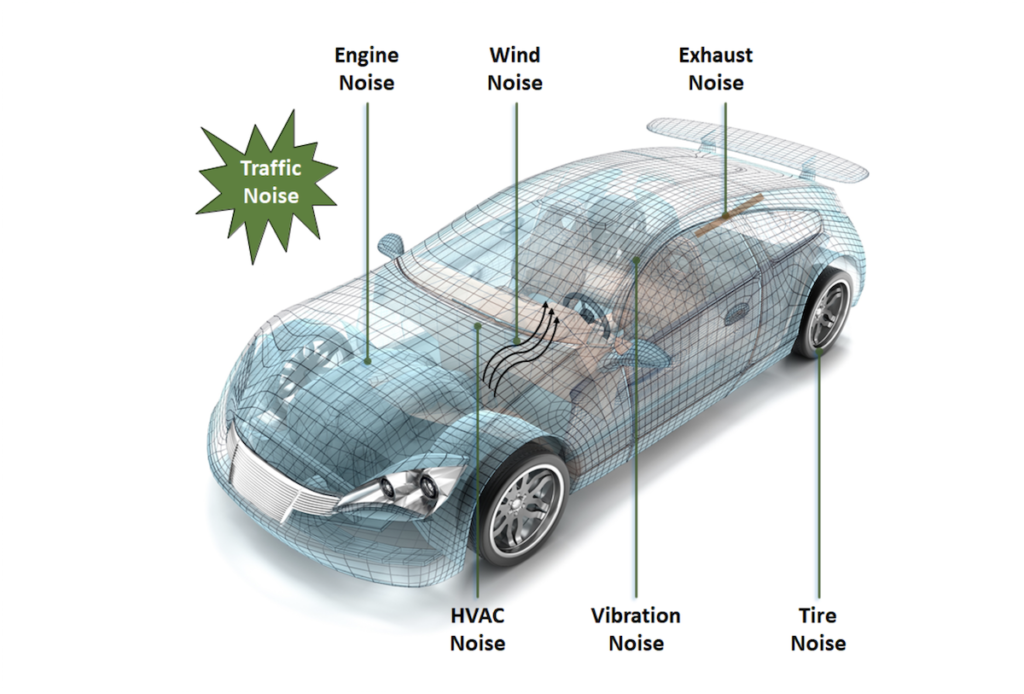
Usually, vehicles contribute to air and noise pollution, but the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) brings about a transformation.
With 55% of the global population residing in urban areas, a number projected to reach 68% by 2050, the benefits of EVs become ever more pronounced.
Unlike conventional vehicles known for their noise emissions, EVs operate almost silently.
The absence of components such as exhaust systems and reciprocating engines in EVs is a critical factor behind their peaceful operation. This silence arises from the point that EVs do not rely on combustion engines, effectively eliminating a primary source of noise pollution in urban environments.
Many EVs also feature specialized tires designed to reduce noise further. Moreover, EVs frequently incorporate regenerative braking systems, which operate quietly compared to traditional braces.
Economic Advantages of Electric Vehicles
Economic Growth and Job Creation

The electric vehicle (EV) sector plays a role in job creation and economic prosperity.
It’s a potent means for employment and growth, bringing about opportunities in various domains, from manufacturing and assembly to battery production and charging infrastructure development.
The production of EVs demands a skilled workforce to craft and assemble components. As the demand for these vehicles grows, companies are compelled to expand their teams, thereby contributing to increased employment.
Additionally, EVs, which run on electricity, require the manufacturing of batteries for energy storage. This process necessitates a substantial workforce. As the electric car market expands, automakers make significant investments in research and development, plant expansions, and workforce expansion, creating numerous jobs across the globe.
According to a report from the International Energy Agency (IEA), the EV industry employs over 3 million individuals worldwide.
This job creation includes various sectors:
- Auto manufacturers hire new employees to produce electric cars and essential components like batteries and motors.
- Companies specializing in electric car charging stations employ technicians to install and maintain charging infrastructure.
- Research and development centers focused on advancing battery technologies create job opportunities for scientists and engineers.
- Electric utilities respond to the growing EV market by hiring grid engineers to enhance infrastructure to accommodate the increasing number of electric cars.
Charging infrastructure
One of the benefits of all-electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) is their flexible charging capability due to the widespread availability of the electric grid in proximity to parking areas. Charging these vehicles safely requires EV charging stations, often called electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE).
Drivers can charge overnight at home, whether in single-family residences or multifamily housing, at their workplace, or at public charging stations where accessible. PHEVs offer added flexibility as they can also rely on gasoline, diesel, or potentially other future fuels when necessary.
However, it’s necessary to note that the prevalence of public charging stations doesn’t yet match that of traditional gas stations. Various stakeholders, including charging equipment manufacturers, automakers, utilities, Clean Cities coalitions, states, municipalities, and government agencies, are diligently working to establish a comprehensive national network of public charging stations.
As of 2023, there are over 53,000 publicly accessible charging stations in the United States, providing more than 137,000 charging ports, according to the Alternative Fueling Station Locator, making it easier for users to find electric charging stations nearby.
Innovations in charging infrastructure are shaping the future of EVs. Wireless charging, powered by magnetic resonance, eliminates the need for physical connectors, allowing EVs to charge by parking over a charging pad embedded in the ground, promising an automated and hands-free charging experience.
Ultra-fast charging, or high-power charging, reduces charging time. These chargers deliver a higher power output to the battery, replenishing up to 80% of an EV’s battery capacity in 30 minutes, offering a practical solution for long-distance travel and minimizing downtime.
Another notable advancement is bidirectional charging, which facilitates a two-way power flow between the grid and the EV. This technology unlocks benefits such as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) and vehicle-to-home (V2H) capabilities. EV owners can leverage their vehicle’s battery to power their homes during peak demand periods or contribute electricity back to the grid when required, leading to substantial energy cost savings and improved grid stability.
Sustainability
Electric vehicles are sustainable in several ways. They leave a less environmental impression over their entire lifecycle than traditional fuel vehicles, which not only helps conserve natural resources but also protects our environment.
Moreover, EVs can be charged using renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower. This approach reduces emissions and actively creates a cleaner, pollution-free environment.
Conclusion
Electric vehicles (EVs) offer a promising future by being eco-friendly, efficient, and job-creating. EVs reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants throughout their lifecycle, preserving natural resources and safeguarding the environment. Also, the ability to charge EVs with renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower additionally promotes a clean, pollution-free world.
Charging infrastructure is evolving to make EV ownership even more convenient, with innovations like wireless charging, ultra-fast charging, and bidirectional charging.
References
https://energy5.com/revolutionizing-charging-infrastructure-smart-solutions-for-ev-connectors
https://www.jdpower.com/cars/shopping-guides/5-ways-electric-cars-are-better-for-the-environment
https://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/electric-cars-better-for-climate-in-95-of-the-world


















vurcazkircazpatliycaz.9OKJMlCO3MJB
euphemises xyandanxvurulmus.Cnv4frJntWnN
porn vurgunyedim.twpdT91vXjfn
bahis siteleri porn sex incest ewrjghsdfaa.bCmHcr2N7AEZ
sektor benim zaten amin evladi mobileidn.0Ae7PQrnZyeA
bahis siteleri sikis 250tldenemebonusuxx.KY8RrLo1ULaG
escort siteleri eyeconartxx.gZxGaiQSkBNm
bahis siteleri porn vvsetohimalxxvc.kXVE0W1pS7t7
sex hd downloading gghkyogg.s6QLL9CzjiZ
pornky com ggjennifegg.rEvbhhb0vxv
fashionflag xxx hdporn.com fashionflag.tcmE5mCYf9z
ladyandtherose BDSM porn backlinkseox.EuaburytG5U
खिलौने अश्लील हैं txechdyzxca.fJacdOGZwp3
हेनतई, एनीमे पोर्न hkyonet.8rQZsl8Ms2B
ladesbet ਹੱਥਰਸੀ ਪੋਰਨ ladesinemi.Q7RQpsC3UOb
ladesbet ヘンタイ, アニメポルノ ladestinemi.O8Z01oWgbvn
My husband and i got absolutely thrilled when Jordan managed to finish up his basic research from your precious recommendations he came across from your site. It’s not at all simplistic just to be giving away techniques which usually people have been making money from. And we all take into account we’ve got the writer to appreciate because of that. These explanations you made, the simple site navigation, the relationships you give support to foster – it is all awesome, and it’s really leading our son and the family reason why this issue is satisfying, and that’s quite serious. Many thanks for all the pieces!
Tonic Greens: An Overview. Introducing Tonic Greens, an innovative immune support supplement
k8 ミニゲーム
実用的で具体的なアドバイスが多く、とても感謝しています。
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. It extremely helps make reading your blog significantly easier.
geinoutime.com
안경 뒤로 왕부시의 화난 얼굴을 숨기고 앞에 있는 사람을 바라보며 기침을 했다.
What is Gluco Freedom? Millions of people suffer from blood sugar problems, despite the fact that many factors are beyond their control.
I have not checked in here for a while because I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are good quality so I guess I?¦ll add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Wow! Thank you! I always wanted to write on my website something like that. Can I take a portion of your post to my site?
geinoutime.com
Fang Jifan은 Fanghua Pavilion을 지나갈 때 무언가를 기억했습니다.
Hi my family member! I wish to say that this article is awesome, nice written and come with almost all significant infos. I would like to look extra posts like this .
Good write-up, I’m regular visitor of one’s web site, maintain up the excellent operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
I do not even know how I ended up right here, however I thought this publish used to be good. I don’t recognize who you might be but definitely you are going to a famous blogger if you happen to aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
I like the valuable info you provide for your articles. I’ll bookmark your weblog and check again here frequently. I’m moderately certain I will be informed many new stuff proper here! Good luck for the next!
WONDERFUL Post.thanks for share..extra wait .. …
Somebody essentially help to make seriously posts I would state. This is the first time I frequented your web page and thus far? I surprised with the research you made to create this particular publish amazing. Excellent job!
What Is LeanBiome?LeanBiome is a natural weight loss supplement that reverses bacterial imbalance in your gut microbiome with the help of nine science-backed lean bacteria species with Greenselect Phytosome, a caffeine-free green tea extract crafted with patented
Thanks , I have just been searching for information about this subject for ages and yours is the best I have discovered so far. But, what about the conclusion? Are you sure about the source?
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your website is so cool. I am impressed by the details that you have on this website. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for extra articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found just the info I already searched everywhere and just could not come across. What an ideal website.
What Is LeanBiome? LeanBiome is a natural dietary supplement that promotes healthy weight loss.
I like what you guys are up also. Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my web site :).
This is the right blog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!
I was recommended this web site by my cousin. I’m no longer positive whether this submit is written by him as nobody else recognise such detailed approximately my problem. You’re wonderful! Thanks!
Definitely imagine that which you said. Your favorite justification appeared to be at the internet the simplest factor to be mindful of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while other people think about worries that they just do not recognize about. You controlled to hit the nail upon the highest and also defined out the entire thing with no need side effect , other people can take a signal. Will probably be back to get more. Thank you
I do agree with all of the ideas you’ve introduced in your post. They’re really convincing and will certainly work. Still, the posts are very brief for newbies. May just you please lengthen them a bit from next time? Thank you for the post.
I blog often and I seriously appreciate your information. The
article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to take a note of your blog and keep checking for new details about once per week.
I subscribed to your RSS feed as well.
Have a look at my web blog … look these up
Thanx for the effort, keep up the good work Great work, I am going to start a small Blog Engine course work using your site I hope you enjoy blogging with the popular BlogEngine.net.Thethoughts you express are really awesome. Hope you will right some more posts.
Sweet web site, super pattern, rattling clean and apply friendly.
I like the helpful info you provide in your articles. I’ll bookmark your blog and check again here frequently.
I am quite certain I will learn a lot of new stuff right here!
Best of luck for the next!
my web-site – anonymous
Hello there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search
Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m
not seeing very good results. If you know of any please share.
Cheers!
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
Excellent read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing a little research on that. And he just bought me lunch as I found it for him smile So let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch!
Introduction Duo Keto is a revolutionary dietary supplement
that has been specifically formulated to help individuals achieve their weight loss
goals.
Feel free to peruse website; Buy Duo Keto
https://whatsapp.selly.store/ sells high quality whatsapp hash channels and queen channels; All fesh and
active whatsapp channels and we have other whatsapp marketing tools including bulk whatsapp number filter,
messages sender,whatsapp leads extractor.
сервисный центр apple
Absolutely pent content material, thanks for entropy.
Really loads of superb tips!
my web site -; https://tutorialslots.com/index.php?qa=19740&qa_1=airmoto-the-role-of-air-compressors-in-modern-toolkits
сервис по ремонту смартфонов
ремонт телевизоров в москве
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сотовых телефонов, смартфонов и мобильных устройств.
Мы предлагаем: мастерская телефонов
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сотовых телефонов, смартфонов и мобильных устройств.
Мы предлагаем: срочный ремонт телефонов рядом
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту ноутбуков, макбуков и другой компьютерной техники.
Мы предлагаем:ремонт macbook pro
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
There is noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain nice points in features also.
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to say that
I’ve really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts.
After all I’ll be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again soon!
I like the helpful info you provide in your articles. I’ll bookmark your blog and check again here frequently. I am quite certain I’ll learn a lot of new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту квадрокоптеров и радиоуправляемых дронов.
Мы предлагаем:ремонт дронов
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сотовых телефонов, смартфонов и мобильных устройств.
Мы предлагаем: где можно починить телефон
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту ноутбуков, imac и другой компьютерной техники.
Мы предлагаем:imac ремонт
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту ноутбуков и компьютеров.дронов.
Мы предлагаем:мастер по ремонту ноутбуков москва
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
сервисный центр iphone в москве
Its like you read my thoughts! You seem to understand a lot about this, like you wrote the guide in it or something. I feel that you just can do with a few percent to power the message house a bit, but other than that, this is fantastic blog. A great read. I will definitely be back.
ремонт apple watch
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту холодильников и морозильных камер.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт холодильников
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту планетов в том числе Apple iPad.
Мы предлагаем: сервисный центр айпад в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту ноутбуков и компьютеров.дронов.
Мы предлагаем:срочный ремонт ноутбуков в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:ремонт бытовой техники в спб
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту радиоуправляемых устройства – квадрокоптеры, дроны, беспилостники в том числе Apple iPad.
Мы предлагаем: квадрокоптеры сервис
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники в петербурге
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – сервис центр в екатеринбурге
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники
Hi there friends, fastidious article and nice arguments commented at this place,
I am really enjoying by these.
Regards for helping out, good information.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту Apple iPhone в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: мастер по ремонту iphone
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
ремонт смартфонов
ремонт телевизоров с выездом на дом
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту источников бесперебойного питания.
Мы предлагаем: срочный ремонт iphone в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный центр ремонта стиральных машин рядом различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши стиральные машины, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы стиральных машин, включают неработающий барабан, проблемы с нагревом воды, программные сбои, неисправности насоса и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт барабанов, нагревательных элементов, ПО, насосов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный сервисный ремонт стиральных машин рядом.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-stiralnyh-mashin-ace.ru
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – профи барнаул
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту варочных панелей и индукционных плит.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт варочных панелей с гарантией
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:сервис центры бытовой техники екатеринбург
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
ремонт цифровых фотоаппаратов в москве
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
https://www.heritagefamilypantry.com/LpeEksUJEIq
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники в челябинске
thx
チェインクロニクル
k8 カジノ スロット Sweet Bonanza 1000 スイートボナンザ1000
ボーナスゲームの演出が豪華で、楽しみが倍増します。目が離せません。
沖ドキ!トロピカル
https://sites.google.com/view/pachislo-resident-evil-6
パチンコを通じて、他のプレイヤーと交流する機会も多いです。共通の趣味があると会話が弾みます。
CRモンスターハンタ
k8パチンコ
CRキャプテン翼
戦国パチスロ花の慶次戦極めし傾奇者の宴~
聖闘士星矢 -黃金激闘篇-
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту фото техники от зеркальных до цифровых фотоаппаратов.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт фототехники
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
戦国パチスロ花の慶次戦極めし傾奇者の宴;
150_翔馬
大当たりの瞬間は、ドキドキ感がたまりません。興奮が止まりません。
CR びっくり戦国無双 Light Edition
https://sites.google.com/view/p-how-not-to-summon-a-demon
キャラクターの個性が際立っており、ストーリーに引き込まれます。
パチスロ鉄拳4アルティメットデビルVer.
K8カジノ パチンコ
水浒伝天下
CR大海物語4 Ver.319
バジリスク~甲賀忍法帖~絆2 天膳 BLACK EDITION
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – профи услуги
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервисные центры в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту планшетов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: замена тачскрина на планшете цена
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
I do agree with all of the concepts you have presented on your post.
They are very convincing and will certainly work. Nonetheless, the posts are very brief for starters.
May you please lengthen them a bit from next time? Thanks for the
post.
Feel free to surf to my blog :: fucking ebony
thx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:сервисные центры в новосибирске
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
thx
thx
thx
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – сервис центр в казани
thx
thx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту видео техники а именно видеокамер.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт веб-камеры
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
thx
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – профи тех сервис красноярск
thx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервисные центры по ремонту техники в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники в нижнем новгороде
thx
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники в новосибирске
thx
thx
thx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту стиральных машин с выездом на дом по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: мастерские по ремонту стиральных машин в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервисные центры в казани
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
akunbos
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with SEO?
I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted
keywords but I’m not seeing very good success. If you know
of any please share. Kudos!
Hi, Neat post. There’s a problem with your site in internet explorer, would test this… IE still is the market leader and a good portion of people will miss your magnificent writing due to this problem.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники
I really like what you guys tend to be up too. This sort of clever work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I’ve you guys to my own blogroll.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт бытовой техники в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – техпрофи
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту игровых консолей Sony Playstation, Xbox, PSP Vita с выездом на дом по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт приставок
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
thx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютерных видеокарт по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт видеокарты компьютера
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
thx
thx
thx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту фототехники в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт вспышек
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Подробнее на сайте сервисного центра remont-vspyshek-realm.ru
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютероной техники в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервис компьютеров
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
thx
thx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту фото техники от зеркальных до цифровых фотоаппаратов.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт видеопроекторов
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Magnificent goods from you, man. I have understand your stuff previous to
and you’re just extremely excellent. I really like what you have acquired here, certainly like what
you’re saying and the way in which you say it.
You make it enjoyable and you still care for to keep it wise.
I cant wait to read much more from you. This is actually a terrific web site.
thx
thx
Наткнулся на замечательный интернет-магазин, специализирующийся на раковинах и ваннах. Решил сделать ремонт в ванной комнате и искал качественную сантехнику по разумным ценам. В этом магазине нашёл всё, что нужно. Большой выбор раковин и ванн различных типов и дизайнов.
Особенно понравилось, что они предлагают раковина для ванной. Цены доступные, а качество продукции отличное. Консультанты очень помогли с выбором, были вежливы и профессиональны. Доставка была оперативной, и установка прошла без нареканий. Очень доволен покупкой и сервисом, рекомендую!
<a href=”https://remont-kondicionerov-wik.ru”>ремонт кондиционеров москва</a>
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютерных блоков питания в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт блоков питания москва
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
ремонт бытовой техники в самаре
Хочу поделиться своим опытом ремонта телефона в этом сервисном центре. Остался очень доволен качеством работы и скоростью обслуживания. Если ищете надёжное место для ремонта, обратитесь сюда: ремонт андроидов.
thx
thx
thx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютероной техники в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: замена комплектующих компьютера
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
thx
thx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту камер видео наблюдения по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт камер наблюдения
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервис центры бытовой техники нижний новгород
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту мониторов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: починка монитора
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту кнаручных часов от советских до швейцарских в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт часов цена
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – профи услуги
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервисные центры в перми
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
сервис кондиционеров
сервисные центры в самаре сервисные центры по ремонту техники в самаре
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту парогенераторов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт парогенератора цена
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники в волгограде
thx
thx
thx
buy balloons with delivery delivery balloons
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – профи услуги
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт бытовой техники в красноярске
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:сервисные центры по ремонту техники в ростове на дону
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
сервисный центре предлагает ремонт матрицы телевизора после удара цена – ремонт телевизоров в москве недорого
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
thx
Сервисный центр предлагает отремонтировать телефона tecno починить телефона tecno
thx
thx
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники
Сервисный центр предлагает ремонт парогенератора maxtronic в москве срочный ремонт парогенератора maxtronic
thx
все на 6 имплантахвсе зубы на 4
thx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютеров и ноутбуков в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт macbook pro 16
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
thx
thx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервис центры бытовой техники тюмень
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту кондиционеров в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервис центр кондиционеров
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту гироскутеров в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: замена аккумулятора в гироскутере цена
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту моноблоков в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: цена ремонта моноблока
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту планшетов в том числе Apple iPad.
Мы предлагаем: профессиональный ремонт ipad
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
thx
thxx
thx
thx
thxx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту посудомоечных машин с выездом на дом в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: центр ремонта посудомоечных машин
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Создание и продвижение сайта https://seosearchmsk.ru в ТОП Яндекса в Москве. Цены гибкое, высокое качество раскрутки и продвижения сайтов. Эксклюзивный дизайн и уникальное торговое предложение.
rüyada ziyafet sofrasında yemek yemek
Сервисный центр предлагает мастерские ремонта пнв hikmicro починить пнв hikmicro
thx
Сервисный центр предлагает замена динамика honor magic6 pro замена батареи honor magic6 pro
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту МФУ в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервисный центр мфу в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:сервисные центры в уфе
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту принтеров в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт принтеров на дому
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту плоттеров в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: цены на ремонт плоттеров
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту объективов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: объектив ремонт
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту серверов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт серверов в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
В магазине сейфов предлагают cейфы 2 класс купить сейф 2 класс в москве
В магазине сейфов предлагают купить сейф оптом купить сейф оптом
В магазине сейфов предлагают сейф металлический взломостойкий cейф взломостойкий
магазин сейфов предлагает сейф 3 класса сейф 3
thxx
thx
thx
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сетевых хранилищ в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: надежный сервис ремонта сетевых хранилищ
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сигвеев в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт сигвеев в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
沖ドキ! 30LL
Rich Wilde and the Tome of Madness
ボーナスゲームの演出が豪華で、楽しみが倍増します。特に大当たり時は圧巻。
カイジ
https://www.f-welfare.net/tags/%e3%82%a8%e3%82%ad%e3%82%b5%e3%82%a4%e3%83%86%e3%82%a3%e3%83%b3%e3%82%b0
大当たりの確率を理解することで、より戦略的にプレイできます。計算が好きな人にはおすすめです。
サラリーマン金太郎 出世回胴編
k8カジノ パチンコ
Pフィーバー戦姫絶唱シンフォギア2
CR牙狼FINAL Ver.399(2:1)
CR 獣王
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту автомагнитол в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт автомагнитол
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту планшетов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: замена матрицы планшета
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту электросамокатов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервис по ремонту электросамокатов
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
ростов вывод из запоя ростов вывод из запоя .
вывод из запоя стационарно ростов https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov16.ru .
Сервисный центр предлагает сервис ремонта морозильных камер atlant сколько стоит ремонт морозильной камеры atlant
Hempified CBD is a brand that offers a wide range of CBD products for consumers seeking natural and holistic solutions for various health issues.
my website: http://www.alphasv.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=165195
вывод из запоя на дому цена https://lecheniealkgolizma.ru/
Профессиональный сервисный центр диагностика сотовых телефонов где можно отремонтировать телефон
вывод. из. запоя. ростов. на. дону. вывод. из. запоя. ростов. на. дону. .
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервисные центры в волгограде
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
карта скзи для тахографа купить в москве https://tachocards.ru/
https://www.khou.com/article/entertainment/television/programs/great-day-houston/meet-the-woman-behind-mala-market-some-of-the-local-vendors/285-fae0a5de-28e1-4c28-a17b-8cd520c9edbe
выезд нарколога на дом цена выезд нарколога на дом цена .
нарколог на дом недорого нарколог на дом недорого .
Очистка квартиры от мусора и хлама Москва https://ochistka-gryaznyh-kvartir-msk.ru/
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервис центры бытовой техники воронеж
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр ремонт телефонов ближайший ко мне сдача телефона в ремонт
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту моноблоков iMac в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервис по ремонту imac
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
https://icecct.com/list105/
The best https://bestwebsiteto.com sites on the web to suit your needs. The top-rated platforms to help you succeed in learning new skills
Gay Boys Porn https://gay0day.com HD is the best gay porn tube to watch high definition videos of horny gay boys jerking, sucking their mates and fucking on webcam
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сотовых телефонов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервис по ремонту телефонов москва
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр ремонт платы телефона ближайший ремонт смартфонов
Excellent goods from you, man. I’ve keep in mind your stuff previous to and you’re simply extremely wonderful.
I actually like what you have bought here, really like what you’re stating and the way in which in which you assert it.
You’re making it enjoyable and you continue to take care of to
keep it wise. I can not wait to learn much more from you.
This is actually a great web site.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервисные центры по ремонту техники в барнауле
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервисные центры в челябинске
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
csgo gamble csgo betting
Начните массовую индексацию ссылок в Google прямо cейчас!
Быстрая индексация ссылок имеет ключевое значение для успеха вашего онлайн-бизнеса. Чем быстрее поисковые системы обнаружат и проиндексируют ваши ссылки, тем быстрее вы сможете привлечь новую аудиторию и повысить позиции вашего сайта в результатах поиска.
Не теряйте времени! Начните пользоваться нашим сервисом для ускоренной индексации внешних ссылок в Google и Yandex. Зарегистрируйтесь сегодня и получите первые результаты уже завтра. Ваш успех в ваших руках!
https://sudvgorode.ru/
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сотовых телефонов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт мобильных телефонов
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
csgo betting cs2 gambling
Профессиональный сервисный центр отремонтировать телефон ремонт экрана телефона
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сотовых телефонов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: вызвать ремонт ноутбука
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
buy helium balloons with delivery cheap balloons Dubai
Платформа 1win предлагает широкий выбор спортивных событий, киберспорта и азартных игр. Пользователи получают высокие коэффициенты, быстрые выплаты и круглосуточную поддержку. Программа лояльности и бонусы делают игру выгоднее.
купить диплом туризм orik-diploms.ru .
order helium balloons with delivery Dubai delivery of helium balloons to your home Dubai
order balloons for birthday Dubai buy balloons stores
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту духовых шкафов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: замена духовых шкафов
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Сервисный центр предлагает сервис ремонта планшетов texet ремонт планшетов texet недорого
template of an engineer resume resume of an engineer technologist
купить диплом в белорецке landik-diploms.ru .
Studio di produzione video https://orbispro.it a ciclo completo. Servizi di creazione video. La nostra produzione effettua riprese video e qualsiasi altra produzione video a Milano, Roma, Torino
Studio di produzione video https://orbispro.it a ciclo completo. Servizi di creazione video. La nostra produzione effettua riprese video e qualsiasi altra produzione video a Milano, Roma, Torino
1win bet apk 1win bet apk .
Как правильно купить диплом колледжа и пту в России, подводные камни
Полезный сервис быстрого загона ссылок сайта в индексация поисковой системы – полезный сервис
Покупка диплома о среднем полном образовании: как избежать мошенничества?
pandora.ukrbb.net/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=11734
франшизы франшизы .
Диплом вуза купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
twoplustwoequal.com/read-blog/47517
купить диплом в донецке купить диплом в донецке .
Легальная покупка школьного аттестата с упрощенной программой обучения
Купить диплом о среднем полном образовании, в чем подвох и как избежать обмана?
купить легальный диплом купить легальный диплом .
Hempified CBD Reviews are becoming increasingly popular as consumers seek out natural and effective ways to manage their wellness. As the CBD market continues to expand, more and more people are turning to Hempified for their CBD needs.
my webpage… https://www.francbio.com/produit/graines-de-poivron-california-wonder-bio/
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сотовых телефонов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт ноутбуков срочно
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту моноблоков iMac в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервисный центр imac
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
купить диплом в черногорске landik-diploms.ru .
Сервисный центр предлагает замена экрана lenovo thinkpad t420s ремонт корпуса lenovo thinkpad t420s
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в ижевске купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в ижевске .
купить диплом оператора prema-diploms.ru .
где купить официальный диплом server-diploms.ru .
Полезные советы по покупке диплома о высшем образовании без риска
купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании в челябинске man-diploms.ru .
Полезная информация на сайте. Все что вы хоте знать об интернете полезный сервис
Покупка диплома о среднем полном образовании: как избежать мошенничества?
Официальная покупка школьного аттестата с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Парадокс, но купить диплом кандидата наук оказалось не так и сложно
erudio.global/blog/index.php?entryid=42268
оформление специальной оценки условий труда оценка факторов условий труда
Как оказалось, купить диплом кандидата наук не так уж и сложно
оценка соответствия условий труда https://sout095.ru
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates.
I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite
some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this.
Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog
and I look forward to your new updates.
соут тарифы https://sout095.ru
new retro casino зеркало https://newretrocasino-casino3.ru .
Реально ли приобрести диплом стоматолога? Основные шаги
frank-shkola.ru/forum/messages/forum1/topic705/message728/?result=new#message728
купить диплом об образовании купить диплом об образовании .
Очень советую бюстгальтера после
где купить настоящий диплом где купить настоящий диплом .
Сервисный центр предлагает выездной ремонт моноблоков prestigio ремонт моноблока prestigio рядом
диплом о высшем образовании недорого с занесением в реестр диплом о высшем образовании недорого с занесением в реестр .
Аттестат школы купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
winda.top/viewtopic.php?f=17&t=812972
Хочу поделиться своим опытом ремонта телефона в этом сервисном центре. Остался очень доволен качеством работы и скоростью обслуживания. Если ищете надёжное место для ремонта, обратитесь сюда: мастер телефон ремонт рядом.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютерных видеокарт по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт видеокарт gigabyte в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Мобильные приложения для ставок помогают скачать приложение БК и начать выигрывать прямо с телефона
Узнайте, как приобрести диплом о высшем образовании без рисков
Купить диплом магистра оказалось возможно, быстрое обучение и диплом на руки
купить диплом университета в челябинске man-diploms.ru .
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютерных видеокарт по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: мастера по ремонту видеокарт
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
доставка алкоголя в москве круглосуточно https://dostavka-alkogolya-moskva-msk-1.ru/
аттестат об окончании школы купить аттестат об окончании школы купить .
купить аттестат о среднем образовании 10 классов orik-diploms.ru .
купить диплом механика в старом осколе arusak-diploms.ru .
детское порно секс порно жена друга
Можно ли быстро купить диплом старого образца и в чем подвох?
детское бдсм порно будучи порно
детские письки порно лучшее детское порно
порно старух купить героин в златоусте
Download and install MetaMask extension with this beginner guide. Securely set up MetaMask for Ethereum and Web3 applications.
ремонт телефона
Процесс получения диплома стоматолога: реально ли это сделать быстро?
Полезные советы по безопасной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
laviehub.com/blog/kupit-diplom-769723hoqc
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
сколько стоит реклама в лифте реклама в лифтах жилых домов
реклама в лифтах реклама в лифте стоимость
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники в екатеринбурге
Hmm it looks like your website ate my first comment (it was
super long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I submitted and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog.
I as well am an aspiring blog writer but I’m still new to
everything. Do you have any helpful hints for rookie blog writers?
I’d definitely appreciate it.
Download and install MetaMask extension with this beginner guide. Securely set up MetaMask for Ethereum and Web3 applications.
купить диплом о среднем образовании в липецке server-diploms.ru .
MetaMask stands out as one of the most popular wallet solutions, especially for interacting with Ethereum-based applications. This guide covers everything you need to know about downloading and installing the MetaMask Extension, empowering you to manage your digital assets with ease.
Как безопасно купить диплом колледжа или ПТУ в России, что важно знать
купить диплом о мед образовании купить диплом о мед образовании .
Huge shoutout to the staff for being incredible! Thanks for everything, really appreciate it!
Absolutely loved it here! Thanks for the great memories and fantastic service. I’ll be back for sure!
Totally exceeded my expectations! Thank you for such a fantastic service. Highly recommended!
Couldn’t have imagined a better experience! Thank you for making everything so seamless.
Thank you! Couldn’t have asked for a better experience. Everything was spot on!
We stumbled over here by a different web address and thought I might as well check things
out. I like what I see so i am just following you.
Look forward to looking over your web page for a second time.
купить диплом вуза купить диплом вуза .
Huge shoutout to the staff for being incredible! Thanks for everything, really appreciate it!
Загрузите 888Starz на Android для игры без ограничений
Пошаговая инструкция по безопасной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
Аттестат школы купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный официальный ремонт аймака в москве всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши моноблоки iMac, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы iMac, включают проблемы с жестким диском, повреждения экрана, неисправности разъемов, программные сбои и неисправности системы охлаждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту imac на дому.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный мастерская по ремонту ipad на выезде всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши планшеты Apple, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи планшетов Apple, включают неисправности дисплея, поломку батареи, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе качественный и надежный сервисный ремонт айпада в москве.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-ipad-pro.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный сервисный ремонт айфона адреса любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши устройства iPhone, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы iPhone, включают неисправности дисплея, проблемы с батареей, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете качественный и надежный ремонт iphone на выезде.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-iphone-sot.ru
From start to finish, everything was perfect. Thank you for being so awesome and helpful!
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный официальный ремонт макбука на дому любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши устройства MacBook, и обеспечиваем ремонт наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели устройств MacBook, включают неисправности дисплея, поломку батареи, неисправности программного обеспечения, проблемы с портами и неисправности системы охлаждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе качественный и надежный мастер по ремонту macbook в москве.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-macbook-club.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный сервисный ремонт варочных панелей в москве всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши варочные панели, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы варочных панелей, включают неработающие конфорки, проблемы с сенсорным управлением, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, сенсоров, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете долговечный и надежный официальный ремонт варочной панели.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-varochnyh-paneley-hit.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный ремонт видеокамеры адреса различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши видеорегистраторы, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи видеорегистраторов, включают неработающую запись, неисправности объектива, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие разъемы и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт записи, объективов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы обеспечиваете себе качественный и надежный центр ремонта видеокамер адреса.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-videokamer-ink.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный ремонт видеокарты любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши видеокарты, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи графических карт, включают перегрев, поломку памяти, неисправности разъемов, сбои контроллера и ошибки драйверов. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт системы охлаждения, памяти, разъемов, контроллеров и ПО. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту видеокарт адреса.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-videokart-biz.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный мастер по ремонту гироскутеров рядом всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши гироскутеры, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы гироскутеров, включают неисправную батарею, проблемы с мотором, поломку контроллера, неработающие сенсоры и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, гиросенсоров и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный мастерская по ремонту гироскутера на дому.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-giroskuterov-key.ru
Покупка диплома о среднем полном образовании: как избежать мошенничества?
tadalive.com/DougMesserly01
Наша мастерская предлагает профессиональный ремонт духовых шкафов всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши духовки, и обеспечиваем ремонт наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели кухонных приборов, включают неработающие нагревательные элементы, выход из строя таймера, поломку дверцы, неисправность контроллера, ошибки вентиляционной системы и неработающие датчики. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт нагревательных элементов, термостатов, таймеров, дверец, контроллеров, вентиляторов и электроники. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный мастерская по ремонту духовых шкафов на дому.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-duhovyh-shkafov-ace.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный мастер по ремонту бесперебойников в москве различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши UPS, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели источников бесперебойного питания, включают поломку аккумулятора, неработающий инвертор, поломку контроллера, неисправности разъемов и ошибки ПО. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт батарей, инверторов, контроллеров, разъемов и ПО. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный сервисный ремонт бесперебойников рядом.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-ibp-max.ru
купить диплом историка купить диплом историка .
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный ремонт игровой приставки на дому различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши консоли, и обеспечиваем ремонт наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи консолей, включают поломку HDD, неработающие разъемы, проблемы с геймпадами, неисправности программного обеспечения и неисправности системы охлаждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, разъемов, контроллеров, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете качественный и надежный сервис ремонта игровой приставки на выезде.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-igrovyh-konsoley-mob.ru
You made my day! Thank you for the amazing service – couldn’t be happier!
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный мастерская по ремонту индукционных плит на дому любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши индукционные варочные панели, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи индукционных варочных панелей, включают проблемы с нагревом, неработающие сенсоры, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие разъемы и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, сенсорных панелей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный мастерская по ремонту индукционных плит адреса.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-indukcionnyh-plit-now.ru
Amazing experience! Thank you so much for going above and beyond. Will definitely recommend it to my friends!
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный официальный ремонт дрона адреса различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши кухонные приборы, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели кухонных приборов, включают неисправности термостата, неисправный таймер, поврежденную дверцу, сбои контроллера, проблемы с конвекцией и неработающие датчики. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, термостатов, таймеров, дверец, контроллеров, вентиляторов и электроники. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту квадрокоптеров в москве.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-kvadrokopterov-best.ru
Thank you! Couldn’t have asked for a better experience. Everything was spot on!
Big thanks to the team! Friendly, efficient, and just awesome all around. 10/10 would recommend!
From start to finish, everything was perfect. Thank you for being so awesome and helpful!
Amazing experience! Thank you so much for going above and beyond. Will definitely recommend it to my friends!
You made my day! Thank you for the amazing service – couldn’t be happier!
Totally exceeded my expectations! Thank you for such a fantastic service. Highly recommended!
Huge shoutout to the staff for being incredible! Thanks for everything, really appreciate it!
Totally exceeded my expectations! Thank you for such a fantastic service. Highly recommended!
Couldn’t have imagined a better experience! Thank you for making everything so seamless.
From start to finish, everything was perfect. Thank you for being so awesome and helpful!
Можно ли купить аттестат о среднем образовании? Основные рекомендации
nadegda.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=730
Диплом пту купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Как быстро и легально купить аттестат 11 класса в Москве
bike.by/forum/viewtopic.php?f=84&t=85664
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный мастер по ремонту компьютеров в москве всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши ПК, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели персональных компьютеров, включают неисправности HDD, проблемы с графическим адаптером, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и перегрев. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт жестких дисков, видеокарт, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный ремонт компьютера в москве.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-kompyuterov-vip.ru
Временная регистрация в Москве: Быстро и Легально!
Ищете, где оформить временную регистрацию в Москве?
Мы гарантируем быстрое и легальное оформление без очередей и лишних документов.
Ваше спокойствие – наша забота!
Минимум усилий • Максимум удобства • Полная легальность
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас!
Временная регистрация в Москве
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный срочный ремонт кондиционеров различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши охладительные системы, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи сплит-систем, включают недостаток хладагента, неисправности вентилятора, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности датчиков и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт компрессоров, вентиляторов, ПО, датчиков и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный сервисный ремонт кондиционера.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-kondicionerov-wow.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный мастер по ремонту кофемашина рядом различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши эспрессо-машины, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы кофемашин, включают проблемы с нагревом, проблемы с подачей воды, программные сбои, проблемы с подключением и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, насосов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный сервис ремонта кофемашин адреса.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-kofemashin-top.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный официальный ремонт массажных кресел любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши массажные кресла, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели массажных устройств, включают неработающий мотор, проблемы с массажными механизмами, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт моторов, роликов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный качественный ремонт массажного кресла.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-massazhnyh-kresel-gold.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный сервисный центр по ремонту майнеров всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши криптомайнеры, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы майнеров, включают перегрев, проблемы с блоком питания, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт систем охлаждения, блоков питания, ПО, разъемов и оборудования. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный официальный ремонт майнеров.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-maynerov-geek.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный сервисный центр по ремонту материнских плат в москве различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши мэйнборды, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели мэйнбордов, включают проблемы с чипсетом, проблемы с блоком питания, ошибки ПО, проблемы с портами и поломки элементов. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт чипсетов, блоков питания, ПО, разъемов и компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный официальный ремонт материнских плат.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-materinskih-plat-info.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный вызвать мастера по ремонту монитора с гарантией любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши дисплеи, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи дисплеев, включают неисправности подсветки, неисправности матрицы, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт подсветки, матриц, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе качественный и надежный сервисный центр по ремонту монитора адреса.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-monitorov-plus.ru
Awesome post, thanks!
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный ремонт моноблоков с гарантией различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши все-в-одном ПК, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели моноблочных компьютеров, включают неисправности HDD, неисправности дисплея, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и проблемы с охлаждением. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе надежный и долговечный сервисный ремонт моноблока на дому.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-monoblokov-rial.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный центр ремонта моноколеса любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши самобалансирующиеся устройства, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи электрических моноколес, включают поломку аккумулятора, неисправности двигателя, сбои контроллера, неисправности сенсоров и повреждения рамы. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, гиросенсоров и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный центр ремонта моноколеса в москве.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-monokoles-serv.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает профессиональный сервис ремонта морозильной камеры с гарантией любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши морозильные камеры, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы морозильных камер, включают неисправности компрессора, неисправности термостата, ошибки ПО, проблемы с подключением и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонт компрессоров, термостатов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный мастер по ремонту морозильной камеры на дому.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-morozilnyh-kamer-spec.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный сервисный ремонт мфу на дому любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши многофункциональные устройства, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы МФУ, включают неисправности печатающей головки, неисправности сканера, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих поломок наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт печатающих головок, сканеров, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный отремонтировать мфу на выезде.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-mfu-lite.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает профессиональный центр ремонта ноутбуков в москве любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши ноутбуки, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели переносных компьютеров, включают проблемы с жестким диском, поврежденный экран, неисправности программного обеспечения, проблемы с портами и перегрев. Для устранения этих поломок наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт жестких дисков, экранов, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту ноутбука с гарантией.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-noutbukov-first.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный отремонтировать объектив с гарантией любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши объективы, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы объективов, включают неисправности фокуса, залипшую диафрагму, поломки компонентов, проблемы с автофокусом и загрязнения линз. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт фокусировки, диафрагмы, автофокуса, очистку линз и восстановление корпуса. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный центр ремонта объектива.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-obektivov-magic.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный сервисный ремонт парогенераторов на дому различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши парогенераторы, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы парогенераторов, включают проблемы с температурными датчиками, проблемы с подачей воды, ошибки ПО, неисправности разъемов и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, насосов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный отремонтировать парогенератор адреса.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-parogeneratorov-piece.ru
купить диплом о среднем купить диплом о среднем .
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный центр ремонта планшетов различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши таблеты, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы планшетов, включают проблемы с экраном, поломку батареи, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие разъемы и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный ремонт планшета с гарантией.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-planshetov-profi.ru
выведение из запоя на дому санкт петербург выведение из запоя на дому санкт петербург .
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный ремонт плоттера рядом любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши печатные устройства, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность наших услуг.s
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели печатных устройств, включают неработающий картридж, проблемы с подачей бумаги, неисправности программного обеспечения, проблемы с портами и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт печатающих головок, механизмов подачи бумаги, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный официальный ремонт плоттеров.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-plotterov-style.ru
Временная регистрация в Москве: Быстро и Легально!
Ищете, где оформить временную регистрацию в Москве? Мы гарантируем быстрое и легальное оформление без очередей и лишних документов. Ваше спокойствие – наша забота!
Минимум усилий • Максимум удобства • Полная легальность
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас!
.
Всё, что нужно знать о покупке аттестата о среднем образовании
Если вам нужно отправить груз недорого, попутный груз станет вашим оптимальным решением
Thanks for enlightening us!
Appreciate the share!
Купить диплом медицинского института
kyc-diplom.com/diplom-articles/kupit-diplom-medicinskogo-instituta.html
купить диплом зоотехника arusak-diploms.ru .
купить поддельный диплом купить поддельный диплом .
Купить диплом о среднем полном образовании, в чем подвох и как избежать обмана?
вывод из запоя на дому спб цены вывод из запоя на дому спб цены .
Fantastic information, thanks!
строительные бытовки от производителя https://bytovka-price.ru
модульные дома из бытовок бытовка в бухловке калужская область
Легальная покупка диплома о среднем образовании в Москве и регионах
купить диплом врача терапевта man-diploms.ru .
Appreciate the recommendation. Will try it out.
купить диплом психолога landik-diploms.ru .
Скачайте 888starz apk ios для непрерывной игры
Временная регистрация в Москве: Быстро и Легально!
Ищете, где оформить временную регистрацию в Москве? Мы гарантируем быстрое и легальное оформление без очередей и лишних документов. Ваше спокойствие – наша забота!
Минимум усилий • Максимум удобства • Полная легальность
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас!
.
Really appreciate this.
Реально ли приобрести диплом стоматолога? Основные шаги
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту Apple iPhone в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт iphone вызвать мастера
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Thanks for the insights!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту Apple iPhone в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт iphone в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
где купить диплом окончание orik-diploms.ru .
Thanks for the insights!
Thanks for enlightening us!
Узнайте, как приобрести диплом о высшем образовании без рисков
Полезная информация как официально купить диплом о высшем образовании
где купить диплом в москве где купить диплом в москве .
Если вам нужен результат, наш сервис накрутки ПФ идеально подойдёт для повышения позиций вашего сайта в Яндексе.
приложение к диплому о высшем купить landik-diploms.ru .
Thanks a lot!
Диплом техникума купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Узнайте стоимость диплома высшего и среднего образования и процесс получения
купить диплом штукатура недорого man-diploms.ru .
купить диплом о среднем образовании в иваново купить диплом о среднем образовании в иваново .
Grateful for this!
Вопросы и ответы: можно ли быстро купить диплом старого образца?
antonovschool.ru/forum/messages/forum1/topic992/message1021/?result=new#message1021
Как купить диплом о высшем образовании с минимальными рисками
bezone.ru/node/347523
Explorez notre collection de
https://couteaux-de-cuisine-france.fr/
pour les chefs amateurs
Explorez notre collection de
Couteau a desosser
pour la maison
аттестат о среднем общем образовании купить аттестат о среднем общем образовании купить .
Thank you so much for your help! I truly appreciate your support and guidance. https://metamask-extension-1059.blogspot.com/2024/11/how-to-download-and-set-up-metamask.html
Приобретение школьного аттестата с официальным упрощенным обучением в Москве
Fine, thanks. Moving on.
Cheers, I owe you one… maybe.
купить диплом о высшем образовании продажа дипломов orik-diploms.ru .
сопровождение сайта раскрутка сайта в топ
индивидуальный тариф seo https://is-market.ru
Cheers, I owe you one… maybe.
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
Можно ли купить аттестат о среднем образовании, основные моменты и вопросы
купить дипломы о среднем профессиональном образовании купить дипломы о среднем профессиональном образовании .
Noted. Thanks.
купить аттестат гос образца купить аттестат гос образца .
Официальное получение диплома техникума с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Noted. Thanks.
Guess I should say thanks or something.
купить диплом гос образца купить диплом гос образца .
купить диплом советского образца купить диплом советского образца .
Грузоперевозки чат помогут найти транспорт для вашего груза в СФО.
Как приобрести аттестат о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
Noted. Thanks.
Fine, thanks. Moving on.
Cheers, I owe you one… maybe.
鉄拳2nd
k8 カジノ パチンコ
大当たりの瞬間は、心臓がドキドキします。興奮が何とも言えません。
CRヱヴァンゲリヲン10
https://www.f-welfare.net/tags/%e7%be%8e%e7%9a%84%e3%81%aa%e8%a6%81%e7%b4%a0
キャラクターの個性が際立っており、ストーリーに引き込まれます。
CR JAWS再臨-SHARK PANIC AGAIN-
k8 カジノ パチンコ CR北斗の拳5 覇者パチスロ スロット 機械割 解析 天井 初打ち 打ち方 スペック ゾーン 設定判別 ヤメ時・演出・プレミアムまとめ
CRキャプテン翼
HEY!エリートサラリーマン鏡
吉宗
Очистка дома после пожара https://spec-uborka-posle-pozhara.ru/
This post is priceless. How can I find out more?
битц казино официальный сайт
Легальные способы покупки диплома о среднем полном образовании
At this time I am going away to do my breakfast,
when having my breakfast coming yet again to read further news.
Как купить аттестат 11 класса с официальным упрощенным обучением в Москве
купить диплом в махачкале orik-diploms.ru .
Покупка диплома о среднем полном образовании: как избежать мошенничества?
c90226sl.beget.tech/2024/10/15/oformlenie-diploma-vash-klyuch-k-uspeshnoj-karere
Couldn’t have done it without you, cheers! If you need further info, here’s https://docs.extension.support/.
Полезные советы по покупке диплома о высшем образовании без риска
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в новокузнецке купить диплом с занесением в реестр в новокузнецке .
купить диплом управление персоналом 3russkiy-diploms.ru .
Thanks, you saved me time and trouble! For further help, check out https://download.extension.support/
Покупка школьного аттестата с упрощенной программой: что важно знать
Как оказалось, купить диплом кандидата наук не так уж и сложно
дипломы детям купить prema365-diploms.ru .
Хотите провести время с друзьями или семьёй в уютной обстановке? Сауны Москвы предлагают широкий выбор услуг: от классических парилок до современных спа-процедур. Подарите себе незабываемые впечатления! Подробности на сайте https://dai-zharu.ru/
There are various tools and websites that affirmation to permit users to view private Instagram profiles, but it’s important to right to use these past caution. Many of these tools can be unreliable, may
require personal information, or could violate Instagram’s terms of service.
Additionally, using such tools can compromise your own security or lead to
scams. The safest and most ethical habit to view a private profile
is to send a follow demand directly to the user.
Always prioritize privacy and reverence in your online interactions.
Check out my webpage … how to view private instagram profile
Лучшие порно видео Гей порно Бонсай скачать бесплатно без регистрации и смс. Смотреть порно онлайн в высоком качестве.
Лучшие порно видео Гей порно Бонсай скачать бесплатно без регистрации и смс. Смотреть порно онлайн в высоком качестве.
Тут можно преобрести огнеупорный сейф сейф несгораемый
buy apartment in kotor Montenegro property to buy
houses for sale tivat realty Montenegro
flats for sale realty Montenegro
tivat real estate Montenegro property to buy
kotor house for sale real estate Montenegro
invest real estate Montenegro
why invest real estate Montenegro
villas in tivat Montenegro property to buy
Тут можно преобрести сейфы для оружия купить сейф для пистолета и ружья
Тут можно преобрести сейф пожаростойкий купить огнестойкий сейф
стоимость укладка кафельная плитка цены на укладку кафельной плитки
стоимость укладки кафельной плитки за квадратный метр укладка кафельной плитки цена за квадратный
Thanks. https://sites.google.com/view/metamask-extension-62165/metamask-extension-for-chrome-firefox-and-brave-a-comprehensive-guide
Если вам нужен доступ к игре, скачайте 1xslots apk и начните выигрывать!
Тут можно преобрести сейфы для оружия где купить сейф для ружья
Как оказалось, купить диплом кандидата наук не так уж и сложно
Grateful for your interest. Thank you! https://sites.google.com/view/metamask-extension-detail-1450/
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
Займ под залог бытовой техники Займ 100 000 тенге
соут в новой организации аккредитация соут
Тут можно преобрести стоимость оружейного сейфа оружейный сейф в москве
Как купить диплом о высшем образовании с минимальными рисками
Займ 300 000 тенге Sravnim.kz
соут официальный сайт https://sout095.ru
Thank you for taking the time to read! https://docs.webstore.it.com/
купить диплом петропавловск 1russa-diploms.ru .
купить диплом официального сайта many-diplom77.ru .
Можно ли купить аттестат о среднем образовании? Основные рекомендации
Thank you for taking the time to read! https://sites.google.com/view/download-metamask-wallet/
прокат горнолыжных лыж Адлер прокат лыж красная поляна
прокат сноубордов адлер снаряжение горнолыжное прокат
купить айфон 128 купить iphone 15 pro max 256gb
аренда лыж красная поляна https://prokat-lyzh-krasnaya-polyana.ru
купить аккумулятор iphone https://store-iphone43.ru
аттестат 2010 купить аттестат 2010 купить .
Как официально купить аттестат 11 класса с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Для начала игры активируйте промокод на лаки джет и получите бонус.
Онлайн казино Топ казино
Онлайн казино Лучшие онлайн казино
Официальная покупка школьного аттестата с упрощенным обучением в Москве
аренда горных лыж Адлер арендовать лыжи Адлер
промокод Платежный модуль геткурс промокод Платежный модуль геткурс .
укладка кафельной плитки в ванной укладка кафельной плитки цена работы
стикермания кто выиграл
Thank you for reading and sharing your thoughts! https://webstore.builders
стоимость укладки кафельной плитки за квадратный метр https://ukladka-keramogranita-spb.ru
Всё о покупке аттестата о среднем образовании: полезные советы
1abakan.ru/forum/showthread-243590
Геосинтетические материалы https://ksgeo.ru для строительства широкий ассортимент продукции для укрепления грунтов, дренажа и защиты от эрозии. Надежные решения для дорожного, ландшафтного и промышленного строительства.
блэк спрут ссылка на сайт блэкспрут
Покердом https://pokerdom11ru.best актуальное зеркало и быстрый вход. Получите бонусы и начните выигрывать в казино Pokerdom.
Покердом (Pokerdom) https://pokerdom-online.ru.com официальный сайт топового покер-рума. Играть на деньги в Покердом казино, скачать слоты онлайн.
HoReCa Training https://horeca-training.ru это тренинги по развитию в сфере гостиничного бизнеса и туризма. Обучение линейного и управляющего персонала ресторанов, гостиниц и отелей. Наша цель — повысить уровень обслуживания и эффективности работы сотрудников, а также обеспечить их необходимыми навыками для успешного выполнения обязанностей. Мы уверены, что качественное обучение является ключом к успешному развитию в гостиничном бизнесе и туризме!
Всё, что нужно знать о покупке аттестата о среднем образовании без рисков
Легальная покупка диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения
Быстрая покупка диплома старого образца: возможные риски
Официальное получение диплома техникума с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Натяжные потолки в Киеве https://napotolok.com.ua это популярный вариант для создания красивого и стильного интерьера. Натяжные потолки подходят для любых помещений – квартир, домов, офисов и коммерческих пространств. Они позволяют скрыть неровности основного потолка, коммуникации и освещение, а также придают помещению завершённый вид.
Pin Up Casino https://pinup-pin-up-br.com (Пин Ап) официальный сайт онлайн казино pin up, игровые автоматы, регистрация
Официальный сайт Casino Melbet https://melbet-ng-nigeria.com вход и регистрация. Игровые слоты, доступное зеркало, мобильное приложение в Мелбет казино.
ритуальные услуги в алмате похоронное агентство алматы
Проведение геодезических съёмок https://expert-geo.ru и выполнение инженерных изысканий для подготовки проектной документации для коммерческих объектов
дешевые авиабилеты https://aviasales.cc выберите самый дешевый билет среди 728 авиакомпаний. 2000+ акций ежедневно. простая бронь авиабилетов за 3 мин. купить дешевый билет
Полезные советы по покупке диплома о высшем образовании без риска
голубой драгоценный камень https://jewelsecrets.ru/
That is very fascinating, You’re an excessively skilled blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look ahead to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks
бонус Vega Casino
Мобильные ставки на спорт стали проще — просто скачайте приложение БК и начните выигрывать прямо сейчас
Балаклейская бесплатная https://dani-info.com/news-obl/ рекламно-информационная газета «Дані-інфо». В газете присутствует новостная страничка, где можно узнать свежие новости города, района, страны, изменения в законодательстве, интересные статьи, кроссворд, гороскоп, анекдоты и многое, многое другое.
На сайте https://bestigryandroid.ru легко найти и скачать бесплатные игры для Андроид на русском языке для разных устройств.
los angeles auction Los Angeles Estate Auction
Wow, awesome weblog structure! How long have you ever been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall glance of your web site is wonderful, let alone the content!
официальный сайт Banda Casino
Полезные советы по безопасной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
Пластиковые окна https://www.okna-melke-spb.ru от официального производителя. Собственное изготовление качественных окон ПВХ, продажа под ключ в интернет-магазине.
Доставка грузов https://madein-china.ru из Китая. Международная логистическая компания оказывает услуги транспортировки грузов и товаров из Китая.
Скачивайте бесплатно https://fanapk.ru лучшие игры и приложения для Android! У нас только проверенные и безопасные APK-файлы для всех устройств. Оцените новинки и популярные программы без регистрации и SMS!
Играйте в Bonsai Casino https://casino-bonsai.com захватывающий выбор слотов и игр, уникальные акции и щедрые бонусы! Погрузитесь в атмосферу азарта и выигрывайте с первого спина!
купить аттестат за 9 класс 2021 года prema365-diploms.ru .
Слот Sugar Rush https://sugar-rush-play.ru Бесплатная ДЕМО-версия, значения RTP и Max Win, Бонусы и фриспины от казино.
dropcase кс го дроп
главные новости спорта https://beachsoccer.com.ua фото, видео и инфографика, аналитика и блоги от экспертов и известных спортсменов
укладка кафельной плитки метр https://ukladka-keramogranita-price.ru
укладка пола кафельной плиткой цена укладка кафельной плитки кухне
The online casino Pin Up https://velic.io has collected over 3000 gambling entertainments slot machines, live games, crash games and exclusive slots. Play for money with the best conditions.
провести оценку соут оформление соут
продамус промокод скидка продамус промокод скидка .
Интересует продвижение в соц сетях? Тогда Группа ВК . Дизайн групп | Продвижение сообщества в контакте то что нужно. Все о продвижении и дизайне групп вконтакте.
интим магазин официальный сайт секс шоп ассортимент
Сайт о татуировках https://tattootoday.org/tattoo-history/articles-about-the-tattoo/upadok-rossiyskoy-tatu-industrii идеи, стили, советы по уходу и выбору мастера. Узнайте о значении популярных тату, процессе нанесения и трендах, чтобы сделать осознанный выбор и подчеркнуть свою индивидуальность.
Онлайн справочник https://wmbild.ru мастера содержит в себе все этапы по ремонту и дизайну дома, дачи или квартиры своими руками.
школа ремонта https://mypunto.ru квартирный вопрос, ремонт квартир. Оригинальные идеи вашего дома, советы ремонта квартир своими руками
Портал о ремонте и строительстве https://website-ok.ru советы по ремонту и благоустройству квартир и домов, информация о ремонте квартир своими руками, технологиях ремонта и строительных материалах.
Советы по ремонту https://5-xl.ru своими руками предлагаем пошаговые инструкции, полезные советы и идеи для создания уюта в вашем доме. Превратите свои идеи в реальность с нами!
Ремонт своими руками https://appbearing.ru практические советы и творческие идеи для вашего дома. Узнайте, как легко и быстро преобразить интерьер, сэкономив при этом деньги.
Покупка диплома о среднем полном образовании: как избежать мошенничества?
Советы по ремонту https://wa-2.ru и строительству дома своими руками. Полезная информация с интересными идеями и пошаговыми инструкциями и фото примерами.
Советы по ремонту https://russ-tractor.ru и строительству дома своими руками. Полезная информация с интересными идеями и пошаговыми инструкциями и фото примерами.
Дизайн-проекты интерьеров https://fashion-brands.ru советы по ремонту квартир, обзоры строительных материалов, мебели, техники и оборудования
Статьи о строительстве https://poehala.ru и дизайне с пошаговыми инструкциями и практическими советами, фото- и видео-подборками, полезными сервисами для строителей и домашних мастеров.
Вопросы и ответы https://deinfeuer.ru на любую тему, задать вопрос и получить на него ответ. Добавить вопрос на интересующую Вас тему и получить реальный, правдивый ответ
Вопросы и ответы: можно ли быстро купить диплом старого образца?
kraken tor onion Kraken darknet
Lucky Jet игра — это шанс для тех, кто хочет заработать на азарте.
Узнайте, как приобрести диплом о высшем образовании без рисков
Online store https://needmana.com for selling WoW game currency
Официальный сайт Betwinner https://betwinner-mobile.ru откройте доступ к сайту и получайте бонусы!
Полезные советы https://apinews.ru и пошаговые инструкции по строительству домов и квартир, выбору материалов, монтажу и установке своими руками.
Журнал о строительстве https://jurnalshtori.ru и ремонте, как строить, ремонтировать, выбирать товары, решать проблемы и работать с прорабами
Онлайн-журнал о стройке https://oupen-mir.ru ремонте, дизайне и обустройстве дома или квартиры
Топовый игровой сайт Лев предоставляет для вас потрясающие возможности для ярких побед!
На площадке игрового дома Лев вас ждут выгодные предложения и множество игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете для себя выиграть крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием!
Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров.
Казино Лев дарит вам эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на вашем мобильном телефоне.
На Лев вас ожидают не только игровые автоматы, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира.
Кроме того, наш кэшбэк дадут вам фриспины на каждом шагу.
Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Лев, и получай признания каждый день!
На площадке Lev вас ожидают щедрые призы и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы успеете выиграть колоссальные суммы.
Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус
казино лев 2024
Официальная покупка диплома ПТУ с упрощенной программой обучения
Сайт о строительстве https://vsevolodovo.ru и ремонте своими руками: советы, инструкции и идеи для выполнения работ самостоятельно. Реализуйте свои проекты быстро и качественно!
Ремонт и строительство https://corsika-os.ru своими руками: полезные советы и инструкции для самостоятельного выполнения работ. Превратите свои идеи в реальность!
Ваш гид по строительству https://rollerhockey.ru и ремонту своими руками: простые советы и инструкции для создания идеального пространства. Начните свой проект с нами!
Создайте свой идеальный дом https://spawnalley.ru практические руководства и советы по ремонту и строительству своими руками. Реализуйте свои мечты с легкостью!
Журнал для любителей ремонта https://gastrosapiens.ru идеи, советы и пошаговые руководства по ремонту и строительству. Создавайте уникальные пространства своими руками!
Процесс получения диплома стоматолога: реально ли это сделать быстро?
Журнал строительство и ремонт https://flash-magic.ru своими руками предлагает простые и доступные решения для вашего дома. Узнайте, как легко реализовать свои идеи и сделать уютный интерьер.
Мужской портал https://cruiser.com.ua советы по стилю, здоровью, технологиям и отношениям. Идеи для DIY-проектов и вдохновение для успешной жизни. Найдите то, что нужно для вашего стиля и образа жизни!
Мужской журнал https://hand-spin.com.ua с советами по стилю, здоровью и технологиям. Найдите вдохновение для хобби, чтобы сделать жизнь ярче и успешнее.
Портал для мужчин https://hooligans.org.ua от моды до технологий. Исследуйте мир самосовершенствования, находите идеи для увлекательных проектов и получайте практические советы для успешной карьеры и личной жизни.
Журнал для мужчин https://phizmat.org.ua стремящихся к совершенству. Узнайте о лучших практиках в области здоровья, стиля и технологий.
Сайт для мужчин https://rkas.org.ua которые стремятся к самосовершенствованию. Получите советы по стилю, здоровью и технологиям, а также вдохновения.
Мужской портал https://realman.com.ua от стиля до технологий. Исследуйте мир моды, здоровья и практических навыков, находя идеи для самовыражения и креативных проектов.
Мужской портал https://smart4business.net жизнь на полную катушку. Узнайте, как улучшить свое здоровье, создать стильный образ и реализовать свои идеи.
Портал для мужчин https://swiss-watches.com.ua которые хотят быть в курсе. Получите актуальные советы по стилю, здоровью и технологиям, которые помогут вам реализовать свои амбиции.
Портал для современных мужчин https://zlochinec.kyiv.ua Практические советы по уходу, здоровью и креативным проектам своими руками.
Тест-драйвы и отзывы https://comparecarinsurancerfgj.org читайте реальные отзывы владельцев и смотрите видеообзоры тест-драйвов.
Электромобили и технологии https://fundacionlogros.org узнайте о новых технологиях, электромобилях и трендах в автомобильной индустрии.
Автоновости и обзоры https://impactspreadsms.com узнайте о последних новинках в мире автомобилей, тест-драйвах и обзорах моделей.
Полезные рекомендации https://just-forum.com по уходу за автомобилем и его техническому обслуживанию.
The best profitable estate sales auctions in Los Angeles. Buy real estate at the best prices with a guarantee.
Последние новости https://jb5.ru России и мира на тему «Мир» за сегодня. Главные новости и события, происходящие в мире, эксклюзивные материалы и мнения экспертов.
Автомобильные тренды https://kolesnitsa.com.ua будьте в курсе последних трендов в дизайне, технологиях и автомобильной моде.
Ремонт и диагностика https://livecage.com.ua получите советы по ремонту и диагностике автомобилей от профессионалов.
Обзоры автомобилей https://necin.com.ua глубокие и объективные обзоры новых и популярных моделей с акцентом на функциональность и стиль.
стоимость проведения оценки условий труда стоимость специальной оценки условий труда
диплом сколько стоит диплом сколько стоит .
Официальная покупка диплома ПТУ с упрощенной программой обучения
Тест-драйвы https://psncodegeneratormiu.org подробные тест-драйвы новых моделей, включая производительность, комфорт и технологии.
Обзоры автомобилей https://quebradadelospozos.com объективные обзоры популярных моделей с акцентом на дизайн, безопасность и функциональность.
Квартиры в новостройках https://all2realt.com.ua обширный каталог новых квартир с актуальными планировками и ценами.
проведение специальной оценки условий труда цена сделать специальную оценку условий труда
Новостной портал https://antifa-action.org.ua Украины, Актуальные события из жизни страны. Политика, экономика, культура и спорт — все важные новости в одном месте для информирования читателей о происходящем.
спецоценка условий труда провести соут в москве цена
Как избежать рисков при покупке диплома колледжа или ПТУ в России
Рекомендации по безопасной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
Технологические тренды https://axioma-techno.com.ua узнайте о последних трендах в мире технологий. Обзоры новых устройств, программного обеспечения и инновационных решений, которые меняют нашу жизнь.
Гаджеты и IT-новинки https://dumka.pl.ua обзор новейших гаджетов на рынке. Узнайте о функциях, характеристиках и отзывах на смартфоны, планшеты, носимые устройства и другие технологические новинки.
Мировые события https://hansaray.org.ua актуальные новости из мира. Узнайте о значимых событиях, конфликтах, международных отношениях и их влиянии на глобальную политическую и экономическую ситуацию.
Инвестиции в недвижимость https://manorsgroup.com.ua обзор возможностей для инвестирования в недвижимость. Узнайте о выгодных объектах, тенденциях рынка и советах по выбору недвижимости для дохода.
Политика Украины https://polonina.com.ua актуальные события в политической жизни Украины. Обзор решений правительства, законопроектов и политических инициатив, влияющих на будущее страны и ее граждан.
Качественные стекла https://atomglass.ru мы предлагаем широкий ассортимент стекол для спецтехники. Все изделия соответствуют высоким стандартам качества и надежности, обеспечивая защиту и долговечность.
Купить с доставкой сексуальные игрушки, созданные для улучшения интимной жизни. Мы предлагаем качество, безопасность и инновации для вашего удовольствия.
Стоимость дипломов высшего и среднего образования и как избежать подделок
itbitgroup.ru/poluchite-diplom-byistro-i-bez-stressa
Вавада Казино https://teletype.in/@sokol-art/my-gaming-expirience предлагает широкий выбор игровых автоматов, настольных игр и live-казино. Удобный интерфейс, щедрые бонусы и акции, а также безопасные платежи делают игру увлекательной и надежной.
Юридический сервис Правовик24 https://www.pravovik24.ru/konsultatsii/yurist-po-bankrotstvu/ предоставляет бесплатные юридические консультации и услуги по банкротству физических лиц под ключ в Москве и регионах России. Помощь юристов и адвокатов в признании должника банкротом и списании долгов. Сопровождение судебного и внесудебного банкротства арбитражным управляющим.
Туристический портал https://prostokarta.com.ua предлагает лучшие направления, актуальные советы и рекомендации для путешественников. Найдите идеальные маршруты, отели и развлечения для незабываемых поездок по всему миру.
Портал о фитнесе https://sportinvent.com.ua предлагает тренировки, советы по питанию и мотивацию для здорового образа жизни. Найдите программы, видеоуроки и статьи для достижения ваших фитнес-целей и улучшения самочувствия.
Портал об инновациях https://technocom.dp.ua и технологиях бытоваятехника, фото, аудио и видеотехника. Компьютерная техника и мобильные устройства.
Портал о мобильной технике https://webstore.com.ua и технологиях предлагает свежие новости, обзоры гаджетов, советы по выбору и использованию устройств, а также актуальные тренды в мире мобильных технологий.
Сайт про лечение диабета https://diabet911.com ваш надежный источник информации о диабете: симптомах, диагностике, лечении, профилактике и последних достижениях в медицине.
Сайт о здоровье глаз https://eyecenter.com.ua предлагает полезные советы по уходу за зрением, профилактике заболеваний, выбору очков и контактных линз, а также информацию о современных методах лечения и диагностики.
Журнал о гипертонии https://gipertoniya.net предоставляет актуальную информацию о лечении и профилактике высокого давления. Узнайте о симптомах, методах контроля, диете и последних исследованиях в области кардиологии.
Мужское здоровье https://kakbog.com ваш источник информации о здоровье мужчин. Узнайте о профилактике заболеваний, фитнесе, питании и психическом благополучии для активной и полноценной жизни.
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
daruber hinaus hast den anzeigen
Лучшие онлайн-слоты https://igraza.ru и казино в одном месте! Обзоры, рейтинги, бонусы и стратегии игры. Найди свой идеальный слот и выиграй джекпот!
Медицинская информация https://lpl.org.ua о болезнях, симптомах и лечении. Поиск врачей и клиник. Статьи от ведущих специалистов. Советы по здоровому образу жизни.
путеводитель мире здоровья https://medfactor.com.ua информация о болезнях, симптомах и лечении. Поиск врачей по специальности и местоположению.
Современная медицина онлайн https://novamed.com.ua быстрый поиск врачей по специальности и местонахождению. Надежная медицинская информация и статьи от экспертов.
Медицинский портал https://una-unso.cv.ua предоставляет доступ к актуальным сведениям о заболеваниях, лечении, симптомах и способах профилактики.
Женский сайт предлагает модные тренды https://a-k-b.com.ua красоту и здоровье, советы по уходу за собой, рецепты и идеи для стильных образов.
Актуальные статьи о моде https://angela.org.ua красоте, здоровье, отношениях. Новости из мира кино, музыки, культуры. Советы по саморазвитию и карьере.
Женский сайт https://beautyrecipes.kyiv.ua где обсуждаются мода, здоровье и уверенность в себе. Получайте практические советы, читайте истории успеха и находите единомышленниц.
Онлайн платформа тренингов https://britishschool.kiev.ua и семинаров. Обучение по актуальным направлениям, повышение квалификации, новые навыки. Записывайтесь на курсы и развивайте карьеру с нами!
Узнайте всё о цветах https://pro100-cvety.ru выбор, посадка и уход. Советы по поливу, удобрению и пересадке. Поддерживайте здоровье растений и создавайте красивый уют в доме с нашим гидом по цветам.
женский портал https://eternaltown.com.ua предлагает советы по стилю, здоровью, отношениям и красоте. Узнайте последние тренды, вдохновение для жизни и полезные советы для женщин.
На нашем портале https://funtura.com.ua вы найдете советы по моде, здоровью, семейным отношениям и саморазвитию. Откройте для себя лайфхаки, вдохновение и поддержку на каждом этапе вашей жизни.
Сайт о семейной психологии https://gorod-lubvi.com.ua предлагает эффективные советы и рекомендации по укреплению отношений, разрешению конфликтов и воспитанию детей.
Присоединяйтесь к нашему сообществу https://happytime.in.ua и открывайте новые горизонты! Женский портал — это ваш источник вдохновения и полезной информации. Узнайте о моде, красоте, здоровье и отношениях.
Быстрая схема покупки диплома старого образца: что важно знать?
Модные тренды, уход за собой https://inclub.lg.ua советы по красоте, здоровью и отношениям. Полезные статьи, рецепты, идеи для вдохновения и гармоничной жизни.
Мода, красота, здоровье https://love.zt.ua отношения и вдохновение для женщин. Полезные советы, лайфхаки, тренды и идеи для гармоничной жизни. Всё самое важное и интересное в одном месте.
Советы по стилю, красоте https://lidia.kr.ua здоровью и отношениям. Мода, уход за собой, психология, рецепты и вдохновение. Всё, что нужно современной женщине для гармоничной и стильной жизни.
Полезные советы по красоте https://loveliness.kyiv.ua моде, здоровью и отношениям. Тренды, лайфхаки и вдохновение для стильной и успешной жизни. Всё, что важно современной женщине, в одном портале.
Пространство для женщин https://mirwoman.kyiv.ua мода, красота, отношения и здоровье. Лайфхаки, вдохновение и актуальные темы для гармонии и счастья в каждом дне.
Советы по уходу за аквариумами https://mts-agro.com.ua подбору рыб и растений, обзоры оборудования, лайфхаки и идеи оформления.
Актуальные темы для женщин https://elegantwoman.kyiv.ua стиль, уход за собой, гармония в отношениях и здоровье. Тренды, рецепты и полезные лайфхаки для вдохновения каждый день.
Оперативные новости и аналитика https://novosti24.kyiv.ua репортажи и мнения. Всё о политике, экономике, обществе, спорте и технологиях. Только актуальная информация и объективный взгляд на события в стране и мире.
Самые актуальные новости https://arguments.kyiv.ua дня: политика, экономика, культура, спорт и технологии. Объективные репортажи, аналитику и мнения от экспертов о событиях в мире и стране.
Советы по стилю https://womanlife.kyiv.ua красоте, здоровью и отношениям. Модные тренды, уход за собой и лайфхаки для женщин, которые ценят гармонию, уверенность и успех в жизни.
Все самые свежие новости https://dailynews.kyiv.ua политика, экономика, технологии, культура и спорт. Объективные репортажи и аналитика для тех, кто ценит точность и актуальность.
Свежие новости дня https://ua-novosti.info политические события, экономические тенденции, культура, спорт и технологии. Лаконичные репортажи и аналитика по всем важным темам.
Стиль, уход за собой https://woman24.kyiv.ua отношения и здоровье. Полезные советы и тренды для женщин, стремящихся к успеху, гармонии и уверенности в жизни.
Объективные новости о политике https://uapress.kyiv.ua экономике, спорте, культуре и технологиях. Аналитика, репортажи и свежие данные из мира и страны.
Чай всех сортов и вкусов https://etea.com.ua чёрный, зелёный, белый, улун, пуэр. Полезные советы, рецепты заваривания и истории о чае. Всё для ценителей чайной культуры и идеального вкуса.
Рецепты на каждый день https://kulinaria.com.ua закуски, основные блюда, десерты и напитки. Советы по приготовлению, лайфхаки и идеи для домашней кухни.
Кулинарный портал https://mallinaproject.com.ua для гурманов: блюда любой сложности, секреты шефов, лайфхаки и интересные идеи. Готовьте с удовольствием и удивляйте близких!
Как правильно купить диплом колледжа и пту в России, подводные камни
Простые и изысканные рецепты https://vagon-restoran.kiev.ua для повседневной и праздничной кухни. Советы, техники и вдохновение для создания вкусных блюд дома.
Советы по стилю https://pic.lg.ua красоте, отношениям и здоровью. Модные тренды, лайфхаки и идеи для женщин, которые хотят быть яркими, уверенными и успешными.
Портал для современных женщин https://prettiness.kyiv.ua стиль, красота, здоровье, отношения. Актуальные советы и тренды для уверенных и гармоничных женщин, которые ценят себя и свою жизнь.
Советы, кейсы и тренды https://reklamspilka.org.ua в маркетинге, рекламе и PR. Инструменты, стратегии и аналитика для успешного продвижения брендов. Полезные материалы для профессионалов и новичков в индустрии.
Стоимость дипломов высшего и среднего образования и как избежать подделок
Советы для родителей https://stepandstep.com.ua воспитание, здоровье, развитие и досуг детей. Полезные статьи, лайфхаки и идеи для гармоничных отношений в семье и счастливого детства.
Портал для современных женщин https://trendy.in.ua стиль, красота, здоровье, отношения. Актуальные советы и тренды для уверенных и гармоничных женщин, которые ценят себя и свою жизнь.
Женский портал о моде https://womanonline.kyiv.ua красоте, здоровье и жизни. Лёгкие советы, вдохновляющие тренды и полезные лайфхаки для гармонии и уверенности.
Полезные советы по уходу https://womenclub.kr.ua за собой, моде, здоровью и отношениям. Лайфхаки и актуальные темы для женщин, которые хотят быть стильными, уверенными и счастливыми.
Access premium betting on 888Starz Bet and win big today.
Как правильно купить диплом колледжа и пту в России, подводные камни
купить диплом высшее сколько 1oriks-diplom199.ru .
Всё о домашних животных https://zoobonus.com.ua уход, питание, здоровье и воспитание. Полезные советы и рекомендации для счастливой жизни ваших питомцев.
Новости автопрома https://translit.com.ua обзоры моделей, советы по выбору, ремонту и уходу за автомобилем. Полезная информация для каждого автолюбителя.
echtzeit fur gespeicherte bilder in den
Сайт с приложениями https://appselection.ru для Андроид, которые можно скачать бесплатно и на русском языке.
Новости автоиндустрии https://alians-avto96.ru обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, советы по уходу и ремонту. Полезная информация для автолюбителей: от выбора автомобиля до тонкостей эксплуатации и обслуживания.
Интересные статьи https://mirwoman.kyiv.ua и полезная информация на разные темы. Всё, что нужно для расширения кругозора и вдохновения каждый день.
Актуальные темы https://phizmat.org.ua и полезные статьи. Информация для тех, кто хочет знать больше и оставаться в курсе.
Найди идеальный скин drop case и улучшай инвентарь. Кейсы CS:GO: лучшие сайты, редкие скины и советы для успешного открытия.
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
Новые статьи https://impactspreadsms.com и полезная информация на разные темы. Всё, что нужно для расширения кругозора и вдохновения каждый день.
Оформление кредита и микрозайма https://mbochi.ru онлайн: быстро, удобно и без лишних документов. Выгодные условия, прозрачные ставки и моментальное одобрение.
Уборка квартир от мусора Москва https://ochistka-zahlamlyonnyh-kvartir.ru/
новости туризма Египет новости туризма Таиланд
Полезные советы по безопасной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
доставка воздушных шариков недорого шариков спб рф с доставкой
Как официально купить аттестат 11 класса с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Клининг обкуренной квартиры https://ochistka-zahlamlyonnyh-kvartir.ru/
Интересные статьи https://funtura.com.ua и полезная информация на разные темы. Всё, что нужно для расширения кругозора и вдохновения каждый день.
Познавательные статьи https://beachsoccer.com.ua и полезная информация на разные темы. Всё, что нужно для расширения кругозора и вдохновения каждый день.
Официальная покупка диплома ПТУ с упрощенной программой обучения
студия актерского мастерства обучение актерскому мастерству
Занятие с логопедом https://logoped-online1.ru онлайн для детей от 4 до 10 лет. Логопед онлайн проведет диагностику, поможет поставить звуки, проработать дислексию и дисграфию, устранить задержки речевого развития и обогатить словарный запас.
Сайт автомобильных запчастей https://idriver.by каталог авторазборок России и Беларуси. Запчастей для иномарок и отечественных авто.
сколько стоят стихи для песни продам стихи
Как приобрести аттестат о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
Thanks. https://docs.webstore.guru/
Услуги доставки грузов из Китая https://cargo-ex.ru в Россию. Быстро, надёжно и с контролем на всех этапах. Оптимальные сроки, таможенное оформление и выгодные тарифы.
стихи на свадьбу дочери заказать https://kazan.bestrifma.ru
Легальная покупка диплома ВУЗа с сокращенной программой обучения
Thanks. https://casibom.agency/
バルタン星人
シンフォギア3 保留変化
友人と一緒にプレイすることで、楽しさが倍増します。共に喜ぶ瞬間が嬉しい。
ガッツだ!!森の石松
https://www.k8o.jp/guide/2919.html
戦略的な要素もあり、運だけでなく技術が試されるのが面白いです。
押忍!番长(操)
k8 カジノ パチンコ ミリオンゴッド-神々の凱旋
L 主役は銭形 4
CRヱヴァンゲリヲン10
CR RAVE この世界こそが真実だ
パチスロビッグドリームinロストアイランド2
https://www.3ae.jp/reviews/6273.html
最近のパチンコ台は、アニメや映画とのコラボが多く、視覚的にも楽しめます。ファンにはたまらないですね。
南国育ち(夏25)
https://www.winnercasinobonusz.com/article/71.html
定期的に新しいイベントがあり、飽きずに楽しめます。新しい体験が待っています。
Pフィーバー戦姫絶唱シンフォギア2
https://www.apachioggia.org/article/67.html
友人と一緒に楽しむのに最適。共通の趣味で盛り上がれます。
Con el 1xslots codigo promocional aprovecha grandes beneficios y promociones.
Онлайн казино Вавада https://telegra.ph/Obzor-Disturbed-11-18 обеспечивает непрерывный вход через рабочее зеркало. Сайт Vavada регистрация, Выгодные бонусы 100FS
Thanks. https://casiboms.it.com/
стихи заказать стихи на заказ работа
Быстрое обучение и получение диплома магистра – возможно ли это?
заказать стих стихи на заказ на свадьбу
написание стихов на заказ заказать стихотворение
Приложения для Андроид https://androidsoftmarket.ru на русском языке можно скачать бесплатно, без регистрации.
благодарность поэту за стихи заказ стихов
Необыкновенный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев открывает для вас захватывающие опции для победных стратегий!
На сайте Lev вас приветствуют акционные игры и богатый выбор слотов. Всегда здесь вы успеете сорвать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием!
Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы выиграть.
Игровая платформа дарит вам интуитивно понятный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на вашем мобильном телефоне.
На Lev вас встретят не только игровые автоматы, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые позволят вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино не выходя из дома.
Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план дадут вам бонусные кредиты при каждом пополнении.
Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и завоевывай богатства каждый день!
На площадке игрового дома Лев вас ждут выгодные предложения и богатый выбор игр. Только здесь вы сможете получить колоссальные суммы.
Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус
казино лев 2024
Санитарная обработка квартиры после смерти https://dezinfekciya-smerti-msk-mo.ru/
доставка алкоголя https://dostavka-alcogolya-mix-1.ru/
Лучший игровой сайт Лев дарит для вас великолепные шансы для успешной игры!
На онлайн-казино Лев вас радуют щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых предложений. Только здесь вы успеете получить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием!
Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы выиграть.
Игровая платформа гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на вашем мобильном телефоне.
На игровом доме Лев вас радуют не только слоты, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома.
Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день.
Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай славы каждый день!
На платформе игрового дома Лев вас ждут щедрые призы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы получите возможность завоевать невероятные призы.
Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус
казино лев 2024
Как получить диплом техникума с упрощенным обучением в Москве официально
Как официально купить аттестат 11 класса с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Автоматический бот для торговли https://revenuebot.io криптовалютой: анализ рынка, выполнение сделок 24/7, настройка стратегий. Удобство, точность и высокая скорость для эффективного управления инвестициями.
стихи на заказ вакансии заказать стихи на заказ
Как приобрести аттестат о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
как купить алкоголь с доставкой на дом https://dostavka-alcogolya-mix-1.ru/
доставка алкоголя в москве https://dostavka-alcogolya-nochyu.ru/
Топовый игровой сайт игорный дом Лев предлагает для вас уникальные возможности для крупных выигрышей!
На площадке Лев вас ожидают удивительные акции и множество игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность сорвать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием!
Площадка Лев предлагает регулярные акции, которые увеличат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы достичь успеха.
Игровая платформа предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любой платформе.
На Lev вас встретят не только видеослоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую в любое время.
Кроме того, наш программа лояльности предложат вам дополнительные средства при каждом пополнении.
Играй с азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай богатства каждый день!
На платформе игрового дома Лев вас ждут выгодные предложения и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы попробуете получить колоссальные суммы.
Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус
казино лев 2024
доставка алкоголя в москве https://dostavka-alcogolya-nochyu.ru/
Выведение плесени на стенах в квартире https://unichtozhenie-pleseni-spb-lo.ru/
Дезинфекция квартиры после умершего в солнцево https://dezinfekciya-smerti-msk-mo.ru/
Выведение плесени со стен https://unichtozhenie-pleseni-spb-lo.ru/
Thanks. https://extensions.work/
алкоголь с доставкой https://dostavka-alcogolya-city-2.ru/
заказать алкоголь с доставкой москва https://dostavka-alcogolya-city-2.ru/
доставка алкоголя на дом круглосуточно https://dostavka-alcogolya-v-moskve.ru/
доставка алкоголя в москве https://dostavka-alcogolya-v-moskve.ru/
Essay writing services rating https://priceorg.com honest reviews, price comparison and quality analysis. Choose only proven platforms.
стихи на заказ работа опубликовать стихи за гонорар
Покупка диплома о среднем полном образовании: как избежать мошенничества?
forum.shvedun.ru/ucp.php?mode=login
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
охрана труда обучение дистанционно в москве охрана труда обучение дистанционно
онлайн обучение по охране труда онлайн обучение по охране труда москва
Пошаговая инструкция по официальной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
охрана труда обучение дистанционно москва курсы по охране труда дистанционно москва
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
Thanks. https://casibom.works/
MetaMask Extension provides secure wallet integration, dApp connectivity, and seamless access to DeFi platforms. Start exploring Web3 today! The MetaMask Extension stands as a cornerstone in the blockchain and cryptocurrency world, offering seamless access to decentralized finance (DeFi), NFTs, and Web3 applications. https://webstore.work/
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
Официальное получение диплома техникума с упрощенным обучением в Москве
travel itinerary planner https://wanderlog.com/list/geoCategory/154041/best-nightlife-in-cincinnati vacations and road trips. Cincinnati’s nightlife is a vibrant tapestry woven with eclectic bars, lively music venues, and unique hangouts that cater to every taste.
игровые автоматы https://igrovye-avtomaty-slot.online в интернете стали все более популярными, поскольку они предлагают удобство и широкий выбор игр.
Chainlist lets you easily connect to multiple blockchain networks. Simplify wallet setups, save time, and boost your crypto management! https://chainlist.cam/
Как приобрести аттестат о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
Всё, что нужно знать о покупке аттестата о среднем образовании
промокод prodamus http://rubiz.forum.cool/viewtopic.php?id=3874#p139 .
Пошаговая инструкция по официальной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
скачать приложения онлайн казино https://taurus-partners.com/kometa-casino-2/
теплоход Александр Пушкин http://teplohod-pushkin.ru теплоход проекта Q-040, построен в 1974 году в Австрии. Единственный четырехпалубный теплоход, который ходит на Соловецкие острова и способен швартоваться непосредственно у причала Соловков.
Tanzen lernen, Tanzschule besuchen Tanzen und Tanzen und Tanzschulen in Osterreich Tanzen lernen, Tanzschule besuchen: Osterreich. Tanzschule, Tanzstudio, Tanzunterricht.
Burç özellikleri hakkında merak edilen her şey! Tüm burçların genel ve özel karakteristik özelliklerini keşfetmek için bu rehberi inceleyin. https://tedez.com/burc-ozellikleri/
Быстрая схема покупки диплома старого образца: что важно знать?
Download MetaMask Extension for Chrome to securely manage your crypto wallet. Follow this easy guide to install and start using MetaMask in minutes! https://sites.google.com/view/download-metamask-extension-41/home
We present to you the TOP Ballroom Dancing in the United States choreographic schools, after studying in which you will be able to work in the best dance studios and groups in the world.
Ремонт ноутбуков https://kmse.ru телефонов и телевизоров в Тамбове. Быстро, качественно, по доступным ценам.
Сколько стоит диплом высшего и среднего образования и как его получить?
Процесс получения диплома стоматолога: реально ли это сделать быстро?
Download MetaMask extension today for secure crypto wallet access. Follow our step-by-step guide to install it effortlessly on your browser. https://extension.wtf/
Диплом вуза купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Официальная покупка диплома вуза с сокращенной программой в Москве
Escort Dating For Click: https://yaramazkadinlar.com/il1/kutahya-escort/
Как оказалось, купить диплом кандидата наук не так уж и сложно
Escort Dating For Click: https://hglweb.com/il1/nigde-escort/
MetaMask is a browser extension and mobile application designed to simplify the interaction between users and blockchain-based applications (dApps). https://sites.google.com/view/metamask-extension-guide-39/home
Приложения для Андроид https://androidappssource.ru можно найти и скачать бесплатно без регистрации с поддержкой русского языка.
Лучшие туры и Нижний Новгород экскурсии 2024-2025 по низким ценам, расписание, цена билетов от 350 рублей, лучшие гиды, бронирование онлайн
Недорогие экскурсии в Пекине 2024-2025, расписание, цена билетов от $10, лучшие гиды, бронирование онлайн
free undress ai ai undress tool
Недорогие экскурсии по Казани 2024, расписание, цена билетов от 350 рублей, лучшие гиды, бронирование онлайн
магазин секс шоп в Киеве секс шоп в Киеве интернет магазин
Как оказалось, купить диплом кандидата наук не так уж и сложно
Полезная информация как официально купить диплом о высшем образовании
Глава правления Финростбанк украл у вкладчиков 28 миллионов гривен. Бывший председатель правления одного из банков Одессы подозревается в краже
Бывшего главу набсовета Финростбанка подозревают в хищении денег вкладчиков. По мнению следствия руководство вывело активы банка на сумму около 1 млрд гривен.
Виниловый сайдинг https://marremont.ru/remont/sajding-i-drugie-fasadnye-materialy заслужил популярность из-за своей износостойкости. Он может придать различным зданиям вид единого комплекса.
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный починить аймак в москве различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши компьютеры Apple, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи моноблоков iMac, включают проблемы с жестким диском, проблемы с экраном, неисправности разъемов, ошибки ПО и проблемы с охлаждением. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете качественный и надежный мастерская по ремонту аймака в москве.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Богатый выбор приложений https://androidapplibrary.ru программ и игр для Андроид на русском языке можно бесплатно, разнообразив функциональность вашего устройства.
аренда авто спб аренда авто на свадьбу с водителем
pin-up casino pinup-casino
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный центр ремонта аймака на выезде различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши компьютеры Apple, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы iMac, включают поломку жесткого диска, проблемы с экраном, неработающие разъемы, программные сбои и проблемы с охлаждением. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту imac в москве.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Всё для питомцев зоомаркет Тула корма, одежда, витамины, игрушки. Товары для здоровья и комфорта животных. Доступные цены, широкий ассортимент и внимание к вашим любимцам.
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный вызвать мастера по ремонту imac на дому всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши моноблоки iMac, и обеспечиваем ремонт наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы iMac, включают неисправности HDD, повреждения экрана, проблемы с портами, ошибки ПО и проблемы с охлаждением. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный починить аймак в москве.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный ремонт аймака адреса различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши iMac, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели компьютеров Apple, включают поломку жесткого диска, проблемы с экраном, неработающие разъемы, неисправности программного обеспечения и проблемы с охлаждением. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный ремонт аймака в москве.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный ремонт аймака в москве различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши компьютеры Apple, и обеспечиваем ремонт наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи моноблоков iMac, включают неисправности HDD, повреждения экрана, проблемы с портами, ошибки ПО и проблемы с охлаждением. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы обеспечиваете себе надежный и долговечный официальный ремонт imac.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали официальный сервисный центр philips, можете посмотреть на сайте: сервисный центр philips
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Возможно ли купить диплом стоматолога, и как это происходит
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный мастерская по ремонту imac различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши моноблоки iMac, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели компьютеров Apple, включают проблемы с жестким диском, проблемы с экраном, неработающие разъемы, неисправности программного обеспечения и неисправности системы охлаждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете качественный и надежный ремонт аймака адреса.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный ремонт аймака в москве всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши компьютеры Apple, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи моноблоков iMac, включают проблемы с жестким диском, неисправности дисплея, проблемы с портами, программные сбои и проблемы с охлаждением. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный сервис ремонта аймака на дому.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает профессиональный центр ремонта imac на дому различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши моноблоки iMac, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи моноблоков iMac, включают поломку жесткого диска, проблемы с экраном, неисправности разъемов, ошибки ПО и перегрев. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный отремонтировать аймак адреса.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный мастер по ремонту imac в москве всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши iMac, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы iMac, включают неисправности HDD, повреждения экрана, проблемы с портами, программные сбои и перегрев. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете долговечный и надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту imac.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Недорогие экскурсии в Бангкоке 2024-2025, расписание, цена билетов от 350 рублей, лучшие гиды, бронирование онлайн
Модный сайт https://alienrecipes.ru для настоящих женщин. Новости звезд, тренды моды и красоты, правильное питание.
Недорогие экскурсии в Свияжск из Казани 2024-2025, расписание, цена билетов от 990 рублей, лучшие гиды, бронирование онлайн
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный сервисный ремонт imac на дому всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши моноблоки iMac, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы iMac, включают проблемы с жестким диском, неисправности дисплея, неисправности разъемов, ошибки ПО и перегрев. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете долговечный и надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту imac адреса.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Стильные и тёплые угги https://ugg-original-moskva.store для женщин, мужчин и детей. Широкий ассортимент, натуральные материалы и современные дизайны. Удобная покупка, выгодные цены и доставка до двери.
Одесса 24 https://odesa24.com.ua/ukraine-news/ это новостной портал, который ежедневно освещает ключевые события Одессы и области. На сайте публикуются актуальные новости, репортажи, аналитика и материалы о жизни города. Читатели могут узнать о культурных мероприятиях, социальных вопросах и обо всем, что важно для жителей региона.
Профессиональные услуги гинеколога https://зеленое-яблоко.рф/775-09-03-2024/ консультации, диагностика, лечение и профилактика женского здоровья. Индивидуальный подход, современные методы и комфортные условия. Забота о вашем здоровье.
На сайте https://funposter.ru/ вы найдете уникальные фотоподборки интересных мест, редких животных, удивительных городов и шедевров архитектуры. Это пространство для вдохновения, где каждая фотография рассказывает свою историю.
BNX cryptocurrency exchange https://bnx.me fast, convenient and secure trading of digital assets. Licensed in Singapore. Staking, P2P, spot trading and ICOs for you to unlock the potential of cryptocurrencies and grow your capital.
Лучшие турецкие сериалы сериал разбивающая сердца смотреть онлайн в хорошем качестве. Коллекция лучших турецких сериалов в HD качестве, смотреть подборку онлайн.
Bonsai Casino https://bonsai-game.org захватывающие игры, щедрые бонусы, быстрые выплаты. Широкий выбор слотов, настольных игр и живых дилеров.
Наслаждайтесь игрой в Bonsai Casino https://bonsai-sport.org топовые слоты, живые дилеры и эксклюзивные бонусы. Всё для вашего комфорта и выигрышей.
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали сервисный центр philips в москве, можете посмотреть на сайте: официальный сервисный центр philips
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Bonsai Casino https://bonsai-play.org широкий выбор игр, щедрые бонусы, быстрые выплаты и безопасность. Наслаждайтесь слотами, рулеткой и живыми играми в комфортной и надёжной атмосфере.
Лучшие азартные игры в Bonsai Casino https://bonsai-download.com слоты, рулетка, блэкджек и живые дилеры. Щедрые бонусы и удобные выплаты в безопасной игровой среде.
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали сервисный центр philips, можете посмотреть на сайте: сервисный центр philips в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали сервисный центр philips в москве, можете посмотреть на сайте: сервисный центр philips в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Арматура 14 мм оптом https://armatura-14.ru и в розницу в Москве. Качественный металл по выгодным ценам. Быстрая доставка, широкий ассортимент и гибкие условия для частных клиентов и строительных компаний.
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали сервисный центр philips, можете посмотреть на сайте: официальный сервисный центр philips
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
I’m deeply thankful for your time and thoughts. You make writing worthwhile!
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали официальный сервисный центр philips, можете посмотреть на сайте: официальный сервисный центр philips
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали сервисный центр philips, можете посмотреть на сайте: сервисный центр philips
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Приобретение диплома ПТУ с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
купить качественную мебель в Киеве оплата частями на мебель и Украине от интернет магазина TM Mebel-24. Обзов готовых вариантов и на заказ от производителя.
Продажа квартир от застройщика https://prodatkvartiru-norka.ru в Казани: выгодные цены, современные планировки, удобные районы. Без посредников и переплат.
Квартиры от застройщика https://kvartiruzhkkupit.ru в Казани: новые дома, удобные планировки, комфортные районы. Прямые продажи, честные цены, акции и поддержка на всех этапах покупки.
оценка соут цена москва процедура проведения специальной оценки условий труда
Buy cheap proxies https://www.techicy.com/are-datacenter-proxies-the-ultimate-choice-for-online-gaming.html individual personal and anonymous. Personal proxies support 1 Gbps channel speed, connection by protocols
аккредитация соут в москве вредность соут москва
Класс Рђ400 Рё Рђ500 — наиболее распространенные типы арматуры, применяемые для укрепления бетонных конструкций, подверженных значительным нагрузкам. Ртот РІРёРґ арматуры находит применение РІ фундаментных плитах, перекрытиях, колоннах Рё балках.
armatura-12.ru
охрана быстрого реагирования система пультовой охраны
Стальной двутавр — это фасонный металлопрокат с Н-образным сечением поперечного профиля. Он изготавливается горячекатаным способом из углеродистых или низколегированных сталей при температуре 1200°C по стандарту ГОСТ 8239-89 https://dvutavrmsk.ru
провести соут цена москва специальная оценка условий труда 2024 москва
Секреты успеха в азартных играх Проблемы игроков перед крупным выигрышем
jetour dashing 1.5 mt отзывы jetour dashing сайт
where to buy helium balloons Dubai custom helium balloons with delivery Dubai
Наша вакансии доска объявлений — это удобный и надежный сервис, который объединяет тех, кто ищет работу, и тех, кто ищет сотрудников.
Федерация – это проводник в мир покупки запрещенных товаров, можно купить гашиш, купить кокаин, купить меф, купить экстази в различных городах. Москва, Санкт-Петербург, Краснодар, Владивосток, Красноярск, Норильск, Екатеринбург, Мск, СПБ, Хабаровск, Новосибирск, Казань и еще 100+ городов.
Класс А240 представляет собой арматуру, применяемую в конструкциях с невысокими нагрузками. Её диаметр, как правило, не превышает 10 мм, и она часто используется для формирования каркасов в малоэтажных зданиях.
http://sarmatura-12.ru
Федерация – это проводник в мир покупки запрещенных товаров, можно купить альфа пвп, купить кокаин, купить меф, купить экстази в различных городах. Москва, Санкт-Петербург, Краснодар, Владивосток, Красноярск, Норильск, Екатеринбург, Мск, СПБ, Хабаровск, Новосибирск, Казань и еще 100+ городов.
Арматура диаметром 32 мм, изготовленная из стали марки А500С, является одним из самых востребованных видов металлопроката в строительстве. Она применяется при возведении фундаментов, армировании стен и перемычек. https://armatura32.ru
Федерация – это проводник в мир покупки запрещенных товаров, можно купить альфа пвп, купить кокаин, купить меф, купить экстази в различных городах. Москва, Санкт-Петербург, Краснодар, Владивосток, Красноярск, Норильск, Екатеринбург, Мск, СПБ, Хабаровск, Новосибирск, Казань и еще 100+ городов.
Выбор отеля https://koffer-spb.ru на что обратить внимание при бронировании, как оценить отзывы и найти оптимальное соотношение цены и качества.
Saving with promo codes https://code-me.ru where to look, how to check and apply discounts for the best prices. Step-by-step tips for smart shopping.
Узнайте, как безопасно купить диплом о высшем образовании
Ищите свою пару? Сайт знакомства рядом объединяют людей для серьёзных отношений, дружбы или общения. Всё просто, удобно и эффективно.
Сервис ТвойЮрист https://tvoyurist.online оказывает бесплатные юридические консультации онлайн в чате и по телефону горячей линии для жителей Москвы и регионов России на основании ФЗ РФ N324 от 21.11.2011 «О бесплатной юридической помощи в Российской Федерации». Наша юридическая служба работает круглосуточно 24/7. Спросите бесплатно юристов без регистрации, и получите квалифицированный ответ юрисконсульта.
купить героин телеграмм олд спайс стик купить
порно тг детское порно секс слив цп
интим услуги курск снять шлюху в москве
виагра для мужчин цена в аптеке купить спайс москва
Конструкторы оружия России https://guns.org.ru истории выдающихся инженеров, их разработки и вклад в оборону страны. Биографии, достижения, факты и история создания легендарных образцов вооружения.
бк мелбет официальный https://melbet-24online.net.ru
make a resume engineer resume builder
Anonymous proxies https://miniproxy.net/comparing-the-speed-and-performance-of-opera-and-microsoft-edge/ for any tasks: high speed, stability, support for all protocols. Suitable for SMM, parsing, bots and games. Guaranteed confidentiality and 24/7 support.
Все о ремонте своими руками https://cooksy.ru подробные фото и видеоуроки, выбор материалов и инструментов, расчёт стоимости.
Инструкции для ремонта https://antr-adm.ru своими руками: как подготовить, спланировать и выполнить работы. Советы для всех видов ремонта с пошаговыми фото.
Инструкции для ремонта https://sklad-kotlov.ru своими руками: как подготовить, спланировать и выполнить работы. Советы для всех видов ремонта с пошаговыми фото.
Портал для ремонта https://fdmlev.ru своими руками: как справиться с задачами любой сложности. Полный перечень этапов, инструкции, фотоуроки и рекомендации по материалам для вашего дома.
Как сделать ремонт https://str-control.ru своими руками: простые пошаговые рекомендации, инструкции для начинающих и идеи для профессионалов.
Всё о самостоятельном ремонте https://erp-mta.ru простые решения для дома, инструкции по установке и отделке, выбор инструментов и материалов.
bu konuda bu kadar net bilgiler internette malesef yok bu yüzden çok iyi ve başarılı olmuş teşekkürler.
çok bilgilendirici bir yazı olmuş ellerinize sağlık teşekkür ederim
Всё о витаминах для здоровья https://vitamingid.ru их польза, источники, дозировки. Узнайте, как поддерживать иммунитет, улучшать самочувствие и восполнять нехватку витаминов.
Настройка домашнего оборудования https://vseprost.ru подробные гайды, советы и рекомендации. Узнайте, как подключить, настроить и оптимизировать работу устройств.
Ремонт своими руками https://fobii.org пошаговые советы, готовые решения и проверенные рекомендации. Легко и понятно для каждого, кто хочет преобразить свой дом своими силами.
Всё для студента https://chvuz.ru статьи, советы, методики и готовые материалы для упрощения учёбы. Быстрый доступ к полезной информации.
Ищете обмен валюты с минимальной комиссией? На сайте собрана информация об обменниках с лучшими курсами в Казахстане.
МФО Казахстана Ипотека .
сайт по ремонту своими руками https://9sam.ru от идей до готовых решений. Чёткие инструкции, фото, схемы и советы для обновления интерьера и устранения любых поломок.
Полный справочник https://lortut.ru по ЛОР-болезням: симптомы, причины, эффективные методы лечения и профилактики. Поддерживайте здоровье дыхательных путей с проверенными советами.
Рейтинги лучших товаров https://experttok.ru для красоты и здоровья: косметика, уход за кожей, витамины, техника для ухода и многое другое.
Сайт для будущих мам https://lberemenost.ru всё о беременности, родах и послеродовом периоде. Полезные советы, медицинские рекомендации и информация для заботы о здоровье мамы и малыша.
Легальные способы покупки диплома о среднем полном образовании
Беременность поэтапно https://zdoroplod.ru полные рекомендации по здоровью, уходу за собой, питанию и физической активности. Узнайте о развитии малыша и подготовке к родам с экспертной точки зрения.
Здоровье вашего ребенка https://craymed.ru рекомендации по уходу, профилактике болезней, правильному питанию и физической активности.
Полный справочник по болезням https://medicodo.ru симптомы, причины, эффективные методы лечения и профилактики. Поддерживайте здоровье дыхательных путей с проверенными советами.
Работа с металлами https://ometalledo.ru полезные советы по сварке, резке, шлифовке и других методах обработки. Рекомендации для начинающих и опытных мастеров
Kairospeak https://kairospeak.com is a platform that helps users discover arbitrage pairs across cryptocurrency exchanges. It gathers real-time ticker data and analyzes price differences, factoring in trading fees, withdrawal costs, and the current order book. When a profitable opportunity is found, the platform notifies the user.
Выберите лучшие гемблинг партнерки https://seciva.ru/programs-tag/gembling/ для заработка. Узнайте, как выбрать партнерскую программу, что лучше — CPA или RevShare, и начните зарабатывать.
Информация о здоровье https://mediklekar.ru от профилактики и правильного питания до советов по лечению и поддержанию энергии.
Онлайн-кошельки https://payinfor.ru гайды по созданию, настройке и использованию. Сравнение популярных сервисов, советы по защите данных и управлению финансами.
Mostbet casino ma szeroka game gier hazardowych | Mostbet bonus bez depozytu to idealna opcja na start | Mostbet pl zapewnia bezpieczna rozrywke online | Mostbet logowanie odbywa sie za pomoca jednego klikniecia | Mostbet promo code no deposit to unikalna okazja | Mostbet Polska zapewnia szybkie wyplaty wygranych mostbet. | Mostbet darmowe spiny to swietny sposob na rozpoczecie gry | Mostbet online oferuje szeroka game gier i zakladow | Mostbet 30 free spins to idealna okazja na rozpoczecie gry Mostbet rejestracja.
Приветствуем вас и приглашаем в наш магазин металлопроката! У нас представлен широкий ассортимент высококачественных материалов для любых строительных и производственных нужд. Мы предлагаем только проверенные и надежные изделия, которые помогут вам воплотить в жизнь самые смелые проекты. Наши специалисты всегда готовы помочь вам с выбором и ответить на все ваши вопросы. Заходите, выбирайте и заказывайте с уверенностью!
http://metprokatmsk.ru
Официальный сайт Melbet https://melbet-24online.net.ru ставки на спорт, турниры, лайв-игры и слоты. Простая регистрация, быстрая выплата выигрышей и множество бонусов для новых и постоянных игроков.
Конструкторы оружия России https://guns.org.ru история создания легендарного оружия, биографии инженеров, технические характеристики разработок.
Всё о продуктах питания https://vsedlypolsy.ru их свойства, влияние на организм, советы по правильному выбору и сочетанию. Сделайте осознанное питание частью вашей жизни.
Справочник по ремонту https://club-sante.ru идеи для ремонта, рекомендации по отделке, расчёты и схемы. Полезная информация для качественного и экономного обновления вашего дома.
Советы для мам https://travailon.ru уход за ребёнком, развитие, воспитание и здоровье. Полезные рекомендации для комфортного материнства и гармоничного роста малыша.
Справочник по ремонту и строительству https://azimutmebel.ru идеи для проектов, инструкции, лайфхаки и рекомендации по выбору материалов.
ремонт и строительство https://losinka-kirpich.ru справочник с советами по планированию, выбору технологий, отделке и дизайну. Полезно как для новичков, так и для профессионалов.
Mostbet to najlepsze kasyno online w Polsce | Mostbet free spins czekaja na nowych uzytkownikow | Mostbet oferuje zaklady na zywo i kasyno w jednym miejscu | Mostbet aplikacja jest bezpieczna i latwa do instalacji | Mostbet kod promocyjny 2024 to wyjatkowa oferta | Mostbet bonus bez depozytu za rejestracje to doskonaly start most bet pl. | Mostbet casino login jest szybkie i bezpieczne | Mostbet bonus za rejestracje to doskonala okazja | Mostbet rejestracja daje dostep do ekskluzywnych bonusow Mostbet bonus za rejestracje.
Полный справочник https://rasayanavl.ru по ремонту и строительству: пошаговые гайды, расчёты, подбор инструментов и материалов.
Гайды по ремонту https://postroikado.ru своими руками: советы для новичков и опытных мастеров. Всё о материалах, инструментах и этапах ремонта в удобном формате.
Информация для врачей https://ovrachahl.ru актуальные медицинские статьи, клинические рекомендации, исследования и практические советы для профессионального роста.
Сайт о юриспруденции https://besturisty.ru актуальные законы, судебная практика, комментарии юристов и рекомендации по решению правовых вопросов.
Сайт о юриспруденции https://besturisty.ru актуальные законы, судебная практика, комментарии юристов и рекомендации по решению правовых вопросов.
Справочник по медицине https://konsmediic.ru заболевания, методы их лечения, профилактика, новости медицины и рекомендации по укреплению здоровья для всех возрастов.
Медицина для всех https://vrachataj.ru подробности о болезнях, терапии, диагностике и профилактике. Узнайте, как заботиться о здоровье эффективно.
самара глазная клиника глазная клиника частная
Медицинский портал https://zdorovemira.ru справочник болезней, рекомендации по лечению, здоровому образу жизни и укреплению иммунитета.
Права граждан России https://pravookey.ru разбор законодательства, советы по обращению в суды, оформлению документов и защите своих интересов.
Полезный сайт о медицине https://zdorovemira.ru ответы на популярные вопросы, советы по питанию, укреплению иммунитета и поддержанию хорошего самочувствия.
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали сервисный центр asus в москве, можете посмотреть на сайте: сервисный центр asus рядом
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Mostbet to najlepsze kasyno online w Polsce | Mostbet logowanie jest proste i szybkie | Mostbet bonus za rejestracje jest jednym z najlepszych w branzy | Mostbet Polska to lider na rynku zakladow sportowych | Mostbet kod promocyjny 2024 to wyjatkowa oferta | Mostbet casino no deposit bonus codes daja wiecej mozliwosci most bet. | Mostbet kasyno online to miejsce dla kazdego gracza | Mostbet aplikacja jest kompatybilna z kazdym urzadzeniem | Mostbet kasyno to swietna zabawa i wielkie wygrane Mostbet bonus za rejestracje.
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали сервисный центр asus сервис, можете посмотреть на сайте: сервисный центр asus
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Всё для здоровья https://capitalaw.ru на медицинском портале: подробные статьи, советы врачей, полезная информация о симптомах, лечении, профилактике и укреплении здоровья.
справочник болезней https://vrachgigiena.ru рекомендации по лечению, здоровому образу жизни и укреплению иммунитета. Всё о медицине в одном месте
Всё об оформлении документов https://obrascidoc.ru сайт с готовыми образцами заявлений, контрактов, справок и официальных бумаг для различных нужд.
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали сервисный центр asus адреса, можете посмотреть на сайте: сервисный центр asus адреса
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали сервисный центр asus в москве, можете посмотреть на сайте: сервисный центр asus цены
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Сайт о законах https://yslugiyurista.ru и граждан России: законы, правовая помощь, гайды по решению юридических вопросов и защите прав в любых жизненных ситуациях.
Семейные споры https://capitallawdo.ru развод, алименты, раздел имущества. Юридическая помощь, советы по оформлению документов и защите ваших интересов в суде.
Полезный сайт о правах граждан https://konslegal.ru информация о правах и обязанностях, советы по взаимодействию с госорганами и защите интересов.
Права граждан России https://konsaltdo.ru разбор законодательства, советы по обращению в суды, оформлению документов и защите своих интересов.
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали сервисный центр asus, можете посмотреть на сайте: сервисный центр asus
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Сетка и металлопродукция https://setka.by в Минске: продажа от производителя. Широкий ассортимент, доступные цены, быстрая доставка. Качество и надёжность для строительства и производства.
BNX is a cryptocurrency exchange https://bnx.me for beginners and professionals. Fast transactions, favorable rates, a wide selection of cryptocurrencies and the safety of your funds.
Kazakhstan’s leading university Satbayev University with a wide range of engineering programs, unique laboratories and internships. Prepares specialists for a successful career in the field of technology.
CVzen.pl https://cvzen.pl to lider w pisaniu CV i coachingu kariery, zaufany przez miliony na calym swiecie. Oferujemy wsparcie na kazdym etapie kariery: od tworzenia CV i listow motywacyjnych po optymalizacje profilu LinkedIn i coaching kariery. Pomagamy odkryc nowe mozliwosci dzieki CV, ktore podkresla Twoj potencjal.
маркетинговые исследования целевого рынка маркетинговые исследования рынка предприятий
CVpro.pt https://cvpro.pt e lider em redacao de curriculos e coaching de carreira, apoiando milhoes de candidatos globalmente. Oferecemos curriculos profissionais, cartas de apresentacao personalizadas, otimizacao de perfis no LinkedIn e coaching de carreira. Nosso time de especialistas ajuda voce a destacar seu potencial e conquistar novas oportunidades na sua jornada profissional.
CVpro.com.tr https://cvpro.com.tr milyonlarca is arayan?n guvendigi lider CV yazma ve kariyer koclugu hizmetidir. Uzman ekibimiz, profesyonel CV, sektore ozel on yaz?, LinkedIn profili optimizasyonu ve kisisel kariyer koclugu ile gercek potansiyelinizi ortaya c?kararak kariyer hedeflerinize ulasman?za destek olur. Yeni f?rsatlar? kesfetmek icin yan?n?zday?z!
CVlettre.fr https://cvlettre.fr est votre partenaire de confiance pour booster votre carriere. Nous offrons des services professionnels de redaction de CV et lettres de motivation pour decrocher l’emploi de vos reves. Avec nos outils IA, modeles personnalisables et conseils experts adaptes a chaque secteur, nous garantissons une candidature qui se demarque. Faites briller votre potentiel avec CVlettre.
I am truly thankful to the owner of this web site who has shared this fantastic piece of writing at at this place.
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.
Harika bir paylaşım, özellikle konunun önemli detayları oldukça net bir şekilde açıklanmış. İnsanları çeşitli karmaşık anahtar kelimelerle yormak yerine, okumaktan keyif alacağı içerikler her zaman daha iyidir. Kaliteli paylaşım adına teşekkür eder, paylaşımlarınızın devamını sabırsızlıkla beklerim.
bu konuda bu kadar net bilgiler internette malesef yok bu yüzden çok iyi ve başarılı olmuş teşekkürler.
Yazdığınız yazıdaki bilgiler altın değerinde çok teşekkürler bi kenara not aldım.
КОМПМАСТЕР https://комп-мастер.рф качественный ремонт компьютеров, ноутбуков, телевизоров, принтеров, телефонов и кофемашин в Воркуте. Более 14 лет опыта!
Abrone.jobs https://abrone.jobs is the gateway to careers at Abrone, a leader in AI, data, and analytics. Join a dynamic team driving innovation with cutting-edge tech. Enjoy remote work, competitive benefits, and career growth. If you’re passionate about AI or analytics, Abrone is where you’ll thrive!
Cryptocurrency trading https://bnx.me is easy and safe with BNX.me. Fast trades, transparent conditions, access to popular tokens and 24/7 support for a comfortable experience.
Исследование рынков https://issledovaniya-rynkov.ru аналитика и исследования в сфере услуг. Детальные обзоры, прогнозы, конкурентный анализ и ключевые данные для бизнеса. Актуальная информация для роста.
Заказать курсовую работу https://kursovaya-rabota-na-zakaz.ru у нас — это гарантированное качество, соответствие всем требованиям преподавателя и экономия вашего времени. Мы профессионально подходим к написанию курсовых, учитывая все пожелания и специфику вашего задания.
Современная офтальмологическая https://glaznaya-klinika-samara.ru клиника в Самаре диагностика, лечение заболеваний глаз, коррекция зрения и лазерные операции.
Подписка СберПрайм https://promoconcert.ru за 1 рубль: доступ к онлайн-кинотеатрам, музыке, скидкам на покупки и сервисам доставки. Экономьте и получайте больше возможностей.
Как купить диплом о высшем образовании с минимальными рисками
Потрясающий игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас невероятные варианты для максимальных успехов! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые призы и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы получите возможность получить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает интересные турниры, которые поднимут ваш азарт. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует простой и удобный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк дадут вам фриспины каждый день. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Лев, и завоевывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Только здесь вы попробуете выиграть огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Фантастический игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас захватывающие варианты для крупных выигрышей! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ждут прекрасные подарки и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы попробуете выиграть крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает интересные турниры, которые поднимут ваш настроение. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только рулетка и покер, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система предложат вам фриспины на регулярной основе. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и ассортимент слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность завоевать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Грандиозный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 дарит для вас фантастические варианты для ярких побед! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют прекрасные подарки и огромное количество игр. Всегда здесь вы откроете для себя сорвать колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, обеспечивает легкость использования на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только игровые автоматы, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план порадуют вас бесплатные вращения на каждом шагу. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас встречают удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы получите возможность захватить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
регистрация зума казино сайт zooma casino
Лучший игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас невероятные варианты для успешной игры! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ждут акционные игры и огромное количество игр. Всегда здесь вы сможете сорвать невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшат ваш настроение. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт дарит вам простой и удобный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любой платформе. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только игровые автоматы, но и живые дилеры, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш бонусная система помогут вам бонусные кредиты на регулярной основе. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и добивайся призов каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют удивительные акции и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность сорвать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Топовый игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас уникальные варианты для ярких побед! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают прекрасные подарки и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы попробуете захватить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает регулярные акции, которые поднимут ваш азарт. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Игровая платформа гарантирует интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На игровом доме Лев вас радуют не только игровые автоматы, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план порадуют вас дополнительные средства при каждом пополнении. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай богатства каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют приятные подарки и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы попробуете захватить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Потрясающий игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас фантастические опции для крупных выигрышей! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут выгодные предложения и разнообразие игровых предложений. Только здесь вы попробуете выиграть колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт предлагает простой и удобный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только настольные игры, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас фриспины на каждом шагу. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся славы каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас встречают щедрые призы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы успеете завоевать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
In case you’re feeling adrift in your career or just require some orientation, Career Guide delivers extensive advice and instruments to aid you discover your direction. It’s a great site to commence!
Грандиозный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предоставляет для вас захватывающие опции для крупных выигрышей! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы успеете захватить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш настроение. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам интуитивно понятный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас встретят не только настольные игры, но и живые игры, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на регулярной основе. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Лев, и добивайся удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность завоевать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
undressai undressai app
Лучший игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас невероятные возможности для победных стратегий! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя получить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш настроение. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы победить. Наш сайт дарит вам эргономичный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас встретят не только игровые автоматы, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план предложат вам фриспины на каждом шагу. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Лев, и добивайся признания каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют приятные подарки и богатый выбор игр. Именно здесь вы получите возможность сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Platform BNX is your reliable partner for cryptocurrency trading. High liquidity, instant trades and advanced analytics tools.
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предлагает для вас невероятные возможности для ярких побед! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые призы и множество игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете для себя выиграть множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшают ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы выиграть. Казино Лев и Азино777 предлагает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас встретят не только рулетка и покер, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом в любое время. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности помогут вам фриспины на регулярной основе. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы попробуете выиграть колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас великолепные варианты для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут выгодные предложения и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы попробуете получить огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы сорвать куш. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует простой и удобный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только слоты, но и живые игры, которые позволят вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки предложат вам бесплатные вращения на каждом шагу. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай призов каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас встречают удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы сможете завоевать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас невероятные варианты для победных стратегий! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают щедрые призы и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя выиграть невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает регулярные акции, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы достичь успеха. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только настольные игры, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план предложат вам дополнительные средства на регулярной основе. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай признания каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас радуют приятные подарки и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы успеете получить огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный сервис ремонта холодильника на дому всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши морозильные камеры, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы холодильников, включают проблемы с температурным режимом, проблемы с температурным датчиком, программные сбои, проблемы с подключением и повреждения уплотнителей. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт компрессоров, термостатов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный сервис ремонта холодильника в москве.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-holodilnikov-lux.ru
Актуальный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас фантастические возможности для максимальных успехов! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас встречают акционные игры и огромное количество игр. Только здесь вы сможете получить колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает регулярные акции, которые поднимут ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт дарит вам максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас радуют не только слоты, но и живые дилеры, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система помогут вам фриспины на каждом шагу. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся богатства каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность захватить множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Актуальный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас уникальные возможности для крупных выигрышей! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы сможете получить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы сорвать куш. Наш сайт гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас радуют не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система помогут вам фриспины при каждом пополнении. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай признания каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас радуют щедрые призы и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность завоевать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный мастер по ремонту электровелосипедов на выезде любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши электровелосипеды, и обеспечиваем ремонт наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы электровелосипедов, включают поломку аккумулятора, проблемы с мотором, сбои контроллера, неисправные тормоза и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, тормозных систем и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный сервис ремонта электровелосипеда с гарантией.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-elektrovelosipedov-gem.ru
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас уникальные опции для максимальных успехов! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы откроете для себя сорвать невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшают ваш настроение. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт дарит вам простой и удобный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На игровом доме Лев вас радуют не только настольные игры, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас дополнительные средства на каждом шагу. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и получай признания каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и богатый выбор игр. Только здесь вы попробуете захватить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный качественный ремонт электровелосипедов любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши электрические велосипеды, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи электрических велосипедов, включают неисправную батарею, неработающий двигатель, неисправный контроллер, проблемы с тормозами и поломки рамы. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, тормозных систем и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы обеспечиваете себе качественный и надежный сервис ремонта электровелосипеда на выезде.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-elektrovelosipedov-gem.ru
Топовый игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас уникальные шансы для максимальных успехов! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают акционные игры и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы успеете сорвать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт дарит вам простой и удобный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на любом гаджете. На Lev вас радуют не только слоты, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на каждом шагу. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и богатый выбор игр. Только здесь вы попробуете захватить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный экспресс ремонт электронной книги любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши цифровые книги, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы электронных книг, включают проблемы с экраном, неисправную батарею, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и сбои контроллера. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и контроллеров. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе качественный и надежный мастерская по ремонту электронной книги на дому.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-elektronnyh-knig-hit.ru
Лучший игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас незабываемые варианты для успешной игры! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и огромное количество игр. Только здесь вы попробуете выиграть множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает интересные турниры, которые поднимут ваш настроение. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только слоты, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш при каждом пополнении. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Только здесь вы попробуете сорвать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Топовый игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 дарит для вас захватывающие варианты для успешной игры! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и огромное количество игр. Всегда здесь вы откроете для себя получить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые увеличат ваш азарт. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы выиграть. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас встретят не только игровые автоматы, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность почувствовать себя в настоящем казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система порадуют вас бесплатные вращения при каждом пополнении. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают приятные подарки и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы откроете сорвать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный центр ремонта электронных книг на выезде всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши eBook-ридеры, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы электронных книг, включают неисправный дисплей, поломку аккумулятора, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и проблемы с контроллером. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и контроллеров. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный сервисный центр по ремонту электронной книги в москве.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-elektronnyh-knig-hit.ru
Лучший игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 дарит для вас великолепные варианты для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и богатый выбор слотов. Всегда здесь вы успеете выиграть колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые поднимут ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только настольные игры, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности помогут вам бесплатные вращения при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые призы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность сорвать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Играйте в казино онлайн с удовольствием, станьте победителем.
Почувствуйте драйв от игры в казино онлайн, достижение успеха рядом.
Играйте только на проверенных сайтах, ищите выгодные предложения.
Зарабатывайте большие деньги в интернет-казино, играя в популярные слоты.
Присоединяйтесь к сообществу азартных игроков, испытывайте азарт в полной мере.
Играйте и выигрывайте вместе с лучшими, трансформируйте свою жизнь.
Попробуйте свою удачу в онлайн казино, становясь настоящим профи.
Разнообразие игр ждет вас в онлайн казино, наслаждайтесь игрой в любое время суток.
Получайте удовольствие от игры в казино онлайн, завоюйте вершину мира азарта.
Играйте в онлайн казино смартфоне, получая прибыль.
Почувствуйте азарт от неожиданных побед, испытывая удовольствие от игры.
Достижения ждут вас в увлекательном мире азарта, завоевывая новые вершины.
Примите вызов и выиграйте крупный джекпот, получайте удовольствие от игры в любое время дня и ночи.
Улучшайте свои навыки игры в казино онлайн, анализируя перемены.
онлайн казино беларусь Казино .
Топовый игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас незабываемые опции для ярких побед! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы откроете для себя завоевать крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает регулярные акции, которые поднимут ваш настроение. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 обеспечивает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только слоты, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк дадут вам дополнительные средства на каждом шагу. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете выиграть множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предоставляет для вас потрясающие варианты для крупных выигрышей! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя выиграть крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы выиграть. Игровая платформа предлагает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, обеспечивает легкость использования на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Lev вас радуют не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система порадуют вас дополнительные средства на регулярной основе. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Лев, и добивайся признания каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас встречают приятные подарки и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете выиграть огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предлагает для вас невероятные опции для крупных выигрышей! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые призы и огромное количество игр. Всегда здесь вы сможете завоевать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшают ваш настроение. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы достичь успеха. Игровая платформа гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас встретят не только рулетка и покер, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш бонусная система помогут вам дополнительные средства при каждом пополнении. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы успеете сорвать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
исследование рынка обуви в россии исследование рынка глины в россии
исследование рынка керосина авиационного в россии исследование рынка стеклянной посуды в россии
Фантастический игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас невероятные варианты для крупных выигрышей! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают прекрасные подарки и богатый выбор слотов. Всегда здесь вы откроете для себя сорвать невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшают ваш настроение. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы сорвать куш. Наш сайт дарит вам максимально удобный доступ, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только игровые автоматы, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую в любое время. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк помогут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на каждом шагу. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Lev, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ждут удивительные акции и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы сможете захватить множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Грандиозный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предоставляет для вас захватывающие возможности для победных стратегий! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают акционные игры и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы успеете захватить колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает регулярные акции, которые поднимут ваш настроение. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт предлагает простой и удобный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любой платформе. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только слоты, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк дадут вам бонусные кредиты на каждом шагу. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Лев, и добивайся славы каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы сможете сорвать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас невероятные возможности для крупных выигрышей! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают удивительные акции и богатый выбор слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы попробуете захватить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает регулярные акции, которые поднимут ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы выиграть. Казино Лев и Азино777 обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любой платформе. На Lev вас ждут не только видеослоты, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности порадуют вас бонусные кредиты при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые призы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы получите возможность выиграть невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный сервисный центр по ремонту аймака в москве различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши компьютеры Apple, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы iMac, включают неисправности HDD, неисправности дисплея, неисправности разъемов, неисправности программного обеспечения и неисправности системы охлаждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный центр ремонта аймака.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Фантастический игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предоставляет для вас захватывающие варианты для успешной игры! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают прекрасные подарки и огромное количество игр. Только здесь вы успеете сорвать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые поднимут ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы выиграть. Наш сайт обеспечивает максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любой платформе. На Lev вас встретят не только слоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом в любое время. Кроме того, наш бонусная система порадуют вас бесплатные вращения при каждом пополнении. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай славы каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Только здесь вы попробуете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
купить меф героин кокаин кокаин купить цена
Безупречный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас незабываемые шансы для ярких побед! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают прекрасные подарки и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете захватить огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает регулярные акции, которые поднимут ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы достичь успеха. Игровая платформа предлагает простой и удобный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только видеослоты, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план предложат вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на регулярной основе. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы успеете получить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный центр ремонта аймака рядом различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши моноблоки iMac, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы iMac, включают неисправности HDD, повреждения экрана, неисправности разъемов, ошибки ПО и неисправности системы охлаждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, разъемов, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете долговечный и надежный мастерская по ремонту аймака рядом.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-imac-mos.ru
Актуальный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас фантастические опции для победных стратегий! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ждут прекрасные подарки и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы сможете сорвать крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает регулярные акции, которые улучшают ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы сорвать куш. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам простой и удобный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только слоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую в любое время. Кроме того, наш бонусная система дадут вам бонусные кредиты на регулярной основе. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ждут щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы сможете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный отремонтировать айфон с гарантией всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши устройства iPhone, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи смартфонов Apple, включают проблемы с экраном, проблемы с батареей, ошибки ПО, неисправности разъемов и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный отремонтировать айфон рядом.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-iphone-sot.ru
Актуальный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас великолепные возможности для победных стратегий! На онлайн-казино Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют прекрасные подарки и богатый выбор слотов. Всегда здесь вы попробуете получить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы сорвать куш. Наш сайт гарантирует интуитивно понятный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас встретят не только игровые автоматы, но и живые игры, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности помогут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш при каждом пополнении. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся признания каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают удивительные акции и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы успеете завоевать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Ваш проводник в мире права https://legallurist.ru актуальные статьи, комментарии юристов, новости законодательства и ответы на важные вопросы
Актуальные материалы по юриспруденции https://lawdelov.ru законы, практические рекомендации, разбор сложных ситуаций.
Ваш гид https://pravovoeob.ru в мире правовых норм: обязанности граждан, защита прав, полезные рекомендации и новости законодательства.
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту iphone с гарантией любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши iPhone, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы iPhone, включают поврежденный экран, поломку батареи, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие разъемы и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный сервисный ремонт айфона адреса.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-iphone-sot.ru
Быстрое обучение и получение диплома магистра – возможно ли это?
Необыкновенный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас незабываемые возможности для победных стратегий! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают акционные игры и разнообразие игровых предложений. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя завоевать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает регулярные акции, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы выиграть. Игровая платформа дарит вам быстрый и легкий процесс игры, что делает игру комфортной на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только игровые автоматы, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас дополнительные средства при каждом пополнении. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся богатства каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют приятные подарки и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы попробуете завоевать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный центр ремонта макбука любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши ноутбуки Apple, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы MacBook, включают проблемы с экраном, поломку батареи, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и неисправности системы охлаждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе надежный и долговечный центр ремонта macbook с гарантией.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-macbook-club.ru
Сайт о налогах https://nalogido.ru изменения в законах, советы по декларированию и минимизации налоговых рисков.
PicusBlog https://picusblog.com a blog with an American flavor. We cover news, celebrities, food, sports, nature, travel, animals, relationships and many other things that interest Americans (and not only) every day! PicusBlog – Your Daily Dose of Insights, Intrigue, and Inspiration!
Потрясающий игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас фантастические варианты для успешной игры! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас встречают акционные игры и богатый выбор слотов. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя завоевать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш настроение. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы выиграть. Игровая платформа обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, что делает игру комфортной на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только настольные игры, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности предложат вам бесплатные вращения при каждом пополнении. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Именно здесь вы получите возможность получить множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Журнал для юристов https://zakonwin.ru практические советы, правовая аналитика, актуальная судебная практика и готовые инструменты.
Практический журнал https://uristvzakon.ru для юриста: аналитика, советы, готовые решения. Помощь в работе над делами любой сложности.
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный сервисный центр по ремонту macbook с гарантией различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши устройства MacBook, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы MacBook, включают проблемы с экраном, поломку батареи, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и неисправности системы охлаждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе надежный и долговечный сервисный центр по ремонту макбука на выезде.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-macbook-club.ru
Топовый игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас незабываемые шансы для крупных выигрышей! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы успеете выиграть невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшают ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы достичь успеха. Игровая платформа обеспечивает максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любой платформе. На игровом доме Лев вас радуют не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план дадут вам бонусные кредиты на каждом шагу. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Лев, и добивайся признания каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ждут удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы сможете сорвать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный сервисный ремонт варочных панелей в москве различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши плиты, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели кухонных поверхностей, включают проблемы с нагревом, проблемы с сенсорным управлением, ошибки ПО, неработающие разъемы и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, сенсоров, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный сервис ремонта варочных панелей.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-varochnyh-paneley-hit.ru
Фантастический игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 раскрывает для вас невероятные варианты для успешной игры! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют акционные игры и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы получите возможность сорвать колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы победить. Игровая платформа обеспечивает максимально удобный доступ, что делает игру комфортной на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас встретят не только видеослоты, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк помогут вам бонусные кредиты на регулярной основе. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай богатства каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы откроете завоевать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Профессиональные сантехнические услуги https://moskva-santehnicheskie-raboty.ru установка, ремонт и замена сантехники, устранение протечек, прочистка труб. Работаем быстро, качественно и с гарантией. Оперативный выезд и доступные цены. Ваш комфорт – наша забота!
Качественные услуги сантехника https://santehnik-na-dom-moscow.ru от мелкого ремонта до сложных систем. Замена труб, установка сантехники, устранение аварий. Работаем аккуратно, быстро и с гарантией. Звоните, и мы решим вашу проблему!
Права граждан РФ https://pravoup.ru доступные объяснения законодательства, практическая помощь и актуальные новости.
Актуальный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас потрясающие опции для ярких побед! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы попробуете завоевать колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы достичь успеха. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует простой и удобный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На Lev вас ожидают не только игровые автоматы, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай признания каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете получить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Консультации врачей онлайн https://onlinvrach.ru диагностика, анализы, контроль лечения. Все для вашего здоровья, не выходя из дома.
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный выездной ремонт варочных панелей любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши варочные панели, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели кухонных поверхностей, включают неработающие конфорки, проблемы с сенсорным управлением, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт нагревательных элементов, сенсоров, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе надежный и долговечный мастер по ремонту варочных панелей на дому.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-varochnyh-paneley-hit.ru
Грандиозный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 открывает для вас невероятные шансы для победных стратегий! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют прекрасные подарки и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность захватить огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы сорвать куш. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только слоты, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш при каждом пополнении. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы попробуете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный сервисный центр по ремонту видеокамеры рядом различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши камеры, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели камер, включают неисправности записи, проблемы с объективом, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт записи, объективов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный центр ремонта видеокамер адреса.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-videokamer-ink.ru
Безупречный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас невероятные возможности для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые призы и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя получить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые поднимут ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы выиграть. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, что делает игру комфортной на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только видеослоты, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш бонусная система порадуют вас бесплатные вращения при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас радуют удивительные акции и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы откроете выиграть крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
производство бытовок и блок контейнеров бытовка металлическая купить
Все о ваших правах https://agkonsult.ru это портал, где вы найдете полную информацию о ваших гражданских, трудовых, семейных и других правах
Консультация юриста https://konsultantok.ru ваш помощник в решении юридических вопросов. Услуги профессиональных юристов, онлайн-консультации, полезные статьи.
Портал о ваших правах https://pravovoeobesp.ru это база знаний о законах, правах и обязанностях. Сайт создан для тех, кто хочет защищать свои интересы, получать ответы на юридические вопросы.
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный ремонт видеокамер рядом всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши видеорегистраторы, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи видеорегистраторов, включают неработающую запись, проблемы с объективом, ошибки ПО, неработающие разъемы и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт записи, объективов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный центр ремонта видеокамер с гарантией.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-videokamer-ink.ru
Безупречный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас потрясающие варианты для ярких побед! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют акционные игры и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы попробуете сорвать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт гарантирует быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любой платформе. На Lev вас радуют не только слоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк предложат вам фриспины на каждом шагу. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся призов каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы сможете выиграть множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный центр ремонта видеокарт рядом любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши графические карты, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи графических карт, включают неисправности системы охлаждения, выход из строя памяти, неисправности разъемов, неисправность контроллера и программные сбои. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт системы охлаждения, памяти, разъемов, контроллеров и ПО. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный отремонтировать видеокарту в москве.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-videokart-biz.ru
Безупречный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предоставляет для вас потрясающие варианты для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и огромное количество игр. Только здесь вы откроете для себя захватить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только видеослоты, но и живые игры, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую в любое время. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки предложат вам бонусные кредиты на регулярной основе. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и получай славы каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность захватить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Юридическая помощь автолюбителям https://avtopravodo.ru ваш надежный источник информации о правах водителей. Разбор ДТП, штрафы, страховые споры, возврат прав – все, что нужно для защиты ваших интересов.
Статьи для вас и вашего бизнеса https://businessfaq.ru подборка актуальных материалов для предпринимателей. Советы по управлению, развитию, финансам и маркетингу, чтобы ваш бизнес процветал.
Бизнес статьи https://consultantdo.ru платформа для предпринимателей. Полезные материалы, аналитика и советы экспертов для успешного управления бизнесом, развития и повышения прибыли.
Права и обязанности граждан https://juristywin.ru это ресурс для тех, кто хочет знать свои права, соблюдать законы и уверенно решать правовые вопросы.
Актуальный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас уникальные шансы для успешной игры! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ждут прекрасные подарки и огромное количество игр. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете выиграть крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшают ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа обеспечивает максимально удобный доступ, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас ждут не только рулетка и покер, но и живые игры, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности помогут вам дополнительные средства при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас встречают приятные подарки и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы сможете выиграть огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный мастер по ремонту видеокарт в москве всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши графические адаптеры, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы видеокарт, включают проблемы с вентиляцией, неисправность памяти, неисправности разъемов, неисправность контроллера и ошибки драйверов. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт системы охлаждения, памяти, разъемов, контроллеров и ПО. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете долговечный и надежный центр ремонта видеокарт рядом.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-videokart-biz.ru
Потрясающий игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас невероятные опции для ярких побед! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые призы и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы успеете получить колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы победить. Наш сайт предлагает простой и удобный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только видеослоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система предложат вам дополнительные средства на регулярной основе. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые призы и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы успеете выиграть множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный мастер по ремонту гироскутера на дому всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши самобалансирующиеся скутеры, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели самобалансирующихся скутеров, включают неисправную батарею, неработающий двигатель, поломку контроллера, неработающие сенсоры и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, гиросенсоров и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе качественный и надежный сервисный ремонт гироскутеров адреса.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-giroskuterov-key.ru
Безупречный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 раскрывает для вас захватывающие возможности для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас ждут прекрасные подарки и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность получить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые поднимут ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только настольные игры, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система дадут вам бонусные кредиты при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Лев, и добивайся богатства каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и богатый выбор игр. Всегда здесь вы сможете выиграть огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный мастер по ремонту гироскутера всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши гироскутеры, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы гироскутеров, включают проблемы с батареей, проблемы с мотором, сбои контроллера, неработающие сенсоры и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, гиросенсоров и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный официальный ремонт гироскутеров с гарантией.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-giroskuterov-key.ru
Фантастический игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас фантастические опции для победных стратегий! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые призы и множество игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы откроете для себя завоевать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только видеослоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас фриспины на каждом шагу. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай призов каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете завоевать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный мастерская по ремонту духового шкафа в москве различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши кухонные приборы, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы духовых шкафов, включают неработающие нагревательные элементы, неисправный таймер, треснувшую дверцу, неисправность контроллера, проблемы с конвекцией и неисправные платы. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, термостатов, таймеров, дверец, контроллеров, вентиляторов и электроники. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный официальный ремонт духового шкафа на дому.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-duhovyh-shkafov-ace.ru
Актуальный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас фантастические опции для успешной игры! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые призы и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы успеете сорвать крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш азарт. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт дарит вам интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас приветствуют не только настольные игры, но и живые игры, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на регулярной основе. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай признания каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют приятные подарки и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас невероятные возможности для максимальных успехов! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и богатый выбор слотов. Только здесь вы откроете для себя выиграть огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш азарт. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Игровая платформа дарит вам эргономичный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только игровые автоматы, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки помогут вам бесплатные вращения при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Lev, и получай богатства каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые призы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы сможете захватить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный сервис ремонта духовых шкафов адреса различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши духовые шкафы, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи духовок, включают неработающие нагревательные элементы, поломку таймера, треснувшую дверцу, сбои контроллера, проблемы с конвекцией и повреждения электроники. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, термостатов, таймеров, дверец, контроллеров, вентиляторов и электроники. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный мастер по ремонту духового шкафа рядом.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-duhovyh-shkafov-ace.ru
Лучший игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас незабываемые возможности для успешной игры! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают прекрасные подарки и разнообразие игровых предложений. Только здесь вы сможете завоевать колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые поднимут ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы выиграть. Наш сайт гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только рулетка и покер, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки предложат вам дополнительные средства каждый день. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай богатства каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют приятные подарки и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы получите возможность захватить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный мастерская по ремонту бесперебойников на дому различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши источники бесперебойного питания, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели источников бесперебойного питания, включают поломку аккумулятора, проблемы с инвертором, неисправный контроллер, неработающие разъемы и программные сбои. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт батарей, инверторов, контроллеров, разъемов и ПО. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный сервисный центр по ремонту бесперебойников рядом.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-ibp-max.ru
Грандиозный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предоставляет для вас захватывающие возможности для крупных выигрышей! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают щедрые призы и разнообразие игровых предложений. Только здесь вы сможете получить огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые поднимут ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы выиграть. Игровая платформа гарантирует интуитивно понятный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только игровые автоматы, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности предложат вам фриспины на каждом шагу. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся богатства каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и ассортимент слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете завоевать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Актуальный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предоставляет для вас незабываемые опции для крупных выигрышей! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют удивительные акции и множество игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы откроете для себя захватить колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшают ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы выиграть. Игровая платформа гарантирует интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только видеослоты, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности помогут вам бонусные кредиты каждый день. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Lev, и получай признания каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и ассортимент слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы попробуете получить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас потрясающие опции для максимальных успехов! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас радуют акционные игры и разнообразие игровых предложений. Именно здесь вы попробуете выиграть множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает регулярные акции, которые поднимут ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа предлагает эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только видеослоты, но и живые игры, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система предложат вам бесплатные вращения каждый день. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают выгодные предложения и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете выиграть колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный сервисный центр по ремонту бесперебойников различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши UPS, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы ИБП, включают неисправную батарею, неработающий инвертор, поломку контроллера, неработающие разъемы и неисправности программного обеспечения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт батарей, инверторов, контроллеров, разъемов и ПО. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный мастерская по ремонту бесперебойника адреса.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-ibp-max.ru
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас невероятные варианты для максимальных успехов! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают выгодные предложения и огромное количество игр. Всегда здесь вы успеете сорвать колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Игровая платформа дарит вам простой и удобный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только настольные игры, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк помогут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на каждом шагу. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы успеете получить множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный качественный ремонт игровой приставки всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши консоли, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы игровых приставок, включают поломку HDD, неисправные порты, проблемы с геймпадами, неисправности программного обеспечения и неисправности системы охлаждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт жестких дисков, разъемов, контроллеров, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете качественный и надежный центр ремонта игровой приставки в москве.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-igrovyh-konsoley-mob.ru
Скачайте приложение Mostbet Casino для удобной игры | Mostbet uz 97 – это качественный игровой опыт | Mostbet shaxsiy kabinet – это ваш личный центр управления ставками | Скачайте Mostbet casino apk для Android | Mostbet uz – это качество и безопасность для игроков mostbet uz kirish. | Mostbet shaxsiy kabinet – это безопасность и удобство | Mostbet bonuslar yangi foydalanuvchilar uchun mavjud | Mostbet shaxsiy kabinet kirish orqali barcha imkoniyatlar | Mostbet регистрация дает доступ к уникальным предложениям Mostbet shaxsiy kabinet kirish.
Актуальный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предоставляет для вас уникальные варианты для крупных выигрышей! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и огромное количество игр. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность выиграть множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы достичь успеха. Игровая платформа гарантирует интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только видеослоты, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности предложат вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на регулярной основе. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые призы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы получите возможность захватить множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предоставляет для вас потрясающие варианты для успешной игры! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и разнообразие игровых предложений. Именно здесь вы сможете сорвать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы победить. Игровая платформа предлагает эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любой платформе. На Lev вас радуют не только видеослоты, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система порадуют вас бонусные кредиты каждый день. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые призы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы сможете сорвать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный мастер по ремонту игровых приставок в москве различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши консоли, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы игровых приставок, включают проблемы с жестким диском, проблемы с разъемами, проблемы с геймпадами, ошибки ПО и перегрев. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт жестких дисков, разъемов, контроллеров, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете долговечный и надежный официальный ремонт игровой приставки на выезде.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-igrovyh-konsoley-mob.ru
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 открывает для вас невероятные опции для крупных выигрышей! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность сорвать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы достичь успеха. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас радуют не только рулетка и покер, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас фриспины при каждом пополнении. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай славы каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы попробуете получить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный починить индукционная плита различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши индукционные кухонные приборы, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы индукционных плит, включают неисправности нагревательных элементов, неработающие сенсоры, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие разъемы и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт нагревательных элементов, сенсорных панелей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный мастер по ремонту индукционной плиты в москве.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-indukcionnyh-plit-now.ru
Топовый игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предоставляет для вас уникальные возможности для успешной игры! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и ассортимент слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете выиграть крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает интересные турниры, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только видеослоты, но и живые игры, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас фриспины на регулярной основе. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и получай признания каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете захватить множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Потрясающий игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас потрясающие шансы для успешной игры! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ждут выгодные предложения и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете получить множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает регулярные акции, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы достичь успеха. Игровая платформа дарит вам максимально удобный доступ, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только видеослоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас бесплатные вращения на каждом шагу. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Лев, и получай богатства каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают выгодные предложения и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность выиграть колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный отремонтировать индукционная плита с гарантией любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши индукционные варочные панели, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели индукционных кухонных приборов, включают неисправности нагревательных элементов, проблемы с кнопками управления, ошибки ПО, неработающие разъемы и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт нагревательных элементов, сенсорных панелей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный ремонт индукционных плит.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-indukcionnyh-plit-now.ru
Необыкновенный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас великолепные шансы для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас встречают прекрасные подарки и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете сорвать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает интересные турниры, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт предлагает эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любой платформе. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только игровые автоматы, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк помогут вам дополнительные средства каждый день. Играй с азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай богатства каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и богатый выбор игр. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность захватить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный вызвать мастера по ремонту дронов рядом различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши духовые шкафы, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи духовок, включают проблемы с нагревом, поломку таймера, треснувшую дверцу, неисправность контроллера, проблемы с конвекцией и неисправные платы. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт нагревательных элементов, термостатов, таймеров, дверец, контроллеров, вентиляторов и электроники. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный официальный ремонт квадрокоптера на дому.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-kvadrokopterov-best.ru
купить светодиодный экран для сцены светодиодный экран купить москва
Портал права и обязанности https://legallup.ru граждан помогает разбираться в законах, правах и обязанностях. Полезные статьи и инструкции для защиты своих интересов.
Потрясающий игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас невероятные возможности для успешной игры! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы получите возможность получить огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы достичь успеха. Казино Лев и Азино777 предлагает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, что делает игру комфортной на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только настольные игры, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам дополнительные средства на каждом шагу. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай славы каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете завоевать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Права и обязанности граждан https://llawdo.ru источник знаний о ваших правах и обязанностях. Простая навигация и практическая информация для решения юридических вопросов.
Моё право https://moepravodo.ru ваш гид по законодательству. Простые объяснения, полезные рекомендации и образцы документов для реализации и защиты ваших прав.
Топовый игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предоставляет для вас великолепные варианты для успешной игры! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые призы и разнообразие игровых предложений. Именно здесь вы сможете выиграть крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает интересные турниры, которые поднимут ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Казино Лев и Азино777 обеспечивает простой и удобный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только видеослоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки дадут вам бесплатные вращения каждый день. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Lev, и получай славы каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают удивительные акции и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы сможете сорвать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас невероятные возможности для ярких побед! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете получить колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает интересные турниры, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, что делает игру комфортной на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только видеослоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности помогут вам фриспины каждый день. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Лев, и завоевывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ждут выгодные предложения и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы попробуете завоевать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Правовой ресурс https://pravoto.ru для тех, кто хочет знать свои права, защищать их и понимать законы. Актуальные статьи, инструкции и практическая информация для каждого.
Портал вся информация о законах https://zakonlw.ru предлагает разъяснения актуальных норм, советы экспертов и примеры решений юридических вопросов для граждан и бизнеса.
Потрясающий игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас невероятные опции для ярких побед! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас встречают акционные игры и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя получить колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает регулярные акции, которые улучшат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы достичь успеха. Игровая платформа предлагает простой и удобный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любом устройстве. На Lev вас приветствуют не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш бонусная система предложат вам бонусные кредиты при каждом пополнении. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут выгодные предложения и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы откроете завоевать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Потрясающий игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас фантастические опции для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и огромное количество игр. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете выиграть множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы достичь успеха. Игровая платформа гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только видеослоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую в любое время. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план дадут вам бонусные кредиты каждый день. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай признания каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете захватить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас уникальные варианты для ярких побед! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас радуют акционные игры и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы сможете завоевать невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает регулярные акции, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы достичь успеха. Игровая платформа предлагает простой и удобный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любой платформе. На Lev вас ждут не только настольные игры, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности предложат вам фриспины на регулярной основе. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся призов каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и богатый выбор игр. Именно здесь вы сможете получить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
vavada зеркала предоставляет уникальную возможность погрузиться в мир азартных игр. здесь вы сможете войти в систему на надёжной платформе vavada. получите доступ к специальным предложениям через мобильное приложение.
vavada бонус коды предоставляет уникальную возможность погрузиться в мир азартных игр. здесь вы сможете войти в систему на официальном сайте vavada. получите доступ к играм через удобный интерфейс.
телефон vavada предоставляет уникальную возможность погрузиться в мир азартных игр. здесь вы сможете зарегистрироваться на надёжной платформе vavada. получите доступ к играм через личный кабинет.
Играйте на https://1wins.pics современные слоты, настольные игры и щедрые бонусы. Удобная платформа и круглосуточная поддержка.
Грандиозный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предлагает для вас фантастические опции для крупных выигрышей! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут акционные игры и огромное количество игр. Всегда здесь вы откроете для себя завоевать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш азарт. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы победить. Игровая платформа обеспечивает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любой платформе. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только слоты, но и живые игры, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система дадут вам бесплатные вращения каждый день. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас уникальные варианты для крупных выигрышей! На онлайн-казино Лев и Азино777 вас встречают щедрые призы и множество игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы откроете для себя захватить огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш настроение. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы победить. Наш сайт обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом гаджете. На Lev вас ждут не только слоты, но и живые игры, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план предложат вам бесплатные вращения каждый день. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся признания каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас встречают щедрые призы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы откроете завоевать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
вызвал шлюху купить мефедрон в интернете
амфетамин кокаин купить мефедрон купить тг
купить марихуану кокаин экстази мефедрон купить мефедрон гашиш
купить амфетамин анапа купить мефедрон ровеньки луганск
Потрясающий игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас фантастические шансы для крупных выигрышей! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают щедрые призы и огромное количество игр. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете для себя выиграть колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает интересные турниры, которые поднимут ваш азарт. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Lev вас ожидают не только игровые автоматы, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система помогут вам фриспины на регулярной основе. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют приятные подарки и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы сможете выиграть невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Потрясающий игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас захватывающие варианты для победных стратегий! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают прекрасные подарки и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы попробуете сорвать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт дарит вам эргономичный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас радуют не только видеослоты, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш бонусная система порадуют вас фриспины на регулярной основе. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся славы каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют приятные подарки и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы откроете захватить огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Потрясающий игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предоставляет для вас незабываемые шансы для победных стратегий! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые призы и богатый выбор слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность получить огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшат ваш настроение. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа предлагает максимально удобный доступ, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только видеослоты, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки помогут вам бесплатные вращения на регулярной основе. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся славы каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность сорвать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
адрес бота телеграм купить закладку героина ебал шлюху
купить насвай в костанае шлюхи самары
Юридический портал https://zashitapravi.ru ваш помощник в правовых вопросах. Законы, практические рекомендации и консультации от профессионалов.
Потрясающий игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 дарит для вас невероятные варианты для ярких побед! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют акционные игры и ассортимент слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы попробуете сорвать крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые поднимут ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Игровая платформа дарит вам простой и удобный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любом гаджете. На Lev вас приветствуют не только видеослоты, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам фриспины при каждом пополнении. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас встречают удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Всегда здесь вы попробуете завоевать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Потрясающий игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас фантастические опции для успешной игры! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые призы и разнообразие игровых предложений. Всегда здесь вы попробуете сорвать множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт дарит вам простой и удобный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только игровые автоматы, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки помогут вам бесплатные вращения при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся удивительных сумм каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас встречают выгодные предложения и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете завоевать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный сервисный центр по ремонту дрона на выезде различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши духовые шкафы, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи духовок, включают неисправности термостата, поломку таймера, поврежденную дверцу, сбои контроллера, проблемы с конвекцией и неисправные платы. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт нагревательных элементов, термостатов, таймеров, дверец, контроллеров, вентиляторов и электроники. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете качественный и надежный сервис ремонта дрона на выезде.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-kvadrokopterov-best.ru
Портал права граждан России https://pravoyes.ru предлагает доступные разъяснения законов, советы по защите прав и юридическую информацию для каждого.
Портал Юриста https://voproslaw.ru удобный сервис для получения юридической помощи, разъяснений законодательства и защиты ваших интересов.
Потрясающий игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас фантастические варианты для победных стратегий! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас встречают акционные игры и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы успеете получить огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, что делает игру комфортной на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только слоты, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план дадут вам фриспины при каждом пополнении. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Лев, и завоевывай богатства каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Именно здесь вы успеете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Онлайн консультант https://konsultantdo.ru в юридических вопросах сервис для быстрого получения правовой помощи. Экспертные советы, разъяснения законов и поддержка в любое время.
Грандиозный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас фантастические шансы для крупных выигрышей! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы попробуете получить огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые увеличат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На игровом доме Лев вас встретят не только слоты, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам ощутить азарт вживую в любое время. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки дадут вам дополнительные средства при каждом пополнении. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и получай признания каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас встречают выгодные предложения и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность сорвать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный ремонт квадрокоптера различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши духовые шкафы, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели кухонных приборов, включают неработающие нагревательные элементы, выход из строя таймера, треснувшую дверцу, сбои контроллера, ошибки вентиляционной системы и повреждения электроники. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт нагревательных элементов, термостатов, таймеров, дверец, контроллеров, вентиляторов и электроники. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе качественный и надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту дрона в москве.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-kvadrokopterov-best.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный починить компьютер рядом всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши персональные компьютеры, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели персональных компьютеров, включают проблемы с жестким диском, проблемы с графическим адаптером, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие разъемы и проблемы с охлаждением. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонт жестких дисков, видеокарт, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете качественный и надежный ремонт компьютера.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-kompyuterov-vip.ru
Помощь в юридических вопросах https://legalyes.ru это оперативные ответы, практические рекомендации и поддержка в сложных юридических ситуациях.
Сервис помощи в юридических https://tvokonsultant.ru вопросах предлагает доступ к экспертам, актуальной информации о законах и удобные решения для правовых задач.
Полный гид по вашим правам https://skpravoyes.ru законы, рекомендации и практические советы в одном месте. Получите ответы на вопросы и разберитесь в юридических тонкостях с нашей помощью.
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный центр ремонта компьютера с гарантией различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши компьютеры, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи ПК, включают поломку жесткого диска, неработающую видеокарту, программные сбои, проблемы с портами и перегрев. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, видеокарт, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный сервис ремонта компьютера адреса.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-kompyuterov-vip.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный мастерская по ремонту кондиционера на выезде любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши кондиционеры, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели охладительных систем, включают недостаток хладагента, проблемы с вентилятором, программные сбои, проблемы с температурными датчиками и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт компрессоров, вентиляторов, ПО, датчиков и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный сервисный центр по ремонту кондиционера.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-kondicionerov-wow.ru
Временная регистрация в Санкт-Петербурге: Быстро и Легально!
Ищете, где оформить временную регистрацию в СПб?
Мы гарантируем быстрое и легальное оформление без очередей и лишних документов.
Ваше спокойствие – наша забота!
Минимум усилий • Максимум удобства • Полная легальность
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас!
Временная регистрация в СПб
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту кондиционеров адреса всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши сплит-системы, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели охладительных систем, включают проблемы с охлаждением, неисправности вентилятора, неисправности программного обеспечения, проблемы с температурными датчиками и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт компрессоров, вентиляторов, ПО, датчиков и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту кондиционеров адреса.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-kondicionerov-wow.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный сервис ремонта кофемашина на выезде различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши эспрессо-машины, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели эспрессо-машин, включают проблемы с нагревом, неработающий насос, программные сбои, проблемы с подключением и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт нагревательных элементов, насосов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный мастерская по ремонту кофемашин с гарантией.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-kofemashin-top.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный сервисный ремонт кофемашин на дому любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши эспрессо-машины, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи кофеварок, включают неисправности нагревательных элементов, неработающий насос, неисправности программного обеспечения, проблемы с подключением и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт нагревательных элементов, насосов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный сервис ремонта кофемашин с гарантией.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-kofemashin-top.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный вызвать мастера по ремонту массажных кресел с гарантией различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши релаксационные кресла, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели массажных устройств, включают проблемы с мотором, неработающие ролики, ошибки ПО, неработающие разъемы и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт моторов, роликов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете надежный и долговечный ремонт массажного кресла на дому.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-massazhnyh-kresel-gold.ru
Mostbet регистрация занимает всего несколько минут | Mostbet oyinlari har xil bonuslarga ega | Mostbet login обеспечивает быстрый доступ к аккаунту | Mostbet официальный сайт – это прозрачность и удобство | Mostbet shaxsiy kabinet kirish orqali foydalanuvchilar uchun qulay mostbetcasinouzkirishgderf com. | Mostbet скачать apk и начните играть прямо сейчас | Mostbet uz 34 – лучший портал для ставок в Узбекистане | Mostbet casino официальный сайт предлагает много бонусов | Mostbet bonuslar bilan o’yindan bahramand bo’ling Mostbet oyinlari.
Mostbet предлагает эксклюзивные бонусы для новых игроков | Ройхатдан ўтиш на сайте Mostbet Uz максимально простой | Mostbet uz com – ваш надежный портал для ставок | Mostbet com – это надежность и гарантии выплат | Ройхатдан ўтиш Mostbet saytida juda oson mostbet online. | Mostbet uz casino – это ваш шанс испытать удачу | Mostbet casino – это яркие эмоции и большие выигрыши | Mostbet официальный сайт – это удобный интерфейс и поддержка | Mostbet oyinlari sizning omadli kuningizni kutmoqda Mostbet официальный сайт.
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный сервис ремонта массажных кресел рядом любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши массажные кресла, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы массажных кресел, включают проблемы с мотором, неисправности роликов, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт моторов, роликов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный починить массажное кресло.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-massazhnyh-kresel-gold.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный вызвать мастера по ремонту майнера на дому различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши устройства для майнинга, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели криптомайнеров, включают проблемы с охлаждением, проблемы с блоком питания, ошибки ПО, неисправности разъемов и неисправности оборудования. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт систем охлаждения, блоков питания, ПО, разъемов и оборудования. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе надежный и долговечный отремонтировать майнер на выезде.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-maynerov-geek.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный сервис ремонта майнера с гарантией различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши устройства для майнинга, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи устройств для майнинга, включают неисправности системы охлаждения, неисправности питания, ошибки ПО, неработающие разъемы и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт систем охлаждения, блоков питания, ПО, разъемов и оборудования. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный отремонтировать майнер с гарантией.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-maynerov-geek.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный центр ремонта материнских плат в москве всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши материнские платы, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы материнских плат, включают проблемы с чипсетом, неисправности питания, программные сбои, проблемы с портами и аппаратные сбои. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт чипсетов, блоков питания, ПО, разъемов и компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный сервисный центр по ремонту материнских платы с гарантией.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-materinskih-plat-info.ru
Актуальный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предлагает для вас великолепные возможности для ярких побед! На онлайн-казино Лев и Азино777 вас встречают акционные игры и разнообразие игровых предложений. Именно здесь вы получите возможность выиграть крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые увеличат ваш настроение. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы выиграть. Наш сайт гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только настольные игры, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности предложат вам бесплатные вращения на регулярной основе. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы попробуете сорвать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Полезные советы от доктора https://doktoronla.ru здоровье, профилактика, лечение и поддержка. Актуальная информация для всех, кто заботится о своем организме.
Узнайте всё о беременности https://beremennydo.ru от первых признаков до подготовки к родам. Практические советы, развитие малыша по неделям и ответы на главные вопросы будущих мам.
Информация для родителей https://forbabydo.ru от планирования беременности до воспитания ребёнка. Рекомендации экспертов, советы по уходу и развитию малышей.
Актуальный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предоставляет для вас незабываемые опции для ярких побед! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас радуют прекрасные подарки и огромное количество игр. Только здесь вы откроете для себя сорвать множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любой платформе. На Lev вас радуют не только рулетка и покер, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план дадут вам бесплатные вращения на каждом шагу. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Лев, и завоевывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы успеете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный мастер по ремонту материнских плат на выезде любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши мэйнборды, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели мэйнбордов, включают неисправности чипсета, проблемы с блоком питания, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и неисправности компонентов. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт чипсетов, блоков питания, ПО, разъемов и компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный сервисный центр по ремонту материнских платы с гарантией.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-materinskih-plat-info.ru
Топовый игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 дарит для вас фантастические возможности для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают выгодные предложения и огромное количество игр. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете для себя сорвать колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые увеличат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы победить. Наш сайт гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система помогут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Lev, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы попробуете захватить множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный починить монитор различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши экраны, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели экранов, включают неисправности подсветки, неисправности матрицы, ошибки ПО, неисправности разъемов и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт подсветки, матриц, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный сервис ремонта монитора на дому.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-monitorov-plus.ru
Необыкновенный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас незабываемые шансы для ярких побед! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют акционные игры и богатый выбор слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете выиграть огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые увеличат ваш азарт. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы выиграть. Игровая платформа предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас ждут не только игровые автоматы, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш бонусная система помогут вам бесплатные вращения при каждом пополнении. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай призов каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы сможете получить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный качественный ремонт монитора различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши экраны, и обеспечиваем ремонт наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели экранов, включают проблемы с подсветкой, поврежденный экран, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие разъемы и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт подсветки, матриц, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете качественный и надежный мастер по ремонту мониторов адреса.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-monitorov-plus.ru
Лучший игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас захватывающие опции для ярких побед! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают прекрасные подарки и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы попробуете получить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы сорвать куш. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует простой и удобный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас радуют не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на каждом шагу. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся призов каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые призы и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы попробуете захватить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Потрясающий игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас фантастические шансы для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют удивительные акции и множество игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете выиграть огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает регулярные акции, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы сорвать куш. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любом устройстве. На Lev вас встретят не только игровые автоматы, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом в любое время. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас дополнительные средства на каждом шагу. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай признания каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы сможете завоевать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный экспресс ремонт моноблока всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши моноблочные компьютеры, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы моноблоков, включают поломку жесткого диска, поврежденный экран, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и неисправности системы охлаждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный ремонт моноблоков.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-monoblokov-rial.ru
Гинекология в деталях https://ginecologdo.ru ответы на важные вопросы о женском здоровье, рекомендации по уходу, профилактике и лечению.
Лечение без лишних сложностей https://medikasv.ru актуальные рекомендации, проверенные способы и полезные материалы для заботы о здоровье.
Топовый игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 раскрывает для вас захватывающие опции для успешной игры! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы успеете завоевать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы выиграть. Казино Лев и Азино777 обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, что делает игру комфортной на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас встретят не только слоты, но и живые дилеры, которые обеспечат вам ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк помогут вам фриспины при каждом пополнении. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся признания каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и богатый выбор игр. Именно здесь вы откроете получить множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Портал о гинекологии для женщин https://ginekologdo.ru полезная информация о здоровье, советы врачей, современные методы лечения и профилактики.
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас великолепные опции для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы сможете завоевать крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшают ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 предлагает простой и удобный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только слоты, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система порадуют вас дополнительные средства на регулярной основе. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай признания каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете захватить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предлагает для вас незабываемые возможности для максимальных успехов! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют акционные игры и огромное количество игр. Всегда здесь вы сможете завоевать множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы сорвать куш. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам интуитивно понятный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на любой платформе. На Lev вас радуют не только настольные игры, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план дадут вам бонусные кредиты каждый день. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы успеете завоевать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Фантастический игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предоставляет для вас великолепные опции для крупных выигрышей! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас ждут выгодные предложения и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы сможете завоевать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы выиграть. Игровая платформа гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас встретят не только игровые автоматы, но и живые игры, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам бонусные кредиты на регулярной основе. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Лев, и добивайся удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют приятные подарки и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете захватить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Собственное производство металлоконструкций. Если вас интересует Навесы в Красном Селе мы предлогаем изготовление под ключ навесы для автомобиля цена
Грандиозный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас незабываемые варианты для максимальных успехов! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые бонусы и множество игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы успеете завоевать невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 обеспечивает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только рулетка и покер, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на каждом шагу. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы получите возможность захватить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Портал о здоровье https://zdorovvonline.ru как сохранить активность, укрепить иммунитет, справляться с болезнями и вести здоровый образ жизни.
Портал о простуде https://prostudailor.ru и ЛОР-заболеваниях: причины, диагностика и современные способы лечения. Берегите здоровье с проверенной информацией.
Все аспекты здоровья https://sfmggu.ru от ухода за телом до профилактики болезней. Достоверная информация и советы для улучшения качества жизни.
Актуальный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас уникальные опции для ярких побед! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут акционные игры и богатый выбор слотов. Именно здесь вы получите возможность завоевать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт гарантирует простой и удобный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас приветствуют не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк дадут вам бесплатные вращения при каждом пополнении. Играй с азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай призов каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые призы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы откроете завоевать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Потрясающий игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предлагает для вас незабываемые опции для успешной игры! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас радуют щедрые призы и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность сорвать невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые поднимут ваш азарт. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы сорвать куш. Казино Лев и Азино777 предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только слоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам дополнительные средства при каждом пополнении. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Лев, и завоевывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность завоевать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Топовый игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас уникальные шансы для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают акционные игры и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы получите возможность сорвать колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Казино Лев и Азино777 предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас ожидают не только рулетка и покер, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план дадут вам фриспины на регулярной основе. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и богатый выбор игр. Всегда здесь вы сможете сорвать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Ремонт своими руками https://nhadian123.com простые идеи, эффективные техники и доступные материалы. Сделайте свой дом уютным легко и самостоятельно.
Лучший игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предлагает для вас фантастические варианты для крупных выигрышей! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые призы и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы попробуете сорвать крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает регулярные акции, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы достичь успеха. Казино Лев и Азино777 обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любой платформе. На игровом доме Лев вас радуют не только рулетка и покер, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые позволят вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш бонусная система дадут вам бонусные кредиты при каждом пополнении. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы успеете захватить огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Тактичные штаны: идеальный выбор для стильных мужчин, как выбрать их с другой одеждой.
Тактичные штаны: удобство и функциональность, которые подчеркнут ваш стиль и индивидуальность.
Как найти идеальные тактичные штаны, который подчеркнет вашу уверенность и статус.
Тактичные штаны для активного отдыха: важный элемент гардероба, которые подчеркнут вашу спортивную натуру.
Как выбрать тактичные штаны под свой стиль?, чтобы подчеркнуть свою уникальность и индивидуальность.
Тактичные штаны: вечная классика мужского гардероба, которые подчеркнут ваш вкус и качество вашей одежды.
Лучший вариант для делового образа: тактичные штаны, которые подчеркнут ваш профессионализм и серьезность.
штани з наколінниками штани з наколінниками .
Сделай ремонт сам https://skovarro.com практичные идеи, инструкции для каждого этапа и рекомендации, чтобы сэкономить время и деньги.
Грандиозный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас незабываемые опции для ярких побед! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас встречают удивительные акции и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы успеете сорвать множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Игровая платформа обеспечивает максимально удобный доступ, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только игровые автоматы, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас фриспины при каждом пополнении. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся призов каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас встречают выгодные предложения и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы успеете захватить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Полезные советы для женщин https://skystream.org здоровье, семья, карьера, красота и уход. Информация, которая помогает оставаться уверенной в любой ситуации.
Временная регистрация в Санкт-Петербурге: Быстро и Легально!
Ищете, где оформить временную регистрацию в СПБ?
Мы гарантируем быстрое и легальное оформление без очередей и лишних документов.
Ваше спокойствие – наша забота!
Минимум усилий • Максимум удобства • Полная легальность
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас!
Временная регистрация в СПБ
Безупречный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас незабываемые варианты для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас встречают акционные игры и множество игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы получите возможность захватить множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает регулярные акции, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы выиграть. Игровая платформа дарит вам интуитивно понятный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас радуют не только слоты, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности предложат вам бонусные кредиты при каждом пополнении. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся богатства каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и ассортимент слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы попробуете сорвать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Актуальный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас незабываемые опции для максимальных успехов! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают акционные игры и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы сможете сорвать множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает регулярные акции, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы выиграть. Наш сайт гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас встретят не только игровые автоматы, но и живые дилеры, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам бесплатные вращения на каждом шагу. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся удивительных сумм каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые бонусы и богатый выбор игр. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность сорвать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Практичные решения для ремонта https://ustbib.ru своими руками: подробные планы, советы по выбору материалов и секреты успешного результата.
Ремонт шаг за шагом https://belbriz.ru полезные лайфхаки, доступные материалы и решения для самостоятельного преображения любого помещения.
Портал о ремонте https://soda102.ru своими руками: как выполнить отделку, заменить сантехнику или обновить интерьер быстро и без помощи мастеров.
Фантастический игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас уникальные опции для победных стратегий! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы успеете сорвать невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает регулярные акции, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа предлагает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, что делает игру комфортной на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только видеослоты, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые дадут вам возможность почувствовать себя в настоящем казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки предложат вам фриспины на каждом шагу. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай признания каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы получите возможность завоевать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Топовый игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас фантастические шансы для крупных выигрышей! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые призы и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы попробуете захватить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Игровая платформа дарит вам быстрый и легкий процесс игры, что делает игру комфортной на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только настольные игры, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую в любое время. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план предложат вам бесплатные вращения каждый день. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Lev, и получай богатства каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете захватить огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас захватывающие опции для победных стратегий! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают прекрасные подарки и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы получите возможность выиграть колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт предлагает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любой платформе. На Lev вас ожидают не только игровые автоматы, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам дополнительные средства при каждом пополнении. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай признания каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы успеете сорвать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Как официально приобрести аттестат 11 класса с минимальными затратами времени
Безупречный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас захватывающие опции для максимальных успехов! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ждут акционные игры и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы попробуете получить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Игровая платформа дарит вам эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас радуют не только видеослоты, но и живые игры, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности предложат вам дополнительные средства на каждом шагу. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Лев, и получай признания каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы сможете получить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 дарит для вас потрясающие опции для ярких побед! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас встречают удивительные акции и огромное количество игр. Только здесь вы попробуете выиграть огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас ждут не только слоты, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом в любое время. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам фриспины на регулярной основе. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и добивайся удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас встречают выгодные предложения и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы сможете завоевать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Актуальный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас потрясающие шансы для крупных выигрышей! На онлайн-казино Лев и Азино777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы успеете завоевать множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшают ваш настроение. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам быстрый и легкий процесс игры, обеспечивает легкость использования на любой платформе. На Lev вас встретят не только игровые автоматы, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам дополнительные средства на каждом шагу. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай призов каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Всегда здесь вы успеете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный мастер по ремонту кондиционера рядом различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши охладительные системы, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы кондиционеров, включают проблемы с охлаждением, неработающий вентилятор, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности датчиков и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт компрессоров, вентиляторов, ПО, датчиков и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный центр ремонта кондиционера в москве.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-kondicionerov-wow.ru
Безупречный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас невероятные возможности для максимальных успехов! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы сможете сорвать невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает регулярные акции, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы выиграть. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам быстрый и легкий процесс игры, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На игровом доме Лев вас радуют не только видеослоты, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую в любое время. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам дополнительные средства на регулярной основе. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность получить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Потрясающий игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас захватывающие возможности для максимальных успехов! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас радуют прекрасные подарки и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы успеете выиграть множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшают ваш настроение. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На игровом доме Лев вас ожидают не только настольные игры, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые призы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность выиграть невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный центр ремонта моноблоков на выезде различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши моноблочные компьютеры, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели моноблочных компьютеров, включают неисправности HDD, проблемы с экраном, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие разъемы и перегрев. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете качественный и надежный сервисный центр по ремонту моноблоков рядом.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-monoblokov-rial.ru
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас захватывающие варианты для успешной игры! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют прекрасные подарки и разнообразие игровых предложений. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете завоевать крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые увеличат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы сорвать куш. Казино Лев и Азино777 предлагает эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только видеослоты, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности предложат вам бесплатные вращения при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся призов каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают выгодные предложения и богатый выбор игр. Всегда здесь вы успеете завоевать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Ремонт дома без мастеров https://hottspb.ru лёгкие и понятные решения для каждого этапа ремонта. Советы по выбору инструментов и материалов.
Подробные инструкции по ремонту https://mbmedicall.com своими руками: ремонт стен, полов, потолков и мебели. Полезные рекомендации для успешного результата.
Необыкновенный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас фантастические варианты для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас встречают прекрасные подарки и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете захватить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые поднимут ваш настроение. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Игровая платформа предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас встретят не только видеослоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на регулярной основе. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай признания каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают выгодные предложения и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы успеете завоевать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный ремонт моноколеса на выезде любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши моноколеса, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы моноколес, включают неисправную батарею, неработающий двигатель, сбои контроллера, проблемы с гиросенсорами и повреждения рамы. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, гиросенсоров и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе качественный и надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту моноколеса на выезде.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-monokoles-serv.ru
Необыкновенный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас потрясающие шансы для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы попробуете захватить огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает интересные турниры, которые поднимут ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы победить. Игровая платформа гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Lev вас встретят не только видеослоты, но и живые дилеры, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки дадут вам бонусные кредиты при каждом пополнении. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и богатый выбор игр. Всегда здесь вы сможете захватить огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Актуальный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас великолепные опции для крупных выигрышей! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые призы и множество игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы попробуете захватить колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает регулярные акции, которые поднимут ваш азарт. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы выиграть. Игровая платформа обеспечивает простой и удобный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Lev вас радуют не только рулетка и покер, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам бесплатные вращения на каждом шагу. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай призов каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы попробуете захватить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
закачать приложения казино https://mymomentum.com.sg/kometa-kazino-onlajn-kazino-igrat-onlajn-na-3/
Наша мастерская предлагает профессиональный вызвать мастера по ремонту морозильной камеры на дому различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши морозильные камеры, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы морозильных камер, включают неисправности компрессора, проблемы с температурным датчиком, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонт компрессоров, термостатов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный центр ремонта морозильной камеры на выезде.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-morozilnyh-kamer-spec.ru
Отказное, или информационное письмо https://pikabu.ru/story/otkaznoe_pismo_dlya_marketpleysov_chto_yeto_za_dokument_i_dlya_chego_nuzhen_12093993 неофициальный документ, который оформляется в добровольном порядке. Он доказывает, что продукция производителя безопасна для потребителя, животных и экологии, но при этом сертификация качества не требуется. Отказные письма нужны для сотрудничества с маркетплейсами и для таможенного оформления импортных товаров. При реализации продукции на Wildberries, OZON или Яндекс.Маркете предприниматели должны предоставить сертификат или декларацию соответствия. Об этом говорит статья 456 ГК РФ. В ней указано, что продавец обязан совместно с передачей товара передать покупателю документы качества, если это позволяет договор купли-продажи.
Сертификат о соответствии https://pikabu.ru/story/dlya_chego_nuzhen_sertifikat_gost_r_iso_9001_pri_uchastii_v_tenderakh_12093517 системы менеджмента качества требованиям стандарта ГОСТ Р ИСО 9001 является официальным документом, удостоверяющим, что система менеджмента качества создана согласно установленным требованиям. Для получения документа о соответствии СМК, необходимо подтвердить, что проведены разработка и внедрение системы, она результативна, эффективно функционирует и постоянно совершенствуется.
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас фантастические варианты для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые призы и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы получите возможность выиграть огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает регулярные акции, которые улучшат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт обеспечивает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любой платформе. На игровом доме Лев вас встретят не только рулетка и покер, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план дадут вам фриспины каждый день. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы сможете сорвать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный официальный ремонт морозильных камер адреса всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши морозильники, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи морозильников, включают проблемы с охлаждением, неработающий термостат, неисправности программного обеспечения, проблемы с подключением и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт компрессоров, термостатов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный официальный ремонт морозильной камеры.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-morozilnyh-kamer-spec.ru
не упустите возможность! vavada casino зеркало — ваш быстрый старт в мире онлайн-развлечений. переходите на зеркало vavada и начните играть прямо сейчас. доступ к казино станет вашим в несколько кликов. удобно на любом устройстве!
Тут можно преобрести сейф взломостойкий купить взломостойкие сейфы купить
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный официальный ремонт мфу в москве любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши МФУ, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи многофункциональных устройств, включают проблемы с печатью, проблемы со сканирующим блоком, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт печатающих головок, сканеров, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный мастер по ремонту мфу с гарантией.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-mfu-lite.ru
Лучший игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас незабываемые варианты для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые бонусы и богатый выбор слотов. Только здесь вы попробуете выиграть множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы сорвать куш. Наш сайт обеспечивает простой и удобный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любом гаджете. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только игровые автоматы, но и живые игры, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план порадуют вас бесплатные вращения на каждом шагу. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся признания каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
хотите окунуться в азартные игры? vavada рабочий сайт позволяет зарегистрироваться в казино vavada. попробуйте телеграм-канал для удобного доступа. оцените широкие возможности: от промокодов до рейтинговых игр.
Служба по контракту https://делохрабрых.рф в зоне СВО: стабильный доход, социальные гарантии, профессиональный рост и защита интересов Родины.
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный центр ремонта мфу с гарантией всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши многофункциональные устройства, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы МФУ, включают проблемы с печатью, проблемы со сканирующим блоком, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт печатающих головок, сканеров, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный выездной ремонт мфу.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-mfu-lite.ru
Your Bitcoin Mixing Solution Laundry Bitcoin is here to help you keep your bitcoin transactions anonymous and private. Trusted, No Logs, Fast and Secure!
Актуальный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас потрясающие шансы для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и разнообразие игровых предложений. Именно здесь вы получите возможность выиграть огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшают ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы сорвать куш. Наш сайт обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, что делает игру комфортной на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Lev вас ждут не только настольные игры, но и живые дилеры, которые обеспечат вам ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки предложат вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш при каждом пополнении. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся признания каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают выгодные предложения и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы успеете выиграть крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
хотите окунуться в азартные игры? vavada на андроид позволяет войти в аккаунт в казино vavada. попробуйте мобильную версию для удобного доступа. оцените широкие возможности: от фриспинов до рейтинговых игр.
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный официальный ремонт ноутбуков рядом различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши ноутбуки, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи лаптопов, включают проблемы с жестким диском, неисправности экрана, ошибки ПО, проблемы с портами и перегрев. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт жестких дисков, экранов, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный центр ремонта ноутбука в москве.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-noutbukov-first.ru
Топовый игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предоставляет для вас потрясающие варианты для ярких побед! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют прекрасные подарки и богатый выбор слотов. Только здесь вы получите возможность выиграть невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас ожидают не только видеослоты, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки помогут вам бонусные кредиты на каждом шагу. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Лев, и получай призов каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас встречают приятные подарки и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы попробуете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Аттестат школы купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Топовый игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предоставляет для вас великолепные опции для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино Лев и Азино777 вас радуют акционные игры и множество игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете получить огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые увеличат ваш настроение. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа обеспечивает простой и удобный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любом гаджете. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только игровые автоматы, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом в любое время. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки дадут вам бонусные кредиты каждый день. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Лев, и добивайся призов каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые призы и богатый выбор игр. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность сорвать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Архитектура кибербезопасности Bs2Best Market Security ссылка b2best.at создание комплексных решений для защиты данных, предотвращения атак и обеспечения стабильности IT-инфраструктуры.
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный мастерская по ремонту ноутбуков всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши переносные компьютеры, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели переносных компьютеров, включают проблемы с жестким диском, неисправности экрана, ошибки ПО, неработающие разъемы и проблемы с охлаждением. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, экранов, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный официальный ремонт ноутбуков на выезде.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-noutbukov-first.ru
iPhone 14 Pro Max vs iPhone 15 Pro Max https://gost-snip.su/blog/iphone-14-pro-max-vs-iphone-15-pro-max-stoit-li-obnovlyatsya/ отличие в дизайне, мощности процессора, камерах и автономности.
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас невероятные возможности для максимальных успехов! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут акционные игры и множество игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы успеете захватить множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план порадуют вас бонусные кредиты при каждом пополнении. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые призы и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность получить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Обучение в Школа Майя инновационные программы, профессиональные педагоги и комфортная среда для развития.
Круглосуточный эвакуатор https://angeldorog.by/evakuator-minsk/ выгодные условия, профессионализм и минимальное время ожидания. Спасём вас из любой ситуации!
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный мастер по ремонту объектива всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши объективы, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели фотообъективов, включают неработающую фокусировку, проблемы с диафрагмой, механические повреждения, проблемы с автофокусом и попадание влаги. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт фокусировки, диафрагмы, автофокуса, очистку линз и восстановление корпуса. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе надежный и долговечный ремонт объектива на дому.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-obektivov-magic.ru
Услуги гинеколога в Варшаве https://forum.pokexgames.pl/member.php?action=profile&uid=51416 регулярные осмотры, планирование беременности, лечение заболеваний. Забота о здоровье каждой женщины.
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный починить объектив адреса всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши линзы, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели фотообъективов, включают неработающую фокусировку, проблемы с диафрагмой, поломки компонентов, проблемы с автофокусом и попадание влаги. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт фокусировки, диафрагмы, автофокуса, очистку линз и восстановление корпуса. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный качественный ремонт объективов.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-obektivov-magic.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный официальный ремонт парогенераторов с гарантией всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши устройства для генерации пара, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы парогенераторов, включают проблемы с температурными датчиками, неработающий насос, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт нагревательных элементов, насосов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете качественный и надежный сервисный ремонт парогенератора рядом.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-parogeneratorov-piece.ru
Потрясающий игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предлагает для вас фантастические возможности для ярких побед! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают прекрасные подарки и огромное количество игр. Всегда здесь вы успеете сорвать множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшают ваш настроение. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы выиграть. Казино Лев и Азино777 предлагает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любом устройстве. На Lev вас встретят не только видеослоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк предложат вам бесплатные вращения каждый день. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы сможете выиграть крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас потрясающие варианты для крупных выигрышей! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые призы и множество игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы получите возможность захватить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые увеличат ваш настроение. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы победить. Игровая платформа обеспечивает максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только настольные игры, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность почувствовать себя в настоящем казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш бонусная система предложат вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш при каждом пополнении. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Именно здесь вы сможете получить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
микрозайм на карту онлайн срочно без отказов https://zajmy-online1.ru
Добро пожаловать на https://b2best.at мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг для всех предприятий: b2best.at от стратегического консалтинга до цифрового маркетинга. Наша команда профессионалов поможет вам оптимизировать процессы и увеличить прибыль. Начните свой путь к успеху с нами!
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный сервис ремонта парогенераторов адреса всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши устройства для генерации пара, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы парогенераторов, включают неисправности нагревательных элементов, проблемы с подачей воды, программные сбои, проблемы с подключением и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, насосов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный ремонт парогенераторов в москве.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-parogeneratorov-piece.ru
Ищете партнера для роста бизнеса? https://bs2best-best.store предлагает решения для предприятий любого уровня: консалтинг, цифровой маркетинг и оптимизация процессов – всё для увеличения прибыли. Начните сотрудничество с нами уже сегодня!
Надежный партнер для вашего бизнеса https://bs2best-best.ru Мы предоставляем полный спектр услуг: b2best.at. От консалтинга до маркетинговых стратегий – наша команда сделает всё для вашего успеха. Доверьтесь профессионалам и двигайтесь к прибыли с нами!
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный мастерская по ремонту планшета адреса различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши планшеты, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели устройств планшетного типа, включают проблемы с экраном, поломку батареи, ошибки ПО, проблемы с портами и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный сервисный ремонт планшета на дому.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-planshetov-profi.ru
Грандиозный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас незабываемые возможности для успешной игры! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас встречают щедрые призы и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы успеете получить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы достичь успеха. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам максимально удобный доступ, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только настольные игры, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на каждом шагу. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай славы каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы получите возможность завоевать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный мастерская по ремонту кофемашина в москве всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши кофемашины, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели эспрессо-машин, включают проблемы с температурными датчиками, неисправности насоса, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт нагревательных элементов, насосов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный отремонтировать кофемашин в москве.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-kofemashin-top.ru
Топовый игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас уникальные варианты для успешной игры! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют акционные игры и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы сможете захватить огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш азарт. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы победить. Игровая платформа предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любой платформе. На Лев и Азино777 вас встретят не только настольные игры, но и живые дилеры, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план порадуют вас дополнительные средства каждый день. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас радуют удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете захватить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный починить планшет на дому различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши таблеты, и обеспечиваем ремонт наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи таблетов, включают неисправности дисплея, неисправности аккумулятора, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный мастерская по ремонту планшетов в москве.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-planshetov-profi.ru
Светодиодные экраны для залов https://svetodiodnyy-ekran.ru решения для ярких презентаций и эффектных мероприятий. Высокое качество изображения, индивидуальные размеры и современные технологии.
Лучшая образовательная Школа Майя обучение, которое работает. Современные методики, опытные преподаватели, удобный график. Мы предлагаем курсы для начинающих и профессионалов.
cryptocurrency exchange service https://swap.cloud/feed/ based in Luxembourg. It offers fully automated instant exchanges between cryptocurrencies with no KYC requirements, ensuring speed and privacy. The platform is designed for users looking for smooth, secure and hassle-free transactions.
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный центр ремонта плоттеров с гарантией любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши плоттеры, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.s
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи графопостроителей, включают неисправности печатающей головки, неисправности механизма подачи, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт печатающих головок, механизмов подачи бумаги, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный починить плоттер на дому.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-plotterov-style.ru
Безупречный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас потрясающие варианты для победных стратегий! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ждут выгодные предложения и разнообразие игровых предложений. Именно здесь вы получите возможность получить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только рулетка и покер, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас дополнительные средства при каждом пополнении. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ждут щедрые бонусы и богатый выбор игр. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность получить огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
Безупречный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 раскрывает для вас фантастические опции для успешной игры! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ждут прекрасные подарки и разнообразие игровых предложений. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность завоевать колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Игровая платформа гарантирует простой и удобный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Lev вас ждут не только настольные игры, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на регулярной основе. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Лев, и получай признания каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы успеете захватить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный сервис ремонта плоттера в москве всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши графопостроители, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.s
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи графопостроителей, включают неработающий картридж, проблемы с подачей бумаги, программные сбои, проблемы с портами и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт печатающих головок, механизмов подачи бумаги, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный ремонт плоттера на дому.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-plotterov-style.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный ремонт приборов ночного видения адреса всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши устройства ночного видения, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели приборов ночного видения, включают неработающие датчики, неисправности оптики, ошибки ПО, неисправности разъемов и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт сенсоров, оптики, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете долговечный и надежный центр ремонта прибора ночного видения адреса.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-pnv-ultra.ru
Потрясающий игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас великолепные варианты для ярких побед! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ждут прекрасные подарки и богатый выбор слотов. Именно здесь вы попробуете завоевать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы победить. Игровая платформа обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любом гаджете. На Lev вас ожидают не только настольные игры, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система помогут вам бонусные кредиты при каждом пополнении. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете завоевать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Актуальный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас уникальные опции для ярких побед! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают прекрасные подарки и богатый выбор слотов. Именно здесь вы сможете получить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш настроение. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На Lev вас радуют не только настольные игры, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш при каждом пополнении. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы попробуете получить множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наша мастерская предлагает профессиональный срочный ремонт приборов ночного видения различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши устройства ночного видения, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели приборов ночного видения, включают неработающие датчики, поврежденные линзы, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт сенсоров, оптики, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный вызвать мастера по ремонту приборов ночного видения адреса.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-pnv-ultra.ru
Необыкновенный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас невероятные опции для крупных выигрышей! На онлайн-казино Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и богатый выбор слотов. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность выиграть множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает регулярные акции, которые улучшат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы выиграть. Наш сайт предлагает максимально удобный доступ, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Lev вас радуют не только видеослоты, но и живые игры, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ждут щедрые призы и богатый выбор игр. Только здесь вы успеете получить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный сервисный ремонт посудомоечной машины в москве всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши устройства для мойки посуды, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы посудомоечных машин, включают неисправности нагревательных элементов, неисправности насосов, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие разъемы и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт нагревательных элементов, насосов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный мастер по ремонту посудомоечных машин с гарантией.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-posudomoechnyh-mashin-expert.ru
Актуальный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас невероятные шансы для успешной игры! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут акционные игры и богатый выбор слотов. Именно здесь вы успеете сорвать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает регулярные акции, которые увеличат ваш настроение. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт обеспечивает эргономичный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только рулетка и покер, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система помогут вам бонусные кредиты на регулярной основе. Играй с азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас встречают выгодные предложения и богатый выбор игр. Всегда здесь вы успеете выиграть невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный сервисный центр по ремонту посудомоечных машин с гарантией любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши устройства для мойки посуды, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы посудомоечных машин, включают неисправности нагревательных элементов, неработающие насосы, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, насосов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы обеспечиваете себе качественный и надежный сервисный центр по ремонту посудомоечных машин на дому.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-posudomoechnyh-mashin-expert.ru
Лучший игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас незабываемые возможности для победных стратегий! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы откроете для себя выиграть огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые увеличат ваш азарт. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа предлагает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только видеослоты, но и живые дилеры, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на регулярной основе. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете завоевать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный мастерская по ремонту принтера любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши устройства для печати, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели устройств для печати, включают неисправности печатающей головки, застревание бумаги, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт печатающих головок, механизмов подачи бумаги, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете долговечный и надежный сервисный центр по ремонту принтера.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-printerov-master.ru
Грандиозный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предоставляет для вас великолепные возможности для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас радуют акционные игры и огромное количество игр. Всегда здесь вы сможете выиграть огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшают ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт дарит вам быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только видеослоты, но и живые дилеры, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам фриспины каждый день. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Лев, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют удивительные акции и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы получите возможность сорвать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный сервис ремонта массажных кресел различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши массажные кресла, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы массажных кресел, включают проблемы с мотором, проблемы с массажными механизмами, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт моторов, роликов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный ремонт массажного кресла на дому.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-massazhnyh-kresel-gold.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный вызвать мастера по ремонту принтера на дому различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши принтеры, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели устройств для печати, включают неисправности печатающей головки, неисправности механизма подачи, ошибки ПО, неработающие разъемы и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт печатающих головок, механизмов подачи бумаги, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный сервисный ремонт принтеров адреса.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-printerov-master.ru
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
Фантастический игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас великолепные возможности для крупных выигрышей! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ждут акционные игры и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы сможете завоевать крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые поднимут ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы победить. Наш сайт предлагает максимально удобный доступ, что делает игру комфортной на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только видеослоты, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система порадуют вас фриспины при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут приятные подарки и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы успеете захватить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный вызвать мастера по ремонту проекторов адреса различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши видеопроекторы, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели видеопроекторов, включают перегоревшую лампу, перегрев, неисправности программного обеспечения, проблемы с подключением и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт ламп, вентиляторов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный сервисный центр по ремонту проектора в москве.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-proektorov-online.ru
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
Грандиозный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предоставляет для вас фантастические шансы для максимальных успехов! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют удивительные акции и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы сможете завоевать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы выиграть. Игровая платформа предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только слоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система предложат вам бонусные кредиты на каждом шагу. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай богатства каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые призы и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
АО Ти И Эл Лизинг https://avtee.ru/avto_v_arendy_turcia_podpiska/ предлагает услуги проката автомобилей в России, Турции, ОАЭ, Черногории, Испании и других странах по всему миру. Широкий выбор авто, выгодные условия и удобное бронирование делают поездки комфортными и доступными для каждого клиента.
РПНУ Лизинг https://rpnu-leasing.ru/novosti/operacionnii-lizing-chto-eto-otlichie-ot-finansovogo-lizinga надежный партнер в лизинге автомобилей, спецтехники и оборудования. Гарантируем отсутствие отказов благодаря индивидуальному подходу к каждому клиенту. Удобные условия и быстрое оформление помогают получить нужное имущество без лишних сложностей.
ООО Спецтехгрупп https://stgauto.ru предоставляет аренду автомобилей в Сочи, Адлере, Калининграде и Краснодаре. Полностью онлайн оформление позволяет быстро забронировать авто без лишних визитов. Удобный сервис и широкий выбор машин для любых задач — от отдыха до работы.
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный экспресс ремонт проектора любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши видеопроекторы, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи проекционных устройств, включают проблемы с лампой, перегрев, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт ламп, вентиляторов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный ремонт проекторов на выезде.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-proektorov-online.ru
Грандиозный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас потрясающие возможности для ярких побед! На онлайн-казино Лев и Азино777 вас встречают выгодные предложения и богатый выбор слотов. Именно здесь вы сможете захватить множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает регулярные акции, которые улучшают ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На Lev вас встретят не только рулетка и покер, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш бонусная система порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся славы каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы попробуете захватить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Learn how to obtain a real estate license in Indiana easily | Gain professional growth with an Indiana realtor license | How to get licensed in real estate in Indiana in no time indiana real estate license ssousa | Achieve financial freedom with an Indiana real estate license | How to apply for an Indiana real estate license without stress | Navigate the real estate licensing process in Indiana smoothly | Enhance your knowledge with Indiana real estate license courses | Find affordable real estate courses in Indiana for beginners | Explore lucrative opportunities with Indiana real estate license indiana-real-estate-license.com.
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный вызвать мастера по ремонту роботов пылесосов на выезде любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши роботы-пылесосы, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы роботов-пылесосов, включают неисправную батарею, проблемы с мотором, программные сбои, неработающие датчики и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт батарей, двигателей, ПО, сенсоров и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный центр ремонта робота пылесоса на дому.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-robotov-pylesosov-servis.ru
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
Безупречный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас захватывающие варианты для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые бонусы и огромное количество игр. Только здесь вы откроете для себя выиграть крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы сорвать куш. Наш сайт дарит вам быстрый и легкий процесс игры, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только видеослоты, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые дадут вам возможность почувствовать себя в настоящем казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам бесплатные вращения каждый день. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай признания каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность завоевать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный вызвать мастера по ремонту робота пылесоса с гарантией различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши роботы-пылесосы, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи роботизированных уборщиков, включают неисправную батарею, проблемы с мотором, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие датчики и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт батарей, двигателей, ПО, сенсоров и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный центр ремонта робота пылесоса в москве.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-robotov-pylesosov-servis.ru
Потрясающий игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предоставляет для вас захватывающие шансы для победных стратегий! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые призы и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы попробуете сорвать множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 предлагает эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только видеослоты, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас фриспины на регулярной основе. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы откроете выиграть множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный мастер по ремонту серверов рядом всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши сервера, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы серверов, включают поломку жесткого диска, неисправности блока питания, ошибки ПО, неработающие сетевые интерфейсы и неисправности компонентов. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонт жестких дисков, блоков питания, ПО, сетевых интерфейсов и компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе надежный и долговечный сервисный ремонт сервера адреса.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-serverov-express.ru
Топовый игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 дарит для вас захватывающие варианты для ярких побед! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых предложений. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете для себя сорвать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшат ваш настроение. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы победить. Наш сайт гарантирует быстрый и легкий процесс игры, обеспечивает легкость использования на любой платформе. На игровом доме Лев вас радуют не только настольные игры, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам фриспины на каждом шагу. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы попробуете получить огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
Грандиозный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас захватывающие опции для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас встречают прекрасные подарки и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы успеете захватить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш настроение. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы достичь успеха. Игровая платформа предлагает максимально удобный доступ, что делает игру комфортной на любой платформе. На Lev вас приветствуют не только игровые автоматы, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас бонусные кредиты на регулярной основе. Играй с азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай признания каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют приятные подарки и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы получите возможность завоевать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
МТЮ Лизинг https://depo.rent предоставляет аренду автомобилей в Крыму, включая Симферополь. Удобный онлайн-сервис позволяет оформить аренду на сайте за несколько минут. Широкий выбор автомобилей и выгодные условия делают поездки по региону комфортными и доступными.
Наша мастерская предлагает профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту серверов на дому всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши серверные системы, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы серверов, включают неисправности HDD, неисправности блока питания, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности сетевых интерфейсов и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, блоков питания, ПО, сетевых интерфейсов и компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете качественный и надежный официальный ремонт сервера с гарантией.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-serverov-express.ru
Новостройки Казани https://kupitkvartiruzhkkvartirenka.ru покупка квартир от застройщика без переплат. Современные жилые комплексы с развитой инфраструктурой.
Квартиры в новых домах Казани https://kvartirazhkkvartirenka.ru yадёжный застройщик, честные цены и широкий выбор планировок.
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный сервисный центр по ремонту сетевых хранилищ любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши серверы хранения данных, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы сетевых хранилищ, включают поломку жесткого диска, неработающий блок питания, ошибки ПО, неработающие сетевые интерфейсы и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт жестких дисков, блоков питания, ПО, сетевых интерфейсов и компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете качественный и надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту сетевого хранилища в москве.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-setevyh-hranilishh-service.ru
Лучший игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предоставляет для вас захватывающие возможности для крупных выигрышей! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут выгодные предложения и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы откроете для себя завоевать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшают ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт обеспечивает эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только настольные игры, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш бонусная система предложат вам дополнительные средства на регулярной основе. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые призы и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы попробуете выиграть колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
Фантастический игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас уникальные шансы для крупных выигрышей! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых предложений. Только здесь вы сможете завоевать колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш азарт. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы победить. Игровая платформа обеспечивает максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас ожидают не только игровые автоматы, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность почувствовать себя в настоящем казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности предложат вам фриспины при каждом пополнении. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Только здесь вы получите возможность выиграть невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный ремонт сетевого хранилища с гарантией всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши NAS-системы, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи NAS-систем, включают неисправности HDD, проблемы с питанием, ошибки ПО, проблемы с сетевыми картами и аппаратные сбои. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт жестких дисков, блоков питания, ПО, сетевых интерфейсов и компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете качественный и надежный отремонтировать сетевое хранилище рядом.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-setevyh-hranilishh-service.ru
Hi to every one, as I am really keen of reading this webpage’s post to be updated regularly. It carries fastidious stuff.
https://barsu.by/
служба открытия дверей срочное вскрытие замков
Топовый игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 раскрывает для вас невероятные шансы для ярких побед! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют прекрасные подарки и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы попробуете завоевать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Игровая платформа обеспечивает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом гаджете. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только настольные игры, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас фриспины при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас встречают приятные подарки и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы получите возможность сорвать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный качественный ремонт сигвеев различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши самобалансирующиеся устройства, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели самобалансирующихся устройств, включают поломку аккумулятора, проблемы с мотором, сбои контроллера, неисправности сенсоров и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, гиросенсоров и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный центр ремонта сигвеев на дому.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-sigveev-expertise.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный починить майнер рядом любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши криптомайнеры, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы майнеров, включают перегрев, проблемы с блоком питания, ошибки ПО, неработающие разъемы и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт систем охлаждения, блоков питания, ПО, разъемов и оборудования. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный мастер по ремонту майнера.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-maynerov-geek.ru
Потрясающий игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас уникальные варианты для ярких побед! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют удивительные акции и множество игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя завоевать множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшают ваш настроение. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы выиграть. Казино Лев и Азино777 обеспечивает простой и удобный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только настольные игры, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки предложат вам бонусные кредиты на каждом шагу. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют приятные подарки и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность завоевать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
Потрясающий игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас фантастические варианты для победных стратегий! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают акционные игры и множество игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете захватить колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт предлагает максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Lev вас встретят не только слоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности порадуют вас бесплатные вращения на регулярной основе. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай славы каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ждут щедрые призы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы успеете завоевать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный сервисный центр по ремонту сигвеев в москве любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши электроскутеры, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи электроскутеров, включают неисправную батарею, проблемы с мотором, сбои контроллера, неисправности сенсоров и повреждения рамы. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, гиросенсоров и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный починить сигвей на выезде.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-sigveev-expertise.ru
Фантастический игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предоставляет для вас уникальные шансы для максимальных успехов! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас радуют акционные игры и разнообразие игровых предложений. Только здесь вы успеете сорвать крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш азарт. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы победить. Наш сайт обеспечивает максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только видеослоты, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай признания каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают выгодные предложения и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы сможете захватить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Служба по контракту https://contract.moscow в Москве: достойное обеспечение, обучение и развитие. Станьте частью сильной команды профессионалов!
Квартиры от застройщика https://kupitkvartiruland.ru в новых домах Казани. Честные цены, гибкие условия покупки и качество, которому можно доверять.
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный сервисный центр по ремонту стиральных машин адреса всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши автоматические стиральные машины, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы стиральных машин, включают неработающий барабан, неработающий нагревательный элемент, ошибки ПО, проблемы с откачкой воды и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт барабанов, нагревательных элементов, ПО, насосов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный мастер по ремонту стиральных машин с гарантией.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-stiralnyh-mashin-ace.ru
Топовый игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предоставляет для вас великолепные возможности для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино Лев и Азино777 вас встречают щедрые призы и огромное количество игр. Всегда здесь вы сможете получить множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш азарт. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы сорвать куш. Наш сайт гарантирует простой и удобный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас встретят не только игровые автоматы, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас дополнительные средства каждый день. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся признания каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ждут удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы попробуете завоевать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Необыкновенный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас незабываемые возможности для максимальных успехов! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют акционные игры и множество игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы успеете завоевать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы достичь успеха. Игровая платформа предлагает простой и удобный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только рулетка и покер, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам бонусные кредиты на каждом шагу. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы попробуете сорвать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный мастерская по ремонту стиральных машин с гарантией различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши автоматические стиральные машины, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы стиральных машин, включают проблемы с барабаном, неработающий нагревательный элемент, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности насоса и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт барабанов, нагревательных элементов, ПО, насосов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный выездной ремонт стиральной машины.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-stiralnyh-mashin-ace.ru
Грандиозный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас фантастические варианты для победных стратегий! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые бонусы и богатый выбор слотов. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя сорвать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает интересные турниры, которые улучшат ваш настроение. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы сорвать куш. Наш сайт дарит вам интуитивно понятный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любом устройстве. На Lev вас радуют не только настольные игры, но и живые игры, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности предложат вам дополнительные средства на регулярной основе. Играй с азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай богатства каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете выиграть невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный мастерская по ремонту сушильных машин на выезде различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши сушильные машины, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы сушильных машин, включают неработающий нагревательный элемент, неисправности барабана, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности фильтра и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, барабанов, ПО, фильтров и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете качественный и надежный починить сушильную машину.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-sushilnyh-mashin-all.ru
Продажа квартир https://kvartirukupitstore.ru в новостройках Казани от застройщика: удобные планировки, современные жилые комплексы и прозрачные условия сделки.
Фантастический игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас незабываемые варианты для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и множество игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя сорвать невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только слоты, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам дополнительные средства на регулярной основе. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Lev, и получай признания каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают выгодные предложения и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы откроете получить множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предоставляет для вас невероятные варианты для успешной игры! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют прекрасные подарки и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете получить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы достичь успеха. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только игровые автоматы, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности помогут вам дополнительные средства каждый день. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Lev, и получай признания каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас встречают выгодные предложения и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы получите возможность получить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный ремонт сушильной машины с гарантией любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши сушильные машины, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы сушильных машин, включают проблемы с нагревом, проблемы с вращением барабана, ошибки ПО, неисправности фильтра и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, барабанов, ПО, фильтров и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный официальный ремонт сушильных машин с гарантией.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-sushilnyh-mashin-all.ru
Грандиозный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас захватывающие шансы для успешной игры! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут прекрасные подарки и огромное количество игр. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность завоевать невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые увеличат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы победить. Игровая платформа дарит вам интуитивно понятный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на любой платформе. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только слоты, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом в любое время. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на каждом шагу. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы попробуете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный сервис ремонта телевизоров с гарантией всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши телевизионные панели, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы телевизоров, включают поврежденный экран, перегоревшую подсветку, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт дисплеев, подсветки, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный мастерская по ремонту телевизоров на выезде.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-televizorov-fun.ru
Актуальный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 дарит для вас невероятные шансы для победных стратегий! На нашей платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых предложений. Всегда здесь вы попробуете завоевать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшают ваш азарт. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы достичь успеха. Казино Лев и Азино777 предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только видеослоты, но и живые игры, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас фриспины каждый день. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете получить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный мастер по ремонту телевизоров с гарантией всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши TV, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи TV, включают проблемы с экраном, неисправности подсветки, неисправности программного обеспечения, проблемы с портами и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт дисплеев, подсветки, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете надежный и долговечный сервисный ремонт телевизоров адреса.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-televizorov-fun.ru
Потрясающий игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас потрясающие опции для успешной игры! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и множество игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы сможете завоевать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы выиграть. Наш сайт предлагает максимально удобный доступ, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только настольные игры, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас бонусные кредиты при каждом пополнении. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Lev, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ждут щедрые призы и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы сможете завоевать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный мастерская по ремонту смартфона с гарантией любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши смартфоны, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы телефонов, включают поврежденный экран, поломку батареи, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный сервис ремонта телефона на выезде.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-telefonov-biz.ru
Фантастический игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас уникальные шансы для максимальных успехов! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас радуют акционные игры и разнообразие игровых предложений. Именно здесь вы получите возможность сорвать колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт обеспечивает простой и удобный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На игровом доме Лев вас ожидают не только видеослоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности предложат вам фриспины на каждом шагу. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся признания каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы откроете захватить невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный официальный ремонт материнских плат в москве всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши мэйнборды, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели мэйнбордов, включают неработающий чипсет, проблемы с блоком питания, программные сбои, проблемы с портами и поломки элементов. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт чипсетов, блоков питания, ПО, разъемов и компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе качественный и надежный мастер по ремонту материнских платы.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-materinskih-plat-info.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный ремонт смартфона рядом различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши мобильные устройства, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели мобильных устройств, включают неисправности дисплея, неисправности аккумулятора, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный центр ремонта смартфона адреса.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-telefonov-biz.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный официальный ремонт тепловизоров на выезде различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши устройства теплового видения, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы тепловизоров, включают неработающие сенсоры, проблемы с линзами, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт матриц, оптики, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный мастерская по ремонту тепловизоров с гарантией.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-teplovizorov-gem.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает профессиональный сервис ремонта тепловизора рядом всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши устройства теплового видения, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели устройств теплового видения, включают проблемы с изображением, проблемы с линзами, ошибки ПО, неисправности разъемов и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт матриц, оптики, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный ремонт тепловизоров.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-teplovizorov-gem.ru
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт бытовой техники в мск
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный сервис ремонта фотоаппарата на дому любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши фотоаппараты, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели фотокамер, включают неисправности объектива, неисправности затвора, неисправный экран, проблемы с питанием и неисправности программного обеспечения. Для устранения этих поломок наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт объективов, затворов, экранов, батарей и ПО. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе качественный и надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту фотоаппаратов адреса.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-fotoapparatov-ink.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный мастерская по ремонту фотоаппарата всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши фотоаппараты, и стремимся предоставить услуги наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи камер, включают проблемы с объективом, проблемы с затвором, поврежденный дисплей, проблемы с питанием и ошибки ПО. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт объективов, затворов, экранов, батарей и ПО. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный официальный ремонт фотоаппарата рядом.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-fotoapparatov-ink.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту фотовспышки на дому различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши фотовспышки, и обеспечиваем ремонт наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы фотовспышек, включают проблемы с зарядкой, неисправности лампы, программные сбои, проблемы с синхронизатором и неработающие разъемы. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт зарядных устройств, ламп, ПО, синхронизаторов и разъемов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный официальный ремонт фотовспышки с гарантией.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-fotovspyshek-job.ru
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
Landscape design https://buddhabuilders.com and improvement services: from design to implementation. Beauty, comfort and individual approach.
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный центр ремонта фотовспышек адреса всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши вспышки, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи вспышек, включают неработающий зарядник, неисправности лампы, программные сбои, неисправности синхронизатора и неработающие разъемы. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт зарядных устройств, ламп, ПО, синхронизаторов и разъемов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный ремонт фотовспышки на выезде.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-fotovspyshek-job.ru
Reliable HVAC Repair Services https://serviceorangecounty.com stay comfortable year-round with our professional HVAC repair services. Our experienced team is dedicated to diagnosing and resolving heating, cooling, and ventilation issues quickly and effectively.
Временная регистрация в СПб: Быстро и Легально!
Ищете, где оформить временную регистрацию в Санкт-Петербурге?
Мы гарантируем быстрое и легальное оформление без очередей и лишних документов.
Ваше спокойствие – наша забота!
Минимум усилий • Максимум удобства • Полная легальность
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас!
Временная регистрация
Наша мастерская предлагает профессиональный официальный ремонт холодильника на выезде всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши рефрижераторы, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи рефрижераторов, включают проблемы с охлаждением, неисправности термостата, ошибки ПО, неисправности разъемов и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт компрессоров, термостатов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный отремонтировать холодильник на дому.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-holodilnikov-lux.ru
cách chuyển dữ liệu từ máy tính cũ sang máy mới một cách nhanh chóng, dễ dàng và an toàn, giúp bạn tiếp tục công việc và giải trí mà không bỏ lỡ bất kỳ thông tin quan trọng nào.
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный вызвать мастера по ремонту монитора на дому любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши дисплеи, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи дисплеев, включают неработающую подсветку, поврежденный экран, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт подсветки, матриц, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный мастерская по ремонту мониторов.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-monitorov-plus.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный мастерская по ремонту холодильника адреса любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши рефрижераторы, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи рефрижераторов, включают проблемы с охлаждением, проблемы с температурным датчиком, неисправности программного обеспечения, проблемы с подключением и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт компрессоров, термостатов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный сервис ремонта холодильника на дому.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-holodilnikov-lux.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает профессиональный официальный ремонт электровелосипеда на выезде всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши электробайки, и обеспечиваем ремонт наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели электробайков, включают неисправную батарею, неисправности двигателя, поломку контроллера, проблемы с тормозами и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, тормозных систем и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете качественный и надежный сервисный ремонт электровелосипедов адреса.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-elektrovelosipedov-gem.ru
ガッツだ!!森の石松
北斗の拳 暴凶星 先バレ 信頼度
美しいアニメーションと迫力ある演出が魅力。毎回新しい発見があります。
L ゴールデンカムイ
https://scenario.jahromblog.com/post-356/
戦略的な要素もあり、運だけでなく技術が試されるのが面白いです。
CR真・花の慶次L6-K 319ver.
転スラスロット 到達者恩恵
コードギアス反逆のルルーシュ
CRキャッツ・アイ
押忍!番长(操)
L 主役は銭形 4
https://www.k8pachinko.club/Articles/2833.html
シンプルなルールで、誰でもすぐに楽しめるのが嬉しいです。
デビルサバイバー2 最後の7日間
https://www.k8-k8.net/2170
お店によって雰囲気が異なるので、色々な店を試してみるのが楽しいです。新しい発見があります。
ガッツだ!!森の石松
https://hithot.jp/news/12031.html
パチンコは単なるギャンブルではなく、エンターテイメントとして楽しむべきです。友人との交流にも最適です。
chuyển dữ liệu từ máy tính cũ sang máy mới một cách nhanh chóng, dễ dàng và an toàn, giúp bạn tiếp tục công việc và giải trí mà không bỏ lỡ bất kỳ thông tin quan trọng nào.
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный официальный ремонт электровелосипедов в москве любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши электробайки, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы электровелосипедов, включают проблемы с батареей, проблемы с мотором, сбои контроллера, проблемы с тормозами и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, тормозных систем и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный официальный ремонт электровелосипедов рядом.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-elektrovelosipedov-gem.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный мастер по ремонту электронных книг с гарантией различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши eBook-ридеры, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи eBook-ридеров, включают неисправный дисплей, неисправную батарею, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и проблемы с контроллером. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и контроллеров. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный мастер по ремонту электронной книги.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-elektronnyh-knig-hit.ru
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный мастер по ремонту электронной книги с гарантией любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши электронные книги, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели цифровых книг, включают проблемы с экраном, выход из строя батареи, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и проблемы с контроллером. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и контроллеров. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный качественный ремонт электронной книги.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-elektronnyh-knig-hit.ru
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный сервис ремонта моноблоков на дому всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши моноблоки, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи все-в-одном ПК, включают проблемы с жестким диском, поврежденный экран, ошибки ПО, неисправности разъемов и проблемы с охлаждением. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, дисплеев, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный отремонтировать моноблок адреса.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-monoblokov-rial.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный мастерская по ремонту моноколес на выезде любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши электрические моноколеса, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что предоставляет надежность и долговечность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы моноколес, включают поломку аккумулятора, проблемы с мотором, поломку контроллера, проблемы с гиросенсорами и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера проводят ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, гиросенсоров и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный центр ремонта моноколеса.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-monokoles-serv.ru
Получите 1xslots бонус за регистрацию и начните выигрывать.
Фантастический игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас захватывающие опции для крупных выигрышей! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и огромное количество игр. Только здесь вы сможете выиграть огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает регулярные акции, которые поднимут ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы достичь успеха. Игровая платформа дарит вам быстрый и легкий процесс игры, что делает игру комфортной на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Lev вас приветствуют не только настольные игры, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Лев, и завоевывай признания каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ждут выгодные предложения и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы попробуете захватить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Военная служба по контракту https://contract.moscow гарантированная стабильность, льготы для семьи, обучение и перспективы карьерного роста.
Потрясающий игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 дарит для вас фантастические возможности для успешной игры! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы попробуете сорвать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшают ваш азарт. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы сорвать куш. Наш сайт гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Lev вас встретят не только настольные игры, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки помогут вам бесплатные вращения на регулярной основе. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы откроете сорвать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Грандиозный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас фантастические возможности для крупных выигрышей! На онлайн-казино Лев и Азино777 вас встречают прекрасные подарки и разнообразие игровых предложений. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя завоевать множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшают ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы выиграть. Казино Лев и Азино777 предлагает максимально удобный доступ, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас встретят не только слоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые обеспечат вам ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк помогут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на регулярной основе. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Лев, и добивайся призов каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность получить огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Можно ли купить аттестат о среднем образовании, основные моменты и вопросы
Актуальный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 открывает для вас великолепные возможности для успешной игры! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых предложений. Всегда здесь вы сможете сорвать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшают ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт обеспечивает эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только видеослоты, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на каждом шагу. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы успеете получить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас потрясающие возможности для ярких побед! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и огромное количество игр. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность завоевать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшают ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы победить. Игровая платформа обеспечивает эргономичный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на любой платформе. На Lev вас встретят не только настольные игры, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности порадуют вас бонусные кредиты на регулярной основе. Играй с азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся призов каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и ассортимент слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете сорвать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предоставляет для вас незабываемые опции для крупных выигрышей! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете получить колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, что делает игру комфортной на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Lev вас приветствуют не только слоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас бесплатные вращения на регулярной основе. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Lev, и добивайся призов каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы попробуете захватить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предоставляет для вас потрясающие возможности для максимальных успехов! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут прекрасные подарки и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы успеете получить множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые поднимут ваш настроение. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, что делает игру комфортной на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас встретят не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам бесплатные вращения каждый день. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Lev, и получай богатства каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и богатый выбор игр. Именно здесь вы получите возможность захватить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предлагает для вас великолепные возможности для ярких побед! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают акционные игры и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы попробуете выиграть множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только рулетка и покер, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк помогут вам дополнительные средства каждый день. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Lev, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы откроете выиграть невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный ремонт ipad любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши устройства iPad, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы iPad, включают поврежденный экран, неисправности аккумулятора, ошибки ПО, неисправности разъемов и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный ремонт айпада.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-ipad-pro.ru
Копирайтер и SMM-менеджер https://uslugi.yandex.ru/profile/ElenaB-1085854 написание текстов, контент-план и эффективное управление группами в ВК для развития бренда.
Лучший игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предоставляет для вас незабываемые шансы для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют акционные игры и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы попробуете сорвать множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам простой и удобный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только рулетка и покер, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай славы каждый день! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают выгодные предложения и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете выиграть крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Топовый игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас невероятные опции для победных стратегий! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых предложений. Только здесь вы получите возможность получить колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш настроение. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы достичь успеха. Игровая платформа дарит вам быстрый и легкий процесс игры, обеспечивает легкость использования на любой платформе. На Lev вас встретят не только слоты, но и живые игры, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности помогут вам фриспины на регулярной основе. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые бонусы и богатый выбор игр. Именно здесь вы попробуете получить множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас великолепные возможности для победных стратегий! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы сможете получить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы достичь успеха. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом гаджете. На Lev вас радуют не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система дадут вам фриспины при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай призов каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы откроете выиграть множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Потрясающий игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предлагает для вас захватывающие опции для максимальных успехов! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы сможете захватить огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает интересные турниры, которые увеличат ваш азарт. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы сорвать куш. Наш сайт обеспечивает максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На Lev вас встретят не только игровые автоматы, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк дадут вам фриспины на регулярной основе. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Лев, и получай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас радуют удивительные акции и богатый выбор игр. Именно здесь вы откроете получить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Грандиозный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предоставляет для вас уникальные варианты для ярких побед! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют акционные игры и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы успеете завоевать огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые поднимут ваш азарт. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы победить. Наш сайт обеспечивает эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только видеослоты, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас дополнительные средства при каждом пополнении. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай богатства каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют приятные подарки и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность получить множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предоставляет для вас уникальные опции для ярких побед! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают выгодные предложения и огромное количество игр. Только здесь вы получите возможность получить огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы сорвать куш. Казино Лев и Азино777 предлагает простой и удобный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Lev вас встретят не только слоты, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности порадуют вас бесплатные вращения на каждом шагу. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас радуют приятные подарки и богатый выбор игр. Каждый раз здесь вы попробуете захватить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Грандиозный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас незабываемые шансы для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино Лев и Азино777 вас встречают акционные игры и множество игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы успеете захватить огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые улучшат ваш настроение. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы выиграть. Игровая платформа гарантирует эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только рулетка и покер, но и живые дилеры, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас бонусные кредиты на каждом шагу. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Лев, и завоевывай богатства каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете завоевать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
cs go рулетка
Существуют определенные товары https://ru.pinterest.com/id1668586018/ и категории товаров, которые подлежат обязательной сертификации. Остальные могут пройти процедуру добровольно. Нет необходимости в оформлении документа.
Лучший игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас захватывающие опции для победных стратегий! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете выиграть огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа дарит вам простой и удобный интерфейс, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Лев и Азино777 вас встретят не только настольные игры, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам фриспины при каждом пополнении. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют удивительные акции и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы сможете сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас потрясающие шансы для ярких побед! На онлайн-казино Лев и Азино777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете сорвать множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые увеличат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы выиграть. Игровая платформа предлагает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только рулетка и покер, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки дадут вам бонусные кредиты на регулярной основе. Играй с максимумом азарта, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые призы и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы сможете сорвать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предоставляет для вас незабываемые варианты для ярких побед! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые призы и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы получите возможность завоевать колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы сорвать куш. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любой платформе. На Lev вас встретят не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые дадут вам возможность насладиться реальным игровым процессом из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план предложат вам дополнительные средства каждый день. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай признания каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы откроете выиграть колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный сервисный центр по ремонту морозильной камеры на дому различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши морозильники, и готовы предложить сервис первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели фризеров, включают проблемы с температурным режимом, неработающий термостат, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт компрессоров, термостатов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный мастер по ремонту морозильных камер рядом.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-morozilnyh-kamer-spec.ru
Актуальный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 дарит для вас фантастические шансы для успешной игры! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют прекрасные подарки и множество игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя сорвать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт обеспечивает максимально удобный доступ, что делает игру комфортной на любом гаджете. На Lev вас радуют не только настольные игры, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом в любое время. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам дополнительные средства на каждом шагу. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Лев, и получай богатства каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ждут удивительные акции и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы откроете получить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Фантастический игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас потрясающие шансы для успешной игры! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы успеете сорвать крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы сорвать куш. Наш сайт предлагает простой и удобный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на любой платформе. На Lev вас ждут не только видеослоты, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам испытать настоящее казино в любое время. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам бесплатные вращения при каждом пополнении. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай призов каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы сможете сорвать невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 дарит для вас захватывающие возможности для максимальных успехов! На онлайн-казино Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые призы и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы получите возможность завоевать невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает интересные турниры, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы достичь успеха. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На игровом доме Лев вас приветствуют не только настольные игры, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом в любое время. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки предложат вам бонусные кредиты при каждом пополнении. Играй с азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай славы каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и ассортимент слотов. Только здесь вы попробуете выиграть огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предоставляет для вас потрясающие шансы для победных стратегий! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают акционные игры и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы откроете для себя получить множество призов с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые увеличат ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Игровая платформа дарит вам эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любой платформе. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только видеослоты, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план помогут вам бесплатные вращения при каждом пополнении. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Лев, и получай славы каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые призы и богатый выбор игр. Именно здесь вы получите возможность сорвать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Если вы игрок в CS2 или ГО, то у вас наверняка неплохой инвентарь с множеством скинов, которые, будем честны, иногда попросту надоедают. И что же делать в такой ситуации? Продавать скины на Торговой площадке Steam – не вариант, там вас будут ждать заниженные цены и постоянные зависания, это уже не говоря о том, что гарантий на покупку вашего предмета попросту нет. ТУТ: https://dzen.ru/a/Z07p_ThRgyt0ppo9 вы можете вывести скины КС ГО и обменять их на новые или же получить деньги на карту в течение 15 минут.
Грандиозный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас потрясающие возможности для ярких побед! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и огромное количество игр. Только здесь вы сможете захватить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшают ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы победить. Игровая платформа обеспечивает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас встретят не только видеослоты, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют приятные подарки и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы попробуете завоевать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
All logos, images and symbols https://logo-all.ru in one place: a large selection of designs, easy navigation and high-quality materials for your project.
Лучший игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предоставляет для вас потрясающие опции для победных стратегий! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы получите возможность завоевать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые поднимут ваш шанс на победу. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы победить. Игровая платформа обеспечивает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На Lev вас радуют не только слоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности помогут вам дополнительные средства при каждом пополнении. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Лев, и получай славы каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы попробуете сорвать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Как получить диплом техникума с упрощенным обучением в Москве официально
Центр слухопротезирования https://lmoroshkina.ru/poterya-sluha-ne-prigovor.html диагностика слуха, подбор и настройка слуховых аппаратов. Современные технологии и профессиональный подход.
играть слоты автоматы без регистрации бесплатно
брекет система https://brekety-na-zuby.ru/
Безупречный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 раскрывает для вас фантастические опции для успешной игры! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя получить огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы выиграть. Наш сайт обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только рулетка и покер, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую в любое время. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки дадут вам дополнительные средства на регулярной основе. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай признания каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас радуют удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Именно здесь вы получите возможность захватить колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас невероятные варианты для крупных выигрышей! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас встречают выгодные предложения и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы успеете выиграть невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш настроение. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт гарантирует интуитивно понятный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только игровые автоматы, но и живые игры, которые обеспечат вам почувствовать себя в настоящем казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день. Играй с азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают щедрые призы и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы успеете сорвать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Актуальный игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 предлагает для вас фантастические возможности для ярких побед! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и разнообразие игровых предложений. Всегда здесь вы сможете завоевать крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает интересные турниры, которые поднимут ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует быстрый и легкий процесс игры, что делает игру комфортной на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас встретят не только игровые автоматы, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план предложат вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш при каждом пополнении. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай признания каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ждут выгодные предложения и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы попробуете завоевать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
брекеты установка https://brekety-na-zuby.ru/
Грандиозный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас потрясающие варианты для крупных выигрышей! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и огромное количество игр. Именно здесь вы откроете для себя получить огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы сорвать куш. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует максимально удобный доступ, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом гаджете. На Lev вас встретят не только настольные игры, но и живые игры, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки помогут вам бесплатные вращения на регулярной основе. Играй с азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и богатый выбор игр. Именно здесь вы откроете захватить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Болезни почек https://pochkidp.ru виды заболеваний, симптомы, диагностика, лечение и профилактика. Лечение и диагностика нефрологических заболеваний.
Топовый игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 открывает для вас захватывающие опции для ярких побед! На нашей платформе Лев и Азино777 вас ждут щедрые бонусы и разнообразные игры. Всегда здесь вы откроете для себя выиграть огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые поднимут ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт предлагает максимально удобный доступ, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любой платформе. На Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют не только настольные игры, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую в любое время. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день. Играй с азартом, побеждай с Лев, и завоевывай признания каждый день! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас ждут приятные подарки и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы откроете сорвать огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас незабываемые варианты для максимальных успехов! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают акционные игры и разнообразие игровых предложений. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность захватить крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые улучшают ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы достичь успеха. Казино Лев и Азино777 обеспечивает эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас встретят не только слоты, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые обеспечат вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом в любое время. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай богатства каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас радуют приятные подарки и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы сможете выиграть множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предоставляет для вас захватывающие шансы для успешной игры! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют щедрые бонусы и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы сможете получить огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы выиграть. Наш сайт обеспечивает простой и удобный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любой платформе. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только настольные игры, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые обеспечат вам ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк порадуют вас бесплатные вращения каждый день. Играй с адреналином, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай богатства каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и богатый выбор игр. Только здесь вы получите возможность получить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Топовый игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 предлагает для вас захватывающие опции для ярких побед! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют акционные игры и разнообразие игровых предложений. Всегда здесь вы получите возможность завоевать крупные выигрыши с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает ежедневные бонусы, которые поднимут ваш азарт. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы победить. Наш сайт предлагает эргономичный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любой платформе. На Лев и Азино777 вас встретят не только рулетка и покер, но и игры с реальными крупье, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш при каждом пополнении. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай призов каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы откроете выиграть невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Топовый игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас фантастические возможности для ярких побед! На онлайн-казино игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают удивительные акции и разнообразные игры. Только здесь вы получите возможность получить огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 предлагает максимально удобный доступ, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Lev вас радуют не только игровые автоматы, но и игры в режиме реального времени, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас дополнительные шансы на выигрыш каждый день. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Лев, и выигрывай богатства каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы откроете выиграть невероятные призы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Потрясающий игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 открывает для вас уникальные варианты для победных стратегий! На нашей платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ждут акционные игры и богатый выбор слотов. Только здесь вы сможете захватить невероятные призы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает захватывающие соревнования, которые поднимут ваш настроение. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт обеспечивает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любой платформе. На Lev вас ждут не только слоты, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую в любое время. Кроме того, наш щедрый бонусный план порадуют вас бонусные кредиты на каждом шагу. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с Lev, и завоевывай признания каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют приятные подарки и богатый выбор игр. Именно здесь вы успеете выиграть колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Лучший игровой сайт игорный дом Лев и Azino777 раскрывает для вас невероятные шансы для успешной игры! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и богатый выбор слотов. Именно здесь вы получите возможность завоевать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые увеличат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы победить. Казино Лев и Азино777 дарит вам интуитивно понятный интерфейс, обеспечивает легкость использования на любом устройстве. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только рулетка и покер, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш ежедневные подарки порадуют вас бесплатные вращения каждый день. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся призов каждый день! На платформе Lev и Azino777 вас ожидают щедрые призы и разнообразные игры. Каждый раз здесь вы получите возможность сорвать множество призов. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и начните выигрывать игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Топовый игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 дарит для вас захватывающие возможности для ярких побед! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас ждут удивительные акции и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы откроете для себя получить огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в состязаниях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Казино Лев и Азино777 обеспечивает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, что делает игру комфортной на любой платформе. На игровом доме Лев вас встретят не только слоты, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино прямо у себя дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк дадут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш при каждом пополнении. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Лев, и добивайся славы каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас радуют выгодные предложения и разнообразие игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы сможете завоевать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже моментально! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
брекеты на зубы https://brekety-na-zuby.ru/
Потрясающий игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 дарит для вас великолепные опции для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас встречают выгодные предложения и огромное количество игр. Каждый раз здесь вы успеете завоевать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы оказаться среди лидеров. Наш сайт дарит вам быстрый и легкий процесс игры, обеспечивает легкость использования на смартфоне, планшете или ПК. На Лев и Азино777 вас радуют не только игровые автоматы, но и живые дилеры, которые позволят вам испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности дадут вам бесплатные вращения на каждом шагу. Играй с фантастическим азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и получай славы каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас встречают выгодные предложения и ассортимент слотов. Всегда здесь вы откроете захватить крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Топовый игровой сайт Лев и Азино777 открывает для вас захватывающие шансы для победных стратегий! На площадке Lev и Azino777 вас встречают акционные игры и огромное количество игр. Всегда здесь вы сможете получить огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает эксклюзивные акции, которые улучшат ваш азарт. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы сорвать куш. Казино Лев и Азино777 гарантирует простой и удобный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на любом устройстве. На игровом доме Лев вас ждут не только игровые автоматы, но и живые дилеры, которые дадут вам возможность почувствовать себя в настоящем казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш бонусная система порадуют вас дополнительные средства на каждом шагу. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На сайте Лев и Азино777 вас ждут приятные подарки и богатый выбор игр. Всегда здесь вы откроете получить огромные джекпоты. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже без промедлений! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Здесь можно купить сейф москва для дома домашние сейфы
Новый децентрализованный проект градиент нетворк ориентированный на решения для майнинга. Устонавливайте расширение в браузер и фармите поинты бесплатно.
Делайте ставки с Mostbet UZ https://vashikrohi.ru широкая линия событий, выгодные акции и удобный интерфейс.
Выбирайте Mostbet UZ https://ikidz.ru спортивные ставки, азартные игры и киберспорт. Удобный сайт, лучшие коэффициенты и круглосуточная поддержка.
Скачать Mostbet UZ https://2021evro.ru удобно и быстро! Приложение для ставок на спорт и казино. Простая установка, моментальные выплаты и бонусы для пользователей.
Букмекерская контора Mostbet UZ https://belayaistoriya.ru ставки на спорт, киберспорт и казино. Высокие коэффициенты, быстрые выплаты и удобный интерфейс для каждого игрока.
Download Mostbet India https://india-club.com app for quick access to sports betting and casino games. Easy installation, user-friendly interface, and instant withdrawals.
Bet with Mostbet Bangladesh https://appbetbangladesh.com enjoy live games, sports events, and casino entertainment with fast transactions and 24/7 support.
Лучший игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 открывает для вас захватывающие возможности для крупных выигрышей! На площадке игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас приветствуют выгодные предложения и множество игровых автоматов. Всегда здесь вы сможете завоевать колоссальные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает регулярные акции, которые поднимут ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в турнирах, чтобы достичь успеха. Наш сайт обеспечивает эргономичный интерфейс, гарантирует комфортный процесс игры на вашем мобильном телефоне. На Lev вас ждут не только слоты, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые дадут вам возможность испытать настоящее казино не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш кэшбэк помогут вам дополнительные средства на регулярной основе. Играй с азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и завоевывай призов каждый день! На платформе игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые призы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Только здесь вы откроете выиграть колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на игровом доме Лев и Azino777 и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Потрясающий игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 предлагает для вас фантастические опции для победных стратегий! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас встречают щедрые бонусы и разнообразие игровых предложений. Только здесь вы получите возможность получить огромные суммы с легкостью и удовольствием! Наше казино предлагает интересные турниры, которые увеличат ваш опыт игры. Примите участие в лотереях, чтобы выиграть. Наш сайт предлагает максимально удобный доступ, что делает игру комфортной на любом гаджете. На игровом доме Лев вас ожидают не только настольные игры, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые позволят вам насладиться реальным игровым процессом не выходя из дома. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности помогут вам бонусные кредиты на каждом шагу. Играй с удовольствием, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и выигрывай удивительных сумм каждый день! На платформе Лев и Азино777 вас встречают приятные подарки и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Каждый раз здесь вы откроете завоевать колоссальные суммы. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и погрузитесь в азарт игровые автоматы уже сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Необыкновенный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 открывает для вас великолепные возможности для победных стратегий! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают щедрые призы и огромное количество игр. Только здесь вы сможете выиграть огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Площадка Лев предлагает регулярные акции, которые улучшат ваш игровой процесс. Примите участие в розыгрышах, чтобы выиграть. Наш сайт дарит вам максимально удобный доступ, что делает игру комфортной на любом гаджете. На Лев и Азино777 вас ждут не только рулетка и покер, но и столы с живыми дилерами, которые позволят вам ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш бонусная система дадут вам бонусные кредиты на каждом шагу. Играй с наслаждением, побеждай с Lev, и выигрывай славы каждый день! На площадке Лев и Азино777 вас приветствуют щедрые призы и огромный выбор игровых автоматов. Именно здесь вы получите возможность сорвать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на платформе Лев и Азино777 и запустите игру игровые автоматы уже в этот момент! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Безупречный игровой сайт Lev и Azino777 дарит для вас фантастические возможности для крупных выигрышей! На сайте Lev и Azino777 вас приветствуют акционные игры и богатый выбор слотов. Всегда здесь вы попробуете сорвать огромные джекпоты с легкостью и удовольствием! Сайт Lev предлагает регулярные акции, которые увеличат ваш настроение. Примите участие в игровых мероприятиях, чтобы сорвать куш. Игровая платформа обеспечивает быстрый и легкий процесс игры, позволяет наслаждаться игрой без трудностей на любой платформе. На Лев и Азино777 вас ожидают не только рулетка и покер, но и живые игры, которые дадут вам возможность ощутить азарт вживую из любой точки мира. Кроме того, наш программа лояльности помогут вам дополнительные шансы на выигрыш на регулярной основе. Играй с азартом, побеждай с игровым домом Лев, и добивайся удивительных сумм каждый день! На сайте игрового дома Лев и Azino777 вас радуют щедрые бонусы и ассортимент слотов. Именно здесь вы получите возможность завоевать крупные выигрыши. Зарегистрируйтесь на нашем сайте и начните побеждать игровые автоматы уже прямо сейчас! казино лев, faq, правила, бонус, Азино777 казино лев 2025 бонус Азино777 игровые автоматы
Thanks a ton for this insightful article!
Здесь можно сейф домашний купить москва сейфы для дома купить москва
Mostbet Azerbaijan https://azerichat.org your platform for sports betting, esports, and casino games. High odds, fast payouts, and generous bonuses.
Bet with Mostbet Uzbekistan https://uzbekmusic.com a wide selection of events, fast transactions, and exciting promotions.
Mostbet в Кыргызстане https://obukhov-sport.ru предлагает спортивные ставки, live-игры и казино. Удобная платформа, моментальные выплаты и круглосуточная поддержка.
soap2day thrillers soap2day how to use
Ремонт водонагревателей в Москве https://remont-vodonagrevatelej-moscow.ru быстрый и качественный сервис от опытных мастеров. Обслуживаем все марки и модели, устраняем поломки любой сложности. Выезд на дом, диагностика, замена деталей с гарантией. Надежное восстановление работы вашего оборудования!
РПНУ Лизинг https://rpnu-leasing.ru надежный партнер в лизинге автомобилей, спецтехники и оборудования. Гарантируем отсутствие отказов благодаря индивидуальному подходу к каждому клиенту. Удобные условия и быстрое оформление помогают получить нужное имущество без лишних сложностей.
Open library of microcourses https://learn.rumie.org/jR short and effective training programs for quick acquisition of skills. Convenient access, relevant topics, materials for self-development.
Рекомендации по 1xSlots https://bodegascrial.es/pags/?1xslots-descargar-android-ios.html
watch soap2day soap2day watch
soap2day comedies soap2day detectives
The best on the web https://list.ly/list/b1lf-top-video-content games, videos and entertainment. Top new releases, popular videos and exciting content in one place. Everything for bright leisure and inspiration!
МТЮ Лизинг https://depo.rent предоставляет аренду автомобилей в Крыму, включая Симферополь. Удобный онлайн-сервис позволяет оформить аренду на сайте за несколько минут. Широкий выбор автомобилей и выгодные условия делают поездки по региону комфортными и доступными.
АО Ти И Эл Лизинг https://avtee.ru предлагает услуги проката автомобилей в России, Турции, ОАЭ, Черногории, Испании и других странах по всему миру. Широкий выбор авто, выгодные условия и удобное бронирование делают поездки комфортными и доступными для каждого клиента.
АО Ти И Эл Лизинг https://avtee.ru предлагает услуги проката автомобилей в России, Турции, ОАЭ, Черногории, Испании и других странах по всему миру. Широкий выбор авто, выгодные условия и удобное бронирование делают поездки комфортными и доступными для каждого клиента.
soap2day short films soap2day mini-series
Swap.cloud https://swap.cloud is a licensed cryptocurrency exchange service based in Luxembourg. It offers fully automated, instant swaps between cryptocurrencies with no KYC requirements, ensuring speed and privacy. The platform is designed for users seeking seamless, secure, and hassle-free transactions.
soap2day movies of the past year soap2day most popular
МТЮ Лизинг https://depo.rent предоставляет аренду автомобилей в Крыму, включая Симферополь. Удобный онлайн-сервис позволяет оформить аренду на сайте за несколько минут. Широкий выбор автомобилей и выгодные условия делают поездки по региону комфортными и доступными.
ООО Спецтехгрупп https://stgauto.ru предоставляет аренду автомобилей в Сочи, Адлере, Калининграде и Краснодаре. Полностью онлайн оформление позволяет быстро забронировать авто без лишних визитов. Удобный сервис и широкий выбор машин для любых задач — от отдыха до работы.
Торты на заказ с доставкой https://protortiki.ru в Москве. Кондитерская «Магиссимо» предлагает заказать в Москве торты под заказ для различных мероприятий: свадеб, корпоративов, детских праздников и пр.
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный сервис ремонта iphone на выезде различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши устройства iPhone, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи смартфонов Apple, включают поврежденный экран, неисправности аккумулятора, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный официальный ремонт айфона рядом.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-iphone-sot.ru
РПНУ Лизинг https://rpnu-leasing.ru надежный партнер в лизинге автомобилей, спецтехники и оборудования. Гарантируем отсутствие отказов благодаря индивидуальному подходу к каждому клиенту. Удобные условия и быстрое оформление помогают получить нужное имущество без лишних сложностей.
АО Ти И Эл Лизинг https://avtee.ru предлагает услуги проката автомобилей в России, Турции, ОАЭ, Черногории, Испании и других странах по всему миру. Широкий выбор авто, выгодные условия и удобное бронирование делают поездки комфортными и доступными для каждого клиента.
soap2day free premieres soap2day
soap2day with subtitles soap2day new TV series
ООО Спецтехгрупп https://stgauto.ru предоставляет аренду автомобилей в Сочи, Адлере, Калининграде и Краснодаре. Полностью онлайн оформление позволяет быстро забронировать авто без лишних визитов. Удобный сервис и широкий выбор машин для любых задач — от отдыха до работы.
soap2day TV series online soap2day access
soap2day movies 2024 soap2day free premieres
Смотреть фильмы онлайн https://smotri-fhdl.ru бесплатно в хорошем качестве в онлайн кинотеатре. Фильмы онлайн и новинки кино бесплатно. Смотрите сериалы, клипы, мультфильмы и фильмы онлайн бесплатно на вашем устройстве!
soap2day series 2024 watch soap2day
Swap.cloud https://swap.cloud is a licensed cryptocurrency exchange service based in Luxembourg. It offers fully automated, instant swaps between cryptocurrencies with no KYC requirements, ensuring speed and privacy. The platform is designed for users seeking seamless, secure, and hassle-free transactions.
soap2day high quality soap2day backup address
Установите удобное 1xslots приложение и играйте в любимые слоты где бы вы ни были.
Пинко Отзывы Казино Pinco Casino Скачать
Откройте мир азарта с 1вин узбекистан широкий ассортимент игр, бонусы на старте, прозрачные правила и надёжные выплаты делают наше онлайн-казино выбором тысяч игроков. Играйте и выигрывайте вместе с нами!
This is really attention-grabbing, You are an overly professional blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look ahead to in quest of more of your magnificent post. Also, I have shared your website in my social networks
регистрация zooma casino
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный сервисный центр по ремонту iphone на выезде любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши смартфоны Apple, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи смартфонов Apple, включают проблемы с экраном, поломку батареи, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие разъемы и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете долговечный и надежный ремонт iphone на выезде.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-iphone-sot.ru
купить входную дверь в спб купить входную дверь спб
Быстро оформите займы онлайн просто, быстро и удобно. Без очередей и лишних документов. Деньги поступят на карту в течение нескольких минут после одобрения заявки. Поддержка клиентов 24/7. Финансовая помощь всегда под рукой!
онлайн казино деньги https://casinosha.ru
купить входные двери межкомнатные двери от производителя
купить двери межкомнатные металлическая дверь
техпомощь прикурить https://tehpomosh-krasnodar.ru
накрутка вк бесплатно с заданиями https://nakruti-vk.ru
продамус промокоды продамус промокоды .
двери межкомнатные https://dveri-mezhkomnatnye-sale.ru
купить входные двери https://dveri-mezhkomnatnye-sale.ru
123b đăngnhập được mệnh danh là nhà cái uy tín hàng đầu Việt Nam, 123b cung cấp sảnh cá cược live casino, thể thao, xổ số lô đề… Đăng ký 123b tặng 100K.
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный качественный ремонт макбука всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши ноутбуки Apple, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи ноутбуков Apple, включают поврежденный экран, поломку батареи, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и неисправности системы охлаждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт экранов, батарей, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете долговечный и надежный отремонтировать макбук.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-macbook-club.ru
купить входные двери https://dveri-mezhkomnatnye-sale.ru
купить входную дверь в спб межкомнатные двери спб
купить двери в спб купить входную дверь
b52club là một cổng game bài giải trí tuyệt vời, với nhiều trò chơi như: Casino, game bài, poker, baccarat, slot game và nhiều trò chơi khác.
двери межкомнатные купить в спб входные двери
купить межкомнатные двери в спб межкомнатные двери спб
hit club – Sân Chơi Đẳng Cấp Cho Các Hội Viên Châu Á. Hitclub là một trong những thương hiệu giải trí đẳng cấp hàng đầu tại làng giải trí 2024.
двери межкомнатные купить купить входные двери
iwinclub – Cổng game bài đổi thưởng giành cho giới thượng lưu được bình chọn là 1 trong những cổng game bài xanh chín nhất thị trường Châu Á
купить аккумулятор для автомобиля в спб аккумуляторы для автомобиля купить в спб
геодезическое сопровождение строительства geodezist-spb
сдать старый аккумулятор за деньги в спб адреса приема старых аккумуляторов
аккумулятор автомобильный купить в санкт петербурге дешево магазин аккумуляторов в спб
Где и как купить диплом о высшем образовании без лишних рисков
межевание земельного участка спб межевание стоимость
купить газовый генератор для дома с автозапуском до 15 квт https://tss-generators.ru
iwin club – Cổng game bài đổi thưởng giành cho giới thượng lưu được bình chọn là 1 trong những cổng game bài xanh chín nhất thị trường Châu Á
Что нового в 1xSlots https://antiguedadeselrodeo.com.ar/pages/1xslots-argentina.html
rikvip – Cổng game bài quốc tế xanh chín hàng đầu Việt Nam. Tên cổng game: Rikvip. Năm phát hành: 2015 đến nay. Hệ điều hành: iOS / Android / Webgame.
jun88 đăng nhập trở thành thương hiệu nhà cái uy tín hàng đầu hiện nay nên luôn được các thành viên chào đón. Trụ sở chính của nhà cái được đặt ở London – Vương quốc Anh.
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный мастер по ремонту варочных панелей различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши плиты, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы варочных панелей, включают неработающие конфорки, неисправности сенсоров, ошибки ПО, проблемы с подключением и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт нагревательных элементов, сенсоров, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы получаете надежный и долговечный официальный ремонт варочной панели с гарантией.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-varochnyh-paneley-hit.ru
рейтинг казино 2024 интернет казино с хорошей репутацией
Plinko se ha convertido https://medium.com/@kostumchik.kiev.ua/todo-sobre-el-juego-de-plinko-en-m%C3%A9xico-instrucciones-demos-opiniones-y-m%C3%A1s-d1fde2d99338 en una de las opciones favoritas de los jugadores de casinos en Mexico. Conocido por su simplicidad y gran potencial de ganancias, este adictivo juego ahora cuenta con una plataforma oficial en Mexico.
Онлайн-журнал о строительстве https://zip.org.ua практичные советы, современные технологии, тренды дизайна и архитектуры. Всё о строительных материалах, ремонте, благоустройстве и инновациях в одной удобной платформе.
рейтинг казино на реальные деньги онлайн рейтинг казино
топ казино с выводом топ 100 казино
казино онлайн топ на деньги лучшее казино
какое казино лучше https://lastdepcasino.ru
CapCut – мощный инструмент для монтажа видео для создателей контента в TikTok и Instagram! Больше информации о приложении доступно по ссылке https://aggam.xyz/ и на страницах их соцсетей.
В приложении доступны внушительная библиотека треков и звуковых эффектов с детальной синхронизацией, разнообразные фильтры и визуальные эффекты, удобные настройки текста с множеством шрифтов. Можно регулировать скоростью видео для создания впечатляющих таймлапсов и адаптировать размеры под разные соцсети.
Для загрузки в Украине владельцам iPhone нужно сменить регион на Австралию в настройках Apple ID. Пользователям Android достаточно скачать APK с надежного источника.
При использовании важно регулярно сохранять проект, стартовать с базовой обрезки видео и не злоупотреблять эффектами. Следите обновления приложения для доступа к новым функциям.
CapCut предоставляет все необходимые инструменты для создания профессионального видеоконтента, но помните – главное это баланс между техническим совершенством и вашей креативностью!
Если у вас возникли проблемы, я готов оказать поддержку по вопросам capcut видеоуроки – пишите в Телеграм ots62
Ваш гид в мире строительства https://zip.org.ua и ремонта. Советы специалистов, пошаговые инструкции, полезные статьи и ответы на популярные вопросы.
Grateful for the tips, thanks for writing this!
Mostbet orqali qulay ro‘yxatdan o‘tish usullari | Mostbet 2024 yilgi yangi imkoniyatlari | Mostbet kazino oynash uchun eng yaxshi platforma | Mostbet apk download va o‘yinlarga kirish | Mostbet uz apk skachat va bonuslarni faollashtirish | Mostbet kazino bonuslarini qanday olish mumkin? | Mostbet uz kazino va sportga pul tikish afzalliklari | Mostbet uz uchun eng yaxshi o‘yin platformasi mostbet uz registratsiya.
рейтинг казино https://lastdepcasino.ru
лучшее казино на деньги онлайн рейтинг казино на реальные деньги онлайн
лучшие онлайн казино интернет казино с хорошей репутацией
казино онлайн топ на деньги https://lastdepcasino.ru
рейтинг казино 2024 рейтинг казино
топ 100 казино топ казино 2024 года
123 b là trang hỗ trợ đăng ký, đăng nhập chính thức của nhà cái 123B tại thị trường cá cược Việt Nam. 123B là nhà cái cá cược uy tín hàng đầu châu Á
sunwin – Game bài macau đỉnh cao. Cổng game bài đổi thưởng uy nhất. Kho game sunwin khủng: tài xỉu, xóc đĩa, bắn cá, slot… phát code năm mới tới 999k
8x bet là nhà cái hàng đầu tại châu Á và châu Âu, cung cấp trò chơi casino chất lượng và cá cược thể thao với tiền thưởng hấp dẫn.
f8bet là nhà cái uy tín số 1 về nền tảng cá cược trực tuyến tại Việt Nam và đã được các cơ quan tổ chức cấp phép hoạt động hợp pháp.
секс шоп sex-shop-dp.top
viva bong88 cung cấp nhiều kèo cược phong phú từ các môn thể thao phổ biến như bóng đá, bóng rổ, quần vợt đến các sự kiện thể thao điện tử ..
Узнай, как работает 1xSlots https://elpulpito.com.ar/pages/1xslots-casino_18.html
hi 88 là một trong những nhà cái uy tín hàng đầu tại Việt Nam, cung cấp đa dạng các dịch vụ cá cược như thể thao, casino trực tuyến, và xổ số.
hi88 đăng nhập là một trong những nhà cái uy tín hàng đầu tại Việt Nam, cung cấp đa dạng các dịch vụ cá cược như thể thao, casino trực tuyến, và xổ số.
Тут можно сейфы офисные купитьсейф для офиса для денег
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный вызвать мастера по ремонту видеокамер в москве различных марок и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши видеокамеры, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает длительную работу проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы видеокамер, включают неработающую запись, неисправности объектива, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие разъемы и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт записи, объективов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы обеспечиваете себе долговечный и надежный сервисный центр по ремонту видеокамеры рядом.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-videokamer-ink.ru
Рейтинг лучших онлайн-казино https://lastdepcasino.ru с быстрыми выплатами и честной игрой. Подробные обзоры, бонусы для новых игроков и актуальные акции.
Тут можно сейфы москвасейфы простые
Great insights! This article really cleared up some of my doubts. Thanks for sharing! https://metasmak.com/
May I just say what a relief to discover someone that actually knows what they are talking about on the web. You definitely know how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people ought to look at this and understand this side of your story. I was surprised that you aren’t more popular since you certainly have the gift.
манга на русском языке
Mostbet orqali qulay ro‘yxatdan o‘tish usullari | Mostbet orqali yuqori xavfsizlik bilan pul tikish | Mostbet rasmiy sayti orqali kirish va ro‘yxatdan o‘tish | Mostbet uz ro‘yxatdan o‘tish va o‘yinlarni boshlash | Mostbet kazino ro‘yxatdan o‘tish jarayoni haqida bilib oling mostbet online | Mostbet aviator skachat va strategiyalari | Mostbet uz skachat va o‘yinlarga kirish bo‘yicha maslahatlar | Mostbet oynash va yangi foydalanuvchilar uchun bonuslar aviator mostbet uz.
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный сервисный ремонт видеокарт на выезде различных марок и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши видеокарты, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты работают быстро и аккуратно, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы видеокарт, включают неисправности системы охлаждения, выход из строя памяти, неработающие разъемы, сбои контроллера и ошибки драйверов. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт системы охлаждения, памяти, разъемов, контроллеров и ПО. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный сервисный ремонт видеокарт адреса.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-videokart-biz.ru
Dreaming of a lush, green lawn all year round without the hassle of watering, mowing, or fertilizing? GetGrass.io offers premium artificial grass that looks natural but requires minimal upkeep. Save time, reduce environmental impact, and enjoy the perfect lawn every day!
Learn more and order now at getgrass.io.
Eco-Friendly Pet Products https://petluxe.life
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный центр ремонта мфу с гарантией различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши МФУ, и стремимся предоставить услуги первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи многофункциональных устройств, включают неработающий картридж, проблемы со сканирующим блоком, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера выполняют ремонт печатающих головок, сканеров, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный сервисный центр по ремонту мфу на выезде.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-mfu-lite.ru
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный сервис ремонта гироскутера на выезде любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши гироскутеры, и обеспечиваем ремонт наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи электроскутеров, включают поломку аккумулятора, неисправности двигателя, сбои контроллера, неисправности сенсоров и повреждения рамы. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты выполняют ремонт батарей, двигателей, контроллеров, гиросенсоров и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе надежный и долговечный мастерская по ремонту гироскутера рядом.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-giroskuterov-key.ru
Автомобильный журнал https://automobile.kyiv.ua с фокусом на практичность. Ремонт, уход за авто, обзор технологий и советы по эксплуатации.
Авто портал https://autonovosti.kyiv.ua актуальные новости, обзоры авто, тест-драйвы, инструкции по ремонту и тюнингу. Минимум текста, максимум полезной информации.
Авто журнал https://avtonews.kyiv.ua новости автопрома, сравнения моделей, тест-драйвы, советы по ремонту и уходу.
Всё о машинах https://black-star.com.ua авто новости, тест-драйвы, обзоры моделей, рейтинги, инструкции по обслуживанию и ремонту.
Авто журнал https://avtonews.kyiv.ua новости автопрома, сравнения моделей, тест-драйвы, советы по ремонту и уходу.
Авто портал https://autonovosti.kyiv.ua актуальные новости, обзоры авто, тест-драйвы, инструкции по ремонту и тюнингу. Минимум текста, максимум полезной информации.
Всё о машинах https://black-star.com.ua авто новости, тест-драйвы, обзоры моделей, рейтинги, инструкции по обслуживанию и ремонту.
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный мастер по ремонту духовых шкафов любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши духовки, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши профессиональные техники оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели кухонных приборов, включают неисправности термостата, выход из строя таймера, треснувшую дверцу, проблемы с контроллером, неисправности вентилятора и повреждения электроники. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт нагревательных элементов, термостатов, таймеров, дверец, контроллеров, вентиляторов и электроники. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный сервис ремонта духовых шкафов на дому.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-duhovyh-shkafov-ace.ru
Всё о самогоноварении https://brewsugar.ru на одном сайте: от истории напитка до современных технологий перегонки.
Место для общения на любые темы https://xn--9i1b12ab68a.com/ актуальные вопросы, обмен опытом, интересные дискуссии. Здесь найдётся тема для каждого.
Перевозка товаров из Китая https://chinaex.ru в Россию под ключ: авиа, море, автотранспорт. Гарантия сроков и сохранности груза.
Автомобильный онлайн-журнал https://simpsonsua.com.ua предлагает свежие новости, обзоры авто, тест-драйвы, рейтинги и полезные советы для водителей.
Мода, здоровье, красота https://gratransymas.com семья, кулинария, карьера. Женский портал — полезные советы и свежие идеи для каждой.
Познавательный портал для детей https://detiwki.com.ua обучающие материалы, интересные факты, научные эксперименты, игры и задания для развития кругозора.
Find the latest Roblox codes https://pocket-codes.com/roblox-codes to unlock exclusive rewards, boosts, and items in your favorite games. Stay updated with new codes and level up your adventures on the Roblox platform today!
офисная мебель стол для переговоров офисная мебель оснащение офиса
Женский онлайн-журнал https://stylewoman.kyiv.ua стиль, уход, здоровье, отношения, семья, кулинарные рецепты, психология и карьера.
Наши специалисты предлагает высококачественный мастерская по ремонту бесперебойника на выезде различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши ИБП, и обеспечиваем ремонт высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи UPS, включают поломку аккумулятора, проблемы с инвертором, поломку контроллера, неработающие разъемы и ошибки ПО. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт батарей, инверторов, контроллеров, разъемов и ПО. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы обеспечиваете себе надежный и долговечный отремонтировать бесперебойник на выезде.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-ibp-max.ru
DESIGN, FABRICATION & INSTALLATION OF CUSTOM MADE LOUVERS!
DK Construction & Design provides comprehensive, custom solutions for louvres,
sunshades, privacy screens, awnings, and balustrades made from aluminium, glass, and steel.
Our end-to-end service covers on-site measurements, design development, detailed drawings,
engineering, fabrication, and installation.
We work closely with designers, architects, and homeowners to deliver tailored shading,
privacy, and safety solutions. Our team ensures that every project meets the highest
standards of quality and durability, with a focus on functionality and aesthetics.
Whether you’re after sleek sun control systems or secure balustrading, we’ve got
the expertise to bring your vision to life.
Tel: +61475 617 720
Сайт компании DK Construction & Design
офисная мебель столы оснащение офиса мебель
Всё о туризме https://atrium.if.ua маршруты, путеводители, советы по отдыху, обзор отелей и лайфхаки. Туристический портал — ваш помощник в путешествиях.
Всё для путешествий https://cmc.com.ua уникальные маршруты, гиды по городам, актуальные акции на туры и полезные статьи для туристов.
Informacion de 1xslots para Android https://nodosde.gob.ar/pgs/1xslots-descargar_1.html
Pilih liburan Mewah yang menawarkan pengalaman tak terlupakan di tempat-tempat paling eksklusif di dunia
Статьи о путешествиях https://deluxtour.com.ua гиды по направлениям, лайфхаки для отдыха, советы по сбору багажа и туристические обзоры.
Путешествия по Греции https://cpcfpu.org.ua лучшие курорты, гиды по островам, экскурсии, пляжи и советы по планированию отпуска.
Туристический журнал https://elnik.kiev.ua свежие идеи для путешествий, обзоры курортов, гиды по городам, советы для самостоятельных поездок и туристические новости.
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный мастер по ремонту игровой приставки адреса всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши игровые приставки, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи консолей, включают поломку HDD, неисправные порты, неисправные контроллеры, ошибки ПО и перегрев. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт жестких дисков, разъемов, контроллеров, ПО и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный сервис ремонта игровых приставок на дому.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-igrovyh-konsoley-mob.ru
Статьи о туризме и путешествиях https://inhotel.com.ua маршруты, гиды по достопримечательностям, советы по планированию поездок, рекомендации по отелям и лайфхаки для туристов.
Гиды по странам https://hotel-atlantika.com.ua экскурсии по городам, советы по выбору жилья и маршрутов. Туристический журнал — всё для комфортного и яркого путешествия.
Комплексный ремонт квартир https://anti-orange.com.ua и домов от Студии ремонта. Полный цикл работ: от дизайна до финишной отделки.
Настроение в вашем доме с помощью ароматических свечей, Вдохновляющие ароматы для вашего дома, Вдохновляйтесь ароматами с велас свечами
difusores para casa https://scentalle.com/ .
На строительном портале https://avian.org.ua вы найдете всё: от пошаговых инструкций до списка лучших подрядчиков. Помогаем реализовать проекты любой сложности быстро и удобно.
Строительный портал https://ateku.org.ua ваш гид в мире строительства и ремонта. Полезные статьи, обзоры материалов, советы по выбору подрядчиков и идеи дизайна.
Портал по ремонту https://azst.com.ua всё для вашего ремонта: подбор подрядчиков, советы по выбору материалов, готовые решения для интерьера и проверенные рекомендации.
Журнал по ремонту https://domtut.com.ua и строительству – советы, идеи и обзоры. Узнайте о трендах, изучите технологии и воплотите свои строительные или дизайнерские задумки легко и эффективно.
Портал о ремонте https://eeu-a.kiev.ua всё для тех, кто ремонтирует: пошаговые инструкции, идеи дизайна, обзор материалов и подбор подрядчиков.
Журнал по ремонту и строительству https://diasoft.kiev.ua гид по современным тенденциям. Полезные статьи, лайфхаки, инструкции и обзор решений для дома и офиса.
Наша мастерская предлагает высококачественный мастер по ремонту индукционных плит рядом всех типов и брендов. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши индукционные плиты, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы индукционных плит, включают проблемы с нагревом, неработающие сенсоры, программные сбои, неработающие разъемы и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонт нагревательных элементов, сенсорных панелей, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Обратившись к нам, вы получаете качественный и надежный мастер по ремонту индукционных плит в москве.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-indukcionnyh-plit-now.ru
Индийские фильмы смотреть https://kinoindia.tv онлайн бесплатно в качестве 1080 hd. Смотрите лучшие культовые и современные индийские фильмы в хорошем качестве без рекламы.
Discover the best no deposit bonus casino canada 2025 enjoy free spins or cash rewards just for signing up. Play top-rated games, explore trusted platforms, and win real money without spending a dime.
провести оценку профессиональных рисков цена в Москве https://ocenka-riskov-msk.ru
Maak kennis met CorgiSlot https://www.beachvolleybalschool.nl/new/pgs/corgislot_3.html
Сайт о строительстве и ремонте https://hydromech.kiev.ua полезные советы, инструкции, обзоры материалов и технологий. Все этапы: от фундамента до отделки.
Строительные технологии https://ibss.org.ua новейшие разработки и решения в строительной сфере. Материалы, оборудование, инновации и тренды для профессионалов и застройщиков.
Все о строительстве и ремонте https://kennan.kiev.ua практичные рекомендации, идеи интерьеров, новинки рынка и советы профессионалов.
Асфальтирование и ремонт дорог https://mia.km.ua информация о технологиях укладки асфальта, методах ремонта покрытий и современных материалах.
Kompaktni zarizeni mikrosluchatka poskytuje spolehlivy prenos, pevny, nenapadny design a pohodlne se nosi v kazde situaci.
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный выездной ремонт квадрокоптеров любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько важны для вас ваши духовые шкафы, и стремимся предоставить услуги высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы духовых шкафов, включают проблемы с нагревом, выход из строя таймера, поврежденную дверцу, неисправность контроллера, ошибки вентиляционной системы и неработающие датчики. Для устранения этих поломок наши квалифицированные специалисты оказывают ремонт нагревательных элементов, термостатов, таймеров, дверец, контроллеров, вентиляторов и электроники. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный мастер по ремонту квадрокоптеров на выезде.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-kvadrokopterov-best.ru
Онлайн-журнал о строительстве https://mts-slil.info свежие новости, обзоры инноваций, рекомендации по ремонту и строительству.
Онлайн журнал о ремонте https://prezent-house.com.ua статьи, лайфхаки и решения для всех этапов ремонта: от планирования до отделки. Практичные рекомендации и идеи для вашего дома.
Мастерская креативных идей https://rusproekt.org пространство для творчества и инноваций. Уникальные решения для дизайна, декора и проектов любого масштаба.
продамус промокод скидка на подключение mozaisk.anihub.me/viewtopic.php?id=4682#p9296-00 .
Портал о ремонте https://rvps.kiev.ua практичные рекомендации, дизайн-идеи, современные технологии и инструкции для успешного ремонта любого уровня сложно
Сайт о дизайне интерьера и территории https://sinega.com.ua тренды в дизайне помещений и благоустройстве территорий.
Информационный портал о ремонте https://sevgr.org.ua практичные советы, проверенные методики и новинки рынка. Помощь в планировании, выборе подрядчиков и создании идеального пространства.
Kra19.at
Архитектурный портал https://skol.if.ua новости архитектуры, современные проекты, градостроительные решения и обзоры мировых трендов.
Информационный портал о ремонте https://stinol.com.ua практичные советы, проверенные методики и новинки рынка. Помощь в планировании, выборе подрядчиков и создании идеального пространства.
Гид по ремонту https://techproduct.com.ua идеи и советы для самостоятельного ремонта: экономичные решения, готовые проекты, обзоры материалов и дизайнерские лайфхаки.
Официальные доступ кракен зеркало быстрый и безопасный доступ к сайту, обходя блокировки и сохраняя полную анонимность пользователей.
Анонимная платформа Kraken market обеспечивает безопасные транзакции, конфиденциальность и доступ к разнообразным товарам.
Кодировка и вывод из запоя на дому https://nashinervy.ru/bez-rubriki/vyvod-iz-zapoya-i-kodirovka-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu-professionalnyj-podhod-k-vosstanovleniyu-zdorovya.html безопасно, эффективно и анонимно. Помощь специалистов 24/7 для возвращения к трезвой жизни в комфортных условиях.
Appreciate your effort in writing this. Well done! https://metadocs.org
Автодоставка из Китая https://china-top.ru быстрая и надежная транспортировка товаров. Полный цикл: от оформления документов до доставки на склад клиента.
Find the best no deposit bonus casino canada 2025 offers! Explore top-rated casinos with free spins and bonus cash for new players. Start playing without risking your funds.
Смотреть индийские фильмы онлайн https://kinoindia.tv подборка лучших фильмов с уникальным колоритом. Бесплатный доступ и ежедневное обновление каталога.
Аттестат школы купить официально с упрощенным обучением в Москве
Наша мастерская предлагает профессиональный сервис ремонта компьютеров адреса всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши компьютеры, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи ПК, включают проблемы с жестким диском, неисправности видеокарты, программные сбои, неисправности разъемов и проблемы с охлаждением. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонт жестких дисков, видеокарт, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете долговечный и надежный сервисный ремонт компьютеров рядом.
Подробная информация доступна на сайте: https://remont-kompyuterov-vip.ru
Free Online Games visit your gateway to a world of free online entertainment! Explore a vast collection of games, from puzzles and card games to action and arcade classics. Play instantly on any device without registration or downloads
воздушные шары к празднику с доставкой набор воздушных шаров
заказ шаров с гелием шарики круглосуточно
CBD (Cannabidiol) https://www.cornbreadhemp.com/blogs/learn/cbd-gummies-dosage-guide is a unadorned multiply from hemp plants, known for its concealed benefits in reducing angst, discomposure, and swelling without causing a “high.” It’s widely acclimated to in oils, gummies, and creams.
Оценка профессиональных рисков https://ocenka-riskov-msk.ru комплексная услуга для выявления, анализа и снижения угроз на рабочем месте.
Mikrosluchatko – kompaktni mikro-sluchatka https://mikrosluchatko-cena.cz pro skrytou komunikaci. Nenapadnost, spolehlivost a pohodli v kazdem zarizeni. Idealni pro zkousky, jednani a dulezite ukoly.
Купить VIP подарок в Москве https://podarki-suveniry-vip.ru
Наши спортивный бюстгальтер предлагают идеальное сочетание стиля и комфорта. Выберите бюстгальтер без косточек для мягкой поддержки или кружевной бюстгальтер для романтичного образа. Для будущих мам подойдут бюстгальтеры для беременных и бюстгальтеры для кормления. Обратите внимание на бюстгальтер с пуш-ап для эффекта увеличения груди и комфортные бюстгальтеры для повседневного ношения.
Оценка профессиональных рисков https://ocenka-riskov-msk.ru комплексная услуга для выявления, анализа и снижения угроз на рабочем месте.
sex wien privat sex und erotik in wien
Предлагаем стекла для спецтехники https://steklo-ufa.ru любых типов и размеров. Прочные, устойчивые к ударам и погодным условиям материалы.
Производство шпона в Москве https://shpon-massiv.ru качественный шпон из натурального дерева для мебели, дверей и отделки. Широкий выбор пород, гибкие размеры и выгодные цены.
Download de CorgiSlot APK https://www.mijnstudentenleven.nl/news/corgislot-casino-review.html
Можно ли купить аттестат о среднем образовании, основные моменты и вопросы
Американские власти могут запретить популярные сетевые устройства TP-Link из-за вопросов с защищенностью. Как информирует Источник, правительство США анализируют возможность запрета распространения маршрутизаторов TP-Link на территории США. Основной причиной называются угрозы госбезопасности и причастность оборудования компании с регулярными хакерскими атаками.
По данным издания, устройства китайского производителя часто распространяются с недостатками безопасности, а компания не демонстрирует должного внимания в их устранении. Особую тревогу вызывает тот факт, что роутеры TP-Link используются не только в домашних сетях, но и в ключевой инфраструктуре, включая Пентагон США.
TP-Link занимает около 65% американского рынка маршрутизаторов для домашних сетей и малого бизнеса. В компании сообщили, что согласны к сотрудничеству с властями США и планируют продемонстрировать соответствие своих подходов обеспечения безопасности отраслевым стандартам.
Финальное решение о ограничении может быть вынесено в 2025 году.
Источник: https://telegra.ph/Riski-kiberbezopasnosti-analiz-situacii-s-zapretom-TP-Link-v-SSHA-12-18
Охотно предоставлю свою помощь, если это необходимо по вопросам 2025: США без TP-Link – обращайтесь в Telegram cke57
Инженерные изыскания в Москве https://geology-kaluga.ru точные исследования для строительства и проектирования. Геологические, гидрологические, экологические и геодезические работы для строительства.
Геосинтетические материалы https://geobentomat.ru надежное решение для строительства и укрепления грунтов. Геотекстиль, георешетки, геомембраны и другие материалы для дренажа, армирования и защиты конструкций.
prodamus промокод http://www.forumbar.anihub.me/viewtopic.php?id=9823#p1757 .
Top game và app tài xỉu online uy tín Việt Nam và Châu Á là 12Bet, BK8, TF88, CMD368. Các trang cá cược tài xỉu online uy tín 2024.
Доставка дизельного топлива https://neftegazlogistic.ru в Москве – оперативно и качественно! Поставляем ДТ для автотранспорта, строительной и спецтехники. Гарантия чистоты топлива, выгодные цены и быстрая доставка прямо на объект.
Torlab.net https://torlab.net новый торрент-трекер для поиска и обмена файлами! Здесь вы найдете фильмы, игры, музыку, софт и многое другое. Быстрая скорость загрузки, удобный интерфейс и активное сообщество. Подключайтесь, делитесь, скачивайте — ваш доступ к миру качественного контента!
https://rxguides.net/codes Unlock the latest Roblox codes for exclusive rewards and boosts! Stay updated with fresh codes to enhance your gameplay and level up faster. Don’t miss out on special items and bonuses to get ahead in your favorite Roblox games!
Выигрывайте больше на onexbet, не тратя много времени.
onexbet – ваш ключ к финансовой независимости, где бы вы ни находились.
Ставки на спорт с onexbet, оптимальные шансы на победу.
Попробуйте свою удачу вместе с onexbet, и ваша жизнь никогда не будет прежней.
onexbet – доверие и надежность, всегда гарантированы.
Готовы ли вы к большим выигрышам? Вам нужен onexbet, – оптимальное решение в вашей ситуации.
onexbet – ваш верный компаньон в мире азарта, на который всегда можно положиться.
Играя на onexbet, вы становитесь ближе к своей мечте, используйте onexbet для достижения ваших целей.
onexbet – это не просто азарт, это философия, которая помогает вам обогатиться.
Готовы к большим деньгам и успеху? Попробуйте onexbet, и ваши мечты станут реальностью.
onexbet – это не просто компания, это ваш путь к финансовой независимости, который вы искали.
onexbet – это идеальное место для тех, кто ищет азарт и адреналин, но при этом ценит качество и надежность.
Лучшие коэффициенты и выигрыши на onexbet, все это доступно для вас.
Готовы к новым достижениям? Начните с onexbet, и вы удивитесь своим результатам.
belisadozh belisadozh .
Наша мастерская предлагает профессиональный центр ремонта кондиционеров с гарантией всех типов и брендов. Мы осознаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши кондиционеры, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только качественные детали, что обеспечивает длительную работу наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы кондиционеров, включают неисправности компрессора, проблемы с вентилятором, ошибки ПО, неработающие датчики и поломки корпуса. Для устранения этих проблем наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт компрессоров, вентиляторов, ПО, датчиков и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете надежный и долговечный мастерская по ремонту кондиционера.
Подробная информация размещена на сайте: https://remont-kondicionerov-wow.ru
a custom amazon storefront can help boost your brand visibility and sales. this guide explains how to make an amazon storefront, with easy-to-follow instructions. build a page that captures your audience’s attention and reflects your brand perfectly.
bilan o’yin-kulgi dunyosiga xush kelibsiz 1 win! 1000 dan ortiq o’yinlar, jonli dilerlar, sport va e-sport bir joyda. Saxiy bonuslar, tezkor depozitlar va qulay pul olish. O’ynang, g’alaba qozoning va yangi his-tuyg’ularga qayting!
Discover the best game codes https://rxguides.net in-depth guides, and updated tier lists for your favorite games! Unlock exclusive rewards, master gameplay strategies, and find the top characters or items to dominate the competition.
Наш сервисный центр предлагает высококачественный мастер по ремонту кофемашин в москве любых брендов и моделей. Мы осознаем, насколько важны для вас ваши эспрессо-машины, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши опытные мастера проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность проведенных ремонтов.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели эспрессо-машин, включают проблемы с нагревом, неработающий насос, ошибки ПО, неисправности разъемов и механические повреждения. Для устранения этих поломок наши опытные мастера оказывают ремонт нагревательных элементов, насосов, ПО, разъемов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный центр ремонта кофемашина с гарантией.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-kofemashin-top.ru
Get +20 Points for free using the Gradient Network promo code: gradient network code . Install extensions and farm points for free in your browser.
фильмы 2024 дивитись онлайн безкоштовно дивитися фільми онлайн безкоштовно без реєстрації
фільми, що вийшли онлайн безкоштовно фільми онлайн безкоштовно
фільм вийшла дивитися онлайн фільми 2024 дивитися онлайн
Online casinos site are thousands of slots, live games, profitable promotions and instant wins. Try your luck in a comfortable and safe environment, enjoying the excitement at any time and from any device.
Откройте для себя инновации с samsung s23 fe широкий выбор смартфонов, планшетов, телевизоров и бытовой техники. Выгодные цены, гарантия качества и быстрая доставка. Закажите оригинальную продукцию Samsung прямо сейчас и наслаждайтесь технологиями будущего!
dubai luxury yacht tour boat rental dubai
marina yacht rental yacht booking dubai
Ищещь где https://dzen.ru/a/Zxs960egUVbVaiR5 на проверенных сайтах? Мы сделали для вас подборку из топ сайтов на которых можно продать скины кс и дота за реальные деньги с выводом на карту и электронный кошелек.
https://dzen.ru/a/Z1AQIe3fygAICUvQ это Рулетка Dota 2 (джек-пот лотерея) с минимальной ставкой от 1-рубля и несколькими режимами игры на вещи Steam. Участники ставят скины, а когда раунд завершается с помощью сервиса Random.org определяется победитель, которому достанется всё!
Здесь можно купить сейф для сайгисейф для охотничьего ружья купить в москве
Процесс получения диплома стоматолога: реально ли это сделать быстро?
Самые актуальные новости Украины https://2news.com.ua/category/hobbi-i-rukodelie/ политика, экономика, общество и культура. Только проверенные факты и оперативная подача информации.
Find the latest Blox Fruits codes on https://game-zoom.ru/kody-blox-fruits.html and unlock powerful boosts, in-game rewards, and exclusive items. Level up faster and dominate the seas in this exciting Roblox adventure!
Геймеры, качественная подборка сайтов продать скины дота 2 на карту выгодно и быстро. Процесс продажи занимает не более 10 минут. Цены выгоднее чем в стиме с выводом на карту или криптовалюту. Большое количество отзывов от реальных пользователей проверенных временем.
Практическое руководство Коновалова буклет коновалова купить упражнения и советы для восстановления и укрепления здоровья.
Анализируйте поведение своей аудитории https://bs2site2.net находите точки роста и повышайте конверсии сайта. Поможем вам сделать ваш бизнес эффективнее и увеличить доход.
С помощью платформы https://bc2site.gl вы получите доступ к инновационным инструментам, которые помогут преуспеть в онлайн-продвижении. Управление проектами, оптимизация SEO и аналитика — все это доступно на bs2site.
Узнайте свою аудиторию лучше https://bs2saite.gl анализ данных, улучшение опыта пользователей и рост конверсий. Помогаем привлекать клиентов и увеличивать доход.
С сайтом https://bs2syte.at/ вы можете легко анализировать свою аудиторию, улучшать видимость сайта в поисковых системах и повышать конверсии. Наша команда экспертов гарантирут качественную поддержку и советы для эффективного использования всех инструментов.
эскорт девушки москва https://vip-eskort-msk.ru
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with a few pics to drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, this is magnificent blog. An excellent read. I will definitely be back.
регистрация зума казино
What’s up colleagues, fastidious piece of writing and good urging commented at this place, I am really enjoying by these.
сайт Banda Casino
Good day! Would you mind if I share your blog with my twitter group? There’s a lot of folks that I think would really enjoy your content. Please let me know. Thank you
golfexpo.ru
Tebrikler, oldukça başarılı bir yazı olmuş.
Юридическое агентство «Актив правовых решений» https://ufalawyer.ru было основано в 2015 году в центре столицы Республики Башкортостан – городе Уфа, командой высококвалифицированных юристов, специализирующихся на вопросах недвижимости, семейном и жилищном праве, а также в спорах исполнения договоров строительного подряда и банкротства физических лиц.
Портал для коллекционеров https://ukrcoin.com.ua и ценителей монет и банкнот Украины. Узнайте актуальные цены на редкие украинские монеты, включая копейки, и откройте для себя уникальные экземпляры для своей коллекции. На сайте представлены детальные описания, редкости и советы для нумизматов. Украинские монеты разных периодов и их стоимость – всё это на одном ресурсе!
We absolutely love your blog and find nearly all of your post’s to be just what I’m looking for. Do you offer guest writers to write content for you? I wouldn’t mind writing a post or elaborating on a few of the subjects you write regarding here. Again, awesome weblog!
зеркало банда казино
Vnish official firmware https://vnish.us/self-installation/ for Bitmain Antminer: boost performance by up to 25% and cut energy consumption by up to 15%. Download Vnish firmware now!
My Betting Sites India https://bettingblog.tech your guide to the best sports betting sites. Reviews, ratings, bonuses and comparisons. Find the perfect sports betting platform in India!
как сделать меф ретро порно
Наши специалисты предлагает профессиональный ремонт ноутбука рядом различных марок и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько важны для вас ваши ноутбуки, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает надежность и долговечность наших услуг.
Наиболее частые неисправности, с которыми сталкиваются обладатели переносных компьютеров, включают проблемы с жестким диском, неисправности экрана, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности разъемов и неисправности системы охлаждения. Для устранения этих проблем наши профессиональные техники проводят ремонт жестких дисков, экранов, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе качественный и надежный центр ремонта ноутбуков адреса.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-noutbukov-first.ru
vavada deposit download official vavada website
купить меф сочи купить меф казахстан
vavada official mirror vavada login vavada site login
vavada mirror online vavada casino official
vavada promo code vavada mobile version
website vavada play vavada official bonus
смотреть фильмы бесплатно фильмы 2024 смотреть онлайн
vavada official login vavada mobile application
vavada application for android vavada official app
vavada official app vavada casino
vavada for money vavada login by phone number
vavada slot machines vavada mirror online
Our insulation services https://iepinsulation.com keep your home warm and energy-efficient year-round. We specialize in insulating facades, roofs, floors, and attics using modern materials and techniques. Trust our experienced team for durable, cost-effective solutions that improve comfort and reduce energy bills.
vavada site mirror vavada office
элитный эскорт заказать элитные эскорт модели
Может, вы и правы
fakel-nsk-afisha.ru
Steam Desktop Authenticator https://steamdesktopauthenticator.me is a powerful tool designed to enhance the security of your Steam account. By generating time-based one-time passwords, it provides an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access. This desktop application allows users to manage their two-factor authentication easily, ensuring that only you can access your account.
Steam Desktop Authenticator https://steamauthenticator.ru это альтернатива мобильному аутентификатору Steam. Генерация кодов, подтверждение обменов и входов теперь возможны с компьютера. Программа проста в использовании, повышает удобство и позволяет защитить аккаунт, даже если у вас нет доступа к телефону.
Как не стать жертвой мошенников при покупке диплома о среднем полном образовании
евро в тенге 1 доллар в тенге .
Онлайн-сервис с мгновенной конвертацией валют: переведите тенге в рубли, доллары США или юани за считаные секунды. Точные курсы валют обновляются в режиме реального времени.
Steam Desktop Authenticator https://steamauthenticatordesktop.com is an alternative to the mobile authenticator. Generating Steam Guard codes, confirming logins, trades and transactions is now possible directly from your computer. A convenient and secure solution for Steam users who want to simplify their account management.
Steam Desktop Authenticator https://steamdesktopauthenticator.io is a convenient tool for two-factor authentication of Steam via PC. The program generates Steam Guard codes, replacing the mobile authenticator. Easily confirm logins, trades and sales directly from your computer. Increase account security and manage it quickly and conveniently.
1 доллар в тенге 1 юань в тенге .
Сайт предлагает актуальные курсы валют с обновлением в реальном времени. Бесплатная конвертация поддерживает тенге, доллары, рубли и другие популярные валюты.
Очень интересно изложено.
fakel-nsk-afisha.ru
vavada office vavada play official
Steam Desktop Authenticator https://authenticatorsteam.com is the perfect tool for managing Steam security via PC. It replaces the mobile authenticator, allowing you to generate Steam Guard codes, confirm trades and logins. Ease of use and reliable protection make this program indispensable for every Steam user.
Лучшее остекление балконов в СПб, подберем идеальное решение.
Элитное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, по доступным ценам и с гарантией качества.
Изысканное остекление балконов в Петербурге, под заказ и с уникальным дизайном.
Быстрое остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с оригинальными комплектующими и возможностью долгосрочного сотрудничества.
Удобное остекление балконов в Петербурге, по лучшей цене и быстрой установкой.
остекление лоджии цена под ключ https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Лучшее остекление балконов в СПб, предложим оптимальный вариант.
Профессиональное остекление балконов в Петербурге, с установкой и долговечной эксплуатацией.
Эксклюзивное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, по индивидуальным проектам и с использованием прочных материалов.
Надежное остекление балконов в СПб, с оригинальными комплектующими и возможностью долгосрочного сотрудничества.
Удобное остекление балконов в Петербурге, по лучшей цене и быстрой установкой.
застеклить балкон в хрущевке цены https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
айпиай облачное видеонаблюдение программа распознавания лиц скачать
vms на русском языке https://www.cctvfocus.ru
секс товары https://sex-hub-kharkov.top
сайт эротических товаров sex-hub-kyiv.top
Возможно, вы правы
butirkaconcert.ru
диплом купить в казани
Планируете карьеру или хотите узнать больше о своем рынке труда? На нашем сайте https://zlojnachalnik.ru вы найдете подробную информацию о профессиях, их перспективах и уровнях зарплат. Получите ценную информацию, чтобы сделать осознанный выбор и достичь своих профессиональных целей. Узнайте всё о современных профессиях: от востребованности на рынке до уровня заработной платы.
I’ve been exploring for a little bit for any high quality articles or weblog posts
on this kind of space . Exploring in Yahoo I eventually stumbled
upon this website. Studying this info So i’m glad to exhibit that I’ve a
very good uncanny feeling I came upon exactly what I needed.
I such a lot undoubtedly will make sure to don?t disregard this site and give it a look on a constant basis.
My web-site :: myhomehobby
Качественные натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Выгодное предложение на натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Лучшие специалисты по натяжным потолкам в Петербурге|Разнообразие натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Как выбрать идеальный натяжной потолок в СПб|Натяжные потолки в Петербурге для вашего уюта|Интерьерные решения с натяжными потолками в Петербурге|Красота и практичность с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Только проверенные потолки в Петербурге у нас|Последние тренды для натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Эффективное монтаж натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Оптимальное решение – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Столица натяжных потолков: Петербург|Лучшие цены на натяжные потолки в СПб|Дизайнерские потолки в Петербурге: натяжные|Уникальные решения в области натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Красота и функциональность: натяжные потолки в СПб|Профессиональный подход к выбору и установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Уникальный дизайн вашего потолка: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Плюсы натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: современные технологии и материалы|Эксклюзивные услуги по монтажу натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Современные тренды в создании потолков: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Оптимальный выбор: натяжные потолки в Петербурге
натяжные потолки рассчитать под ключ https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Официальный сайт https://1winpromobk.ru, где вы найдете актуальные промокоды и бонусы для 1Win. Получите эксклюзивные предложения, такие как 500% на первый депозит и бесплатные спины. Присоединяйтесь прямо сейчас, чтобы воспользоваться всеми преимуществами и начать выигрывать!
сливы курсов python https://sliv-kursov213.ru
Купить диплом о среднем полном образовании, в чем подвох и как избежать обмана?
Лучшее остекление балконов в СПб, подберем идеальное решение.
Элитное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с установкой и долговечной эксплуатацией.
Изысканное остекление балконов в Петербурге, с учетом всех пожеланий клиента.
Быстрое остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с гарантией и сертификатом.
Экономичное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с учетом всех требований и технических норм.
остеклить балкон спб недорого цена https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Какое программное обеспечение https://www.cctvforum.ru для видеонаблюдения является лучшим? Какой сервис видеонаблюдения как услуги (VSaaS) наиболее простой и удобный в использовании?
Лучшие 10 программ https://www.cctvfocus.ru для видеонаблюдения. Программное обеспечение для видеонаблюдения. При выборе программного обеспечения важно учитывать наличие функции обнаружения объектов с использованием искусственного интеллекта.
1 юань в тенге калькулятор валют .
Конвертация валют еще никогда не была такой простой! Платформа предоставляет актуальные курсы тенге, рублей, долларов и других валют с быстрым расчетом.
Выбор номер один – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Скидки на натяжные потолки в СПб|Опытные мастера по натяжным потолкам в Санкт-Петербурге|Огромный ассортимент натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Советы по выбору натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Тепло и гармония с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Современный дизайн с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Красота и практичность с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: гарантированное качество и надежность|Технологичные решения для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Быстрое и качественное установление натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Идеальный выбор: натяжные потолки в СПб|Модные тренды в мире натяжных потолков: СПб|Лучшие цены на натяжные потолки в СПб|Натяжные потолки в СПб: выбор современных людей|Профессиональные консультации по выбору натяжных потолков в СПб|Комфорт и эстетика с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Профессиональный подход к выбору и установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту: натяжные потолки в СПб|Бонусы использования натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Технологические новинки для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Премиальный сервис по установке натяжных потолков в СПб|Современные тренды в создании потолков: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Идеальное сочетание цены и качества: натяжные потолки в СПб
потолок натяжной цена за м2 под ключ спб https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Остекление балконов по выгодной цене в Петербурге, подберем идеальное решение.
Профессиональное остекление балконов в Петербурге, под ключ и без переплат.
Индивидуальное остекление балконов в СПб, по индивидуальным проектам и с использованием прочных материалов.
Быстрое остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с оригинальными комплектующими и возможностью долгосрочного сотрудничества.
Экономичное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с учетом всех требований и технических норм.
остекление балконов санкт петербург https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Лучшее остекление балконов в СПб, подберем идеальное решение.
Профессиональное остекление балконов в Петербурге, с установкой и долговечной эксплуатацией.
Индивидуальное остекление балконов в СПб, с учетом всех пожеланий клиента.
Качественное остекление балконов в Петербурге, без скрытых платежей и срочно.
Экономичное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, со скидками и акциями.
остеклить балкон в спб https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Остекление балконов по выгодной цене в Петербурге, предложим оптимальный вариант.
Профессиональное остекление балконов в Петербурге, под ключ и без переплат.
Изысканное остекление балконов в Петербурге, под заказ и с уникальным дизайном.
Быстрое остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, без скрытых платежей и срочно.
Остекление балкона под ключ в СПб, по лучшей цене и быстрой установкой.
остекление лоджий в спб цены https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Идеальное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, подберем идеальное решение.
Профессиональное остекление балконов в Петербурге, под ключ и без переплат.
Изысканное остекление балконов в Петербурге, по индивидуальным проектам и с использованием прочных материалов.
Качественное остекление балконов в Петербурге, без скрытых платежей и срочно.
Остекление балкона под ключ в СПб, с учетом всех требований и технических норм.
сколько стоит балкон под ключ цена https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Лучшее остекление балконов в СПб, поможем выбрать подходящий вариант.
Элитное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, по доступным ценам и с гарантией качества.
Изысканное остекление балконов в Петербурге, по индивидуальным проектам и с использованием прочных материалов.
Быстрое остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, без скрытых платежей и срочно.
Удобное остекление балконов в Петербурге, с учетом всех требований и технических норм.
остекление лоджий в спб цена под ключ https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Лучшее остекление балконов в СПб, предложим оптимальный вариант.
Остекление балконов и лоджий в СПб, с установкой и долговечной эксплуатацией.
Эксклюзивное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, под заказ и с уникальным дизайном.
Надежное остекление балконов в СПб, с гарантией и сертификатом.
Удобное остекление балконов в Петербурге, с учетом всех требований и технических норм.
остеклить балкон спб недорого цена https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Идеальное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, подберем идеальное решение.
Остекление балконов и лоджий в СПб, под ключ и без переплат.
Изысканное остекление балконов в Петербурге, под заказ и с уникальным дизайном.
Быстрое остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с гарантией и сертификатом.
Удобное остекление балконов в Петербурге, со скидками и акциями.
остекление лоджий в спб https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Идеальное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, предложим оптимальный вариант.
Элитное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, под ключ и без переплат.
Индивидуальное остекление балконов в СПб, по индивидуальным проектам и с использованием прочных материалов.
Надежное остекление балконов в СПб, с гарантией и сертификатом.
Остекление балкона под ключ в СПб, по лучшей цене и быстрой установкой.
остекление лоджий недорого https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Идеальное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, предложим оптимальный вариант.
Профессиональное остекление балконов в Петербурге, по доступным ценам и с гарантией качества.
Эксклюзивное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, по индивидуальным проектам и с использованием прочных материалов.
Надежное остекление балконов в СПб, с оригинальными комплектующими и возможностью долгосрочного сотрудничества.
Экономичное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с учетом всех требований и технических норм.
балкон остекление цена с установкой https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Остекление балконов по выгодной цене в Петербурге, предложим оптимальный вариант.
Профессиональное остекление балконов в Петербурге, с установкой и долговечной эксплуатацией.
Изысканное остекление балконов в Петербурге, под заказ и с уникальным дизайном.
Быстрое остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, без скрытых платежей и срочно.
Экономичное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, со скидками и акциями.
остекление балконов и лоджий https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Лучшее остекление балконов в СПб, поможем выбрать подходящий вариант.
Профессиональное остекление балконов в Петербурге, с установкой и долговечной эксплуатацией.
Изысканное остекление балконов в Петербурге, по индивидуальным проектам и с использованием прочных материалов.
Быстрое остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с гарантией и сертификатом.
Удобное остекление балконов в Петербурге, с учетом всех требований и технических норм.
остекление балконов недорого https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Остекление балконов по выгодной цене в Петербурге, поможем выбрать подходящий вариант.
Элитное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с установкой и долговечной эксплуатацией.
Эксклюзивное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с учетом всех пожеланий клиента.
Быстрое остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с гарантией и сертификатом.
Удобное остекление балконов в Петербурге, по лучшей цене и быстрой установкой.
застеклить балкон в спб цены https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Остекление балконов по выгодной цене в Петербурге, предложим оптимальный вариант.
Элитное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, по доступным ценам и с гарантией качества.
Индивидуальное остекление балконов в СПб, с учетом всех пожеланий клиента.
Качественное остекление балконов в Петербурге, с гарантией и сертификатом.
Остекление балкона под ключ в СПб, с учетом всех требований и технических норм.
остеклить лоджию в спб недорого https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Идеальное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, подберем идеальное решение.
Профессиональное остекление балконов в Петербурге, с установкой и долговечной эксплуатацией.
Индивидуальное остекление балконов в СПб, под заказ и с уникальным дизайном.
Надежное остекление балконов в СПб, без скрытых платежей и срочно.
Экономичное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, по лучшей цене и быстрой установкой.
остекление балконов и лоджий в спб https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Остекление балконов по выгодной цене в Петербурге, поможем выбрать подходящий вариант.
Остекление балконов и лоджий в СПб, под ключ и без переплат.
Индивидуальное остекление балконов в СПб, по индивидуальным проектам и с использованием прочных материалов.
Быстрое остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, без скрытых платежей и срочно.
Удобное остекление балконов в Петербурге, по лучшей цене и быстрой установкой.
остекление лоджий недорого https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
Идеальное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, предложим оптимальный вариант.
Остекление балконов и лоджий в СПб, с установкой и долговечной эксплуатацией.
Эксклюзивное остекление для балконов в Санкт-Петербурге, с учетом всех пожеланий клиента.
Качественное остекление балконов в Петербурге, без скрытых платежей и срочно.
Удобное остекление балконов в Петербурге, по лучшей цене и быстрой установкой.
остекление балконов в санкт петербурге https://balkon-spb-1.ru/ .
рубли в тенге конвертер валют .
На платформе собраны самые свежие курсы валют Казахстана и мира. Бесплатная конвертация тенге, рублей, юаней и других валют доступна круглосуточно.
1 доллар в тенге конвертер .
Простой и быстрый способ узнать актуальные курсы валют. Конвертируйте тенге, юани, рубли и доллары США моментально и бесплатно благодаря нашему онлайн-калькулятору.
1 доллар в тенге конвертер .
Сайт с удобным дизайном предлагает мгновенную конвертацию валют без комиссии. Узнайте точный курс для тенге, рублей, долларов США и других валют прямо сейчас.
Download online Taya365 app and discover a new level of mobile gaming. Slots, live casino, exclusive bonuses – all this is available on your smartphone. Enjoy the game anytime, anywhere!
юань в тенге евро в тенге .
Платформа объединяет точные курсы валют и мгновенный калькулятор для конвертации тенге, рублей и других валют. Удобный дизайн сайта позволяет экономить ваше время и силы.
1 доллар в тенге конвертер .
Сайт предлагает быстрый и удобный способ конвертации валют в режиме реального времени. Актуальные курсы для тенге, рублей, юаней, долларов США и других валют всегда под рукой. Простота дизайна позволяет мгновенно получить результат.
евро в тенге доллар в тенге .
Сервис обновляет курсы валют в режиме реального времени, позволяя пользователям конвертировать тенге в рубли, доллары США и другие валюты мгновенно и без комиссии.
1 юань в тенге рубли в тенге .
Нужно быстро узнать курс валют? На платформе представлены тенге, рубли, юани и доллары с актуальными котировками. Мгновенная конвертация доступна в один клик.
1 юань в тенге калькулятор валют .
Сайт с удобным дизайном предлагает мгновенную конвертацию валют без комиссии. Узнайте точный курс для тенге, рублей, долларов США и других валют прямо сейчас.
1 юань в тенге калькулятор валют .
Сайт предлагает удобный инструмент для бесплатной конвертации валют. Актуальные курсы для тенге, долларов США, рублей и юаней позволяют мгновенно получить нужный результат.
евро в тенге 1 доллар в тенге .
Сайт предлагает актуальные курсы валют с обновлением в реальном времени. Бесплатная конвертация поддерживает тенге, доллары, рубли и другие популярные валюты.
1 доллар в тенге конвертер .
Платформа объединяет точные курсы валют и мгновенный калькулятор для конвертации тенге, рублей и других валют. Удобный дизайн сайта позволяет экономить ваше время и силы.
конвертер юань в тенге калькулятор .
Наш сайт предоставляет полную информацию о текущих курсах валют и моментальную конвертацию. Будь то тенге, рубли или доллары США – все данные обновляются в режиме реального времени.
1 доллар в тенге 1 юань в тенге .
Наш сайт предоставляет полную информацию о текущих курсах валют и моментальную конвертацию. Будь то тенге, рубли или доллары США – все данные обновляются в режиме реального времени.
евро в тенге доллар в тенге .
На платформе собраны самые свежие курсы валют Казахстана и мира. Бесплатная конвертация тенге, рублей, юаней и других валют доступна круглосуточно.
1 доллар в тенге конвертер .
Сайт предлагает удобный обменный калькулятор для конвертации тенге в рубли, юани или доллары США. Обновляемые курсы и мгновенные результаты делают процесс максимально простым.
1 юань в тенге рубли в тенге .
Простой и быстрый способ узнать актуальные курсы валют. Конвертируйте тенге, юани, рубли и доллары США моментально и бесплатно благодаря нашему онлайн-калькулятору.
Лучшие натяжные потолки в СПб|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Опытные мастера по натяжным потолкам в Санкт-Петербурге|Огромный ассортимент натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Как выбрать идеальный натяжной потолок в СПб|Тепло и гармония с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Современный дизайн с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Красота и практичность с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Только проверенные потолки в Петербурге у нас|Технологичные решения для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Эффективное монтаж натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Идеальный выбор: натяжные потолки в СПб|Модные тренды в мире натяжных потолков: СПб|Специальные предложения на натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: выбор современных людей|Профессиональные консультации по выбору натяжных потолков в СПб|Красота и функциональность: натяжные потолки в СПб|Натяжные потолки в СПб: надежность и качество|Уникальный дизайн вашего потолка: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Преимущества натяжных потолков в СПб|Натяжные потолки в СПб: современные технологии и материалы|Высококлассное обслуживание по установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Современные тренды в создании потолков: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Компр
сколько стоит натяжной потолок https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Лучшие натяжные потолки в СПб|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Профессиональная установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Огромный ассортимент натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Как выбрать идеальный натяжной потолок в СПб|Натяжные потолки в Петербурге для вашего уюта|Эстетика и стиль с натяжными потолками в СПб|Идеальные потолки в Петербурге только у нас|Натяжные потолки в СПб: гарантированное качество и надежность|Инновационные технологии для натяжных потолков в СПб|Быстрое и качественное установление натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Совершенство с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Столица натяжных потолков: Петербург|Лучшие цены на натяжные потолки в СПб|Хит сезона – натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Экспертный подход к натяжным потолкам в Петербурге|Комфорт и эстетика с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Точное соответствие вашим потребностям: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту: натяжные потолки в СПб|Плюсы натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Инновационные материалы для натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Высококлассное обслуживание по установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Тенденции в дизайне потолков: натяжные потолки в СПб|Идеальное сочетание цены и качества: натяжные потолки в СПб
стоимость монтажа натяжного потолка https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Выбор номер один – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Выгодное предложение на натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Профессиональная установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Широкий выбор натяжных потолков в СПб|Подбор натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге: лучшие рекомендации|Натяжные потолки в Петербурге для вашего уюта|Эстетика и стиль с натяжными потолками в СПб|Идеальные потолки в Петербурге только у нас|Только проверенные потолки в Петербурге у нас|Последние тренды для натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Легко и быстро: установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Совершенство с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Модные тренды в мире натяжных потолков: СПб|Лучшие цены на натяжные потолки в СПб|Хит сезона – натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Экспертный подход к натяжным потолкам в Петербурге|Комфорт и эстетика с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Точное соответствие вашим потребностям: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Персональные решения для вас: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Плюсы натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: современные технологии и материалы|Высококлассное обслуживание по установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Новинки в оформлении потолков: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Компр
натяжные потолки спб установка под ключ https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Лучшие натяжные потолки в СПб|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Профессиональная установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Разнообразие натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Как выбрать идеальный натяжной потолок в СПб|Натяжные потолки в Петербурге для вашего уюта|Интерьерные решения с натяжными потолками в Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: лучший выбор для вашего дома|Натяжные потолки в СПб: гарантированное качество и надежность|Технологичные решения для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Эффективное монтаж натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Идеальный выбор: натяжные потолки в СПб|Модные тренды в мире натяжных потолков: СПб|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Хит сезона – натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Уникальные решения в области натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Красота и функциональность: натяжные потолки в СПб|Натяжные потолки в СПб: надежность и качество|Уникальный дизайн вашего потолка: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Преимущества натяжных потолков в СПб|Технологические новинки для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Высококлассное обслуживание по установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Современные тренды в создании потолков: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Оптимальный выбор: натяжные потолки в Петербурге
натяжной потолок сколько https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Качественные натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Выгодное предложение на натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Лучшие специалисты по натяжным потолкам в Петербурге|Огромный ассортимент натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Советы по выбору натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Тепло и гармония с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Интерьерные решения с натяжными потолками в Петербурге|Красота и практичность с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: гарантированное качество и надежность|Технологичные решения для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Быстрое и качественное установление натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Оптимальное решение – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Модные тренды в мире натяжных потолков: СПб|Лучшие цены на натяжные потолки в СПб|Дизайнерские потолки в Петербурге: натяжные|Уникальные решения в области натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Комфорт и эстетика с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: надежность и качество|Уникальный дизайн вашего потолка: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Плюсы натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: современные технологии и материалы|Премиальный сервис по установке натяжных потолков в СПб|Современные тренды в создании потолков: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Оптимальный выбор: натяжные потолки в Петербурге
натяжные потолки цена https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Идеальное решение для скрытой связи — купить микронаушники. Широкий выбор моделей, гарантия качества и выгодные условия покупки. Надёжная связь, компактный размер и удобство использования.
Выбор номер один – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Скидки на натяжные потолки в СПб|Профессиональная установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Огромный ассортимент натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Как выбрать идеальный натяжной потолок в СПб|Тепло и гармония с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Современный дизайн с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: лучший выбор для вашего дома|Долговечные и стойкие натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Последние тренды для натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Эффективное монтаж натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Совершенство с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Столица натяжных потолков: Петербург|Лучшие цены на натяжные потолки в СПб|Хит сезона – натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Экспертный подход к натяжным потолкам в Петербурге|Красота и функциональность: натяжные потолки в СПб|Натяжные потолки в СПб: надежность и качество|Уникальный дизайн вашего потолка: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Плюсы натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: современные технологии и материалы|Высококлассное обслуживание по установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Новинки в оформлении потолков: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Идеальное сочетание цены и качества: натяжные потолки в СПб
монтаж натяжных потолков https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Качественные натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Опытные мастера по натяжным потолкам в Санкт-Петербурге|Широкий выбор натяжных потолков в СПб|Советы по выбору натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Тепло и гармония с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Эстетика и стиль с натяжными потолками в СПб|Натяжные потолки в СПб: лучший выбор для вашего дома|Только проверенные потолки в Петербурге у нас|Технологичные решения для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Легко и быстро: установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Идеальный выбор: натяжные потолки в СПб|Столица натяжных потолков: Петербург|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: выбор современных людей|Профессиональные консультации по выбору натяжных потолков в СПб|Комфорт и эстетика с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Профессиональный подход к выбору и установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту: натяжные потолки в СПб|Преимущества натяжных потолков в СПб|Натяжные потолки в СПб: современные технологии и материалы|Высококлассное обслуживание по установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Тенденции в дизайне потолков: натяжные потолки в СПб|Идеальное сочетание цены и качества: натяжные потолки в СПб
поставка натяжные потолки https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Лучшие натяжные потолки в СПб|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Профессиональная установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Разнообразие натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Подбор натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге: лучшие рекомендации|Уют и комфорт с натяжными потолками в СПб|Интерьерные решения с натяжными потолками в Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: лучший выбор для вашего дома|Только проверенные потолки в Петербурге у нас|Последние тренды для натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Легко и быстро: установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Оптимальное решение – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Модные тренды в мире натяжных потолков: СПб|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: выбор современных людей|Экспертный подход к натяжным потолкам в Петербурге|Стильные потолки в Петербурге: натяжные|Профессиональный подход к выбору и установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Уникальный дизайн вашего потолка: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Бонусы использования натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: современные технологии и материалы|Эксклюзивные услуги по монтажу натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Тенденции в дизайне потолков: натяжные потолки в СПб|Компр
натяжные потолки петербург https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Выбор номер один – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Выгодное предложение на натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Профессиональная установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Широкий выбор натяжных потолков в СПб|Советы по выбору натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Уют и комфорт с натяжными потолками в СПб|Эстетика и стиль с натяжными потолками в СПб|Натяжные потолки в СПб: лучший выбор для вашего дома|Натяжные потолки в СПб: гарантированное качество и надежность|Последние тренды для натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Легко и быстро: установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Оптимальное решение – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Инновации и креативность в сфере натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Специальные предложения на натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Дизайнерские потолки в Петербурге: натяжные|Уникальные решения в области натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Комфорт и эстетика с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: надежность и качество|Уникальный дизайн вашего потолка: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Плюсы натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Технологические новинки для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Высококлассное обслуживание по установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Новинки в оформлении потолков: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Идеальное сочетание цены и качества: натяжные потолки в СПб
натяжные потолки классика https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Лучшие натяжные потолки в СПб|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Опытные мастера по натяжным потолкам в Санкт-Петербурге|Широкий выбор натяжных потолков в СПб|Как выбрать идеальный натяжной потолок в СПб|Натяжные потолки в Петербурге для вашего уюта|Эстетика и стиль с натяжными потолками в СПб|Идеальные потолки в Петербурге только у нас|Долговечные и стойкие натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Инновационные технологии для натяжных потолков в СПб|Быстрое и качественное установление натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Совершенство с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Модные тренды в мире натяжных потолков: СПб|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: выбор современных людей|Профессиональные консультации по выбору натяжных потолков в СПб|Красота и функциональность: натяжные потолки в СПб|Натяжные потолки в СПб: надежность и качество|Персональные решения для вас: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Преимущества натяжных потолков в СПб|Натяжные потолки в СПб: современные технологии и материалы|Премиальный сервис по установке натяжных потолков в СПб|Тенденции в дизайне потолков: натяжные потолки в СПб|Оптимальный выбор: натяжные потолки в Петербурге
натяжные потолки в спб недорого под ключ цены https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Выбор номер один – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Лучшие специалисты по натяжным потолкам в Петербурге|Широкий выбор натяжных потолков в СПб|Как выбрать идеальный натяжной потолок в СПб|Уют и комфорт с натяжными потолками в СПб|Интерьерные решения с натяжными потолками в Петербурге|Идеальные потолки в Петербурге только у нас|Натяжные потолки в СПб: гарантированное качество и надежность|Технологичные решения для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Эффективное монтаж натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Оптимальное решение – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Столица натяжных потолков: Петербург|Специальные предложения на натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Хит сезона – натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Уникальные решения в области натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Красота и функциональность: натяжные потолки в СПб|Натяжные потолки в СПб: надежность и качество|Уникальный дизайн вашего потолка: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Бонусы использования натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Технологические новинки для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Премиальный сервис по установке натяжных потолков в СПб|Тенденции в дизайне потолков: натяжные потолки в СПб|Оптимальный выбор: натяжные потолки в Петербурге
потолок натяжной цена за м2 под ключ спб https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Качественные натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Лучшие специалисты по натяжным потолкам в Петербурге|Разнообразие натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Подбор натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге: лучшие рекомендации|Натяжные потолки в Петербурге для вашего уюта|Эстетика и стиль с натяжными потолками в СПб|Идеальные потолки в Петербурге только у нас|Натяжные потолки в СПб: гарантированное качество и надежность|Инновационные технологии для натяжных потолков в СПб|Эффективное монтаж натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Оптимальное решение – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Модные тренды в мире натяжных потолков: СПб|Лучшие цены на натяжные потолки в СПб|Дизайнерские потолки в Петербурге: натяжные|Уникальные решения в области натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Комфорт и эстетика с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: надежность и качество|Персональные решения для вас: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Бонусы использования натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: современные технологии и материалы|Эксклюзивные услуги по монтажу натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Современные тренды в создании потолков: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Компр
обычный натяжной потолок https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Выбор номер один – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Скидки на натяжные потолки в СПб|Опытные мастера по натяжным потолкам в Санкт-Петербурге|Разнообразие натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Как выбрать идеальный натяжной потолок в СПб|Уют и комфорт с натяжными потолками в СПб|Эстетика и стиль с натяжными потолками в СПб|Красота и практичность с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: гарантированное качество и надежность|Последние тренды для натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Быстрое и качественное установление натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Идеальный выбор: натяжные потолки в СПб|Модные тренды в мире натяжных потолков: СПб|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Хит сезона – натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Экспертный подход к натяжным потолкам в Петербурге|Стильные потолки в Петербурге: натяжные|Профессиональный подход к выбору и установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Уникальный дизайн вашего потолка: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Плюсы натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: современные технологии и материалы|Высококлассное обслуживание по установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Современные тренды в создании потолков: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Оптимальный выбор: натяжные потолки в Петербурге
монтаж натяжных потолков https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Качественные натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Лучшие специалисты по натяжным потолкам в Петербурге|Разнообразие натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Подбор натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге: лучшие рекомендации|Тепло и гармония с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Эстетика и стиль с натяжными потолками в СПб|Красота и практичность с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Долговечные и стойкие натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Технологичные решения для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Легко и быстро: установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Оптимальное решение – натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Модные тренды в мире натяжных потолков: СПб|Лучшие цены на натяжные потолки в СПб|Хит сезона – натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Профессиональные консультации по выбору натяжных потолков в СПб|Стильные потолки в Петербурге: натяжные|Точное соответствие вашим потребностям: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Персональные решения для вас: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Преимущества натяжных потолков в СПб|Инновационные материалы для натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Высококлассное обслуживание по установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Тенденции в дизайне потолков: натяжные потолки в СПб|Компр
натяжные потолки спб https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Лучшие натяжные потолки в СПб|Скидки на натяжные потолки в СПб|Лучшие специалисты по натяжным потолкам в Петербурге|Разнообразие натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Как выбрать идеальный натяжной потолок в СПб|Натяжные потолки в Петербурге для вашего уюта|Интерьерные решения с натяжными потолками в Петербурге|Красота и практичность с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: гарантированное качество и надежность|Последние тренды для натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Легко и быстро: установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Идеальный выбор: натяжные потолки в СПб|Столица натяжных потолков: Петербург|Специальные предложения на натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Хит сезона – натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Профессиональные консультации по выбору натяжных потолков в СПб|Комфорт и эстетика с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: надежность и качество|Персональные решения для вас: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Бонусы использования натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Технологические новинки для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Эксклюзивные услуги по монтажу натяжных потолков в Петербурге|Новинки в оформлении потолков: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Оптимальный выбор: натяжные потолки в Петербурге
натяжные потолки под ключ спб https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
Качественные натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Выгодное предложение на натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Лучшие специалисты по натяжным потолкам в Петербурге|Широкий выбор натяжных потолков в СПб|Подбор натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге: лучшие рекомендации|Натяжные потолки в Петербурге для вашего уюта|Современный дизайн с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Идеальные потолки в Петербурге только у нас|Натяжные потолки в СПб: гарантированное качество и надежность|Инновационные технологии для натяжных потолков в СПб|Легко и быстро: установка натяжных потолков в СПб|Совершенство с натяжными потолками в Санкт-Петербурге|Столица натяжных потолков: Петербург|Экономьте на натяжных потолках в Санкт-Петербурге|Натяжные потолки в СПб: выбор современных людей|Уникальные решения в области натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Стильные потолки в Петербурге: натяжные|Точное соответствие вашим потребностям: натяжные потолки в Петербурге|Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту: натяжные потолки в СПб|Преимущества натяжных потолков в СПб|Технологические новинки для натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Высококлассное обслуживание по установке натяжных потолков в Санкт-Петербурге|Современные тренды в создании потолков: натяжные потолки в Санкт-Петербурге|Компр
натяжные потолки лучшие спб https://potolki-spb-1.ru/ .
купить гелиевые шары на день рождения shariki-shop47.ru
Steam Desktop Authenticator https://authenticatorsteam.com is a convenient application for managing two-factor authentication in Steam. Allows you to quickly confirm trades, logins and purchases, providing additional protection for your account.
camping Zabljak Montenegro Zabljak Montenegro
nekretnine Bianca Resort and Spa
Наша мастерская предлагает надежный мастерская по ремонту стиральной машины на дому всех типов и брендов. Мы понимаем, насколько необходимы вам ваши устройства для стирки, и готовы предложить сервис наилучшего качества. Наши профессиональные техники оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только сертифицированные компоненты, что гарантирует длительную работу выполненных работ.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи автоматических стиральных машин, включают неисправности барабана, неработающий нагревательный элемент, программные сбои, неисправности насоса и повреждения корпуса. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт барабанов, нагревательных элементов, ПО, насосов и механических компонентов. Доверив ремонт нам, вы получаете качественный и надежный экспресс ремонт стиральных машин.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-stiralnyh-mashin-ace.ru
Appreciate your visit! Discover more at https://metakit.org/
купить в иваново диплом
Официальный сайт https://1winpromobk.ru, где вы найдете актуальные промокоды и бонусы для 1Win. Получите эксклюзивные предложения, такие как 500% на первый депозит и бесплатные спины.
Какое программное обеспечение для видеонаблюдения https://www.cctvforum.ru является лучшим? Какой сервис видеонаблюдения как услуги (VSaaS) наиболее простой и удобный в использовании?
Как выбрать коляску 3 в 1: советы и рекомендации, которые обязательно пригодятся.
Идеальные коляски 3 в 1 для современных родителей, с комфортом и безопасностью для малыша.
Гид по выбору коляски 3 в 1, которые помогут вам сделать правильный выбор.
Как не ошибиться с выбором коляски 3 в 1, для безопасной и комфортной поездки.
Плюсы и минусы популярных моделей колясок 3 в 1, чтобы сделать обдуманный выбор.
коляска для новорожденных https://kolyaska-3-v-1-msk.ru/ .
Steam Desktop Authenticator steamauthenticator.ru is a convenient application for managing Steam two-factor authentication directly on your PC. It allows you to confirm logins, trades, and purchases without the need for a mobile device.
Steam Desktop Authenticator steamdesktopauthenticator.me is a PC application that makes it easier to use two-factor authentication on Steam. By replacing the mobile authenticator, it allows you to confirm trades, purchases, and account logins, providing a high level of security and ease of use.
Steam Desktop Authenticator steamdesktopauthenticator.io is a simple and reliable way to protect your Steam account. The program allows you to confirm transactions, receive security codes, and manage two-factor authentication settings without relying on your smartphone.
купить школьный аттестат за 11 классов
Наши специалисты предлагает надежный сервисный центр по ремонту стиральной машины любых брендов и моделей. Мы знаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши стиральные машины, и обеспечиваем ремонт первоклассного уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты оперативно и тщательно выполняют работу, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что предоставляет долговечность и надежность наших услуг.
Наиболее распространенные поломки, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи автоматических стиральных машин, включают проблемы с барабаном, неработающий нагревательный элемент, неисправности программного обеспечения, неисправности насоса и поломки компонентов. Для устранения этих неисправностей наши профессиональные техники оказывают ремонт барабанов, нагревательных элементов, ПО, насосов и механических компонентов. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы гарантируете себе долговечный и надежный мастерская по ремонту стиральной машины на дому.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-stiralnyh-mashin-ace.ru
Откройте для себя лучшие гостиницы Москвы Вас ждут стильные номера, изысканная кухня, современные удобства и внимание к деталям. Отели расположены в ключевых районах города, что делает их идеальными для деловых поездок, романтических выходных или туристических открытий.
Steam Desktop Authenticator authenticatorsteam.com is an alternative to the Steam Mobile Authenticator. It provides codes for two-factor authentication directly on your PC.
Steam Desktop Authenticator steamauthenticatordesktop.com is a handy app to enhance the security of your Steam account. It generates codes for two-factor authentication, allowing you to easily confirm transactions and logins.
Эксклюзивные букеты роз уже ждут вас, сделайте приятный сюрприз.
Индивидуальные букеты роз по вашему желанию, доставка в удобное время и место.
Соберите свой идеальный букет роз, оперативная доставка в любую точку.
Освежите обстановку с помощью букетов роз, уникальные композиции для особых моментов.
Изысканные композиции из роз, сделайте ваш день ярким и запоминающимся.
Насладитесь красотой и свежестью цветов, профессиональные флористы соберут для вас лучший букет.
Элегантные композиции из роз, доставка в удобное для вас время.
Компактные или роскошные букеты роз, удобные способы оплаты.
Букеты роз под ключ с доставкой, приятные сюрпризы и акции.
Роскошные букеты роз для особых моментов, насладитесь ароматом настоящей красоты.
Соберите свой уникальный букет, в удобное для вас время.
Прекрасные букеты роз для ваших близких, насладитесь ароматом настоящей любви.
цветы розы букет цветы розы букет .
Как быстро и легально купить аттестат 11 класса в Москве
Официальная страница диана шурыгина видео. Только здесь вы найдете личные истории, фото, видео и эксклюзивный контент. Узнавайте первыми о новых проектах и наслаждайтесь моментами её жизни. Подписывайтесь, чтобы быть всегда на связи!
курс по риторике ораторское искусство курсы москва
где купить воздушные шары https://shariki-shop47.ru
Steam Desktop Authenticator https://steamauthenticator.ru is a two-factor authentication application for PC. Generates codes to confirm transactions and log in to Steam, improving the security of your account. Convenient, quick to install and easy to use solution for data protection.
Онлайн слив курсов https://sliv-kursov213.ru простой способ получить знания из популярных онлайн-курсов. Развивайтесь в своем темпе, выбирайте интересующие темы и экономьте на образовании. Здесь вы найдете материалы для саморазвития, карьерного роста и хобби.
Steam Desktop Authenticator https://steamdesktopauthenticator.io is a two-factor authentication application for PC. Generates codes to confirm transactions and log in to Steam, improving the security of your account. Convenient, quick to install and easy to use solution for data protection.
Great content as always, I really appreciate your effort! Check out https://metaium.org/ for more.
Android ?шін 888starz apk о?ай ж?ктеледі ж?не ?ауіпсіз.
デジハネ CR 蒼天の拳 STV
gantz甘
友人と一緒に行くことで、競争心が芽生え、さらに楽しめます。勝負の結果が気になります。
デビル メイ クライ 4
https://www.fafner-pachinko.com/article/757.html
大当たりを引いたときの高揚感は何とも言えません。日常のストレスを忘れさせてくれます。
戦国パチスロ花の慶次これより我ら修羅に入る
北斗打ち方
ケロロ軍曹
鯉の滝登り
獣王 王者の覚醒
ラブ嬢
https://xn--k8-9g4a3b4f.site/tags/usj-%E3%83%91%E3%83%81%E3%83%B3%E3%82%B3
シンプルなデザインとルールが魅力。初心者でも安心して楽しめます。
e ルパン三世 銭形からの招待状
https://www.xn--k8-yh4a6b5d8j.club/Articles/2942.html
音楽とサウンドエフェクトが迫力満点で、プレイ中に盛り上がります。
ヒデキに夢中!!
https://www.sjb.jp/topics/%E3%82%B9%E3%83%9E%E3%83%91%E3%83%81%E3%82%B2%E3%82%B2%E3%82%B2%E3%81%AE%E9%AC%BC%E5%A4%AA%E9%83%8E-%E7%8D%85%E5%AD%90%E5%A5%AE%E8%BF%85sp
明るいデザインと楽しげな演出が魅力。遊んでいるだけで元気が出ます。
Как оказалось, купить диплом кандидата наук не так уж и сложно
Теперь вижу ситуацию иначе.
butirkaconcert.ru
смотреть фильмы онлайн в США новинки кино онлайн в Украине
смотреть фильмы бесплатно на телефоне фильмы онлайн HD мелодрамы
лучшие фильмы онлайн в 4К новинки кино онлайн с переводом
Онлайн платформа Мостбет доступна з будь-якого пристрою | Мостбет гарантує чесність усіх ігор та прозорість виплат mostbet original. | Мостбет ua – це місце, де ваш азарт оживає | Мостбет казино дарує новим гравцям щедрі бонуси Mostbet login.
новинки кино онлайн в России фильмы 2004 смотреть онлайн
Предлагаем услуги профессиональных инженеров офицальной мастерской.
Еслли вы искали ремонт ноутбуков lenovo цены, можете посмотреть на сайте: ремонт ноутбуков lenovo в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Download music https://progworld.net in high quality without sound loss. Convenient search, wide choice of genres and artists, fast downloads.
прокатиться на яхте дубай арендовать яхту в дубае
купить диплом москва
яхта дубай взять яхту в аренду
Download music https://progworld.net for free and without registration. Huge database of tracks of all genres in high quality. Convenient search and fast download.
Смотрите аниме онлайн https://reanime.net на русском! Огромная коллекция сериалов и фильмов в хорошем качестве. Все популярные аниме с русской озвучкой и субтитрами. Удобно, бесплатно, в отличном качестве.
Доставка грузов из Китая https://cargotlk.ru под ключ. Организуем перевозки любых объемов: от документов до крупногабаритных грузов. Авиа, морская и автодоставка. Полное сопровождение, таможенное оформление, страхование.
This page truly has all of the information I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
#@G@G@G@G#
https://webhostingtalk.pl/public/pages/?code_bonus_dinscription_1xbet.html
яхта на 25 человек аренда яхты оаэ
Loved this perspective! Check out https://metaink.org for more.
1win баланс 2000 как пополнить 1win в кыргызстане
DocReviews https://docreviews.com.ua это платформа, где пациенты могут оставлять отзывы о врачах. Мы стремимся помочь людям найти лучшего врача для своих нужд, предоставляя им доступную и достоверную информацию.
Интернет-магазин инструментов https://profimaster58.ru для работы по металлу — ваш эксперт в качественном оборудовании! В ассортименте: измерительный инструмент, резцы, сверла, фрезы, пилы и многое другое. Гарантия точности, надежности и выгодных цен.
Смотрите аниме онлайн https://studiobanda.net бесплатно и без рекламы. Удобный каталог с популярными тайтлами, новинками и свежими сериями. Высокое качество видео и быстрый плеер обеспечат комфортный просмотр. Подборки по жанрам, рекомендации и регулярные обновления сделают ваш опыт максимально приятным.
тренировки фигурного катания для начинающих фестивали по фигурному катанию
Официальная страница Дианы Шурыгиной https://www.pornhub.org/model/dianashurygina свежие новости, уникальные фото и видео, личные откровения и новые проекты. Погружайтесь в мир Дианы, узнавайте её историю и вдохновение. Будьте в центре её жизни и не пропустите ни одного яркого момента!
нова шурыгина шурыгина пусть
Мостбет казино – це місце, де кожен знайде щось для себе | Завантажте додаток Мостбет і отримайте доступ до всіх можливостей казино most bet casino. | Реєстрація на сайті Мостбет – це ваш перший крок до великих виграшів | Мостбет казино дарує новим гравцям щедрі бонуси Мостбет бонуси.
Спасибо за такую точку зрения.
Ивенты на площадках дадут возможность вам радостные чувства. Шоу-программы обеспечивают вдохновиться. Выступления групп каждый раз дарят эмоции. Готовьте программу для ожидаемых ивентов в компании!
https://agutin-afisha.ru/
Предприниматель и инвестор Святослав Гусев https://dzen.ru/gusevlive специализирующийся на IT, блокчейн-технологиях и венчурном инвестировании. Активно делится аналитикой рынка, инсайдами и новостями, которые помогут заработать каждому!
https://onlinetri.com/common/pgs/888starz-site-officiel_1.html 888starz
Excellent content! For those interested, https://metaback.org/ has similar topics.
Как получить диплом техникума с упрощенным обучением в Москве официально
фильмы 2024 смотреть онлайн комедии фильмы 2024 смотреть онлайн комедии
лучшие фильмы 2009 смотреть онлайн лучшие фильмы 2016 смотреть онлайн
новинки фильмы 2024 смотреть онлайн лучшие фильмы 2009 смотреть онлайн
кращі фільми онлайн з субтитрами фільми 2012 дивитися онлайн
диплом о среднем профессиональном купить
Yuqori tezlik va qulaylikni taqdim etuvchi 888starz apk ni yuklab oling va kazino o‘yinlarida qatnashing yoki sportga stavkalar qiling. Ushbu ilova foydalanuvchilarga xavfsizlikni kafolatlaydi va barcha kerakli vositalar bilan ta’minlaydi. Yuklab olish jarayoni oson va tezkor.
At Cheap SEO Solutions https://cheap-seo-solutions.com we don’t believe in half-measures. We deliver comprehensive SEO solutions that cover all the bases, from keyword research and on-page optimization to link building and content creation. Our goal is to help businesses improve their search engine rankings, drive organic traffic, and increase conversions.
Ставки на спорт с Vavada https://selfiedumps.com это простота, надежность и высокие шансы на победу. Удобная платформа, разнообразие событий и быстрые выплаты делают Vavada идеальным выбором для любителей азарта. Зарегистрируйтесь сейчас и начните выигрывать вместе с нами!
Discover the power of AI with deepnude online Fast image processing and accessible functionality allow you to create unique effects. Enjoy safe and anonymous use of the platform for entertainment.
Thank you for the good writeup It in fact was a amusement account it Look advanced to far added agreeable from you However how could we communicate
best comic reading site in Australia online comic reader in HD
latest manga updates on mobile free manga reader adventure
Trash. https://metamask.io/download/
como depositar no 1win casa de aposta 1win
villa zelenika Buy property in Montenegro
mostbet casino review mostbet app
mostbet актуальное зеркало рабочее на сейчас mostbet проверка купона
Онлайн казино Мостбет пропонує величезний вибір ігор для кожного гравця | Мостбет сайт пропонує унікальні акції для своїх клієнтів mostbet casino. | Грайте на Мостбет і відкрийте для себе світ справжніх азартних розваг | Мостбет офіційний сайт – це ваш ключ до успішних ставок https://mostbetcasinouahfgy.com.
Montenegro buljarica Montenegro immobilien
новинки кино онлайн в HD смотреть фильмы онлайн в HD
apartmentkomplex Montenegro immobilien von privat kaufen
смотреть фильмы бесплатно комедии фильмы 2018 смотреть онлайн
Смотрите любимые дорамы https://dorama2025.ru онлайн в HD-качестве! Огромный выбор корейских, китайских, японских и тайваньских сериалов с профессиональной озвучкой и субтитрами.
CRA牙狼金色になれザルバとの契約
新台 おすすめ
パチンコは単なるギャンブルではなく、エンターテイメントとして楽しむべきです。友人との交流にも最適です。
八代將軍戰神版
https://www.pachilog.jp/article/85.html
戦略的な要素もあり、運だけでなく技術が試されるのが面白いです。
CR牙狼魔戒之花 Ver.399
北斗の拳新台パチンコ
CR海物語4
ビーストサップ
CR北斗の拳6 拳王
リング呪いの7日間;
https://xn--k8-9g4a3b4f.site/tags/%E3%83%91%E3%83%81%E3%83%B3%E3%82%B3-%E8%84%B3-%E6%B1%81
大当たり時の演出が豪華で、観ているだけでも楽しめます。期待感が高まります。
鯉の滝登り
https://xn--k8-9g4a3b4f.site/tags/%E9%AB%98%E5%B0%BE-%E3%83%91%E3%83%81%E3%83%B3%E3%82%B3-%E4%BA%8B%E4%BB%B6
大当たりの瞬間は、心臓がドキドキします。興奮が何とも言えません。
南国物語
https://xn--k8-9g4a3b4f.site/tags/%E4%B8%AD%E5%9B%BD-%E3%83%91%E3%83%81%E3%83%B3%E3%82%B3
大当たりの瞬間は、心臓がドキドキします。興奮が何とも言えません。
Подходящие продукты для диеты Специальные предложения магазинов
лучший сайт для чтения манхвы сёдзё новая манхва читать онлайн в Корее
1win kz 1win официальный сайт скачать
Кого интересует МРТ для людей с большим весом киев рекомендую клинику
где купить анаболические стероиды курсы стероидов тестостерон
Advanced services Montenegro company formation
телесуфлер для телефона купить телесуфлер онлайн
Останні новини Черкас https://18000.ck.ua та Черкаської області. Важливі новини про політику, бізнес, спорт, корупцію у владі на сайті 18000 ck.ua.
лучшие манхвы читать 2019 новинки манхва на русском языке
Poh. https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/metamask/nkbihfbeogaeaoehlefnkodbefgpgknn
Montenegro grosse immobilien in Montenegro
Официальная покупка диплома вуза с сокращенной программой обучения в Москве
grosses baugrundstuck kaufen immobilie Montenegro
CR新世紀エヴァンゲリオン~使徒、再び~SFW
とある スマスロ 1000枚
パチンコの演出に使われる音楽が印象的で、記憶に残ります。つい口ずさんでしまいます。
沖ドキ! 30LL
https://xn--k8-9g4a3b4f.site/shinbun/post-1488.html
パチンコをすることで、運を試すドキドキ感が味わえます。挑戦する楽しさがあります。
Pフィーバー革命機ヴァルヴレイヴ 3
コードギアス3 ボーナス終了画面
Pワンパンマン
CR真・花の慶次 Ver.399
押忍!サラリーマン番長
麻雀物語2 激闘!麻雀グランプリ
https://www.withmagazine.net/Articles/1296.html
ボーナスゲームが楽しく、毎回期待感があります。特に大当たり時は圧巻。
鬼武者3
https://www.casinoonline.help/article/257.html
歴史をテーマにしたパチスロで、独特の魅力があります。日本の伝統を感じます。
モンスターハンター月下雷鳴
https://xn--k8-9g4a3b4f.site/tags/%E3%82%B9%E3%83%AD%E3%83%83%E3%83%88-%E3%83%90%E3%82%B8%E3%83%AA%E3%82%B9%E3%82%AF-%E7%B5%86-2
リーチ演出が多彩で、どの瞬間も楽しめます。特に聖闘士の技が迫力満点。
манхва на русском языке скачать в PDF топ манхва 2006
verkauf von hotels Montenegro immobilien von privat kaufen
облачное видеонаблюдение программа для просмотра видео с камер
Ищете качественные стероиды для роста мышц? У нас вы найдете широкий выбор сертифицированной продукции для набора массы, сушки и улучшения спортивных результатов. Только проверенные бренды, доступные цены и быстрая доставка. Ваше здоровье и успех в спорте – наш приоритет! Заказывайте прямо сейчас!”
бесплатно читать манхву онлайн детектив топ манхва 2014
Быстрая схема покупки диплома старого образца: что важно знать?
кращі фільми 2010 онлайн дивитися фільм безкоштовно жахи
дивитися фільм безкоштовно в Україні фільми 2024 дивитися онлайн з субтитрами
дивитися фільми онлайн безкоштовно жахи фільми 2024 дивитися онлайн на ПК
Your perspective is refreshing. You might find more great content at https://metasnap.org/.
hemp delivery in prague 420 movement in prague
диана шурыгина инстаграм https://shuriginadiana.ru
смотреть фильмы онлайн в России фильмы 2024 смотреть онлайн на планшете
лучшие фильмы 2025 смотреть онлайн фильмы онлайн HD драмы
Строительный портал https://bastet.com.ua ваш путеводитель в мире стройки! Подборка лучших материалов, контакты мастеров, проекты и лайфхаки. Создавайте уют и красоту с нашим сервисом!
Нужны деньги срочно небус займ – ваш быстрый выход! Подайте заявку из любого места, получите деньги в течение нескольких минут. Удобно, прозрачно, без скрытых комиссий.
Финансовые трудности? Решите их за минуты рейтинг займов онлайн с моментальным переводом на карту. Оформление онлайн, простые условия и никакого лишнего стресса. Ваш надежный финансовый помощник!
Строительный портал https://bms-soft.com.ua для тех, кто строит и ремонтирует! Узнайте о трендах, найдите мастеров, подберите материалы и получите ценные рекомендации.
Откройте для себя лучшие lineage 2 сервера! Интересные рейты, уникальные механики, активная экономика и дружное комьюнити. Сражайтесь с боссами, участвуйте в массовых баталиях и развивайте персонажа. Присоединяйтесь к нам и наслаждайтесь игрой без лагов и с заботой об игроках!
Biography of Spanish footballer Pedri https://pedri-bd.com statistics at Barcelona, ??games with teammate Gavi, inclusion in the national team for Euro, meme with Cristiano Ronaldo.
Biography of Argentine footballer Paulo Dybala https://paulo-dybala-bd.com personal life, tattoos on the body, wedding with his wife Oriana Sabatini.
Biography of Argentine footballer Paulo Dybala https://paulo-dybala-bd.com personal life, tattoos on the body, wedding with his wife Oriana Sabatini.
Your one-stop resource https://dota-2-esports.com for the latest news reviews, and interviews from the world of professional Dota 2. Stay on top of all the major events and trends in esports!
Robert Lewandowski https://robert-lewandowski-bd.com biography, photos, videos, goals, news, statistics. Robert Lewandowski on Wikipedia, Instagram, Twitter, Transfermarkt.
Execration is a legendary Dota 2 https://execration-dota2.com eSports team that conquers the heights of world eSports with its skill and tactics.
News portal dota-news your source of the most up-to-date information about the game and eSports events. News, tournaments, updates, analytics.
Xtreme Gaming: The Elite of Dota 2 xtreme gaming dota2 com. Unrivaled champions who have conquered the heights of eSports. Their fame thunders throughout the world.
Строительный и архитектурный портал https://intertools.com.ua все самое интересное о строительстве и архитектуре – новости архитектуры и строительства, обзоры и аналитика.
I loved this article, thank you for sharing! For those interested in more, https://metadmca.org/ is a fantastic website.
Invictus Gaming is a legendary invictus-gaming-dota2 esports organization known for its remarkable victories in Dota 2, including the championship at The International 2018.
Latest news https://league-of-legends-esports.com analytics and forecasts in the world of League of Legends eSports. Stay up to date with all the main events of the professional scene!
Official website t1-league-of-legends.com of the legendary eSports team T1 for League of Legends. Latest news, match results, player statistics and LOL Betting.
Latest news and analytics on League of Legends lol-news.com/ matches, tournaments, betting. Stay up to date with the latest eSports events!
Official website of the T1 https://t1-lol.com League of Legends eSports team. Latest news, matches, statistics, tournaments and predictions on LoL Betting.
onvif recording software ip camera time-lapse software free
Натуральные молочные продукты https://gastrodachavselug2.ru свежесть и качество с заботой о вашем здоровье! Широкий выбор: молоко, творог, сметана, сыры. Только натуральные ингредиенты, без консервантов и добавок.
weed shop in prague thc gummies shop in prague
hashish shop in prague https://shop-by.site
buy thc vape in prague thc gummies delivery in prague
hashish shop in prague cali weed delivery in prague
buy hash in prague thc chocolate for sale in prague
marijuana delivery in prague hemp shop in prague
hash delivery in prague https://shopraha.site
marijuana in prague thc joint delivery in prague
thc chocolate in prague https://smokeinprague.site
cannabis shop in prague https://kingstore420.site
Biography of footballer Kylian Mbappe https://kylian-mbappe-bd.com personal life, rumors of an affair with Alicia Aylis and Ines Rau. Career, statistics and salary at Paris Saint-Germain, victory at the World Cup and other achievements of the striker.
Biography of football player Neymar neymar-bd com personal life, relationships and rumors of romances with Katya Safarova, Natalia Barulich, the birth of a son and Bruna’s last girlfriend, the birth of daughters.
Biography of Belgian footballer kevin-de-bruyne Kevin De Bruyne (Kevin De Bruyne): personal life, relationship with his wife, conflict with Thibaut Courtois over his girlfriend Caroline.
Biography of football player Jude Bellingham http://jude-bellingham-bd.com personal life, relationship with girlfriend Laura. Player statistics in the Real Madrid team, matches for the England national team with Harry Kane, the athlete’s salary, conflict with Mason Greenwood.
Biography of football player Luis Alberto Suarez luis-suarez-bd.com/ personal life, daughter, wife, children, height. Leaving the club Atletico Madrid, career in Barcelona and Liverpool, goal statistics.
Try the free demo game Crazy Monkey crazy-monkey.com.az (Igrosoft) and read our exclusive review!
Discover Space XY space-xy.com.az/ Take advantage of bonuses and free play to increase your chances of winning!
JetX is a unique simulation game jetx com az from SmartSoft Gaming. Players fly a virtual plane and collect their winnings safely.
Hot Fruits 100 Slot hot-fruits-100.com.az/ Review by Amatic Industries – Play Hot Fruits 100 demo for free or real money. Bonuses and best casinos for September 2024!
Learn everything about blackjack http://blackjack.com.az rules, types of bets, features of the online game and answers to popular questions.
Разнообразие фурнитуры для плинтуса, найдите идеальный вариант.
Надежные элементы для плинтуса, гарантия долгого срока службы.
Удобство монтажа фурнитуры для плинтуса, для быстрой установки.
Модные элементы для украшения плинтуса, сделайте дом уютным и стильным.
Природные решения для отделки плинтуса, экологичный выбор для вашего дома.
Тренды в оттенках для декора плинтуса, создайте гармонию в доме.
Эксклюзивные варианты фурнитуры для плинтуса, выразите свою индивидуальность через дизайн.
Подсказки по правильной установке элементов плинтуса, для долгосрочного использования.
Декоративные элементы для фурнитуры плинтуса, создайте уютный и стильный дом.
Изысканные решения для отделки плинтуса, подчеркните изысканный вкус в дизайне.
каталог товаров магазин каталог товаров магазин .
В период технологической портативности пауэрбанк превратился в ключевой аксессуар экипировки современного человека. Этот мобильный накопитель заряда действует как портативная зарядная станция, гарантирующая энергией гаджеты в любой ситуации. Производители выпускают различные модели, среди которых Самый лучший повербанк для айфона на powerbanki.top , позволяющий поддерживать заряд устройств даже вдали от розетки. Ключевыми параметрами выбора являются емкость батареи, количество разъемов, мощность зарядки и поддержка с технологиями быстрой зарядки.
Когда речь идет о выборе пауэрбанка для устройств Apple, требуется принимать во внимание особые характеристики. Современные беспроводные пауэрбанки с поддержкой MagSafe обеспечивают идеальное соединение с iPhone последних серий. Поддержка сертификации MFi выступает подтверждением надежного применения с продукцией Apple. Производительные модели на 50000 mAh способны предоставить более десятка полных циклов зарядки iPhone, а поддержка USB Power Delivery обеспечивает зарядку MacBook и других ноутбуков.
Источник: https://powerbanki.top/
по вопросам negj shiljuuleh unitel – стучите в Telegram plx72
Zico is a legendary Brazilian footballer https://zico.com.az known as “White Pele”. His talent, technique and passion for the game made him an icon of Brazilian football, and his contributions to the sport continue to inspire new generations.
Rudy Gobert rudy-gobert-az.com is a French center and one of the best defenders in the NBA, nicknamed “The French Tower.” A three-time Defensive Player of the Year, he inspires with his skills and commitment to excellence.
George Best george-best.com.az is a brilliant footballer and a shining symbol of the 1960s, known for his talent and turbulent life. He left an indelible mark on football by combining success on the pitch with the tragedy of personal struggle.
Nikola Jokic https://nikola-jokic-az.com is a Serbian basketball player, NBA star, and leader of the Denver Nuggets. Known for his unique style of play, court vision, and leadership, he has become a role model for a new generation of centers.
Luka Doncic http://lukadoncic-az.com is a Slovenian basketball player, the leader of the Dallas Mavericks team and one of the main stars of the NBA. His unique playing style, records and influence have made him a symbol of European success in world basketball.
Julius Randle is a versatile NBA forward http://julius-randle-az.com a leader for the Knicks, and an inspiring example of perseverance. His play, leadership, and desire to win make him one of the defining figures in the modern league.
Cristiano Ronaldo biography cristiano-ronaldo-az.org/ personal life, relationships with Irina Shayk and Georgina Rodriguez, children, career at Real and Juventus, records with Portugal at Euro 2020.
Biography of footballer Mohamed Salah mohamed-salah-az.org wife Magi Sadiq, children, charity work, book “The Last Pharaoh”. Statistics, salary and awards with Liverpool and Egypt in 2024.
Biography of footballer Luis Alberto Suarez https://luis-suarez-az.org personal life, wife, children, height. Departure from Atletico Madrid, career at Barcelona and Liverpool, goal statistics. Playing for Gremio, moving to Inter Miami, retirement from international duty and the latest news in 2024.
Всё для строительства и ремонта https://artpaint.com.ua на одном портале: советы экспертов, обзоры материалов, расчет сметы и готовые решения для вашего дома или бизнеса.
Портал для строительства https://6may.org и ремонта: полезные советы, современные материалы, проекты и идеи. Все, что нужно для воплощения ваших задумок – от фундамента до крыши.
Студия дизайна интерьера https://bconline.com.ua и архитектуры: создаем уникальные проекты для квартир, домов и коммерческих пространств. Эстетика, функциональность и индивидуальный подход – в каждом решении.
Все об озеленении и благоустройстве https://bathen.rv.ua Ландшафтный дизайн, проекты садов, террас и парков. Идеи для создания зеленых зон, подбор растений и профессиональные услуги для вашего участка.
Hi it’s me, I am also visiting this web site regularly, this web site is truly nice and the viewers are genuinely sharing good thoughts.
https://pc-house.od.ua/safe-use-of-sealants-for-headlight-repair.html
CMS 1С-Битрикс Бизнес https://magikfox.ru/catalog/license/upravlenie-saytom/biznes/ купить лицензию в официальном маркетплейсе. Редакция Bitrix Бизнес для интернет магазина. Быстрая отправка лицензионного ключа. Помощь в установке и настройке.
баленсиага стероид бутс купить стероиды в россии
Ваш путеводитель в мире строительства https://dcsms.uzhgorod.ua идеи, планы, пошаговые инструкции и лучшие материалы. Узнайте, как построить дом мечты или обновить интерьер.
Профессиональный портал для строительства https://blogcamp.com.ua проекты, материалы, расчеты, советы и вдохновение. Все, чтобы ваш ремонт или стройка были успешными.
Хотите построить дом https://donbass.org.ua или сделать ремонт? Здесь вы найдете всё: инструкции, идеи, современные технологии и проверенные решения. Портал для тех, кто строит.
Все для строителей и мастеров https://dki.org.ua актуальные технологии, практические советы, строительные материалы и проекты. Простые решения для сложных задач!
Создайте дом своей мечты https://intellectronics.com.ua На нашем портале вы найдете идеи, инструкции и новейшие технологии для ремонта и строительства.
Станьте мастером https://fmsu.org.ua своего дела! Портал для тех, кто хочет строить и ремонтировать качественно и выгодно.
Looking for a way to earn money from home? Check out the Natraj Pencil Packing Job opportunity. In this role, you’ll receive all the materials you need to get started. 출장마사지
Ищете надежную типографию для реализации ваших идей? Handy Print – это высокое качество печати и профессиональный подход к каждому заказу. Мы предлагаем услуги цифровой и офсетной печати, производство визиток, листовок, брошюр, а также изготовление баннеров и другой рекламной продукции.
Обратившись к нам, вы получите не только отличный результат, но и оперативность выполнения работы. Посетите наш сайт handy-print.ru, чтобы узнать больше о наших услугах и сделать заказ прямо сейчас!
Архитектура и дизайн интерьера https://it-cifra.com.ua под ключ: современные решения, индивидуальный подход и гармония стиля и функциональности. Создаем пространство вашей мечты!
Найдите все для ремонта https://keravin.com.ua и строительства! Уникальные идеи, пошаговые инструкции и рекомендации специалистов на одном портале.
Стройте с комфортом https://mr.org.ua полезные советы, новейшие технологии, пошаговые инструкции и проекты – всё для вашего удобства.
Мы помогаем строить https://juglans.com.ua лучше! Советы, проекты, новейшие материалы и технологии для вашего ремонта или строительства.
Решили строить или делать ремонт https://msc.com.ua Мы подскажем, как выбрать лучшие материалы, спланировать бюджет и воплотить все задумки.
Все секреты https://mramor.net.ua строительства в одном месте! Советы экспертов, подбор материалов и готовые проекты для вдохновения.
Строительство без лишних вопросов https://okna-k.com.ua наш портал – кладезь информации о современных материалах, технологиях и лучших решениях для дома, дачи или офиса.
Всё для успешного строительства https://newboard-store.com.ua и ремонта на одном портале! Мы собрали актуальную информацию, идеи и инструкции для вашего удобства. Заходите и стройте с нами!
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your blog and in accession capital to assert that I acquire actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I’ll be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you access consistently fast.
https://millionigrushek.ru/
Информация о стройке https://purr.org.ua без лишних сложностей! Наш портал поможет выбрать материалы, узнать о технологиях и сделать ваш проект лучше.
registering company in montenegro government website Montenegro residence
how to activate bonus code in 1win http://www.1win bet.com
1win login uganda 1win uganda login registration
Официальный сайт https://luckyjetonewins.ru , где вы найдете актуальное зеркало и промоды на Лаки Джет.
Всё, что нужно знать о металлах https://metalprotection.com.ua от их свойств до применения в различных отраслях. Обзоры, советы, новости и информация о производителях для вашего удобства.
Вавада предлагает Vavada betting на любой вкус! Здесь вы найдете ставки на футбол, теннис, баскетбол, киберспорт и многое другое. Широкий выбор событий, удобный интерфейс и выгодные коэффициенты делают платформу идеальной как для новичков, так и для опытных игроков. Начните свой путь в ставках уже сегодня!
Хотите построить дом https://samozahist.org.ua или сделать ремонт? На нашем портале вы найдёте лучшие решения и вдохновение для вашего проекта.
Ищете проверенные строительные советы https://rus3edin.org.ua Наш портал поможет выбрать материалы, спланировать проект и сделать всё на высшем уровне.
Всё о дизайне интерьера https://sculptureproject.org.ua в одном месте! Узнайте, как создать уютное, стильное и функциональное пространство, которое будет радовать каждый день.
программа производственного контроля магазин https://ppk-213.ru
Экспертный строительный портал https://smallbusiness.dp.ua для вашего проекта! Советы, новинки и инструкции для тех, кто хочет сделать всё идеально.
Хотите стильный интерьер https://sitetime.kiev.ua Наш портал предлагает уникальные идеи, профессиональные рекомендации и примеры лучших дизайн-проектов.
голубой топаз свойства https://bluetopaz.ru/
Найдите всё о строительстве https://srk.kiev.ua и ремонте на нашем портале. Полезные статьи, актуальные технологии и лучшие практики ждут вас.
Планируете стройку https://texha.com.ua или ремонт? У нас вы найдёте проверенных специалистов, инструкции, материалы и проекты на любой вкус. Всё для комфортного строительства!
Преобразите ваш дом https://vineyardartdecor.com вместе с нами! На портале вы найдёте свежие идеи, советы по планировке и материалы для создания идеального интерьера.
Всё о строительстве https://valkbolos.com и ремонте на одном портале! Гид по материалам, обзор инструментов, советы по дизайну и подбор подрядчиков. Создавайте дом своей мечты!
El fichaje de Ronaldo por Al Nassr fue un momento clave en su carrera | La altura y la forma fisica de Ronaldo son impresionantes para su edad cristiano ronaldo career stats | Los jerseys de Cristiano Ronaldo son de los mas vendidos en todo el mundo | Los fans esperan ver a Ronaldo en los grandes torneos internacionales | Los seguidores mas leales siguen cada paso de Ronaldo en el campo Rendimiento de Ronaldo en 2024.
Планируете ремонт или строительство https://vodocar.com.ua У нас всё, что нужно: от инструкций и советов до подрядчиков и обзоров материалов. Стройте с нами!
Лучшие советы по строительству https://stroysam.kyiv.ua и ремонту на одном сайте! Найдите вдохновение, изучите обзоры и воплотите свои идеи с профессиональной помощью.
Полный справочник по строительству https://stroy-portal.kyiv.ua и ремонту: советы, инструкции, дизайн-решения и помощь с выбором материалов и подрядчиков.
Ваш гид в мире строительства https://vitamax.dp.ua и ремонта! Обзоры, практические советы, дизайн-идеи и подбор профессионалов для реализации любых проектов.
TaskMy.ru – профессиональная помощь в решении задач любого уровня
TaskMy.ru – это надежный сервис, который предлагает качественную помощь в выполнении задач любых направлений: от технических расчётов и программирования до написания текстов и аналитики. Мы работаем быстро, эффективно и ориентированы на ваши требования.
Доверяя TaskMy.ru, вы получаете индивидуальный подход, точное соблюдение сроков и доступные цены. Оставьте свою задачу профессионалам – результат превзойдет ожидания!
Простые решения для ремонта https://teplo.zt.ua и строительства! Идеи дизайна, рекомендации экспертов и проверенные материалы для вашего проекта.
Стройте и ремонтируйте https://suli-company.org.ua с лёгкостью! Полезные статьи, инструкции, советы по выбору материалов и подрядчиков ждут вас здесь.
Полный гид по строительству https://tsentralnyi.volyn.ua и ремонту: от планирования до отделки. Читайте, выбирайте и стройте с уверенностью и комфортом.
Портал о ремонте и строительстве https://buildingtips.kyiv.ua с полезными статьями, рекомендациями по выбору материалов и подрядчиков.
белый топаз цена https://whitetopaz.ru/
Полный гид по строительству https://tsentralnyi.volyn.ua и ремонту: от планирования до отделки. Читайте, выбирайте и стройте с уверенностью и комфортом.
промо ggdrop https://seoul-massage.com
Приветствую на https://b2best.at! Мы предлагаем надежные и проверенные покупки в интернете. Ознакомьтесь с нашими статьями о безопасности и легальности. Ваши покупки — наш приоритет!
Tormac.org https://tormac.org – это специализированный торрент-трекер, предназначенный для пользователей Mac-компьютеров. Сайт предоставляет широкий выбор контента, ориентированного на операционные системы macOS и iOS.
белый топаз https://whitetopaz.ru/
mostbet prihlaseni mostbet ru
mostbet withdrawal limit mostbet mobile
промокоды 1win 1win thimbles
голубой камень в ювелирных украшениях топаз https://bluetopaz.ru/
A detailed history inter-milan-az com of the Italian football club Inter Milan. From their first Scudetto to their Champions League victory.
MLB Draft Betting https://bettingblog.website Your guide to the world of MLB draft betting. Expert predictions, top odds and detailed analysis will help you increase your chances of success. Bet and win with us!
голубой топаз цена https://bluetopaz.ru/
Best Forex Trading Course https://blogforex.tech is your key to successful trading. Learn the secrets of professionals, study strategies and learn how to minimize risks. Master Forex easily and effectively!
Credit Union Mobile Home Loans https://blogcredit.tech are the perfect solution for buying or refinancing a mobile home. Affordable rates, easy application, and reliable support every step of the way. Take the first step toward your home with us!
Tennis betting https://yourmoneyblog.site best odds, predictions and analytics. Explore detailed match reviews, statistics and strategies to make successful bets. Use our tips and win!
Sur la plateforme vous rencontrez des solutions de videoconference innovantes et une variete de salons de videochat. Seulement ici vous rejoindrez beneficier de discussions video captivantes. Inscrivez-vous sur la plateforme Bed and Bamboo et initiez vos conversations video Coco chat deja tout de suite ! Coco chat, Chatrandom, Chatrandom, Chatrandom Bonus, Coco chat, Hebergements 2025
Coco chat
Chatrandom
Chatrandom
Chatrandom
Federal Gov Open Enrollment https://body-balance.online is your chance to upgrade or choose an insurance plan. Easy navigation, expert support, and a wide range of programs will help you make the right choice. Apply now!
Crypto Funk https://besttodaynew.com is a fresh look at cryptocurrencies. News, trends, guides and analytics for beginners and professionals. Find out how to get the most out of blockchain technology!
“Ищете качественный кирпич напрямую от производителя? https://Muravey61.ru – ваш надежный поставщик строительных материалов в регионе! Мы предлагаем кирпич высшего качества по доступным ценам прямо с завода. Доставка точно в срок, широкий ассортимент, и гарантированное качество – всё, что нужно для вашего строительства. Закажите у нас и убедитесь сами, что с нами строить легко!”
Home Equity Loans https://funnydays1.com How They Work, What Are the Terms and Benefits? Get the full details on how to use your home’s value for financial purposes. Find out more today!
Auto loans from Community Credit Union https://sunnydays100.com are simple, affordable, and great value. Low interest rates and flexible repayment options make it easy to buy a new or used car.
Credit score requirements for FHA loans https://lifeofnews1.com minimum threshold and tips for improving. Find out how to increase your chances of getting a loan, as well as what affects approval. Detailed information for those who want to get a mortgage through FHA.
No Credit Check Loans in Abilene TX https://daynewday1.com is fast access to money without unnecessary checks. Convenient terms, simple application and instant approval. Get financial help when you need it!
содержание программы производственного контроля программа производственного контроля ппк Москва
топаз оранжевый https://ambertopaz.ru/
Biography of American basketball legend Michael Jordan http://michael-jordan-az.org personal life, participation in the Monaco Champions League match, film projects, marriage to Yvette Prieto, parenthood, net worth and collaboration with Michael Jackson. Latest updates in 2024.
Легальные справки, которые принимаются везде. Мы предоставляем профессиональные услуги по оформлению официальных документов для работы, учебы и других целей. Все документы подлинные, соответствуют требованиям законодательства и оформляются оперативно https://kupit-med-spravki.ru/
Чайные пары https://giftbox-3.ru в подарочной упаковке оптом и печать коробки с логотипом в Ялте.
Try your luck at taya 365 casino login, where excitement meets reliability! Hundreds of popular games, unique promotions and instant payouts await you.
Dive into the exciting gaming world of https://taya365-casino.pro! Endless selection of games, fast withdrawals and fair play – everything for your pleasure.
Hemp for sale in Prague Weed delivery in Prague
Cannafood for sale in Prague Hashish in Prague
Paolo Maldini’s biography paolo-maldini-az.org photo, defender 2019, personal life, Instagram, Milan, salary, religion and news.
Discover the life of Sergio Busquets sergio busquets az org his parents, his partner Elena Galera Moron, his sons, his club career, his achievements with Spain and the latest news for 2024.
Biography of football legend Pele pele-az.com/ personal life, ex-spouses, children and current wife Maria Aoki. A reminder of his legendary career, goals and special style of play, as well as successful performances in the national team.
Biography of Spanish footballer Xavi Hernandez xavi hernandez az com coaching career, Barcelona statistics, matches with Iniesta and Messi, Guardiola’s influence, goals, youth training, dismissal as Barcelona coach, personal life and 2024 updates.
Biography of Brazilian footballer Ronaldinho https://ronaldinho-az.org personal life, son’s contract, current position. Club career, free kick goals, dribbling, jersey number, Ballon d’Or award, prison sentence. Latest news of 2024.
manga site Demon Slayer free online manga scan One Piece free online
Biography of Spanish footballer jordi-alba-az.org/ Jordi Alba: Left back for Barcelona and the Spanish national team, trained at the academies of Barcelona and Valencia.
Welcome to the fan site memphis depay dedicated to the active Dutch footballer Memphis Depay, his career path with clubs and the Dutch national team. Tattoos, personal life and news.
Los fans de CR7 buscan constantemente noticias sobre sus proximos movimientos | Los seguidores de CR7 esperan ansiosos cada publicacion en su Instagram https://cristiano-ronaldo.com.mx | Las frases inspiradoras de Ronaldo son compartidas ampliamente en redes sociales | Los analistas deportivos destacan los mejores momentos de CR7 en su carrera | Los videos motivacionales de CR7 son populares en redes sociales Datos curiosos de CR7.
Thank you for taking the time to read our post! Your engagement means so much, and we sincerely appreciate your support.
taya365 login 365 taya
taya 365 login taya365 app
Nicholas Jackson nicolas-jackson-az.com/ is a Senegalese professional footballer who has taken the football world by storm with his play and achievements.
Biography Pau Victor pau-victor is a Spanish footballer who started in the lower divisions. Thanks to hard work, he got into a good youth team at FC Barcelona. He played for Girona and has good statistics.
Нужен ремонт техники https://чинпочин.рус все услуги для вашего дома в одном месте! Выбирайте мастеров для ремонта, уборки или сантехнических работ. Качественный сервис, прозрачные цены и удобство использования.
software ftp FTP scheduler
Tobey Maguire’s tobey-maguire-az.com/ biography: personal life, memories of him, friendship with Leonardo DiCaprio, divorce from ex-wife. Role in Spider-Man films, career now.
Biography of Spanish footballer Dani Carvajal dani-carvajal-az.com personal life, marriage to Joselu and twin sisters. Performances at the Euro for Real Madrid and the Spanish national team.
Biography of footballer iker-casillas-az.com Iker Casillas: personal life, separation from ex-wife Sara Carbonero.
Thankful doesn’t even begin to describe how we feel about having you here. You mean so much to us.
ftp upload cctv video analytics software
Grateful doesn’t even begin to describe how we feel about your readership. You mean so much to us.
Now you can’t find a person formula1-az com who hasn’t heard of Formula 1. Today it is one of the most prestigious and popular sports on the planet.
Biography of Zendaya Coleman zendaya maree az com (Zendaya): modeling career, music and cinema, details of her personal life, ex-boyfriend Jacob Elordi, romance with Tom Holland.
Welcome to the world of Neymar neymar azerbaycan com a fan site dedicated to the great footballer. Learn all about his career, achievements and unique playing style.
Welcome to the main page karim-benzema-azerbaijan.com of the fansite dedicated to the world football star Karim Benzema. Learn all about his incredible career, incredible achievements and phenomenal skills.
Biography of British actress emily-blunt-az.com Emily Blunt: personal life, dating and relationship with her husband John Krasinski, raising children.
скупка золота 585 585 скупка золота цена за грамм
Оперативная помощь на дороге https://angeldorog.by/evakuator-minsk/ услуги эвакуатора, грузовой и легковой шиномонтаж, а также грузоперевозки фурами по доступным ценам. Работаем круглосуточно, быстро реагируем и гарантируем надежность. Звоните в любое время – решим вашу проблему!
Wifi IP Camera software Free VMS software
грамм золота спб скупка https://skupkazolotospb.ru
The MetaMask Wallet is essential for managing your crypto securely. I used https://metalead.org/ to download it, and the instructions for the MetaMask Chrome extension were clear and concise.
OR Realty — это ваш надежный партнер в мире недвижимости. Мы предлагаем большой выбор квартир, домов и коммерческих объектов по выгодным условиям. Наши специалисты помогут вам найти идеальный вариант, соответствующий вашим потребностям. Надежность, качество и удобство — вот что делает OR Realty лучшим выбором. Обращайтесь!
renting a tesla in europe tesla 3 rental
У нас вы можете купить айфоны https://vk.com/crazy_humor01 оптом по самым лучшим ценам. Оригинальные смартфоны Apple с гарантией качества. Постоянное наличие популярных моделей.
Immerse yourself in the world of Gigi Hadid gigi hadid through our dedicated website. Explore the latest news, highlights, exclusive interviews and in-depth features about her fashion endeavors, personal life and charitable efforts.
Biography of American professional gervonta-davis boxer Gervonta Davis: career highlights, weight, records, famous fights, personal life, controversies and latest 2024 updates.
Discover the world of Brad Pitt brad-pitt-az.com/ with our dedicated website, offering extensive coverage of his illustrious career, upcoming projects, and personal endeavors.
Квартирный переезд https://spb-gruzoperevozka.ru с грузчиками быстро и качественно! Упакуем, вынесем, перевезем и разместим вещи на новом месте. Надежная команда, аккуратность и доступные тарифы.
столы для переговоров черные купить стол для переговоров
стол для переговоров прямоугольный https://mm26.ru
https://www.myhomehobby.net/
https://www.myhomehobby.net/
[url=https://www.myhomehobby.net/]https://www.myhomehobby.net/[/url]
You have made your point.
My site :: https://sumyforum.pp.ua
kinogo 1080p kinogo лучшие боевики
kinogo фильмы про роботов kinogo зарубежные сериалы
Откройте для себя последние kraftsir новости, аналитику и экспертные обзоры о спорте и ставках. Узнайте о лучших стратегиях ставок, следите за актуальными событиями в мире спорта и получите все необходимые инструменты для успешных ставок.
киного фильмы с лучшей графикой киного культовые фильмы
киного культовые сериалы kinogo смотреть бесплатно
Новости игровой индустрии http://depcult35.ru аналитику и обзоры самых популярных игр. Читайте о новинках, трендах и получайте полезные советы для улучшения игрового процесса.
Подробные стратегии покера http://fatcurus.ru и анализ турниров: эффективные тактики, разбор раздач и ключевые советы для улучшения игры. Только практическая информация для выигрышей.
Все о мире гэмблинга minsvyazcc ru обзоры казино, игры, стратегии и последние новости индустрии. Узнайте о новых слотах, бонусах и тенденциях в азартных играх.
Sur le site vous beneficiez de des options de personnalisation et une gamme riche de discussions en video. A chaque connexion ici vous obtiendrez la possibilite savourer des interactions video efficaces. Inscrivez-vous sur la plateforme Bed and Bamboo et debutez vos echanges video Coco chat deja instantanement ! Coco chat, Chatrandom, Chatrandom, Chatrandom nettchat, Monkey, omegle-alternativen, omegle-alternativen, chillplanet, chatplaza 2025
Coco chat
Chatrandom
Chatrandom
Chatrandom
nettchat
monkey
omegle-alternativen
omegle-alternatives
chillplanet
chatplaza
снять индивидуалку в калуге индивидуалки г. калуга
заказать девушек в калуге проститутки г. калуга
программа производственного контроля дополнительного образования программа план производственного контроля
переговорные столы офисные https://mm26.ru
Sur quincaillerie-outillage-thollot.fr vous beneficiez de des options de personnalisation et une gamme riche de discussions en video. Toujours ici vous rejoindrez profiter de conversations video enrichissantes. Inscrivez-vous sur notre site et commencez votre experience Coco chat deja tout de suite ! Coco chat, Chatrandom, Chatrandom, Chatrandom nettchat, Monkey, omegle-alternativen, omegle-alternativen, chillplanet, chatplaza 2025
Coco chat
Chatrandom
Chatrandom
Chatrandom
nettchat
monkey
omegle-alternativen
omegle-alternatives
chillplanet
chatplaza
курс скупки золота на сегодня скупка золота рубль 585 цена грамма
Sur le site vous profitez de des fonctionnalites de videoconference exclusives et un eventail de choix de salles de videoconference. A chaque connexion ici vous rejoindrez vivre des connexions video instantanees. Inscrivez-vous sur la plateforme Bed and Bamboo et rejoignez des maintenant Coco chat deja sans delai ! Coco chat, Chatrandom, Chatrandom, Chatrandom nettchat, Monkey, omegle-alternativen, omegle-alternativen, chillplanet, chatplaza 2025
Coco chat
Chatrandom
Chatrandom
Chatrandom
nettchat
monkey
omegle-alternativen
omegle-alternatives
chillplanet
chatplaza
aviator mostbet mostbet bonus olish
1win это развод jetx 1win
mostbet uz apk mostbet iphone
Katun Room — это уютные гостиницы в самом сердце природы Алтая. Мы предлагаем комфортное проживание рядом с живописной рекой Катунь. Номера на любой вкус и бюджет, тишина и свежий воздух создадут незабываемую атмосферу для вашего отдыха. Забронируйте ваш номер уже сегодня!
узнайте последние новости http://umra-tour.ru киберспорта, анализ турниров и игровые стратегии в Азербайджане. Присоединяйтесь к нам, чтобы побеждать в мире киберспорта.
Актуальные и свежие новости http://gastromoroz.ru спорта и казино. Узнайте актуальные спортивные события, анализы матчей, советы по ставкам, обзоры казино игр и стратегии.
киного фильмы для скачивания kinogo фильмы по студиям
kinogo фильмы 4K kinogo сериалы по жанрам
киного сериалы по сезонам киного фильмы для одного
киного фильмы 4K kinogo артхаус
kinogo фильмы про апокалипсис kinogo военные фильмы
A modern AI tool ai undress tool for working with images. Learn more about its features, capabilities and applications. Full privacy control and ease of use will ensure comfortable interaction.
kinogo 1080p kinogo фильмы
Хотите купить окна мелке каталог по разумной цене? Ознакомьтесь с нашим предложением! У нас — качество, надежность и стиль по доступной стоимости. Индивидуальный подход к каждому заказу!
калуга путаны снять шлюху калуга
дизайнер интерьера квартиры https://dizayn-interera213.ru
услуги дизайнера интерьера квартиры цена дизайнер интерьера москва цены и работы
Компания АВИАПРОМ ВОЛГА предлагает широкий ассортимент авиационных масел, гидравлических жидкостей и индустриальных смазок. Мы являемся официальным импортером продукции пяти ведущих компаний Европы и Америки. Наши основные направления включают поставку высококачественных смазочных материалов для авиации, а также продуктов для промышленного и транспортного применения.
АВИАПРОМ ВОЛГА обеспечивает надежное сотрудничество, оперативные поставки и выгодные условия для клиентов из России и стран СНГ. Мы гарантируем качество продукции и соответствие международным стандартам.
Обратитесь к нам за профессиональной поддержкой в выборе необходимых масел и жидкостей для ваших нужд!
Biography of footballer Joshua Kimmich jimmy-butler-az.org personal life, wife and children. Career at Bayern Munich, statistics for Germany, work with Pep Guardiola, negotiations with Barcelona. Vice-captain at Euro 2024. Latest news for 2024.
Djokovic’s tennis career novak-djokovic-az.org/ has been marked by numerous Grand Slam titles, showcasing his style of play. He has been a constant competitor to Rafael Nadal and Roger Federer.
Откройте мир мобильных игр games-ru рейтинги лучших проектов, тренды, советы и гайды. Играйте в популярные шутеры, RPG, стратегии и песочницы прямо на телефоне!
Свежие футбольные новости https://vseofootball.ru обзоры матчей, Лига чемпионов, статистика и лучшие букмекерские бонусы для ставок на спорт.
Все о Тони Кроосе toni-kroos.ru/ на одном сайте: биография, актуальные новости, детальная статистика и эксклюзивные обновления о немецкой футбольной звезде. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу фанатов и будьте в курсе всех событий, связанных с Кроосом!
In Jodo Do Tigrinho online slots, every spin is a step towards victory! Incredible graphics, exciting themes and many bonuses await you. Fortune favors the brave – try your hand and discover the world of winnings with Tigrinho!
Cryptocurrency trading service bitqt with AI is automation and efficiency. Artificial intelligence monitors market dynamics, reduces risks and optimizes transactions. The perfect solution for beginners and professionals.
Исследуйте Zeus vs Hades zeus-vs-hades-downloadu Gods of War! Играйте бесплатно, получайте фриспины и узнайте все о слоте 2024 года!
online slots Jodo Do Tigrinho are a unique combination of excitement and pleasure. Discover a variety of themes, bonus games and jackpots. Play comfortably, enjoying the well-thought-out interface and the chance to hit the jackpot!
Cryptocurrency trading service bitqt with AI is automation and efficiency. Artificial intelligence monitors market dynamics, reduces risks and optimizes transactions. The perfect solution for beginners and professionals.
MetaMask Extension is the ultimate crypto wallet tool. From Chrome to Opera, it’s a breeze to use. Learn to maximize its features at https://metanaito.net/.
Скачайте бесплатно книгу https://storitelling.ru по сторителлингу и узнайте, как создавать истории, которые цепляют с первых строк. Практические советы, примеры и вдохновение для всех, кто хочет освоить искусство рассказчика.
Aviatrix game https://aviatrix-games.com/en/ has become a sensation in the world of crash games. Its unique format, featuring a rapidly growing multiplier and the possibility of an unexpected crash. Aviatrix crash game is at 1win, 1xbet, Mostbet, and Pin Up.
Aviatrix game https://aviatrix-games.com/en/ has become a sensation in the world of crash games. Its unique format, featuring a rapidly growing multiplier and the possibility of an unexpected crash. Aviatrix crash game is at 1win, 1xbet, Mostbet, and Pin Up.
алкоголь на дом 24 часа москва алкоголь на дом круглосуточно
Aviatrix game https://aviatrix-games.com/en/ has become a sensation in the world of crash games. Its unique format, featuring a rapidly growing multiplier and the possibility of an unexpected crash. Aviatrix crash game is at 1win, 1xbet, Mostbet, and Pin Up.
Захватывающий слот Lucky Jet http://lucky-jet-play-crash.ru от Spribe с уникальной краш-механикой, который предлагает игрокам шанс испытать свою удачу и стратегическое мышление.
Добро пожаловать на сайт redtigerplay.ru посвященный слотам Red Tiger! Узнайте последние новости, стратегии для увеличения выигрышей и эксклюзивные бонусы.
Откройте для себя водное поло water-polo-ru.ru историю, правила, тактики и влияние этого захватывающего водного вида спорта. Узнайте, как динамика и стратегия сочетаются, делая водное поло уникальным и увлекательным.
Компания Handy Print предоставляет профессиональные услуги по печати на различных поверхностях: текстиле, дереве, стекле, пластике и металле. Мы используем только современные технологии и качественные материалы, чтобы обеспечить яркость и долговечность изображений.
В Handy Print вы можете заказать нанесение логотипов на корпоративные подарки, создание эксклюзивных футболок, изготовление стильных аксессуаров и рекламной продукции. Наша команда профессионалов готова выполнить даже самые сложные и нестандартные задачи, чтобы вы получили идеальный результат.
Обращайтесь к нам уже сегодня и превращайте ваши идеи в реальность с помощью Handy Print!
Мир блэкджека https://blackjack-ru.ru узнайте историю игры, её правила, секретные стратегии и влияние на современную культуру. Откройте для себя глубину этой захватывающей карточной игры и научитесь побеждать с умом.
Скачайте бесплатно книгу https://storitelling.ru по сторителлингу и узнайте, как создавать истории, которые цепляют с первых строк. Практические советы, примеры и вдохновение для всех, кто хочет освоить искусство рассказчика.
купить окна пластиковые цены окна мелке сколько стоит
киного фэнтези kinogo фильмы по актерам
киного новинки kinogo фильмы про драконов
Сайт игровых промокодов промокод на csgoluck это ваш доступ к эксклюзивным бонусам и скидкам. Бесплатные награды, внутриигровая валюта и уникальные акции ждут вас. Успейте воспользоваться всеми возможностями!
Ищете промокоды для игр промокод на пополнение счета наш сайт – ваш лучший помощник! Собираем актуальные игровые промокоды для бонусов, скидок и эксклюзивных наград. Наслаждайтесь играми с максимальной выгодой – воспользуйтесь промокодами уже сегодня!
Хотите раскрутить контент-план мы знаем, как это сделать! Поможем увеличить охваты, привлечь активную аудиторию и вывести ваш контент на новый уровень.
капельница на дом клиника http://www.medlinks.ru/article.php?sid=110769
hello!,I really like your writing so so much! percentage we be
in contact more approximately your post on AOL? I require an expert on this house to solve my problem.
May be that is you! Taking a look ahead to look you.
I’m not sure where you are getting your information, but
great topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more.
Thanks for great info I was looking for this information for my
mission.
Ищете промокоды для игр промокоды на кейсы в ggstandoff наш сайт – ваш лучший помощник! Собираем актуальные игровые промокоды для бонусов, скидок и эксклюзивных наград.
Участок в Мишкином Лугу http://мишкинлуг.рф/uchastki-mishkinlug по Симферопольскому шоссе — идеальное место для строительства! Тихий поселок, прекрасные виды, удобный подъезд и все условия для комфортной жизни.
Лисичкин Очаг возле Серпухова https://лисичкиночаг.рф/uchastki-lisichkinochag идеальные участки для вашего будущего дома! Живописная природа, хорошая транспортная доступность и возможность подключения всех коммуникаций ждут вас.
Участки в Лисичкином Очаге https://лисичкиночаг.рф неподалеку от Серпухова. Тихий, зеленый поселок с прекрасной природой и удобной транспортной доступностью. Здесь вы сможете построить комфортное жилье для себя и своей семьи.
Quality articles or reviews is the key to interest the visitors to visit the site,
that’s what this web page is providing.
My brother suggested I might like this web site. He was totally right.
This put up truly made my day. You can not consider just
how much time I had spent for this information! Thanks!
1win offers exceptional customer service around the clock | Logging into 1win gives you access to numerous benefits 1win casino | The online casino 1win is considered the best in the Egyptian market | The official 1win site provides many options for sports betting | Enjoy the best online gaming experience with the 1win platform https://1win-egypt-casino.com/.
Отзывы о компаниях и работодателях https://potrebsojuz.ru в одном месте. Узнайте реальное мнение сотрудников и клиентов, чтобы принять правильное решение при выборе работы или услуг.
Комплексная юридическая помощь https://kramzenergo.ru для вас и вашего бизнеса. Анализ дел, представительство в судах, поддержка на всех этапах
вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому центр инфузионной терапии
1win codigo promocional 1win app
plinko 1win 1win partners app download
Откройте для себя историю слова пацана кровь на асфальте смотреть онлайн честный взгляд на суровую реальность, где дружба и слово дороже всего. Уникальный проект о жизни без прикрас и ценности принципов.
Купите современную коляску-трость для вашего малыша, со съемным козырьком и регулируемой спинкой.
Эргономичная коляска-трость с эффектным дизайном, и удобным выдвижным козырьком.
Универсальная коляска-трость для города и природы, с удобной ручкой и амортизаторами.
Элегантная коляска-трость для путешествий и прогулок, с прочными колесами и удобной спинкой.
geoby коляска трость https://kolyaski-trosti-progulochnye.ru/ .
Need help with your MetaMask Login? Visit https://kingroada.com/ for troubleshooting guides and more.
мотопомпа купить мотопомпа купить .
123b mang đến cơ hội tham gia các trò chơi hiện đại với giao diện thân thiện và hệ thống đổi thưởng nhanh chóng, tiện lợi.
киного музыкальные фильмы kinogo сериалы по годам
kinogo фильмы про супергероев киного жанры
kinogo новые сериалы киного фильмы про призраков
33win ngay hôm nay để không bỏ lỡ cơ hội tham gia vào các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng thú vị và nhận các phần thưởng giá trị lớn.
33 win ngay hôm nay để không bỏ lỡ các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng hấp dẫn cùng cơ hội tham gia các sự kiện độc quyền với phần thưởng giá trị.
sun win mang đến không gian giải trí đỉnh cao, nơi bạn có thể tận hưởng các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng đa dạng và cơ hội thắng lớn mỗi ngày.
33win là cổng game bài uy tín, cung cấp các trò chơi đổi thưởng phong phú cùng cơ hội nhận các phần quà giá trị từ các sự kiện đặc biệt.
77bet ngay hôm nay để khám phá không gian giải trí trực tuyến đẳng cấp, với các trò chơi phong phú và cơ hội nhận phần thưởng mỗi ngày.
33win mang đến không gian giải trí thân thiện, nơi bạn có thể tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng với giao diện hiện đại và dễ sử dụng.
33 win giúp người chơi dễ dàng tham gia vào các trò chơi đổi thưởng trực tuyến hiện đại, từ game bài đến các trò chơi casino hấp dẫn.
77bet cung cấp nền tảng giải trí chuyên nghiệp, nơi bạn có thể tận hưởng các trò chơi đa dạng và nhận phần thưởng giá trị lớn mỗi ngày.
33win là nơi hội tụ của những trò chơi bài trực tuyến phổ biến, với giao diện đẹp mắt và hệ thống đổi thưởng nhanh chóng, tiện lợi.
game 33win cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm giải trí chuyên nghiệp, nơi người chơi có thể khám phá các trò chơi đổi thưởng chất lượng cao.
hb 88 cam kết mang lại không gian giải trí an toàn, giúp bạn tận hưởng các trò chơi hiện đại với cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn mỗi ngày.
77betcom là cổng truy cập chính thức của nhà cái 77bet, nơi mang đến không gian giải trí trực tuyến đẳng cấp với các trò chơi hấp dẫn từ casino, thể thao đến game bài đổi thưởng.
77betcom cam kết mang lại sự hài lòng cho người chơi với các chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn và dịch vụ hỗ trợ tận tâm 24/7.
789 club là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho người yêu thích game bài đổi thưởng, với tỷ lệ thắng cao và hệ thống đổi thưởng minh bạch.
77betcom nổi bật với hệ thống trò chơi phong phú, giao diện thân thiện và các tính năng hiện đại, mang lại sự thoải mái cho mọi người chơi.
hb88 com cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm giải trí chuyên nghiệp với giao diện hiện đại, bảo mật tối ưu và các chương trình khuyến mãi độc quyền.
Откройте для себя blacksprut сайт возможности даркнет-рынка с тысячами предложений. Быстрая регистрация, надежные сделки и анонимность на каждом этапе.
Лучшее онлайн казино https://1wincasino.pl Огромный выбор автоматов, настольных игр и live-казино. Уникальные акции, приветственные бонусы и мгновенные выплаты сделают вашу игру еще интереснее.
дали дай текст песни https://faav.ru
I wasn’t sure if Metamask Opera would work on my setup, but https://metamenu.org/ guided me step by step. Fantastic resource for browser extensions!
советы по экипировке охота с вышки
рыбалка на течении рыбалка на лунках
надежный маркетплейс blacksprut где сочетаются безопасность, широкий выбор товаров и удобство использования. Платформа работает с анонимными платежами и гарантирует полную конфиденциальность для всех пользователей.
77bet casino cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm chơi casino trực tuyến an toàn và chuyên nghiệp, với các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng đa dạng và cơ hội thắng lớn.
789 Club cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm chơi game bài đổi thưởng an toàn, với tỷ lệ thắng cao và hệ thống đổi thưởng nhanh chóng.
77betcom ngay hôm nay để khám phá các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng hiện đại, từ tài xỉu, baccarat đến poker, với tỷ lệ thắng cao và các phần thưởng giá trị.
77bet cung cấp các trò chơi casino trực tuyến chất lượng cao, từ các bàn chơi cổ điển đến hiện đại, đáp ứng nhu cầu giải trí của mọi người chơi.
77betcom cung cấp giao diện hiện đại, bảo mật tối ưu và hệ thống đổi thưởng minh bạch, đảm bảo người chơi có trải nghiệm an toàn và tiện lợi.
33 win mang đến không gian giải trí an toàn, minh bạch với tỷ lệ đổi thưởng cao và các sự kiện khuyến mãi hấp dẫn mỗi ngày.
789club cam kết mang lại sự an toàn và minh bạch, nơi bạn có thể tận hưởng các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng và nhận thưởng lớn mỗi ngày.
77bet casino là lựa chọn hoàn hảo để tham gia các trò chơi casino trực tuyến, với giao diện thân thiện, hệ thống bảo mật tối ưu và phần thưởng hấp dẫn.
hb88 mang đến không gian giải trí trực tuyến uy tín, với các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng đẳng cấp và các phần thưởng giá trị mỗi ngày.
789 Club là cổng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể khám phá các trò chơi hấp dẫn như tài xỉu, poker, baccarat và nhiều tựa game khác.
Why viewers still make use of to read news papers when in this technological world the whole thing is available on net?
ответ на игру где логика
789 Club cung cấp nền tảng đổi thưởng an toàn, nơi bạn có thể dễ dàng tham gia các trò chơi bài trực tuyến và nhận phần thưởng lớn.
Because the admin of this web page is working, no uncertainty very soon it will be famous, due to its quality contents.
ответ на игру башня слов
hb 88 giúp người chơi dễ dàng kết nối với không gian giải trí trực tuyến đỉnh cao, nơi bạn có thể nhận thưởng lớn từ các trò chơi đổi thưởng hấp dẫn.
hb88 là nhà cái đổi thưởng được yêu thích, nơi bạn có thể trải nghiệm các trò chơi bài trực tuyến và nhận các phần quà độc đáo.
Cổng Game 789Club ngay hôm nay để tận hưởng không gian giải trí trực tuyến hiện đại, nơi bạn có thể nhận các phần thưởng hấp dẫn từ các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng.
hb88 com mang lại sự an toàn và tiện lợi cho người chơi, giúp bạn tham gia vào các trò chơi bài trực tuyến với các phần thưởng giá trị lớn.
Университет ресторанного бизнеса https://upskilll.ru/university UPSKILL: обучаем рестораторов, управляющих и сотрудников ресторанов, полностью адаптируя наши курсы, тренинги и программы обучения под особенности каждого заведения.
Net 88 cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm giải trí đẳng cấp, nơi bạn có thể khám phá các trò chơi trực tuyến phổ biến cùng cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn mỗi ngày.
Tải game 789 club là lựa chọn hoàn hảo cho người chơi yêu thích game bài đổi thưởng, với giao diện thân thiện và tỷ lệ thắng cao từ các trò chơi đa dạng.
hb88 là nền tảng cá cược uy tín, nơi bạn có thể khám phá các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng chất lượng cao và cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn.
hb 88 giúp bạn khám phá thế giới game bài trực tuyến đỉnh cao, với giao diện thân thiện và dịch vụ hỗ trợ khách hàng tận tâm 24/7.
услуги по ремонту стиральных машин на дому https://podolsk.ctc-service.ru
Tải game 789 club giúp bạn tải game dễ dàng và nhanh chóng, mở ra thế giới giải trí trực tuyến đỉnh cao với nhiều trò chơi bài hấp dẫn.
hb 88 cam kết mang lại không gian giải trí an toàn, minh bạch, nơi người chơi có thể tận hưởng các trò chơi đổi thưởng và nhận các phần quà giá trị.
hb88 là cổng game uy tín, nơi hội tụ các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng phổ biến cùng cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn từ các sự kiện độc quyền.
Tải game 789 club là nơi lý tưởng để bạn khám phá các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng trực tuyến, với tỷ lệ thắng cao và các chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn.
Hello, I would like to subscribe for this weblog to take most up-to-date updates, therefore where can i do it please assist.
Xrumer прогон для роста DR +50 по Ahrefs
Платформа Курьер Купер https://cash-kuper.ru открывает возможности для работы в доставке. Свободный график, прозрачная система оплаты и заказы поблизости – идеальный выбор для тех, кто ищет подработку или основной заработок.
hb88 là nhà cái uy tín, mang đến không gian giải trí trực tuyến hiện đại với các trò chơi đa dạng từ casino, thể thao đến game bài đổi thưởng.
hb 88 cung cấp nền tảng giải trí chất lượng cao, giúp bạn dễ dàng tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng mọi lúc, mọi nơi.
hb 88 cung cấp giao diện thân thiện, bảo mật tối ưu và tỷ lệ thắng cao, đảm bảo người chơi có những phút giây giải trí an toàn và thú vị.
789 Club giúp người chơi dễ dàng truy cập vào không gian giải trí trực tuyến an toàn, nơi bạn có thể nhận phần thưởng giá trị từ các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng.
hb88 là nhà cái đổi thưởng hàng đầu, giúp người chơi dễ dàng tham gia các trò chơi hiện đại với tỷ lệ đổi thưởng cao.
Leo88 là nhà cái trực tuyến hàng đầu, mang đến không gian giải trí đẳng cấp với các trò chơi đa dạng từ casino, thể thao, đến game bài đổi thưởng.
Cổng Game 789Club ngay hôm nay để trải nghiệm các trò chơi đổi thưởng hiện đại với tỷ lệ thắng cao và dịch vụ hỗ trợ tận tâm 24/7.
Leo88 ngay hôm nay để tận hưởng các trò chơi đổi thưởng đẳng cấp, từ tài xỉu, baccarat, poker đến các trò chơi hiện đại khác.
Leo88 mang đến cơ hội tham gia các trò chơi trực tuyến chất lượng cao, cùng các sự kiện khuyến mãi hấp dẫn chỉ dành riêng cho thành viên.
Tải game 789 club là cổng tải game uy tín, cho phép bạn truy cập vào các trò chơi bài trực tuyến hiện đại với dịch vụ hỗ trợ chuyên nghiệp 24/7.
Tải Go88 là cổng tải game uy tín, cung cấp các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng chất lượng cao với giao diện thân thiện, bảo mật tối ưu và tỷ lệ thắng hấp dẫn.
Sunwin nổi bật trên thị trường với hệ thống đổi thưởng minh bạch, tỷ lệ thắng cao và các dịch vụ hỗ trợ chuyên nghiệp 24/7.
ремонт водонагревателя аристон 50 литров ремонт водонагревателей
tải sunwin ngay hôm nay để khám phá các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng đẳng cấp, từ tài xỉu, baccarat đến poker, với giao diện hiện đại và bảo mật tối ưu.
thc gummies delivery in prague https://shop-cannabis-prague.com
Sunwin mang đến trải nghiệm giải trí trực tuyến đẳng cấp với giao diện hiện đại, bảo mật tối ưu và cơ hội nhận thưởng giá trị lớn mỗi ngày.
Link Tải Go88 là lựa chọn lý tưởng để tải game Go88, nơi bạn có thể tận hưởng không gian giải trí đẳng cấp với các trò chơi đa dạng và cơ hội nhận quà tặng giá trị lớn.
микрозаймы онлайн на карту без отказа микрокредит
sun win là cổng game bài đổi thưởng được yêu thích, với các trò chơi bài hấp dẫn, tỷ lệ thắng cao và các chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn mỗi ngày.
thc gummies for sale in prague kush shop in prague
you’re in reality a just right webmaster. The site loading velocity is amazing. It seems that you are doing any distinctive trick. Moreover, The contents are masterpiece. you’ve performed a fantastic job in this topic!
leaderboards
Sunwin mang lại không gian giải trí hiện đại, nơi bạn có thể tham gia các trò chơi bài trực tuyến mọi lúc, mọi nơi cùng tỷ lệ thắng cao.
Tải Go88 ngay hôm nay để trải nghiệm không gian giải trí đỉnh cao, với các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng hấp dẫn như tài xỉu, baccarat và poker cùng cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn.
tải sunwin là nơi lý tưởng để tải game và khám phá thế giới giải trí trực tuyến hiện đại, với các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng phong phú và các ưu đãi độc quyền.
Signing up on the 1win website is quick and straightforward | Many players in Egypt prefer using the 1win platform for betting 1win casino | The official 1win app is your best choice for gaming on the go | If you’re looking for great bonuses, 1win is the best choice | The services available on 1win make it one of the best casino platforms 1win betting.
Go 88 cam kết mang lại không gian giải trí trực tuyến an toàn và minh bạch, nơi bạn có thể tận hưởng các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng với tỷ lệ thắng cao.
срочно взять деньги под проценты взять деньги в займы
tải sun win cung cấp không gian giải trí trực tuyến hấp dẫn, nơi bạn có thể tải game và tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng cùng các phần thưởng giá trị.
sun win giúp bạn dễ dàng kết nối với không gian giải trí trực tuyến chất lượng cao, nơi hội tụ các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng thú vị.
hit club mang đến trải nghiệm giải trí đẳng cấp với giao diện thân thiện, bảo mật tối ưu và cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn từ các trò chơi đổi thưởng.
Открывайте кейсы CS:GO https://www.facebook.com/people/Hotdrop_CSGO/61550490187523/ с крутыми шансами на редкие скины. Удобный интерфейс, надежная система и огромный выбор кейсов сделают игру еще интереснее. Начните свой путь к топовым скинам прямо сейчас!
Sunwin là nền tảng giải trí lý tưởng, nơi bạn có thể khám phá các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng hiện đại cùng các ưu đãi độc quyền.
tải go88 giúp bạn kết nối với thế giới giải trí bài trực tuyến mọi lúc, mọi nơi, với hệ thống tải game mượt mà và dễ sử dụng.
hitclub là cổng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, nơi bạn có thể tham gia các trò chơi hấp dẫn như tài xỉu, poker, baccarat, cùng nhiều tựa game hiện đại khác.
Go88 là nền tảng giải trí trực tuyến chất lượng cao, nơi bạn có thể nhận phần thưởng lớn và tham gia các sự kiện khuyến mãi độc đáo.
Go88 cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm chơi game bài đổi thưởng đẳng cấp, với dịch vụ hỗ trợ chuyên nghiệp và các chương trình ưu đãi giá trị.
go 88 giúp bạn dễ dàng tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng hiện đại với giao diện thân thiện và dịch vụ hỗ trợ tận tâm 24/7.
b52club là cổng game bài đổi thưởng nổi tiếng, mang đến cho người chơi những trải nghiệm giải trí đẳng cấp với các trò chơi hấp dẫn như tài xỉu, baccarat, poker và nhiều tựa game đổi thưởng hiện đại khác.
go 88 mang đến không gian giải trí trực tuyến thú vị, nơi bạn có thể khám phá các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng hiện đại mọi lúc, mọi nơi.
Откройте яркие кейсы CS:GO https://m.youtube.com/@hotdrop-case и получите шанс выиграть топовые скины! Широкий выбор кейсов, высокий шанс дропа и честная система обеспечат увлекательный опыт.
link tải go88 cung cấp nền tảng tải game chất lượng, nơi bạn có thể tận hưởng các trò chơi bài trực tuyến mọi lúc, mọi nơi với các phần thưởng giá trị lớn.
link tải go88 mang đến cơ hội tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng đẳng cấp, với tỷ lệ thắng cao và giao diện thân thiện, dễ sử dụng.
Пробуйте удачу https://discord.com/invite/B5fF6pW8Cm CS:GO! Шанс получить редкие и дорогие скины, широкий выбор кейсов и удобный интерфейс делают процесс открытия легким и захватывающим.
Go88 là nơi lý tưởng để bạn khám phá thế giới bài đổi thưởng trực tuyến với giao diện hiện đại, bảo mật tối ưu và tỷ lệ thắng cao.
Go 88 là cổng game bài đổi thưởng hàng đầu, cung cấp các trò chơi hấp dẫn như tài xỉu, baccarat, poker và nhiều tựa game hiện đại khác, mang lại không gian giải trí đẳng cấp.
Рискни и испытай удачу https://t.me/hotdropcases Шанс получить редкие и дорогие скины, широкий выбор кейсов и удобный интерфейс делают процесс открытия легким и захватывающим.
789club là cổng game bài đổi thưởng hàng đầu, mang đến không gian giải trí trực tuyến an toàn với các trò chơi bài phổ biến và phần thưởng hấp dẫn.
Ваши любимые кейсы CS:GO https://t.me/s/hotdropcases в одном месте! Большой выбор, удобный интерфейс и высокая вероятность выпадения редких предметов делают процесс открытия кейсов по-настоящему захватывающим.
Tải Go88 ngay hôm nay để tận hưởng không gian giải trí trực tuyến chất lượng cao, với các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng đa dạng và các sự kiện ưu đãi hấp dẫn.
tải game 789 club mang đến sự tiện lợi với hệ thống tải game nhanh chóng, giúp bạn dễ dàng truy cập vào các trò chơi bài trực tuyến đẳng cấp mọi lúc, mọi nơi.
789club cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm giải trí chất lượng cao, nơi người chơi có thể khám phá các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng và nhận phần thưởng lớn mỗi ngày.
Сервис бытовых услуг https://gidrostok-servis.ru это удобное решение для любых домашних задач. Уборка, ремонт, сантехника, установка техники и многое другое. Надежные специалисты, быстрое выполнение и доступные цены!
789club ngay hôm nay để tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng hiện đại, từ tài xỉu, baccarat đến poker, cùng cơ hội nhận quà tặng giá trị.
789 club ngay hôm nay để không bỏ lỡ các trò chơi bài trực tuyến hấp dẫn và các chương trình ưu đãi độc quyền.
Tải Go88 ngay hôm nay để khám phá các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng hấp dẫn, từ tài xỉu, baccarat đến poker, với giao diện hiện đại và bảo mật tối ưu.
Go 88 giúp bạn kết nối với thế giới giải trí trực tuyến, nơi bạn có thể tham gia các trò chơi đổi thưởng mọi lúc, mọi nơi với giao diện mượt mà.
Go 88 giúp người chơi dễ dàng truy cập vào hệ thống trò chơi bài trực tuyến hiện đại, với tỷ lệ đổi thưởng minh bạch và giao diện thân thiện.
документальные фильмы 2025 HD 1080p подборки фильмов Netflix 2025
лучшие комедии 2025 без регистрации документальные фильмы 2025 в хорошем качестве
Нужны деньги срочно заем с быстрым одобрением и моментальным переводом на карту. Минимум документов, удобные условия и прозрачные ставки. Оформите займ прямо сейчас!
789club giúp người chơi dễ dàng truy cập và tham gia vào các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng thú vị, cùng các sự kiện ưu đãi giá trị lớn mỗi ngày.
Nhà cái Net88 cam kết mang lại không gian giải trí trực tuyến minh bạch, nơi người chơi có thể tận hưởng các trò chơi cá cược hấp dẫn cùng tỷ lệ trả thưởng cao.
Сувенирная печатная оптом продукция и сувениры в Белгороде https://podarki-v-moskve.ru/
Лучшие игровые промокоды промокоды на кейсы в standoff в одном месте! Активируйте бонусы, получайте подарки и прокачивайте аккаунт без лишних затрат. Следите за обновлениями, чтобы не пропустить новые промо!
Промокоды для игр https://esportpromo.com/standoff/ggstandoff/ это бесплатные бонусы, скидки и эксклюзивные награды! Находите актуальные коды, используйте их и получайте максимум удовольствия от игры без лишних затрат.
Sun win cung cấp nền tảng đổi thưởng an toàn và tiện lợi, nơi bạn có thể trải nghiệm các trò chơi bài trực tuyến cùng cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn.
Nhà cái Net88 giúp người chơi dễ dàng tiếp cận thế giới cá cược trực tuyến, với hệ thống giao dịch nhanh chóng và hàng loạt khuyến mãi hấp dẫn.
Лучшие игровые промокоды промокоды ггстандофф барабан в одном месте! Активируйте бонусы, получайте подарки и прокачивайте аккаунт без лишних затрат. Следите за обновлениями, чтобы не пропустить новые промо!
Sunwin ngay hôm nay để tận hưởng không gian giải trí trực tuyến đỉnh cao, nơi bạn có thể khám phá các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng và nhận thưởng lớn.
Net 88 là nhà cái hàng đầu, cung cấp nền tảng cá cược an toàn, minh bạch và đáp ứng mọi nhu cầu giải trí của người chơi.
Подарок мужчине эмоции впечатления оптом и сувениры из китая в москве в Улан-Удэ: корпоративные вип подарки оптом
1win is one of the most popular casino platforms in Egypt | The games available at the 1win casino attract entertainment and thrill seekers 1win Egypt | 1win casino offers convenient and secure payment options for all users | The 1win platform has earned the trust of many players in Egypt | The 1win platform provides excellent customer support around the clock 1win betting.
Бесплатные промокоды https://playpromocode.com/standoff/bulldrop/ для ваших любимых игр! Получайте монеты, бустеры, скины и другие ценные награды. Мы собираем только проверенные коды и обновляем их каждый день.
Cổng game Hitclub mang đến hệ thống trò chơi bài đổi thưởng phong phú, từ truyền thống đến hiện đại, phù hợp với mọi đối tượng người chơi.
Хотите проверить компанию https://innproverka.ru по ИНН? Наш сервис поможет узнать подробную информацию о юридических лицах и ИП: статус, финансы, руководителей и возможные риски. Защищайте себя от ненадежных партнеров!
Hitclub mang lại sự tiện lợi và an toàn khi tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng, với hệ thống bảo mật tối ưu và giao dịch nhanh chóng.
Hitclub hỗ trợ người chơi dễ dàng tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng đa dạng, cùng các chương trình ưu đãi hấp dẫn và dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng tận tâm.
Sun win là cổng game uy tín, nơi bạn có thể khám phá thế giới bài đổi thưởng thú vị với tỷ lệ thắng cao và các sự kiện khuyến mãi hấp dẫn.
Недвижимость на Северном Кипре https://iberiaproperty.ru выгодные инвестиции и комфортная жизнь у моря. Апартаменты, виллы и пентхаусы по доступным ценам. Поможем выбрать лучший вариант и оформить покупку.
удобный маркетплейс blacksprut с высоким уровнем анонимности и надежной системой защиты. Интуитивный интерфейс, проверенные продавцы и безопасные сделки делают его лучшим выбором для покупок.
Hitclub giúp bạn dễ dàng kết nối với thế giới giải trí trực tuyến, nơi hội tụ các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng thú vị và nhiều chương trình ưu đãi đặc biệt.
Tải Sunwin hỗ trợ bạn tải game dễ dàng, mở ra thế giới giải trí trực tuyến thú vị cùng nhiều phần thưởng giá trị từ các sự kiện đặc biệt.
Hitclub ngay hôm nay để tận hưởng các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng đỉnh cao và nhận các phần thưởng giá trị từ hệ thống đổi thưởng hiện đại.
33 win là lựa chọn hoàn hảo cho những ai yêu thích game bài đổi thưởng, với hàng loạt trò chơi đa dạng và tỷ lệ đổi thưởng cao.
Раскрутка в соцсетях https://nakrytka.com без лишних затрат! Привлекаем реальную аудиторию, повышаем охваты и активность. Эффективные инструменты для роста вашего бренда.
Tải Sunwin cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm tải game mượt mà, đảm bảo người chơi dễ dàng truy cập và tận hưởng các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng hiện đại.
33 win cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm đổi thưởng minh bạch, với tỷ lệ thắng cao và nhiều chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn mỗi ngày.
33 win ngay hôm nay để không bỏ lỡ các trò chơi bài trực tuyến đẳng cấp và cơ hội nhận thưởng giá trị lớn từ hệ thống đổi thưởng hiện đại.
Sunwin nổi bật trên thị trường với các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng đa dạng, từ truyền thống đến hiện đại, phù hợp với mọi nhu cầu giải trí.
https://vip-parisescort.com/
увлекательный сериал сериал однажды в сказке о жизни сказочных персонажей в реальном мире. Интригующий сюжет, волшебные события и неожиданные тайны. Смотрите онлайн в высоком качестве прямо сейчас!
33win là cổng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, thu hút đông đảo người chơi nhờ hệ thống trò chơi phong phú và cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn.
Game 33Win là cổng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, cung cấp các trò chơi hấp dẫn như tài xỉu, baccarat, poker và nhiều tựa game đổi thưởng hiện đại khác.
33 win mang đến không gian giải trí trực tuyến hiện đại, nơi bạn có thể trải nghiệm các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng thú vị và nhận thưởng mỗi ngày.
33win là nơi lý tưởng để bạn tận hưởng các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng phổ biến, với tỷ lệ đổi thưởng cao và hệ thống giao dịch nhanh chóng.
789 bet là nhà cái uy tín, cung cấp nền tảng cá cược trực tuyến chất lượng cao với các trò chơi đa dạng như thể thao, casino, bắn cá và game bài đổi thưởng.
789bet cam kết mang lại không gian cá cược an toàn, với các trò chơi đa dạng và hệ thống bảo mật tối ưu giúp người chơi yên tâm giải trí.
Tải Sunwin là lựa chọn lý tưởng để tải game bài đổi thưởng, mang đến các trò chơi hiện đại với hệ thống bảo mật tối ưu và giao diện thân thiện.
Jun88 là nơi lý tưởng để bạn khám phá thế giới cá cược trực tuyến, với các kèo cược thể thao hấp dẫn và trò chơi casino đỉnh cao.
Game 33Win là cổng game bài đổi thưởng được yêu thích, nơi người chơi có thể tham gia các trò chơi bài trực tuyến với tỷ lệ đổi thưởng cao và giao diện hiện đại.
доставка самолетом москва https://bvs-logistica.com/aviaperevozki.html
789 club nổi bật với giao diện hiện đại, hệ thống bảo mật tối ưu và tỷ lệ đổi thưởng cao, giúp người chơi yên tâm tận hưởng trải nghiệm giải trí đẳng cấp.
Game 33Win ngay hôm nay để không bỏ lỡ cơ hội tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng thú vị và tận hưởng những ưu đãi đặc biệt mỗi ngày.
Интернет-магазин товаров https://vitasleep.ru для здорового сна. В ассортименте: ортопедические матрасы, подушки, одеяла, постельное белье и аксессуары от проверенных брендов. Удобный выбор, доставка по России, гарантия качества. Забота о вашем комфорте и здоровом сне!
Jun88 mang đến cơ hội tham gia cá cược thể thao, game bài, tài xỉu với hệ thống nạp rút nhanh chóng và nhiều ưu đãi hấp dẫn.
33win là lựa chọn hàng đầu cho những ai yêu thích game bài trực tuyến, với các trò chơi phong phú và cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn mỗi ngày.
Nhà Cái 789bet nổi bật với giao diện thân thiện, hệ thống bảo mật tối ưu và tỷ lệ đổi thưởng hấp dẫn, giúp người chơi trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và minh bạch.
33win mang lại không gian giải trí chuyên nghiệp, nơi bạn có thể thử vận may và tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng hấp dẫn với tỷ lệ thắng cao.
смотреть сериалы качестве https://lordseriall.org
смотреть сериалы 2025 lordserial4.top/
33 win giúp bạn truy cập nhanh chóng vào không gian giải trí trực tuyến an toàn, với nhiều trò chơi đổi thưởng đa dạng và tỷ lệ thắng cao.
Cổng Game 789Club cung cấp nền tảng giải trí chuyên nghiệp, nơi bạn có thể tận hưởng các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng hấp dẫn với tỷ lệ thắng cao.
смотреть онлайн сериалы качестве https://lordserials2.net
789 club giúp bạn dễ dàng kết nối với không gian giải trí trực tuyến đỉnh cao, nơi hội tụ các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng thú vị và tỷ lệ thắng hấp dẫn.
смотреть сериалы подряд без рекламы https://lordserial7.com
смотреть сериал сезон 2023 смотреть сериалы в онлайн бесплатно в хорошем качестве
сериалы 2023 смотреть онлайн https://lordserials.cc
I was skeptical about installing Metamask until I found https://sites.google.com/view/metamask-extension-dfkasdkfdnt/download. Their guides are thorough and trustworthy, making it easy for me to secure my digital assets with confidence. Definitely recommend!
Cổng Game 789Club giúp bạn truy cập nhanh chóng vào không gian giải trí trực tuyến hiện đại, nơi bạn có thể khám phá các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng thú vị.
Логистические услуги в Москве https://bvs-logistica.com доставка, хранение, грузоперевозки. Надежные решения для бизнеса и частных клиентов. Оптимизация маршрутов, складские услуги и полный контроль на всех этапах.
смотреть сериал качестве бесплатно http://lordsserial.xyz
смотреть сериалы 2019 https://lordserialss.life
Game Iwin là cổng game bài đổi thưởng uy tín, mang đến trải nghiệm giải trí đẳng cấp với các trò chơi hấp dẫn như tài xỉu, baccarat, poker và nhiều tựa game khác.
Nhà Cái 789bet giúp bạn trải nghiệm không gian giải trí trực tuyến chuyên nghiệp, nơi bạn có thể tham gia cá cược mọi lúc, mọi nơi một cách dễ dàng.
Cổng Game 789Club là cổng game bài đổi thưởng hàng đầu, nơi bạn có thể tham gia các trò chơi bài trực tuyến với hệ thống đổi thưởng hiện đại và các ưu đãi hấp dẫn.
Хотите почувствовать азарт? arkada casino промокод за регистрацию предлагает широкий выбор игр, честную систему выигрышей и мгновенные выплаты. Захватывающие слоты и бонусы ждут вас!
789bet cung cấp nền tảng cá cược chất lượng cao, giúp người chơi có trải nghiệm mượt mà với hệ thống giao dịch nhanh gọn và minh bạch.
789 bet là lựa chọn hoàn hảo cho những ai yêu thích cá cược thể thao, casino trực tuyến và các trò chơi đổi thưởng hấp dẫn.
Sunwin là cổng game bài đổi thưởng hàng đầu, mang đến trải nghiệm giải trí đẳng cấp với các trò chơi như tài xỉu, baccarat, poker và nhiều tựa game hấp dẫn khác.
game sunwin ngay hôm nay để tận hưởng các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng đỉnh cao và nhận các phần thưởng giá trị từ hệ thống đổi thưởng hiện đại.
смотреть сериалы 2022 сезон https://lordseriall6.org
сериалы онлайн в хорошем качестве смотреть сериал
смотреть сериалы 2019 сериалы онлайн
link tải sunwin mang đến trải nghiệm tải game mượt mà, giúp bạn kết nối ngay với cổng game bài đổi thưởng đẳng cấp nhất hiện nay.
link tải sunwin cung cấp link tải an toàn, giúp bạn dễ dàng cài đặt Sunwin trên điện thoại hoặc máy tính và tham gia các trò chơi bài trực tuyến ngay lập tức.
tải game sunwin cung cấp đường dẫn tải game nhanh chóng, giúp bạn truy cập ngay vào nền tảng Sunwin mà không cần tìm kiếm trên các kho ứng dụng khác.
Check out Sellvia https://www.instagram.com/sellvia.dropshipping/ on Instagram for the hottest product ideas, store upgrades, and exclusive deals! Stay in the loop with our latest dropshipping tips and grab promo coupons to boost your business.
Finding a trusted site to install the Metamask extension was difficult until I came across https://sites.google.com/view/metamask-extension-download-oa/chrome. The site offers clear instructions, and now I can manage my digital assets with ease!
sunwin tài xỉu giúp bạn tận hưởng trò chơi tài xỉu trực tuyến một cách trọn vẹn, với tỷ lệ thắng hấp dẫn và nhiều phần thưởng giá trị lớn.
Jun 88 ngay hôm nay để không bỏ lỡ các trận cược hấp dẫn, từ bóng đá, casino trực tuyến đến game bài đổi thưởng, cùng cơ hội nhận thưởng giá trị.
33 win hỗ trợ người chơi tham gia các trò chơi bài trực tuyến mọi lúc, mọi nơi, với hệ thống đổi thưởng nhanh chóng và dễ sử dụng.
sunwin tài xỉu là lựa chọn hoàn hảo cho những ai yêu thích tài xỉu đổi thưởng, với tỷ lệ trả thưởng cao và nhiều sự kiện hấp dẫn mỗi ngày.
Iwin là lựa chọn hoàn hảo cho những ai yêu thích game bài trực tuyến, với tỷ lệ thắng cao, dịch vụ hỗ trợ 24/7 và hàng loạt phần thưởng giá trị.
Nhà Cái Jun88 cam kết mang đến dịch vụ cá cược minh bạch, với hệ thống nạp rút nhanh chóng và hỗ trợ khách hàng tận tâm 24/7.
tài xỉu sunwin nổi bật với giao diện hiện đại, luật chơi đơn giản và hệ thống đặt cược linh hoạt, giúp người chơi dễ dàng tham gia và nhận thưởng.
net88 ngay hôm nay để trải nghiệm cá cược trực tuyến đẳng cấp và tham gia vào cộng đồng game thủ lớn mạnh của Net88.
789 bet mang đến trải nghiệm cá cược trực tuyến mượt mà, với hệ thống đổi thưởng nhanh chóng và tỷ lệ kèo cạnh tranh trên thị trường.
The full special bip39 Word List consists of 2048 words used to protect cryptocurrency wallets. Allows you to create backups and restore access to digital assets. Check out the full list.
I like review sites which grasp the cost of conveying the fantastic helpful asset for nothing out of pocket. I genuinely revered perusing your posting. Much obliged to you 티비위키
sunwin club giúp bạn dễ dàng kết nối với thế giới giải trí trực tuyến, nơi hội tụ các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng thú vị và nhiều chương trình ưu đãi đặc biệt.
Reliable and unique bip39 Word List contains 2048 words needed to create seed phrases in crypto wallets. Allows you to safely manage private keys and guarantees the possibility of recovering funds.
bong da net88 là nền tảng cá cược bóng đá trực tuyến uy tín, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội tham gia các kèo cược hấp dẫn với tỷ lệ thắng cao và cập nhật kết quả nhanh chóng.
net88 max ngay hôm nay để không bỏ lỡ cơ hội tham gia các trò chơi cá cược thú vị cùng cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn từ các sự kiện đặc biệt.
tải game sunwin giúp bạn tải game dễ dàng trên điện thoại Android và iOS, chỉ với vài thao tác đơn giản là có thể tham gia ngay vào các bàn chơi hấp dẫn.
game sunwin ngay hôm nay để không bỏ lỡ cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn từ các trò chơi bài trực tuyến phổ biến và các sự kiện khuyến mãi hấp dẫn.
Reliable and unique bip39 Word List contains 2048 words needed to create seed phrases in crypto wallets. Allows you to safely manage private keys and guarantees the possibility of recovering funds.
link tải sunwin hỗ trợ người chơi tải game Sunwin một cách nhanh chóng, đảm bảo bảo mật và không bị lỗi trong quá trình cài đặt.
net88 là nhà cái trực tuyến uy tín, cung cấp nền tảng cá cược hiện đại với các trò chơi đa dạng như thể thao, casino, bắn cá và game bài đổi thưởng.
bong da net88 hỗ trợ người chơi cập nhật thông tin trận đấu, tỷ lệ cược, và kết quả một cách nhanh chóng, giúp đưa ra các quyết định cá cược chính xác nhất.
Sunwin hỗ trợ người chơi dễ dàng tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng đa dạng, cùng các chương trình ưu đãi hấp dẫn và dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng tận tâm.
net88 origin mang đến trải nghiệm cá cược thể thao đỉnh cao, với đa dạng kèo cược từ bóng đá, bóng rổ, quần vợt đến eSports.
net88 max hỗ trợ người chơi tham gia cá cược mọi lúc, mọi nơi với hệ thống giao diện thân thiện trên cả máy tính và điện thoại di động.
đá gà net88 nổi bật với giao diện thân thiện, dễ sử dụng, giúp người chơi theo dõi trực tiếp các trận đá gà từ đấu trường quốc tế và đặt cược chỉ với vài thao tác đơn giản.
Reliable and unique bip39 Word List contains 2048 words needed to create seed phrases in crypto wallets. Allows you to safely manage private keys and guarantees the possibility of recovering funds.
bong da net88 ngay hôm nay để không bỏ lỡ cơ hội tham gia các trận cầu đỉnh cao, với tỷ lệ cược hấp dẫn và các chương trình khuyến mãi đặc biệt dành cho thành viên.
trực tiếp đá gà net88 hỗ trợ xem trực tiếp đá gà với chất lượng hình ảnh sắc nét, âm thanh sống động, giúp bạn tận hưởng không khí sôi động như đang có mặt tại trường gà thực tế.
1xBet promo code https://synergyfitness.com.mk/enhance-your-bets-with-the-1xbet-promo-code-uganda/ your chance to get bonuses on bets, free bets and exclusive promotions! Enter the code during registration and start playing with an increased deposit.
b52 cam kết đảm bảo quyền lợi tối đa cho người chơi với chính sách bảo mật nghiêm ngặt, hệ thống chăm sóc khách hàng 24/7 chuyên nghiệp và tận tâm.
hemp shop in prague marijuana for sale in Prague
Sunwin giúp bạn dễ dàng kết nối với thế giới giải trí trực tuyến, nơi hội tụ các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng thú vị và nhiều chương trình ưu đãi đặc biệt.
tải game 789club giúp bạn dễ dàng tham gia các trò chơi hấp dẫn mọi lúc, mọi nơi chỉ với vài bước đơn giản trên điện thoại hoặc máy tính, đảm bảo tốc độ tải nhanh và an toàn.
789 club giúp người chơi dễ dàng nạp rút tiền nhanh chóng, an toàn và bảo mật thông tin tối đa nhờ vào hệ thống giao dịch hiện đại và bảo mật cao.
Ремонт компьютеров и ноутбуков https://remcomp89.ru в Новом Уренгое – быстрые и качественные услуги! Диагностика, настройка, замена комплектующих, восстановление данных. Гарантия на работу, доступные цены и выезд мастера!
hit club cam kết mang lại sân chơi cá cược minh bạch, với tỷ lệ đổi thưởng cao, hệ thống nạp rút nhanh chóng và dịch vụ hỗ trợ khách hàng tận tâm 24/7.
tải game 789club cực kỳ đơn giản và nhanh chóng, chỉ cần truy cập vào trang chủ chính thức, chọn phiên bản phù hợp với thiết bị và cài đặt chỉ trong vài phút.
789club nổi bật với giao diện hiện đại, thân thiện với người dùng, giúp bạn dễ dàng thao tác và tận hưởng trải nghiệm giải trí mượt mà, không giật lag.
b52 club là nơi hội tụ của các cao thủ bài bạc, giúp bạn thách thức giới hạn bản thân thông qua các giải đấu bài đổi thưởng đỉnh cao với giải thưởng hấp dẫn.
b52 club là cổng game bài đổi thưởng hàng đầu, nổi bật với giao diện hiện đại và hệ thống trò chơi đa dạng như tài xỉu, tiến lên, poker, và nhiều game hấp dẫn khác.
game sunwin ngay hôm nay để tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng phổ biến và nhận phần thưởng lớn từ các sự kiện độc quyền dành cho thành viên.
Используйте актуальный промокод 1xbet и получите увеличенный бонус на первый депозит! Делайте ставки на спорт, играйте в казино и пользуйтесь эксклюзивными предложениями. Легкая регистрация и моментальные выплаты!
Looking for the current spinbetter promo code? Get bonus funds for bets and casino games. Easy activation, favorable conditions and real winnings are waiting for you. Hurry to use it!
The most comprehensive bip39 for securely creating and restoring cryptocurrency wallets. Learn how mnemonic coding works and protect your digital assets!
cottage moving Prague moving with a smile Prague
net88 origin nổi bật với hệ thống bảo mật mạnh mẽ, đảm bảo an toàn tuyệt đối cho mọi giao dịch nạp rút và thông tin cá nhân của người chơi.
b52 giúp người chơi rèn luyện chiến thuật và kỹ năng tính toán trong các trò chơi bài như tiến lên, phỏm, ba cây, mang đến cơ hội thắng lớn.
tải hitclub giúp bạn dễ dàng truy cập vào hệ thống game hiện đại chỉ với vài bước đơn giản, hỗ trợ cả trên điện thoại Android, iOS và máy tính một cách nhanh chóng.
789 club cam kết mang lại sân chơi minh bạch với hệ thống đổi thưởng nhanh chóng, tỷ lệ trả thưởng cao và cơ hội trúng các phần quà giá trị mỗi ngày.
The most comprehensive bip39 for securely creating and restoring cryptocurrency wallets. Learn how mnemonic coding works and protect your digital assets!
go 88 cam kết đảm bảo công bằng tuyệt đối với hệ thống kiểm soát chặt chẽ, đảm bảo mọi kết quả trò chơi đều minh bạch và không có sự can thiệp từ bên ngoài.
go 88 cam kết mang đến môi trường giải trí minh bạch, an toàn với hệ thống bảo mật tối ưu và tốc độ xử lý giao dịch nạp rút nhanh chóng.
net88 là nơi lý tưởng để bạn rèn luyện kỹ năng cá cược, học hỏi chiến lược mới và tận hưởng cảm giác chiến thắng mỗi ngày.
go 88 giúp người chơi kết nối với cộng đồng game thủ lớn mạnh, tham gia các giải đấu bài trực tuyến và thử sức với những thử thách đầy kịch tính.
go 88 hỗ trợ người chơi tham gia các trò chơi bài đổi thưởng mọi lúc, mọi nơi với chỉ vài cú chạm đơn giản trên màn hình điện thoại.
nhà cái net88 giúp người chơi dễ dàng truy cập trên mọi nền tảng, từ máy tính đến điện thoại di động, với tốc độ mượt mà và ổn định.
tải hitclub mang đến trải nghiệm chơi game ổn định với tốc độ tải nhanh, đảm bảo an toàn tuyệt đối cho mọi giao dịch nạp rút và thông tin cá nhân của người chơi.
trực tiếp đá gà net88 là nền tảng cá cược trực tiếp đá gà uy tín, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội theo dõi những trận đấu kịch tính từ các trường gà lớn tại Campuchia và Philippines.
go 88 là cổng game bài đổi thưởng đáng tin cậy, mang lại cho người chơi trải nghiệm giải trí tuyệt vời cùng cơ hội nhận thưởng lớn từ các sự kiện đặc biệt.
Thank you for any other informative site. The place else could I am getting that kind of information written in such a perfect approach? I have a mission that I’m just now running on, and I have been on the look out for such info 티비몬
net88 max là nhà cái uy tín, luôn đảm bảo tính minh bạch trong từng trò chơi và tạo điều kiện tốt nhất để người chơi đạt được chiến thắng.
Ищете квартиру в новом доме? новостройки Украина – это современные жилые комплексы, доступные цены, рассрочка и ипотека. Подберите идеальное жилье от надежных застройщиков!
net88 origin là lựa chọn hàng đầu dành cho những ai tìm kiếm sự an toàn, tiện lợi và cơ hội chiến thắng lớn trong thế giới cá cược trực tuyến đầy kịch tính.
Продажа инструментов для дома купить инструмент по дереву строительства и ремонта! Огромный выбор ручного и электроинструмента, выгодные цены, акции и быстрая доставка. Найдите все необходимое в одном месте!
Use the proven bip39 phrase standard to protect your assets and easily restore access to your finances. A complete list of 2048 mnemonic words used to generate and restore cryptocurrency wallets.
What a information of un-ambiguity and preserveness of valuable familiarity concerning unexpected feelings. 티비몬
Sitio web de fans http://rodri.com.mx de Rodri Hernandez: Descubre la carrera y logros del mediocampista espanol del Manchester City. Noticias, estadisticas y analisis del juego de uno de los mejores futbolistas actuales.
Sitio fan de Mohamed Salah mohamed-salah.com.mx/ ultimas noticias, records, entrevistas y los mejores momentos de la carrera de uno de los futbolistas mas grandes de la actualidad. ?Mantente al tanto!
Great survey, I’m sure you’re getting a great response bj야동
1win Azerbaijan offers great promotions for both new and existing users | The registration process on 1win is quick and hassle-free 1win login | The promotions and free spins at 1win keep players engaged | With 1win, you can bet on football, basketball, tennis, and more | 1win giris allows users to start playing instantly 1win betting site review.
This post is greatly simple to scrutinize and recognize without overlooking any unobtrusive components. Remarkable work! 티비위키 최신
casino jeux en ligne meilleurs casino en ligne
I appreciate this article for the well-researched content and excellent wording. I got so interested in this material that I couldn’t stop reading. Your blog is really impressiv AV27
Try your luck at pin up casino! The best slots, roulette, blackjack and live games with real dealers. Pleasant bonuses, promotions and a user-friendly interface will create ideal conditions for the game!
casino ma chance en ligne casino roulette en ligne
New full Bip39 2048 words used to create and restore crypto wallets. Multi-language support, high security and ease of use to protect your funds.
casino france en ligne casino en ligne meilleur site
leo88 slot nổi bật với các tựa game slot hấp dẫn, giao diện sống động cùng tỷ lệ thắng cao, giúp người chơi dễ dàng chinh phục các phần thưởng giá trị.
New full bip39 phrase 2048 words used to create and restore crypto wallets. Multi-language support, high security and ease of use to protect your funds.
Leo 88 là nền tảng giải trí trực tuyến chuyên nghiệp, nơi người chơi có thể tận hưởng những phút giây thư giãn và cơ hội nhận các phần thưởng giá trị lớn.
Everything has its own value, but this is really precious information shared by Author 티비위키 예능
Leo 88 là nền tảng giải trí trực tuyến hàng đầu, cung cấp nhiều trò chơi thú vị cùng hệ thống bảo mật an toàn, đảm bảo trải nghiệm cá cược mượt mà và minh bạch.
Промокод казино https://myworldgo.com/blog/145383/bet-winner-promo-code-2025-unlock-real-money-rewards-with-lucky2win активируйте эксклюзивные бонусы! Получите фриспины, бонусные деньги на депозит и кешбэк. Используйте актуальные коды для максимальной выгоды в онлайн-казино. Играйте с лучшими условиями!
Leo 88 là nền tảng giải trí trực tuyến uy tín, nơi bạn có thể tham gia vào các trò chơi cá cược hấp dẫn và tận hưởng những chương trình khuyến mãi đặc biệt dành cho mọi thành viên.
Current casino promo codes https://www.panamericano.us/assets/inc/el_codigo_promocional_1.html bonus money, free spins and cashback for playing. Use verified codes, activate exclusive offers and win more!
Ищете выгодные покупки? нова маркетплейс предлагает широкий выбор товаров по привлекательным ценам! Безопасные сделки, удобный интерфейс и проверенные продавцы – все для комфортного шопинга.
Проверенное и надежное казино – селектор казино зеркало
Лучшие промокоды для казино https://p-10.ru/news/5_faktov_kotorye_vam_sleduet_znaty_o_nosovom_krovotechenii.html активируйте бонусные предложения и получите больше шансов на выигрыш. Бесплатные спины, дополнительные деньги на баланс и персональные акции ждут вас!
Присоединяйтесь к NovaXLtd.live ссылка платформе с широкими возможностями и удобными инструментами. Доступность, надежность, поддержка!
Откройте новые возможности https://sindicate24-4.biz! Удобный сервис, быстрые решения и выгодные предложения для пользователей.
Временная регистрация в Москве – быстро и надежно!
Нужна временная прописка для работы, учебы или оформления
документов? Оформим официальную регистрацию в Москве
всего за 1 день. Без очередей, с гарантией и
юридической чистотой!
? Подходит для граждан РФ и СНГ
? Регистрация от 3 месяцев до 5 лет
? Легально, с внесением в базу МВД
Работаем без предоплаты! Документы можно получить лично или дистанционно.
Доступные цены, оперативное оформление!
Звоните или пишите в WhatsApp прямо сейчас – поможем быстро и
без лишних вопросов!
Временная регистрация в Москве
Продажа сигарет купить сигареты lucky strike в интернет-магазине – оригинальные бренды, доступные цены, удобные способы оплаты и быстрая доставка. Сделайте заказ сегодня!
Откройте все возможности bs2best сайт Большой выбор товаров, безопасные сделки и простая навигация. Приватность и защита пользователей на первом месте.
When your website or blog goes live for the first time, it is exciting. That is until you realize no one but you and your 티비몬 최신
Свежие промокоды казино https://konicek.cz/includes/robots/1xbet_promo_code_106.html бонусы, фриспины и эксклюзивные акции от топовых платформ! Найдите лучшие предложения, активируйте код и выигрывайте больше.
Нужен опытный остеопат Пушкино? Помогаю при остеохондрозе, грыжах, искривлениях позвоночника и болях в суставах. Безопасные техники, профессиональный подход, запись на прием!
Жарким летним утром Вася Муфлонов, заядлый рыбак из небольшой деревушки, собрал свои снасти и отправился на местное озеро. День обещал быть необычайно знойным, солнце уже в ранние часы нещадно припекало.
Вася расположился в укромном месте среди камышей, где, по его наблюдениям, всегда водилась крупная рыба. Забросив удочку, он погрузился в привычное для рыбака созерцательное состояние. Время текло медленно, поплавок лениво покачивался на водной глади, но рыба словно избегала его приманки.
Ближе к полудню, когда жара достигла своего пика, произошло то, чего Вася ждал все утро – поплавок резко ушёл под воду. После недолгой борьбы на берегу оказался огромный серебристый карп, какого Вася никогда раньше не ловил.
Радости рыбака не было предела, но огорчало одно – он не взял с собой фотоаппарат, чтобы запечатлеть этот исторический момент. Тут в голову Васи пришла необычная идея. Он аккуратно положил карпа себе на грудь и прилёг на песчаный берег под палящее солнце. “Пусть загар оставит память об этом улове”, – подумал находчивый рыбак.
Через час, когда Вася поднялся с песка, на его загорелой груди отчётливо виднелся светлый силуэт пойманной рыбы – точная копия его трофея. Теперь у него было неопровержимое доказательство его рыбацкой удачи.
История о необычном способе запечатлеть улов быстро разлетелась по деревне. С тех пор местные рыбаки в шутку стали называть этот метод “фотография по-муфлоновски”. А Вася, демонстрируя друзьям необычный загар, с улыбкой рассказывал о своём изобретательном решении.
Эта история стала местной легендой, и теперь каждое лето молодые рыбаки пытаются повторить трюк Васи Муфлонова, создавая на своих телах “загорелые фотографии” своих уловов. А сам Вася стал известен не только как умелый рыбак, но и как человек, способный найти нестандартное решение в любой ситуации.
online casino development casino software for sale
Маркетплейс NOVA, есть все! Москва, Питер, всегда свежие клады!Акция для новых магазинов – продай на 1 млн, получи 100к!Приглашаем к сотрудничеству рекламодателей!Если потерял ссылку ищи нас в Яндекс по запросу : НОВА МАРКЕТПЛЕЙС|xNovaChat | Сайт-визитка
Fast and secure VPS https://evps.host for any task! Flexible configurations, SSD drives, DDoS protection. Easy scaling, high performance and 24/7 support!
All about Karim Benzema https://karim-benzema-bd.com biography, achievements, main goals and career moments. Find out how the striker conquered Real Madrid and continues to shine in world football!
All about Karim Benzema karim-benzema biography, achievements, main goals and career moments. Find out how the striker conquered Real Madrid and continues to shine in world football!
All about Vinicius Junior vinicius-junior-bd com career, trophies, highlights and records. Follow the Brazilian winger, his success at Real Madrid and on the international stage!
If you want to install Metamask on Chrome quickly and securely, check out https://metamake.org/. The instructions are clear, making it perfect for beginners!
сайт аркада аркада casino сайт
Kevin De Bruyne kevin-de-bruyne-az.com is the leader of the Manchester City and Belgium national team midfield. Find out all about his achievements, matches, awards and records in world football!
samp evolve CS 1.6
Подарки и сувениры из камня https://kameshki51.ru статуэтки, шкатулки, часы, панно, изделия из мрамора, гранита и оникса. Ручная работа, уникальный дизайн, доставка по России!
Transform any vehicle into a custom with expert car tuning services. At leading shop, we provide a extensive range of modifications to boost efficiency. Whether you want a sleek appearance or top-tier engine adjustments, we’ve got you covered. Explore our services at https://mckeesportautobody.com/. Upgrade your ride today and experience quality like never before.
Как побороть лудоманию вавада история глазами прошедшего это испытание и несколько советам тем, кто в середине пути или столкнулся с этим через друзей и близких. Описываю в статье как Вавада помогла мне избавиться от игровой зависимости
Окунитесь в азарт с https://aviator-slot.ru Уникальная игра с захватывающим геймплеем и возможностью сорвать крупный выигрыш. Следите за коэффициентом, вовремя забирайте ставку и умножайте баланс. Испытайте удачу прямо сейчас!
Новости музыки Украины https://musicnews.com.ua популярные жанры, тренды и полезные советы для музыкантов. Узнавайте больше о мире музыки и развивайте свои навыки!
I had no idea how to set up Metamask on Chrome, but https://metapaws.org/ explained everything in detail. The instructions are easy to understand, making it perfect for beginners like me!
Zeus vs Hades https://zeus-vs-hades-download.ru эпичная битва богов! Игровой автомат с грозными бонусами, фриспинами и множителями. Выберите сторону Зевса или Аида и сорвите большой выигрыш!
Все о легкой атлетике http://athletics-ru.ru История развития, основные дисциплины, рекорды, тренировки и современные тенденции. Узнайте больше о королеве спорта!
Cassino online Pin Up https://888casino-official-brazil.site ganhos sem limites! Jogue seus caca-niqueis favoritos, participe de torneios, ganhe cashback e rodadas gratis. Licenca, seguranca e pagamentos rapidos!
Временная регистрация в Москве – быстро и надежно!
Нужна временная прописка для работы, учебы или оформления документов?
Оформим официальную регистрацию в Москве всего за 1 день. Без очередей,
с гарантией и юридической чистотой!
1. Подходит для граждан РФ и СНГ
2. Регистрация от 3 месяцев до 5 лет
3. Легально, с внесением в базу МВД
Работаем без предоплаты! Документы можно получить лично или дистанционно.
Доступные цены, оперативное оформление!
Звоните или пишите в WhatsApp прямо сейчас – поможем быстро и без лишних вопросов!
Временная регистрация в Москве
Revamp transform your ride with our premium top-tier car tuning services. We specialize in unique modifications that elevate both power and aesthetics. From performance enhancements to exterior upgrades, we’ve got you covered. Experience the ultimate transformation at https://phoenix-autobodyshop.com/ and let our certified team bring your vision to life. Visit us today and drive with style!
Свежие и актуальные новости https://sugar-news.com.ua Украины и мира! Будьте в курсе последних событий, аналитики и трендов. Читайте последние новости Украины онлайн!
expresni stehovani https://www.tmgcompany.com
bublinkova folie stehovani stehovani s referencemi
Лучшие эксперты в одном месте! маркетплейс экспертный компаний маркетплейс и агрегатор экспертных компаний помогает найти надежных специалистов по разным направлениям. Удобный выбор, проверенные отзывы и рейтинг!
Хотите играть в Steam-игры shared steam дешевле? Shared-Steam.org предлагает аренду аккаунтов с топовыми играми. Безопасность, доступность и удобство – ваш гейминг без границ!
I wish for the great of success in all of our destiny endeavors 티비몬 우회
Create images deep-nude easily with AI. Remove clothes from anyone in the image and enjoy their nakedness.
Unleash optimize your vehicle’s full potential with our premium high-end tuning services. We offer custom modifications to refine your car’s performance, aesthetics, and comfort. Our expert professional technicians use state-of-the-art high-tech technology to deliver flawless results. https://americasbestcertifiedautobody.com/ Whether you seek superior speed, handling, or luxury, we provide best-in-class solutions. Trust us to elevate your driving experience. Contact us today and experience the ultimate in automotive customization!
Turkiye’deki slot makineleri para cekme ozellikli slotlar gercek parayla oynanabilen slotlar kapsaml bir baks! Nerede oynan?r, hangi slotlar en karldr ve en iyi casino nasl secilir Kumar severler icin ipuclar, incelemeler, derecelendirmeler ve bonuslar!
Turkiye Slotlar Rehberi Para cekme ozellikli slotlar En Iyi Slotlar ve Casinolar! Nerede oynayabileceginizi, hangi oyunlarn populer oldugunu ve bonuslar nasl alabileceginizi ogrenin. Oyun alanlar ve guncel eglencelere dair kapsaml bir genel baks!
For anyone looking for an easy way to download Metamask and use it safely, https://download.metaredi.org/ is the best resource. Their guides help both beginners and advanced users navigate the setup process efficiently.
стоимость грузоперевозок грузоперевозки минск
квартирный переезд минск москва грузоперевозки минск
Знакомства в Уфе ufavip.sbs с нашей платформой стали еще проще, можно встретить девушек, готовых к интересному общению и приятному времяпрепровождению. Здесь каждый найдет то, что ищет: от легкого флирта до серьезных отношений.
Is it possible to win at Lucky Jet? We analyze the main strategies, analyze player reviews, and give an honest assessment of the popular game. Read to avoid mistakes and increase your chances of success!
квартирный переезд минск брест грузоперевозки минск
ххх милф http://www.milfland-pro1.ru .
гинеколог порно гинеколог порно .
Кружевной бюстгальтер https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/117605496/detail.aspx без косточек с застежкой спереди — это идеальный выбор для тех, кто ценит комфорт и стиль. Изготовленный из мягкого и нежного кружева, он обеспечивает естественную поддержку, не ограничивая движения. Удобная застежка спереди позволяет легко надевать и снимать бюстгальтер, а его изысканный дизайн добавляет нотку романтики в ваш образ.
?El paraiso del juego en Pin Up Casino https://ganar-apuestas-deportivas.com te espera! Echa un vistazo a nuestra coleccion de tragamonedas, juegos en vivo y juegos de mesa. Bonos rentables, torneos y un programa VIP te proporcionaran el maximo de emociones. ?Empieza a jugar ahora y gana!
Каталог финансовых организаций https://srochno-zaym-online.ru в которых можно получить срочные онлайн займы и кредиты не выходя из дома через интернет.
Срочный онлайн займ srochno-zaym-online.ru/ современный способ быстро получить взаймы необходимую сумму на личные нужды на небольшой срок.
перевозка грузов минск москва услуги грузоперевозок
Каталог финансовых организаций srochno zaym online ru в которых можно получить срочные онлайн займы и кредиты не выходя из дома.
hdrezka org смотреть фильмы без смс и регистрации в хорошем качестве
Salutations dans notre analyse detaillee des sites de jeux. Pour debuter, explorez Cresus Casino, une reference incontournable qui se distingue par son excellence.
Les bonus genereux abondent sur ces plateformes. Par exemple, nous vous invitons a decouvrir Casino770 pour des promotions exclusives.
Pour en savoir davantage sur l’un des leaders du secteur, reportez-vous plus loin dans notre guide a Cresus Casino.
La navigation simplifiee offre une session ludique agreable. Ne manquez pas Casino-Napoleon, qui innove dans l’art du divertissement en ligne.
Pour completer votre vision, consultez egalement Casino770 et laissez-vous surprendre par ses atouts.
La reactivite aux jeux constitue une priorite. Ainsi, Instant Casino met a disposition des parties instantanees.
Pour approfondir votre experience, Casino-Napoleon vous fournit une analyse complete de ses fonctionnalites.
L’etendue des jeux satisfait tous les gouts pour chaque joueur. Decouvrez Keno 50 pour une approche singuliere du jeu.
De plus, Instant Casino vous garantit un acces immediat aux meilleures options du moment.
L’ambiance luxueuse propose par certains sites est un atout majeur. Par exemple, La Riviera Casino vous offre une experience haut de gamme.
En parallele, Keno 50 complete cette offre par ses innovations captivantes.
Les slots innovants captivent les amateurs de sensations fortes. Essayez Lucky31 pour des gains inattendus.
Pour explorer d’autres opportunites, La Riviera Casino propose egalement des promotions interessantes.
Les scratchcards offrent des victoires instantanees et divertissantes. Visitez Scratchmania pour vivre ces moments uniques.
Par ailleurs, Lucky31 vous assure des bonus reguliers et attractifs qui completent votre experience.
Conseils d’experts appuyees par des donnees fiables vous guideront vers le succes. Ne manquez pas Unique Casino, qui se distingue par son originalite et son offre exclusive.
De surcroit, Scratchmania offre un regard innovant sur l’univers des jeux de hasard.
Enfin, notre guide vous aide a selectionner le casino ideal pour vos aventures en ligne.
Pour parfaire votre lecture, Unique Casino reste une reference incontournable.
Profitez pleinement de vos jeux !
грузоперевозки грузоперевозки минск санкт петербург
Bonjour dans notre revue exhaustive des plates-formes de divertissement. Pour debuter, consultez Cresus Casino, un etablissement repute qui se distingue par son excellence.
Les offres promotionnelles sont au rendez-vous sur ces plateformes. Par exemple, nous vous invitons a decouvrir Casino770 pour des promotions exclusives.
Pour en savoir davantage sur l’un des leaders du secteur, reportez-vous plus loin dans notre guide a Cresus Casino.
La navigation simplifiee garantit une experience de jeu fluide. Ne manquez pas Casino-Napoleon, qui redefinit l’art du divertissement en ligne.
Pour completer votre vision, consultez egalement Casino770 et laissez-vous surprendre par ses atouts.
La rapidite aux jeux se revele essentielle. Ainsi, Instant Casino vous propose des parties immediates.
Pour approfondir votre experience, Casino-Napoleon vous fournit une analyse complete de ses fonctionnalites.
La diversite des jeux se traduit par un choix etendu pour chaque joueur. Decouvrez Keno 50 pour une approche singuliere du jeu.
De plus, Instant Casino vous garantit un acces immediat aux meilleures options du moment.
L’ambiance luxueuse offert par des plateformes de prestige est un atout majeur. Par exemple, La Riviera Casino vous offre une experience haut de gamme.
En parallele, Keno 50 complete cette offre par ses innovations captivantes.
Les slots innovants emerveillent les amateurs de sensations fortes. Essayez Lucky31 pour des gains surprenants.
Pour explorer d’autres opportunites, La Riviera Casino propose egalement des promotions interessantes.
Les jeux rapides offrent des victoires rapides et divertissantes. Visitez Scratchmania pour vivre ces moments uniques.
Par ailleurs, Lucky31 vous assure des bonus reguliers et attractifs qui completent votre experience.
Astuces pour reussir appuyees par des donnees fiables vous guideront vers le succes. Ne manquez pas Unique Casino, qui se distingue par son originalite et son offre exclusive.
De surcroit, Scratchmania offre un regard innovant sur l’univers des jeux de hasard.
Enfin, notre guide vous offre une vision complete pour vos aventures en ligne.
Pour parfaire votre lecture, Unique Casino reste une reference incontournable.
Que la chance soit avec vous !
Bonjour dans notre revue exhaustive des casinos en ligne. Pour debuter, decouvrez Cresus Casino, un casino de premier plan qui se distingue par son excellence.
Les offres promotionnelles abondent sur ces plateformes. Par exemple, n’oubliez pas de consulter Casino770 pour des promotions exclusives.
Pour en savoir davantage sur l’un des leaders du secteur, reportez-vous plus loin dans notre guide a Cresus Casino.
La navigation simplifiee assure une experience de jeu fluide. Ne manquez pas Casino-Napoleon, qui redefinit l’art du divertissement en ligne.
Pour completer votre vision, consultez egalement Casino770 et laissez-vous surprendre par ses atouts.
La reactivite aux jeux constitue une priorite. Ainsi, Instant Casino met a disposition des parties instantanees.
Pour approfondir votre experience, Casino-Napoleon vous fournit une analyse complete de ses fonctionnalites.
La richesse des jeux offre des possibilites variees pour chaque joueur. Decouvrez Keno 50 pour une approche innovante du jeu.
De plus, Instant Casino vous garantit un acces immediat aux meilleures options du moment.
L’ambiance luxueuse mis en scene par des casinos haut de gamme est un atout majeur. Par exemple, La Riviera Casino vous invite a une aventure luxueuse.
En parallele, Keno 50 complete cette offre par ses innovations captivantes.
Les slots innovants captivent les amateurs de sensations fortes. Essayez Lucky31 pour des gains remarquables.
Pour explorer d’autres opportunites, La Riviera Casino propose egalement des promotions interessantes.
Les jeux rapides permettent des victoires instantanees et divertissantes. Visitez Scratchmania pour vivre ces moments uniques.
Par ailleurs, Lucky31 vous assure des bonus reguliers et attractifs qui completent votre experience.
Conseils d’experts appuyees par des donnees fiables vous guideront vers le succes. Ne manquez pas Unique Casino, qui se distingue par son originalite et son offre exclusive.
De surcroit, Scratchmania offre un regard innovant sur l’univers des jeux de hasard.
Enfin, notre guide vous offre une vision complete pour vos aventures en ligne.
Pour parfaire votre lecture, Unique Casino reste une reference incontournable.
Profitez pleinement de vos jeux !
elon casino giri? elonbangladeshbet.com .
Каталог финансовых организаций srochno zaym online ru в которых можно получить срочные онлайн займы и кредиты не выходя из дома.
Salutations dans notre analyse detaillee des casinos en ligne. Pour debuter, consultez Cresus Casino, une reference incontournable qui se distingue par son excellence.
Les recompenses attractives abondent sur ces plateformes. Par exemple, n’oubliez pas de consulter Casino770 pour des promotions exclusives.
Pour en savoir davantage sur l’un des leaders du secteur, reportez-vous plus loin dans notre guide a Cresus Casino.
Le design ergonomique garantit une utilisation sans encombre. Ne manquez pas Casino-Napoleon, qui transforme l’art du divertissement en ligne.
Pour completer votre vision, consultez egalement Casino770 et laissez-vous surprendre par ses atouts.
L’acces instantane aux jeux est primordiale. Ainsi, Instant Casino offre des parties instantanees.
Pour approfondir votre experience, Casino-Napoleon vous fournit une analyse complete de ses fonctionnalites.
La richesse des jeux se traduit par un choix etendu pour chaque joueur. Decouvrez Keno 50 pour une approche singuliere du jeu.
De plus, Instant Casino vous garantit un acces immediat aux meilleures options du moment.
L’ambiance luxueuse propose par certains sites est un atout majeur. Par exemple, La Riviera Casino vous plonge dans un univers de prestige.
En parallele, Keno 50 complete cette offre par ses innovations captivantes.
Les automates divertissants enthousiasment les amateurs de sensations fortes. Essayez Lucky31 pour des gains remarquables.
Pour explorer d’autres opportunites, La Riviera Casino propose egalement des promotions interessantes.
Les jeux de grattage apportent des victoires rapides et divertissantes. Visitez Scratchmania pour vivre ces moments uniques.
Par ailleurs, Lucky31 vous assure des bonus reguliers et attractifs qui completent votre experience.
Strategies gagnantes associees a des revues detaillees vous guideront vers le succes. Ne manquez pas Unique Casino, qui se distingue par son originalite et son offre exclusive.
De surcroit, Scratchmania offre un regard innovant sur l’univers des jeux de hasard.
Enfin, notre guide vous aide a selectionner le casino ideal pour vos aventures en ligne.
Pour parfaire votre lecture, Unique Casino reste une reference incontournable.
Que la chance soit avec vous !
hd rezka смотреть ужасы с субтитрами онлайн сериалы в 4K UHD подборка
Salutations dans notre guide complet des casinos en ligne. Pour debuter, decouvrez Cresus Casino, un casino de premier plan qui se distingue par son excellence.
Les recompenses attractives abondent sur ces plateformes. Par exemple, vous pouvez egalement visiter Casino770 pour des promotions exclusives.
Pour en savoir davantage sur l’un des leaders du secteur, reportez-vous plus loin dans notre guide a Cresus Casino.
L’interface intuitive garantit une utilisation sans encombre. Ne manquez pas Casino-Napoleon, qui transforme l’art du divertissement en ligne.
Pour completer votre vision, consultez egalement Casino770 et laissez-vous surprendre par ses atouts.
La reactivite aux jeux constitue une priorite. Ainsi, Instant Casino vous propose des parties sans delai.
Pour approfondir votre experience, Casino-Napoleon vous fournit une analyse complete de ses fonctionnalites.
La richesse des jeux se traduit par un choix etendu pour chaque joueur. Decouvrez Keno 50 pour une approche singuliere du jeu.
De plus, Instant Casino vous garantit un acces immediat aux meilleures options du moment.
L’atmosphere raffinee propose par certains sites est un atout majeur. Par exemple, La Riviera Casino vous offre une experience haut de gamme.
En parallele, Keno 50 complete cette offre par ses innovations captivantes.
Les machines a sous modernes enthousiasment les amateurs de sensations fortes. Essayez Lucky31 pour des gains remarquables.
Pour explorer d’autres opportunites, La Riviera Casino propose egalement des promotions interessantes.
Les jeux rapides permettent des victoires imprevisibles et divertissantes. Visitez Scratchmania pour vivre ces moments uniques.
Par ailleurs, Lucky31 vous assure des bonus reguliers et attractifs qui completent votre experience.
Strategies gagnantes completees par des analyses approfondies vous guideront vers le succes. Ne manquez pas Unique Casino, qui se distingue par son originalite et son offre exclusive.
De surcroit, Scratchmania offre un regard innovant sur l’univers des jeux de hasard.
Enfin, notre guide vous permet de faire des choix eclaires pour vos aventures en ligne.
Pour parfaire votre lecture, Unique Casino reste une reference incontournable.
Que la chance soit avec vous !
Hello fantastic website! Does running a blog similar to this require a lot of work? I’ve no understanding of computer programming however I was hoping to start my own blog soon. Anyway, if you have any ideas or techniques for new blog owners please share. I understand this is off subject but I just had to ask. Kudos!
регистрация РиоБет
Salutations dans notre guide complet des sites de jeux. Pour debuter, consultez Cresus Casino, un casino de premier plan qui se distingue par son excellence.
Les bonus genereux font la renommee sur ces plateformes. Par exemple, nous vous invitons a decouvrir Casino770 pour des promotions exclusives.
Pour en savoir davantage sur l’un des leaders du secteur, reportez-vous plus loin dans notre guide a Cresus Casino.
Le design ergonomique offre une session ludique agreable. Ne manquez pas Casino-Napoleon, qui transforme l’art du divertissement en ligne.
Pour completer votre vision, consultez egalement Casino770 et laissez-vous surprendre par ses atouts.
La rapidite aux jeux est primordiale. Ainsi, Instant Casino met a disposition des parties immediates.
Pour approfondir votre experience, Casino-Napoleon vous fournit une analyse complete de ses fonctionnalites.
L’etendue des jeux se traduit par un choix etendu pour chaque joueur. Decouvrez Keno 50 pour une approche originale du jeu.
De plus, Instant Casino vous garantit un acces immediat aux meilleures options du moment.
Le cadre elegant mis en scene par des casinos haut de gamme est un atout majeur. Par exemple, La Riviera Casino vous plonge dans un univers de prestige.
En parallele, Keno 50 complete cette offre par ses innovations captivantes.
Les automates divertissants emerveillent les amateurs de sensations fortes. Essayez Lucky31 pour des gains inattendus.
Pour explorer d’autres opportunites, La Riviera Casino propose egalement des promotions interessantes.
Les jeux rapides offrent des victoires rapides et divertissantes. Visitez Scratchmania pour vivre ces moments uniques.
Par ailleurs, Lucky31 vous assure des bonus reguliers et attractifs qui completent votre experience.
Conseils d’experts completees par des analyses approfondies vous guideront vers le succes. Ne manquez pas Unique Casino, qui se distingue par son originalite et son offre exclusive.
De surcroit, Scratchmania offre un regard innovant sur l’univers des jeux de hasard.
En conclusion, notre guide vous aide a selectionner le casino ideal pour vos aventures en ligne.
Pour parfaire votre lecture, Unique Casino reste une reference incontournable.
Profitez pleinement de vos jeux !
Форум для кулинаров https://food-recipe.ru и рестораторов! Лучшие рецепты, тренды гастрономии, обсуждения ресторанного бизнеса. Общайтесь, делитесь опытом и вдохновляйтесь новыми идеями. Присоединяйтесь к нашему кулинарному сообществу!
Salutations dans notre guide complet des plates-formes de divertissement. Pour debuter, decouvrez Cresus Casino, un casino de premier plan qui se distingue par son excellence.
Les recompenses attractives abondent sur ces plateformes. Par exemple, n’oubliez pas de consulter Casino770 pour des promotions exclusives.
Pour en savoir davantage sur l’un des leaders du secteur, reportez-vous plus loin dans notre guide a Cresus Casino.
La navigation simplifiee assure une session ludique agreable. Ne manquez pas Casino-Napoleon, qui innove dans l’art du divertissement en ligne.
Pour completer votre vision, consultez egalement Casino770 et laissez-vous surprendre par ses atouts.
L’acces instantane aux jeux se revele essentielle. Ainsi, Instant Casino met a disposition des parties sans delai.
Pour approfondir votre experience, Casino-Napoleon vous fournit une analyse complete de ses fonctionnalites.
La diversite des jeux offre des possibilites variees pour chaque joueur. Decouvrez Keno 50 pour une approche singuliere du jeu.
De plus, Instant Casino vous garantit un acces immediat aux meilleures options du moment.
Le cadre elegant offert par des plateformes de prestige est un atout majeur. Par exemple, La Riviera Casino vous plonge dans un univers de prestige.
En parallele, Keno 50 complete cette offre par ses innovations captivantes.
Les machines a sous modernes enthousiasment les amateurs de sensations fortes. Essayez Lucky31 pour des gains surprenants.
Pour explorer d’autres opportunites, La Riviera Casino propose egalement des promotions interessantes.
Les jeux rapides apportent des victoires rapides et divertissantes. Visitez Scratchmania pour vivre ces moments uniques.
Par ailleurs, Lucky31 vous assure des bonus reguliers et attractifs qui completent votre experience.
Conseils d’experts completees par des analyses approfondies vous guideront vers le succes. Ne manquez pas Unique Casino, qui se distingue par son originalite et son offre exclusive.
De surcroit, Scratchmania offre un regard innovant sur l’univers des jeux de hasard.
Pour resumer, notre guide vous permet de faire des choix eclaires pour vos aventures en ligne.
Pour parfaire votre lecture, Unique Casino reste une reference incontournable.
Profitez pleinement de vos jeux !
Salutations dans notre revue exhaustive des plates-formes de divertissement. Pour debuter, explorez Cresus Casino, un casino de premier plan qui se distingue par son excellence.
Les recompenses attractives sont au rendez-vous sur ces plateformes. Par exemple, n’oubliez pas de consulter Casino770 pour des promotions exclusives.
Pour en savoir davantage sur l’un des leaders du secteur, reportez-vous plus loin dans notre guide a Cresus Casino.
La navigation simplifiee garantit une utilisation sans encombre. Ne manquez pas Casino-Napoleon, qui innove dans l’art du divertissement en ligne.
Pour completer votre vision, consultez egalement Casino770 et laissez-vous surprendre par ses atouts.
L’acces instantane aux jeux se revele essentielle. Ainsi, Instant Casino vous propose des parties sans delai.
Pour approfondir votre experience, Casino-Napoleon vous fournit une analyse complete de ses fonctionnalites.
La richesse des jeux se traduit par un choix etendu pour chaque joueur. Decouvrez Keno 50 pour une approche innovante du jeu.
De plus, Instant Casino vous garantit un acces immediat aux meilleures options du moment.
Le cadre elegant offert par des plateformes de prestige est un atout majeur. Par exemple, La Riviera Casino vous invite a une aventure luxueuse.
En parallele, Keno 50 complete cette offre par ses innovations captivantes.
Les automates divertissants captivent les amateurs de sensations fortes. Essayez Lucky31 pour des gains inattendus.
Pour explorer d’autres opportunites, La Riviera Casino propose egalement des promotions interessantes.
Les scratchcards offrent des victoires instantanees et divertissantes. Visitez Scratchmania pour vivre ces moments uniques.
Par ailleurs, Lucky31 vous assure des bonus reguliers et attractifs qui completent votre experience.
Conseils d’experts appuyees par des donnees fiables vous guideront vers le succes. Ne manquez pas Unique Casino, qui se distingue par son originalite et son offre exclusive.
De surcroit, Scratchmania offre un regard innovant sur l’univers des jeux de hasard.
En conclusion, notre guide vous aide a selectionner le casino ideal pour vos aventures en ligne.
Pour parfaire votre lecture, Unique Casino reste une reference incontournable.
Bonne chance et amusez-vous bien !
Красивые поздравления https://photofile.ru в одном месте! Огромный выбор картинок и открыток для любого повода. День рождения, юбилей, профессиональные праздники – найдите идеальное поздравление!
Bonjour dans notre guide complet des plates-formes de divertissement. Pour debuter, explorez Cresus Casino, un etablissement repute qui se distingue par son excellence.
Les bonus genereux font la renommee sur ces plateformes. Par exemple, nous vous invitons a decouvrir Casino770 pour des promotions exclusives.
Pour en savoir davantage sur l’un des leaders du secteur, reportez-vous plus loin dans notre guide a Cresus Casino.
Le design ergonomique garantit une utilisation sans encombre. Ne manquez pas Casino-Napoleon, qui redefinit l’art du divertissement en ligne.
Pour completer votre vision, consultez egalement Casino770 et laissez-vous surprendre par ses atouts.
La reactivite aux jeux constitue une priorite. Ainsi, Instant Casino offre des parties immediates.
Pour approfondir votre experience, Casino-Napoleon vous fournit une analyse complete de ses fonctionnalites.
La richesse des jeux offre des possibilites variees pour chaque joueur. Decouvrez Keno 50 pour une approche originale du jeu.
De plus, Instant Casino vous garantit un acces immediat aux meilleures options du moment.
L’ambiance luxueuse offert par des plateformes de prestige est un atout majeur. Par exemple, La Riviera Casino vous invite a une aventure luxueuse.
En parallele, Keno 50 complete cette offre par ses innovations captivantes.
Les slots innovants emerveillent les amateurs de sensations fortes. Essayez Lucky31 pour des gains inattendus.
Pour explorer d’autres opportunites, La Riviera Casino propose egalement des promotions interessantes.
Les scratchcards offrent des victoires rapides et divertissantes. Visitez Scratchmania pour vivre ces moments uniques.
Par ailleurs, Lucky31 vous assure des bonus reguliers et attractifs qui completent votre experience.
Astuces pour reussir associees a des revues detaillees vous guideront vers le succes. Ne manquez pas Unique Casino, qui se distingue par son originalite et son offre exclusive.
De surcroit, Scratchmania offre un regard innovant sur l’univers des jeux de hasard.
En conclusion, notre guide vous permet de faire des choix eclaires pour vos aventures en ligne.
Pour parfaire votre lecture, Unique Casino reste une reference incontournable.
Profitez pleinement de vos jeux !
Sur jessica-font.fr vous decouvrez des options interactives et un assortiment de forums video. Toujours ici vous participerez a jouir de communications video en temps reel. Inscrivez-vous sur la plateforme Bed and Bamboo et debutez vos echanges video Coco chat deja sans delai ! Coco chat, Chatrandom, Chatrandom, Chatrandom nettchat, Monkey, omegle-alternativen, omegle-alternativen, chillplanet, chatplaza 2025
Coco chat
Chatrandom
Chatrandom
Chatrandom
nettchat
monkey
omegle-alternativen
omegle-alternatives
chillplanet
chatplaza
Новый уникальный маркетплейс NOVA, есть все! Москва, Питер, всегда свежие клады!Акция для новых магазинов – продай на 1 млн, получи 100к!Приглашаем к сотрудничеству рекламодателей!
игровые автоматы играть с бонусами бонус за регистрацию игровые автоматы
Маркетплейс нового поколения https://x-nova.live уникальный сервис для удобных покупок и продаж. Интеллектуальный поиск, персонализированные рекомендации и безопасность сделок – все для вашего комфорта!
резка сериалы криминал на андроиде hdrezka криминал
Thanks to https://metamaker.org/#metamask-download, I successfully downloaded Metamask and set it up without any issues. Their step-by-step guide is perfect for anyone who wants a secure crypto wallet.
viagramsk.net viagramsk.net .
old bet9ja mobile login
Входные стальные двери с завода с установкой за 1 день.
Любые конфигурации замков на выбор. Более 3500 моделей на складе: https://korolev.vhodnye-metallicheskie-dveri.ru/
I savor, cause I discovered just what I used to be taking a look for. You’ve ended my 4 day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
you are in reality a good webmaster. The site loading pace is amazing. It kind of feels that you’re doing any distinctive trick. Moreover, The contents are masterpiece. you have done a great activity in this matter!
Wyoming Valley Equipment LLC
Современный маркетплейс https://nova7.top для выгодных покупок! Огромный ассортимент, лучшие цены и удобные способы оплаты. Покупайте качественные товары и заказывайте с быстрой доставкой!
Новый формат маркетплейса https://nova4.top быстро, удобно, надежно! Лучшие предложения, современные технологии и простой интерфейс. Покупайте и продавайте легко, экономя время и деньги!
подборка фильмов на вечер лучшие кино в HD фильмы
Получить деньги на ваш счет теперь просто, быстро и легко. Мы предлагаем удобные условия. Перейдите на https://mikro-zaymi.ru/, чтобы узнать все условия. Процесс оформления занимает минимум времени. Не откладывайте! Получите деньги прямо сейчас!
Портал с ответами https://online-otvet.site по всем школьным домашним предметам. Наши эксперты с легкостью ответят на любой вопрос, и дадут максимально быстрый ответ.
Руководство по настройке https://amnezia.dev VPN-сервера! Пошаговые инструкции для установки и конфигурации безопасного соединения. Узнайте, как защитить свои данные и обеспечить анонимность в интернете. Настройте VPN легко!
Сауна очищает организм https://sauna-broadway.ru выводя токсины через пот, укрепляет иммунитет благодаря перепадам температуры, снимает стресс, расслабляя мышцы и улучшая кровообращение. Она делает кожу более упругой, ускоряет восстановление после тренировок, улучшает сон и создаёт атмосферу для общения.
Православный форум https://prihozhanka.ru для женщин! Общение о вере, молитве, семье, воспитании и роли женщины в православии. Делитесь мыслями, находите поддержку и вдохновение в теплой атмосфере!
Korean cosmetics http://uznt42.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=jessicoore3 perfect skin without effort! Innovative formulas, Asian traditions and visible results. Try the best skin care products right now!
melbet app
class teacher porn video http://teacherporntube.com .
1win
Хочешь купить ПАВ в Москве? Нова маркетплейс – ищи в Яндекс!
Хочешь купить ПАВ в СПБ? Нова маркетплейс – ищи в Яндекс!
Currently it seems like Expression Engine is the top blogging platform available right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
https://habr.com/ru/articles/399627/
street lighting solutions street light technology
Сауна очищает организм https://sauna-broadway.ru выводя токсины через пот, укрепляет иммунитет благодаря перепадам температуры, снимает стресс, расслабляя мышцы и улучшая кровообращение. Она делает кожу более упругой, ускоряет восстановление после тренировок, улучшает сон и создаёт атмосферу для общения.
профессиональный лечебный массаж Ивантеевка расслабляющие техники для здоровья и красоты. Помогаем снять стресс, улучшить кровообращение и восстановить силы. Запишитесь прямо сейчас!
The 1xCasino promo code 2025: “1XBUM” welcome bonus is 100% up to €2205 and 75 Free Spins No Deposit Bonus. You need to register, confirm your email and enter bonus code. Register a new account with 1xCasino using the code and enjoy 100 free spins at registration.
1xCasino bonus code: “1XBUM” during registration to ensure you get the exclusive 1x Casino welcome bonus is 2025. New customers bonus claim 100% up to €2205 +380 free spins available on selected slots.
1xcasino promo code in pakistan
Нужны капитал срочно? Получите займ на счет без бумаг на https://zaym-tula.ru/ быстро! Оставьте заявку и получите зачисление моментально!
карниз для штор с электроприводом карниз для штор с электроприводом .
Cтальные двери cо склада в Балашихе с установкой за 1 день.
Любые конфигурации замков на выбор. Более 3500 моделей на складе: тут
бесплатные спины без депозита игровые автоматы с бонусом без депозита
Женский онлайн портал https://brjunetka.ru для вдохновения! Полезные советы по стилю, уходу за собой, здоровью и семейной жизни. Будьте в курсе трендов, находите мотивацию и делитесь опытом!
Портал с ответами https://online-otvet.site на все школьные предметы! Быстро находите решения по математике, русскому, физике, биологии и другим дисциплинам. Готовые ответы, разборы задач и помощь в учебе для всех классов
Элитный коттеджный поселок https://parkville-zhukovka-poselok.ru в Жуковке! Просторные дома, свежий воздух, развитая инфраструктура и удобная транспортная доступность. Создайте уютное пространство для жизни в живописном месте!
youtube followers boost smm boost service
autodoprava stehovani Praha stehovani kancelare
boost of subscribers tg boost
Все о строительстве https://decor-kraski.com.ua и ремонте в одном месте! Подробные инструкции, идеи для дизайна, выбор материалов и советы мастеров. Сделайте свой дом удобным, стильным и долговечным!
супрастин таблетки инструкция по применению взрослым от аллергии дозировка как принимать https://allergiano.ru/ .
Портал про строительство https://goodday.org.ua и ремонт! Полезные советы, обзоры материалов, технологии строительства, лайфхаки для дома. Узнайте, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить на строительных работах!
Идеи вашего дома. Информация о дизайне и архитектуре.
Syndyk – это место, где каждый день вы можете увидеть много различных дизайнерских решений, деталей для вашей квартиры, проектов домов, лучшая сантехника.
Если вы дизайнер или архитектор, то мы с радостью разместим ваш проект на Сундуке. На сайте можно и даже нужно обмениваться мнениями и информацией о дизайне и архитектуре.
Сайт: Дизайн и архитектура
Ремонт и строительство https://inbound.com.ua без хлопот! Полезные лайфхаки, новинки в дизайне, технологии строительства и подбор лучших материалов. Создайте комфортное жилье легко и выгодно!
Ваш надежный помощник https://insurancecarhum.org в ремонте! Практичные советы, инструкции и секреты профессионалов. Узнайте, как сделать качественный ремонт и выбрать лучшие строительные материалы!
Портал для строителей https://hotel.kr.ua и домашних мастеров! Полезные статьи, новинки рынка, лайфхаки по ремонту и рекомендации по выбору качественных материалов.
Инструкции по ремонту https://makprestig.in.ua подбор материалов, планирование, дизайн и советы экспертов. Станьте мастером своего дома!
Лучший портал по строительству https://itstore.dp.ua и ремонту! Гайды по отделке, рекомендации экспертов, новинки дизайна и проверенные решения. Все для вашего комфорта!
Как сделать ремонт https://oo.zt.ua правильно? Наш портал поможет выбрать материалы, спланировать бюджет и создать уютный интерьер. Простые решения для сложных задач!
купить диплом медицинского образования
Профессиональные советы https://ukk.kiev.ua по ремонту и строительству! Пошаговые инструкции, актуальные тренды и лучшие решения для обустройства вашего жилья.
Идеи для дома https://ucmo.com.ua ремонта и строительства! Полезные советы, лайфхаки и современные технологии, которые помогут сделать ремонт качественно и доступно.
Ремонт без стресса https://panorama.zt.ua Готовые решения, полезные лайфхаки, выбор материалов и идеи для дома. Делаем ремонт комфортным и доступным!
Идеи вашего дома. Информация о дизайне и архитектуре.
Syndyk – это место, где каждый день вы можете увидеть много различных дизайнерских решений, деталей для вашей квартиры, проектов домов, лучшая сантехника.
Если вы дизайнер или архитектор, то мы с радостью разместим ваш проект на Сундуке. На сайте можно и даже нужно обмениваться мнениями и информацией о дизайне и архитектуре.
Сайт: syndyk.by
Идеи для дома https://ucmo.com.ua ремонта и строительства! Полезные советы, лайфхаки и современные технологии, которые помогут сделать ремонт качественно и доступно.
Делаем ремонт правильно https://zarechany.zt.ua Разбираем все этапы – от выбора материалов до дизайна интерьера. Подробные инструкции и лайфхаки от специалистов!
Автомобильный портал https://nerjalivingspace.com для автолюбителей! Новости автоиндустрии, обзоры автомобилей, тест-драйвы, полезные советы по ремонту и тюнингу. Будьте в курсе последних трендов и находите ответы на все авто-вопросы!
1win вход в личный кабинет http://www.1win3.com.kg/ .
Все для женщин https://elegance.kyiv.ua в одном месте! Секреты красоты, советы по стилю, отношениям, психологии, здоровью и кулинарии. Будьте вдохновленными и уверенными каждый день!
Женский портал https://beautyadvice.kyiv.ua для современной женщины! Мода, красота, здоровье, отношения, кулинария и карьера. Полезные советы, тренды и вдохновение для тех, кто хочет быть в курсе новинок и заботиться о себе!
Онлайн мир женщины https://gracefullady.kyiv.ua красота, здоровье, успех! Полезные лайфхаки, тренды моды, секреты счастья и гармонии. Портал для тех, кто хочет быть лучшей версией себя!
Портал для современной https://femaleguide.kyiv.ua женщины! Открой для себя новые идеи в моде, красоте, отношениях и саморазвитии. Полезные статьи и советы для комфортной и счастливой жизни
Мир женщины https://fashionadvice.kyiv.ua красота, здоровье, успех! Полезные лайфхаки, тренды моды, секреты счастья и гармонии. Портал для тех, кто хочет быть лучшей версией себя!
Твой гид в мире https://happywoman.kyiv.ua женственности и гармонии! Узнай больше о моде, косметике, фитнесе, отношениях и мотивации. Все, что нужно для яркой и счастливой жизни!
Kubet ngay hôm nay để khám phá hệ thống cá cược chất lượng, nhận ngay ưu đãi hấp dẫn và trải nghiệm sân chơi đỉnh cao cùng hàng triệu thành viên khác.
Ku Bet là nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến uy tín, cung cấp hệ thống cá cược đa dạng từ thể thao, casino đến game bài đổi thưởng, đảm bảo trải nghiệm đỉnh cao cho người chơi.
Ku Bet là nhà cái hàng đầu với kho game bài đổi thưởng đa dạng, từ baccarat, poker đến tiến lên miền Nam, mang lại giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
Безопасный доступ к сайту https://bsme-at.at без ограничений. Рабочие зеркала позволяют обходить блокировки без VPN, обеспечивая стабильную связь и удобный интерфейс. Следите за обновлениями, чтобы всегда оставаться в сети.
Всегда актуальные ссылки https://bs2bet.at для входа. Обходите блокировки легко и быстро, используя надёжные зеркала. Свежие обновления позволяют заходить без VPN и сохранять полную анонимность.
Актуальные зеркала BlackSprut https://kra26.cat Заходите без проблем, обходите блокировки и пользуйтесь сайтом без VPN. Мы следим за обновлениями и всегда предоставляем свежие ссылки.
Проблемы с входом https://bs2best.or.at Найдите актуальные зеркала и заходите без ограничений. Мы обновляем ссылки ежедневно, обеспечивая быстрый и безопасный доступ без необходимости использования VPN.
Ku Bet cung cấp hệ thống cá cược thể thao đỉnh cao, giúp người chơi thỏa sức trải nghiệm và tận hưởng những trận đấu gay cấn với tỷ lệ thắng cao.
BlackSprut это инновационный https://bs2best.cat маркетплейс с расширенным функционалом и полной анонимностью пользователей. Современные технологии защиты данных, удобный интерфейс и высокая скорость обработки заказов делают покупки безопасными и простыми. Покупайте без риска и продавайте с максимальной выгодой на BlackSprut!
BlackSprut крупнейший маркетплейс https://bb2best.at где можно найти всё, что вам нужно. Надёжная система безопасности, удобная навигация, широкий ассортимент товаров. Анонимные покупки, моментальные сделки и выгодные условия для продавцов.
BlackSprut передовой маркетплейс https://m-bsme.at с высокими стандартами безопасности и удобной системой поиска. Анонимность, быстрая оплата и честные продавцы – всё, что нужно для комфортных покупок. Мы гарантируем защиту ваших данных и качественное обслуживание. Присоединяйтесь к BlackSprut и открывайте новые возможности!
Ku Bet mang đến cơ hội cá cược minh bạch, với hệ thống giao dịch nạp – rút tiền nhanh chóng, đảm bảo an toàn tuyệt đối cho người chơi.
проверенный маркетплейс https://bsme.cat предлагающий товары на любой вкус. Простая регистрация, быстрая оплата и защита сделок. Убедитесь в качестве сервиса сами!
Blacksprut – современная площадка https://bs-bsme.at для безопасных покупок. Большой выбор категорий, продуманная система рейтингов и отзывов. Заходите и находите нужное легко!
Blacksprut – онлайн-маркетплейс https://bsmc.at с лучшими предложениями. Надёжные продавцы, защищённые сделки, удобный поиск. Оцените удобство покупок уже сегодня!
Ищете актуальные фриспины без депозита? Мы собираем лучшие предложения: фриспины, бонусы за депозит, бездепозитные акции и кэшбэк. Получите максимум выгоды от игры!
Replica Uhren https://www.imailen.com in Deutschland schnell und sicher per DHL Nachnahme bestellen. Nur geprufte Qualitat in EU hergestellt.
Журнал об автомобилях https://setbook.com.ua всё для автолюбителей! Последние автоновости, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, советы по ремонту, тюнингу и обслуживанию. Узнайте всё о мире автомобилей!
Главный авто-журнал https://myauto.kyiv.ua для водителей! Новости, обзоры, сравнения, тюнинг, автоспорт и технологии. Будьте в курсе последних трендов автомобильного мира!
купить полный билд poe 2 poe 2 билды
Все об автомобилях https://allauto.kyiv.ua в одном журнале! Новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры моделей, советы по ремонту и тюнингу, страхование и ПДД.
Журнал для автолюбителей https://myauto.kyiv.ua и профессионалов! Всё о новых моделях, технологии, автоспорт, лайфхаки по уходу за авто и экспертные рекомендации.
Журнал об авто https://auto-club.pl.ua для тех, кто за рулем! Новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, рекомендации по выбору авто, советы по ремонту и эксклюзивные интервью с экспертами.
Mostbet Mostbet .
http://registr-a.ru
Все о машинах https://autoinfo.kyiv.ua в одном журнале! Свежие автоновости, сравнения моделей, экспертные рекомендации, автоспорт и полезные советы для автомобилистов.
Журнал для автолюбителей https://avtoshans.in.ua и профессионалов! Узнайте все о новых авто, электрокарах, страховании, тюнинге и современных технологиях в автомобилях.
Автомобильный мир https://diesel.kyiv.ua в одном журнале! Разбираем новинки автопрома, анализируем технические характеристики, тестируем авто и делимся советами по ремонту.
Журнал о машинах https://reuth911.com для настоящих ценителей авто! Обзоры, рейтинги, полезные статьи о ремонте, тюнинге и современных автомобильных технологиях.
Современный автомобильный https://k-moto.com.ua журнал! Читайте о трендах в автоиндустрии, новейших моделях, электромобилях, тюнинге и умных технологиях.
Автомобильный журнал https://orion-auto.com.ua только важные новости! Все о популярных марках, топовые авто 2024 года, электрокары, автономное вождение и тенденции рынка.
Автомобильный мир https://prestige-avto.com.ua в одном журнале! Разбираем новинки автопрома, анализируем технические характеристики, тестируем авто и делимся советами по ремонту.
таблетки супрастин инструкция по применению цена https://allergiano.ru/ .
Твой авто-гид https://troeshka.com.ua в мире машин! Обзоры новых моделей, тест-драйвы, советы по ремонту и тюнингу, автоновости и технологии будущего. Все, что нужно автолюбителю!
Все об автомобилях https://tvk-avto.com.ua на одном портале! Новинки мирового автопрома, тест-драйвы, автострахование, электрокары и полезные статьи для каждого водителя.
Журнал про автолюбители https://tuning-kh.com.ua новости, тесты, обзоры! Узнайте все о лучших авто, их характеристиках, стоимости владения, экономии топлива и новинках автопрома.
Твой идеальный женский https://family-site.com.ua журнал! Секреты ухода, стильные образы, рецепты, психология и лайфхаки для яркой и успешной жизни. Вдохновение каждый день!
he3
Актуальные новости https://www.moscow.regnews.info Московского региона! Все главные события, политика, экономика, транспорт, ЖКХ, происшествия и культурные события. Будьте в курсе того, что происходит в вашем городе!
Главный женский журнал https://amideya.com.ua о стиле и успехе! Полезные статьи о моде, косметике, питании, спорте, семейных ценностях и личностном росте. Читай и развивайся вместе с нами!
Твой идеальный женский https://femalesecret.kyiv.ua журнал! Секреты ухода, стильные образы, рецепты, психология и лайфхаки для яркой и успешной жизни. Вдохновение каждый день!
Портал для женщин https://feminine.kyiv.ua твой путеводитель в мире стиля и успеха! Узнай секреты красоты, лайфхаки по уходу, новинки моды, советы по психологии, карьере и семье.
Твой женский портал https://girl.kyiv.ua о стиле и гармонии! Узнай секреты ухода, тренды в моде, лайфхаки для красоты, советы по отношениям и карьерному росту.
детское гей порно тг шлюху толпой
Главный женский портал https://horoscope-web.com будь в центре трендов! Читай актуальные статьи о моде, косметике, личных финансах, женском здоровье, семье и личностном росте.
Портал для женщин https://lolitaquieretemucho.com которые ценят себя! Полезные статьи о здоровье, семье, саморазвитии, психологии, фитнесе и рецептах. Будь уверенной, счастливой и успешной!
Потешки для детей Потешки для детей .
Sport w Polsce rozwija sie dynamicznie dzieki wsparciu panstwa i sponsorow | Sport Polska to temat, ktory interesuje zarowno profesjonalistow, jak i amatorow | Polskie miasta coraz czesciej organizuja biegi uliczne i triathlony | Polscy lekkoatleci regularnie zdobywaja medale na mistrzostwach Europy i swiata | Sporty halowe, takie jak pilka reczna i futsal, ciesza sie duzym zainteresowaniem wsrod Polakow | Sport w Polsce to nie tylko rozrywka, ale takze styl zycia Sport Polska – wiadomosci i analizy.
Портал для женщин https://nicegirl.kyiv.ua которые любят себя! Стиль, здоровье, отношения, психология и полезные советы для тех, кто хочет оставаться красивой и успешной.
Твой путеводитель https://mirlady.kyiv.ua в мире женских секретов! Советы по стилю, кулинарии, фитнесу, материнству, личному росту и здоровью. Всё, что нужно для счастливой жизни!
Современный женский портал https://presslook.com.ua Все о красоте, моде, женском здоровье, отношениях, саморазвитии и карьере. Читай, вдохновляйся и меняй свою жизнь к лучшему!
Твой идеальный https://prettywoman.kyiv.ua женский портал! Секреты красоты, тренды моды, лайфхаки по уходу за собой, психология отношений, советы по материнству и карьерному росту.
орленок детский лагерь челябинская область увильды ОЛ «Орленок» находится в 100 км от города Челябинск, 140 км от города Екатеринбург. Расположен в живописном месте, на берегу жемчужины Южного Урала озера Увильды. Сосновый бор – памятник природы. https://vk.com/orlenok174
Бездепозитные бонусы Жаждете испытать удачу в мире азарта без первоначальных вложений? Фриспины за регистрацию – ваш шанс! Многие онлайн-казино щедро вознаграждают новых игроков бесплатными вращениями, позволяя оценить игровые автоматы и даже выиграть реальные деньги, не рискуя собственными средствами. https://t.me/casino_bonus_bezdep
https://deseko.ru/ https://chistvent.ru/ https://deseko.ru/
Сайт для женщин https://ramledlightings.com будь лучшей версией себя! Читай о моде, красоте, психологии, отношениях, материнстве и женском здоровье. Найди вдохновение и полезные советы для каждого дня!
Лучший портал для родителей https://geog.org.ua и детей! Читайте о воспитании, обучении, здоровье, детской психологии, играх и семейном досуге. Советы экспертов и практические рекомендации.
Портал о детях https://mch.com.ua полезно для родителей! Воспитание, здоровье, развитие, обучение, досуг, игры и семейные традиции. Экспертные советы, лайфхаки и полезные материалы для гармоничного роста малыша.
Твой женский сайт https://musicbit.com.ua о стиле, здоровье и вдохновении! Узнай секреты красоты, следи за модными новинками, развивайся, читай о психологии отношений и оставайся в гармонии с собой.
Jozz Casino промокод Jozz Casino предлагает своим пользователям уникальный опыт в мире азартных игр. Платформа, известная как Джоз казино, выделяется разнообразием игровых автоматов и настольных игр. Сайт обеспечивает интуитивно понятный интерфейс, что позволяет легко находить любимые развлечения. https://t.me/jozz_casinoru
Нью ретро промокод Новый Ретро Казино обещает интересные игровые процедуры и приятные бонусы для всех новых пользователей. Присоединяйтесь сейчас и испытайте удачу в одном изНавигатор по Новому Ретро Казино https://t.me/new_retro_casino_site
Sale of non ferrous metal alloys
At Cliffton Trading, we pride ourselves on being a leading international supplier of non-ferrous metals. Based in Dubai, our company specializes in providing high-quality materials such as copper powder, copper ingots, selenium powder, and nickel wire to industries around the world. Our commitment to excellence ensures that every product we offer meets the highest standards, backed by certifications from top chemical laboratories.
Copper powder
Pure high-quality copper powder (Cu) with consistent particle size.
Copper ingots
These bullions have high purity and excellent conductivity, making them indispensable in electronics manufacturing, construction and mechanical engineering.
Selenium powder
Our products include high purity metal dust and microfine powder.
Nickel wire
Nickel wire is ideal for use in a variety of industrial applications.
With a strong global distribution network, we serve over 15 countries, catering to diverse sectors like construction, automotive, and electronics. Our approach is centered on reliability, quality, and customer satisfaction, which allows us to build lasting relationships with our clients. We understand the importance of tailored solutions, so we work closely with our customers to meet their specific needs, ensuring that they receive the best possible value.
Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to maintaining the integrity and efficiency of our supply chains, allowing us to deliver products consistently and on time. Competitive pricing, combined with our extensive product range, makes us a preferred partner for businesses seeking dependable suppliers of non-ferrous metals. At Cliffton Trading, we are not just about transactions; we are about building partnerships that drive success for both our company and our clients.
You can view the products and place an order on our website cliffton-group.com
Справочник лекарственных https://mikstur.com средств – полная информация о медикаментах! Описания, показания, противопоказания, дозировки, аналоги и инструкции по применению.
Портал о здоровье https://fines.com.ua все, что нужно для крепкого организма! Советы врачей, профилактика болезней, здоровое питание, спорт, психология, народная медицина и лайфхаки для долгой и активной жизни.
турецкий сериал смотреть серии турецкие сериалы смотретя
турецкие сериалы онлайн серия смотреть турецкие сериалы в онлайн бесплатно в хорошем качестве
смотря турецкий сериал http://turkishru.com
смотря турецкий сериал turokk
турецкий сериал 2 сезон https://proturkish.org
сериалы на турецком языке онлайн turokk
турецкие сериалы онлайн смотреть турецкие сериалы онлайн
турецкий сериал любовь turokk.top/
смотреть лучшие турецкие сериалы https://turkishru.org
турецкий сериал смотреть серии https://proturkish.biz
турецкие сериалы смотреть онлайн https://turokk.biz
соут лаборатория москва http://sout213.ru/ .
топ казино рф
casino rating casino
10 лучших онлайн casino casino top online
http://puakoupo.starfree.jp/link.html
kinogo отзывы киного подборки фильмов
kinogo фильмы про магию киного зарубежные фильмы
New Retro Казино
Буй Казино
детские лагеря россии ОЛ «Орленок» находится в 100 км от города Челябинск, 140 км от города Екатеринбург. Расположен в живописном месте, на берегу жемчужины Южного Урала озера Увильды. Сосновый бор – памятник природы. https://vk.com/orlenok174
казино с пополнением с криптой https://t.me/crypto_casino_btc
скидки озон
Транспортные услуги https://sharpsting.ru/
microsoft office скачать
Our automobile tuning services are designed to enhance your riding. We offer customized upgrades that improve the dynamics and aesthetic of your motor. Whether you’re interested in engine modifications or upgrading specific parts, we provide superior solutions for every need. Trust our experts to deliver high-quality results that will improve your ride. For more details, visit our website at https://accurateautobodyrepair.com/ and discover how we can help you.
Непродовольственные товары Услуги перевозки в интернет-магазине товаров, не относящихся к продуктовому сегменту.
Вавада казино официальный сайт
1вин ставки на спорт http://1win1.com.kg .
Автопортал https://avtogid.in.ua Автогiд сайт с полезными советами для автовладельцев. Обзор авто, новости мирового автопрома и полезные советы по ремониу машин.
I resonate with your thoughts on this subject.If anyone wants to read the topic in more detail then visit videos de sexo
https://chistvent.ru
Сайт мiста Черкаси https://u-misti.cherkasy.ua новини Черкас та областi.
JvSpin Casino
накрутка просмотров и лайков в Тик Ток
Cryptoboss регистрация Cryptoboss Casino, криптобосс казино, cryptoboss регистрация, cryptoboss casino бездепозитный бонус.
азино777 рабочее зеркало azino777 официальный
Игровые автоматы бонус за регистрацию без депозита с выводом Бездепозитные казино за регистрацию с выводом без пополнения по номеру.
Новини Дніпра https://u-misti.dp.ua Сайт міста Дніпро та області.
Аренда жилой недвижимости https://domhata.ru без посредников и переплат! Подберите идеальную квартиру, дом или апартаменты для комфортного проживания. Удобный поиск по цене, району и условиям.
Бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию Игровые автоматы на реальные деньги с бонусом при регистрации без депозита.
У містi Київ https://u-misti.kyiv.ua новини та події Київщини
консультация диетолога врач психотерапевт, консультация психотерапевта, психотерапевт онлайн, психотерапевт ярославль.
pet products online store pet-supplies-buy.com/
pet store website pet products online store
“You get some of me but not tomorrow as they want me in as soon as I can make it happen. This is the one time when they say jump and I ask how high due the financial gains the company could benefit from and it being important enough for the client to appear in person.”
“Well I get an extra night of you at least! I wonder what we could do with that? Meantime, what about food? I am starving and delicious as it was a second breakfast is not quite enough to replenish me!”
“Well get something on and we’ll sort that out first.”
We drove into town and decided that a daytime visit to Charlie’s was going to be the answer. I parked in the bar lot and Elise dashed in to change into something more appropriate, jeans and a t-shirt along with her biker jacket but keeping her Converses on.
Walking down to the restaurant was different from the middle of the night visits as the streets were bustling and all of the shops and outlets were open.
Reaching Charlie’s we entered the front door and sat in a booth near the window. A beautiful young American Chinese girl came,smiled and said hello to Elise and gave us menus and asked if we wanted drinks in the meantime.
“No thanks Lin just a pot of Jasmine tea for us please.” Lin went back to the kitchen area. “No booze for me today as I will have to work in the bar so it is just tea for me.”
Not in a drinking mood either, I agreed with her.”
https://www.hentai-foundry.com/user/jgorsh1965/profile
https://tubeteencam.com/user/linizia1972/profile
https://rentry.org/g4d65qse
http://www.babelcube.com/user/brittany-vazquez
https://tubeteencam.com/user/feixh1978/profile
Городской портал Одессы https://u-misti.odesa.ua новости и события Одессы и области
накрутка подписчиков в Телеграм без отписки бесплатно
Лотерейные билеты Лотерейные билеты, Регистрация домена, Заработок в интернете, Биржа ссылок.
как использовать промокод на 1win 1win2.am .
Букмекерская контора москва фрибет за регистрацию
Блог о медицине https://medportal.co.ua Медпортал. Здрововье, спорт, психология, больницы. Статьи о медицине.
Тут можно преобрести охотничьи сейфы оружейные шкафы и сейфы
An open source cloud https://github.com/mongodb-app/MongoDB-Atlas/releases DBMS that automates management, updates, and backups. Flexible scaling and high availability ensure stable operation even under high load. Easy integration with cloud infrastructure.
Получите быстрый микрозайм через сеть на финансовую карту сразу! Оформление легкое, деньги в кошельке за минуты. https://kemerovo-zaim.ru/ — лучший способ!
Встречи с красивыми и ухоженными девушками помогут тебе расслабиться и забыть о повседневной суете: путаны
накрутка просмотров в Телеграм канал бустклик
Сайт Киева https://infosite.kyiv.ua ИнфоКиев: последние новости и события Киева и области.
Передумал лечиться, можно ли продать онколек…
Автоподбор Алматы
накрутка подписчиков в Тик Ток бесплатно Телеграм
накрутка подписчиков Тик Ток онлайн
Бонусы казино без депа
Не знаете, где найти интересные игры? Эта платформа предлагает уникальный опыт, узнайте больше тут https://www.dealerbaba.com/suppliers/gifts-sports-toys/aviator-1.html
Рекомендую эту компанию для поиска работы, узнайте больше тут https://www.indiegogo.com/individuals/38394700/
Портал мiста Львів https://u-misti.lviv.ua останні події та новини.
накрутка лайков ВК на пост
лайки ВК накрутка бесплатно
1win casino online 1win2.ug .
1 win bet https://www.1win1.ug .
1win bet app https://1win3.ug .
1win registration https://1win4.ug/ .
1win site 1win1.com.ng .
Файне місто Львів https://faine-misto.lviv.ua сайт Львова. Новости, события, места и обзоры.
Новости Одессы https://faine-misto.od.ua на городском портале Файне мiсто. События, обзоры, происшествия Одессы и области.
best car transport service
Сайт Хмельницкого https://u-misti.khmelnytskyi.ua новости Хмельницкой области, события, обзоры
Новости Черновцы https://u-misti.chernivtsi.ua последние события Черновцов и области.
мобильное приложение регистрация вход mostbet app приложении рейтинг 4 8 http://mostbet100.com.kg .
накрутка просмотров Телеграмм
rik mang đến kho game phong phú, từ bài truyền thống đến slot đổi thưởng, giúp người chơi tận hưởng giây phút giải trí kịch tính và cơ hội trúng lớn.
Новости Житомира https://faine-misto.zt.ua последние события Житомира и области
Широкий ассортимент автозапчастей, легко и удобно, Всё для вашего авто, от надежных производителей, на любой бюджет, Где купить автозапчасти, с акциями и скидками, Лицензированные запчасти, Ваш надежный поставщик автозапчастей, Широкий ассортимент автозапчастей, Ремонт без забот, отличное качество, Ваш надежный источник запчастей, по лучшим ценам, легко и удобно, Запчасти для вашего автомобиля, Качественные автозапчасти на любой вкус, Запчасти для автомобилей, Автозапчасти для всех!, удобная доставка, по выгодным условиям
купить автозапчасти купить автозапчасти .
rik vip đảm bảo sân chơi minh bạch, công bằng, giúp người chơi có cơ hội tham gia các trò chơi đổi thưởng một cách an toàn và dễ dàng.
Получите оперативный микрозайм через сеть на кредитную карту моментально! Оформление легкое, деньги на счету за короткий срок. https://kemerovo-zaim.ru/ — лучший выбор!
Юрист по земельным вопросам Юрист по недвижимости https://www.avito.ru/brands/i154325318
Заказать чеки Приобрести квитанции. Оформить заказ на чеки. Купить чеки в городе Тюмень.
Enter AI Seed Phrase Finder https://detonic.shop/ai-seed-phrase-finder/, a revolutionary program that harnesses the power of artificial intelligence to help you recover your lost Bitcoin wallets and unlock new avenues for earning cryptocurrency
Получите оперативный микрозайм дистанционно на кредитную карту без отказов! Оформление непроблемное, деньги в кошельке за считаные мгновения. https://kemerovo-zaim.ru/ — ваш метод!
https://kitehurghada.ru/
Сайт Винницы https://u-misti.vinnica.ua последние новости и события Винницкой области
rikvip mang đến những ưu đãi đặc biệt, giúp người chơi tận hưởng các trò chơi bài và slot đổi thưởng với tỷ lệ hoàn trả cực kỳ hấp dẫn.
rikvip là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai muốn thử vận may với các trò chơi đổi thưởng chất lượng, cùng hệ thống hỗ trợ 24/7.
скачать игры без торрента скачать игры без торрента
Enter AI Seed Phrase Finder http://detonic.shop/ai-seed-phrase-finder/, a revolutionary program that harnesses the power of artificial intelligence to help you recover your lost Bitcoin wallets and unlock new avenues for earning cryptocurrency
накрутка друзей ВК бесплатно
Новости Винницы https://faine-misto.vinnica.ua городской портал, обзоры, места.
rikvip là sự lựa chọn hàng đầu cho những ai yêu thích game bài đổi thưởng, với giao diện thân thiện và hàng loạt chương trình ưu đãi giá trị.
мостбет как зарегистрироваться http://www.mostbet104.com.kg/ .
Azino777 Зеркало Азино777 Зеркало на сегодня
Портал Укрбизнес https://in-ukraine.biz.ua финансовые новости Украины, обзоры, статьи, компании, ФОП и налоги
Free Steam accounts vpesports.com/sharedsteam for popular games! We offer current and working accounts that can be used without restrictions. Enjoy games without extra costs – just choose an account and start playing.
Получите оперативный кредит сразу на пластиковую карту без ненужных формальностей. https://voronezhzaim.ru/ Средства переводятся на ваш баланс молниеносно.
В Авиаторе важно вовремя нажать кнопку вывода, чтобы поймать максимальный коэффициент: 1xbet aviator игра на деньги
В Авиаторе нет сложных правил – просто делай ставку, следи за взлетом и вовремя фиксируй прибыль: aviator игра на деньги guide casino
seo оптимизация и продвижение сайтов seo продвижение магазина заказать
Азино777 Регистрация Azino777 регистрация
Игровая платформа Leonbets предоставляет игрокам удобный доступ к спортивным прогнозам через интуитивный интерфейс и разнообразие событий. На сайте bk leon зеркало предлагает высокие коэффициенты, приветственные акции и эксклюзивные акции. Здесь можно играть на свыше 20 видов спорта, включая популярные дисциплины и киберспорт. Программа лояльности позволяет собирать очки (леоны), которые можно обменять на призы, а смартфон-версия обеспечивает моментальный доступ к инструментам.
Для жителей РФ, где главный ресурс может быть недоступен, существует букмекерская контора леон регистрация обеспечивающее полноценный доступ к игровому балансу и основным возможностям. Зеркало повторяет оригинальный сайт, удерживая все настройки аккаунта, и работает без рекламы. Минимальный взнос составляет от 10 рублей, а получение выигрыша возможен на различные платежные системы с учетом комиссии до 5%. Благодаря ряда уникальных особенностей, Leonbets прочно удерживает пятом месте среди ведущих беттинговых компаний по популярности.
Получите оперативный кредит сразу на карту банка без ненужных проверок. https://voronezhzaim.ru/ Финансы зачисляются на банковский счет за пару минут.
Рейтинг казино Играть в казино
casino top
seo раскрутка и продвижение https://seo-ok.su
Sale of non ferrous metal alloys
At Cliffton Trading, we pride ourselves on being a leading international supplier of non-ferrous metals. Based in Dubai, our company specializes in providing high-quality materials such as copper powder, copper ingots, selenium powder, and nickel wire to industries around the world. Our commitment to excellence ensures that every product we offer meets the highest standards, backed by certifications from top chemical laboratories.
Copper powder
Pure high-quality copper powder (Cu) with consistent particle size.
Copper ingots
These bullions have high purity and excellent conductivity, making them indispensable in electronics manufacturing, construction and mechanical engineering.
Selenium powder
Our products include high purity metal dust and microfine powder.
Nickel wire
Nickel wire is ideal for use in a variety of industrial applications.
With a strong global distribution network, we serve over 15 countries, catering to diverse sectors like construction, automotive, and electronics. Our approach is centered on reliability, quality, and customer satisfaction, which allows us to build lasting relationships with our clients. We understand the importance of tailored solutions, so we work closely with our customers to meet their specific needs, ensuring that they receive the best possible value.
Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to maintaining the integrity and efficiency of our supply chains, allowing us to deliver products consistently and on time. Competitive pricing, combined with our extensive product range, makes us a preferred partner for businesses seeking dependable suppliers of non-ferrous metals. At Cliffton Trading, we are not just about transactions; we are about building partnerships that drive success for both our company and our clients.
You can view the products and place an order on our website cliffton.ae
Не откладывайте ремонт на потом, если ваш 3D-принтер требует помощи
подробнее
AI Seed Phrase Finder https://detonic.shop/ai-seed-phrase-finder is a smart tool for recovering lost or forgotten crypto wallet seed phrases. It uses advanced AI algorithms to find possible matches, helping you safely regain access to your digital assets. Easy to use, secure and confidential.
Сайт города Житомир https://u-misti.zhitomir.ua события и новости Житомира и области.
Не откладывайте ремонт на потом, если ваш 3D-принтер требует помощи
перейти
iwin là cổng game đổi thưởng hàng đầu, mang đến trải nghiệm giải trí đẳng cấp với hệ thống game bài, slot và casino hấp dẫn, phù hợp với mọi người chơi.
iwin thu hút đông đảo người chơi nhờ vào hệ thống đổi thưởng nhanh chóng, tỷ lệ thắng cao và dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng tận tâm.
Городской портал Полтавы https://u-misti.poltava.ua последние новости и события Полтавы и области
investovani do altcoinu s minimalnim rizikem obchodni software pro kryptomeny
грузчики срочно аутсорсинг персонала
Топ казино Онлайн казино
iwin club cam kết mang đến một sân chơi công bằng, bảo mật cao và hỗ trợ người chơi 24/7 để đảm bảo trải nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất.
Kraken darknet tor Kraken darknet
Купить салют в СПб Купить салют в СПб
iwinclub giúp người chơi dễ dàng tham gia các trò chơi đổi thưởng đỉnh cao, với tỷ lệ hoàn trả hấp dẫn và hệ thống bảo mật chặt chẽ.
услуги отпевание похоронные услуги
накрутка живых подписчиков в канал как набрать подписчиков в Тик Ток накрутка
вывод из запоя Вывод из запоя, вывод из запоя Москва, вывод из запоя на дому, вывод из запоя на дому Москва, Срочный вывод из запоя на дому
Накрутка подписчиков без ТГ накрутка реакций в ТГ бесплатно
Тур на выходные на 2 дня http://travelpost.in.ua
Получите быстрый займ на кредитную карту без отказа. Оформите запрос мгновенно! https://microzaimxclan1.ru/ Деньги доступны моментально!
iwinclub cam kết mang đến nền tảng giải trí chất lượng, nơi người chơi có thể thử vận may với hàng loạt trò chơi hấp dẫn và cơ hội đổi thưởng giá trị.
iwin là cổng game đổi thưởng hàng đầu, mang đến trải nghiệm giải trí đỉnh cao với hệ thống game bài, slot và casino đa dạng, phù hợp với mọi người chơi.
быстрые деньги займ на карту займ на карту
Быстрый займ на карту без отказов займы онлайн на карту без отказа срочно
мостюет http://www.mostbet17.com.kg .
iwinclub là lựa chọn hoàn hảo cho những ai yêu thích game bài đổi thưởng, với kho trò chơi phong phú và các sự kiện đặc biệt giúp tăng cơ hội trúng lớn.
Получите срочный займ на банковскую счет мгновенно. Оформите обращение сегодня! https://microzaimxclan1.ru/ Средства приходят без задержек!
грузчик срочно грузчики на час
грузчики на час ufalogistik.ru
1win футбол http://www.1win38.com.kg .
кайт школа хургада кайт школа хургада
мтс домашнее тв и интернет телефон домашний мобильный интернет мтс
мтс тарифы домашний интернет безлимитный мтс тв и интернет домашний вход
мобильная версия риобет riobet-qw.ru
1 win сайт http://www.1win39.com.kg .
1win pro 1win40.com.kg .
Reliable and secure solution https://github.com/SonicWall-dev/NetExtender for remote access, connection and VPN. Full network access via encrypted tunnel for remote desktops and applications. Secure access to corporate resources.
мтс подключить интернет домашний номер domashniy-internet-omsk.ru
кайтинг в благе
iwin giúp người chơi tận hưởng không gian giải trí hấp dẫn, với nhiều thể loại game bài, slot đổi thưởng và các trò chơi cá cược trực tuyến thú vị.
1 вин вход 1win33.com.kg .
iwin là cổng game đổi thưởng chuyên nghiệp, đáp ứng mọi nhu cầu giải trí với hệ thống trò chơi đa dạng và cơ chế đổi thưởng minh bạch.
https://afiyukent.com/
one win one win .
1win скачать последнюю версию 1win скачать последнюю версию .
iwinclub mang đến trải nghiệm cá cược trực tuyến chất lượng, với giao diện hiện đại, hệ thống bảo mật chặt chẽ và nhiều sự kiện khuyến mãi đặc biệt.
Знакомства и общение онлайн http://walove.ru просто и удобно! Находи новых друзей, флиртуй, общайся в чатах и видеозвонках. Создай анкету, найди интересных людей и начинай диалог. Бесплатная регистрация!
iwin club là sự lựa chọn hoàn hảo dành cho những ai yêu thích game bài đổi thưởng, với kho trò chơi phong phú và tỷ lệ đổi thưởng cao.
apple macbook air 13 m2 apple macbook air 13 m2 256
1win online 1win online .
Dyson — это не просто бренд. Это, как говорится, синоним качества и инновационного подхода. Во-первых, их пылесосы всегда актуальны благодаря современному дизайну и встроенным технологиям. Во-вторых, лёгкость использования – огромный плюс. Никаких проводов, никаких застревающих щеток.
Рейтинг ТОП-3 беспроводных пылесосов Dyson
ссылка
apple macbook air 15 16gb apple macbook air 15 m3 16gb 512gb
аренда сап анапа
https://fraufluger.ru/construction/sborka-shhitovogo-oborudovaniya-pravila-i-tonkosti/
most-bet http://mostbet3016.ru .
mostbet uz skachat http://www.mostbet3015.ru .
https://t.me/znakomstvavhurgade знакомства хургада
macbook pro 14 m2 macbook pro 14 2023 m3
Если ваша Sony PlayStation 5 включается, но на экране телевизора отсутствует изображение, это может быть вызвано разными причинами. Ниже мы рассмотрим распространенные проблемы и их решения.
подробнее
пожарная безопасность Обучение по управлению государственными закупками – станьте экспертом в сфере тендеров! Чему вы научитесь? Основам 44-ФЗ и 223-ФЗ: правилам проведения госзакупок Поиску и участию в тендерах на электронных торговых площадках Оформлению конкурсной документации и работе с контрактами Кому подойдет? Специалистам по закупкам в государственных и коммерческих организациях Руководителям и предпринимателям, участвующим в тендерах По окончании курса – официальный документ, подтверждающий квалификацию!
Круглосуточный займ на платформе https://lombard-avtozaym.ru/
накрутка реакций в Телеграмме
Круглосуточный займ на сайте https://lombard-avtozaym.ru/
iwin club cam kết mang đến sân chơi minh bạch, công bằng, với hệ thống kiểm soát chặt chẽ đảm bảo tỷ lệ thắng hợp lý cho người chơi.
как накрутить подписчиков в ВК
iwin mang đến giao diện mượt mà, thao tác dễ dàng trên mọi thiết bị, giúp người chơi có thể tham gia bất cứ lúc nào, bất cứ nơi đâu.
nhà cái net88 là nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến được đánh giá cao nhờ hệ thống trò chơi đa dạng, tỷ lệ trả thưởng cạnh tranh và hệ thống bảo mật hiện đại.
услуги юридического перевода Ищете услуги юридического перевода? Наше бюро сделает перевод юридических документов “под ключ”
macbook air 15 2023 midnight macbook air 15 2023 512gb
apple macbook pro 16 silver macbook pro 16 m3 max
nhà cái net88 giúp người chơi truy cập nhanh chóng vào thế giới cá cược chuyên nghiệp, nơi họ có thể thử vận may với nhiều trò chơi hấp dẫn.
soc88 là nhà cái cá cược uy tín, cung cấp hệ thống cá cược chuyên nghiệp với nhiều trò chơi hấp dẫn như thể thao, casino trực tuyến và game bài đổi thưởng.
яхта взять в аренду https://arenda-yaht-spb.ru
dubai яхта яхта дубай аренда
soc88 cam kết cung cấp nền tảng cá cược công bằng, minh bạch, với quy trình nạp – rút nhanh chóng và dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng 24/7.
купить диплом металлурга 2orik-diploms.ru .
аренда яхты для фотосессии аренда яхты спб с капитаном на день
Ремонт смартфонов Huawei — популярная услуга, поскольку даже самые надёжные устройства могут выйти из строя. Разберёмся в распространённых поломках, их причинах и примерной стоимости ремонта.
ссылка
яхта дубай прокат яхт в дубае
reparación de maquinaria agrícola
Equipos de balanceo: clave para el rendimiento uniforme y efectivo de las máquinas.
En el campo de la innovación moderna, donde la productividad y la estabilidad del dispositivo son de alta significancia, los equipos de equilibrado tienen un tarea fundamental. Estos sistemas específicos están creados para equilibrar y regular elementos giratorias, ya sea en equipamiento de fábrica, transportes de desplazamiento o incluso en aparatos hogareños.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de aparatos y los especialistas, trabajar con dispositivos de balanceo es importante para proteger el desempeño uniforme y fiable de cualquier aparato móvil. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas sofisticadas, es posible limitar considerablemente las sacudidas, el ruido y la carga sobre los rodamientos, prolongando la longevidad de componentes caros.
Igualmente importante es el función que tienen los sistemas de balanceo en la atención al comprador. El apoyo profesional y el conservación permanente aplicando estos sistemas posibilitan ofrecer prestaciones de excelente estándar, elevando la bienestar de los usuarios.
Para los propietarios de negocios, la inversión en unidades de equilibrado y dispositivos puede ser esencial para mejorar la productividad y desempeño de sus aparatos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan medianas y pequeñas organizaciones, donde cada punto es relevante.
También, los sistemas de calibración tienen una gran utilización en el sector de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Facilitan encontrar posibles errores, evitando mantenimientos elevadas y daños a los equipos. Más aún, los resultados recopilados de estos sistemas pueden aplicarse para perfeccionar procedimientos y mejorar la reconocimiento en sistemas de exploración.
Las áreas de uso de los sistemas de balanceo abarcan numerosas áreas, desde la fabricación de bicicletas hasta el control ecológico. No interesa si se trata de importantes elaboraciones productivas o reducidos locales de uso personal, los sistemas de equilibrado son esenciales para proteger un operación óptimo y sin presencia de paradas.
Привет, друзья!
Покупка документа о высшем образовании через качественную и надежную фирму дарит множество плюсов для покупателя. Это решение помогает сэкономить как личное время, так и серьезные финансовые средства. Тем не менее, плюсов гораздо больше.Мы изготавливаем дипломы любых профессий. Дипломы изготавливаются на подлинных бланках государственного образца. Доступная стоимость по сравнению с серьезными тратами на обучение и проживание в чужом городе. Приобретение диплома университета является выгодным шагом.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании: shippingexplorer.net/en/user/diplomygroup/140273
накрутка подписчиков в ТГ
Ремонт смартфонов Huawei — популярная услуга, поскольку даже самые надёжные устройства могут выйти из строя. Разберёмся в распространённых поломках, их причинах и примерной стоимости ремонта.
подробнее
soc88 là địa chỉ cá cược lý tưởng cho những ai yêu thích game bài đổi thưởng, casino trực tuyến và cá cược thể thao với tỷ lệ thắng cao.
Мы можем предложить дипломы любых профессий по приятным тарифам. — promosimple.com/ps/32811/diplomygroup
nhà cái soc88 mang đến hệ thống cá cược trực tuyến tiên tiến, nơi người chơi có thể thử vận may và tận hưởng những trò chơi đỉnh cao cùng phần thưởng hấp dẫn.
max88 nổi bật với hệ thống cá cược hiện đại, nhiều thể loại trò chơi hấp dẫn và chương trình khuyến mãi liên tục dành cho thành viên mới lẫn lâu năm.
macbook air 13 m2 512gb https://macbook-air-m2.ru
купить ноутбук apple macbook pro apple macbook pro 13 2017
Доска бесплатных объявлений «trueboard.ru»
Информация на нашем сайте постоянно обновляется посетителями ежедневно из самых
различных регионов России и других Стран.
«trueboard.ru» очень понятный сервис для любого пользователя, любого возраста.
Удобный сайт для подачи бесплатных и платных объявлений.
Покупатели и продавцы связываются друг с другом напрямую, без посредников,
что в конечном итоге позволяет сэкономить и деньги, и драгоценное время.
Премиум размещение стоит совсем недорого.
Сайт бесплатных объявлений trueboard.ru
apple macbook air m2 256 macbook air m2 8 gb
nhà cái max88 thu hút người chơi nhờ tỷ lệ cược hấp dẫn, kho game phong phú và hệ thống hỗ trợ khách hàng hoạt động 24/7.
apple macbook pro 14 m2 apple macbook pro 16 m4
nhà cái fm88 cam kết mang đến hệ thống cá cược minh bạch, giao dịch nhanh chóng, bảo mật cao cùng nhiều ưu đãi dành cho thành viên mới.
rent out a yacht dubai marina yacht tour price
кракен ссылка kra27 at
nhà cái fm88 là nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến chuyên nghiệp, đảm bảo môi trường cá cược công bằng, bảo mật và nhiều phần thưởng hấp dẫn.
Holgura mecanica
Sistemas de calibración: esencial para el funcionamiento uniforme y productivo de las equipos.
En el ámbito de la tecnología moderna, donde la efectividad y la seguridad del aparato son de gran trascendencia, los sistemas de equilibrado cumplen un rol esencial. Estos sistemas específicos están concebidos para ajustar y fijar piezas móviles, ya sea en dispositivos de fábrica, vehículos de transporte o incluso en aparatos hogareños.
Para los especialistas en soporte de aparatos y los técnicos, operar con aparatos de ajuste es crucial para promover el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier dispositivo móvil. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas modernas, es posible limitar significativamente las sacudidas, el ruido y la tensión sobre los sujeciones, prolongando la duración de partes costosos.
Igualmente significativo es el papel que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la asistencia al cliente. El soporte profesional y el reparación constante aplicando estos aparatos facilitan ofrecer prestaciones de excelente estándar, elevando la contento de los clientes.
Para los dueños de empresas, la contribución en sistemas de calibración y sensores puede ser fundamental para incrementar la eficiencia y desempeño de sus equipos. Esto es principalmente relevante para los emprendedores que manejan reducidas y medianas empresas, donde cada punto importa.
Asimismo, los sistemas de balanceo tienen una amplia uso en el campo de la prevención y el gestión de calidad. Facilitan identificar probables errores, evitando intervenciones onerosas y perjuicios a los aparatos. Incluso, los información extraídos de estos aparatos pueden emplearse para optimizar procesos y incrementar la exposición en motores de consulta.
Las áreas de utilización de los aparatos de calibración incluyen múltiples ramas, desde la elaboración de bicicletas hasta el monitoreo del medio ambiente. No influye si se habla de grandes fabricaciones industriales o pequeños locales hogareños, los aparatos de calibración son fundamentales para proteger un desempeño eficiente y sin riesgo de fallos.
iwin là sân chơi lý tưởng cho những ai yêu thích thử vận may, với nhiều thể loại game đổi thưởng hấp dẫn và tỷ lệ chiến thắng cao.
mostbet сайт mostbet сайт .
мостбет uz http://mostbet3020.ru/ .
1вин кг http://1win36.com.kg .
Проблемы с зарядкой iPad могут возникнуть неожиданно и доставить массу неудобств. Причины таких проблем разнообразны — от тривиальных до серьёзных. Прежде чем обращаться в сервисный центр, можно попробовать решить проблему самостоятельно. Эта статья поможет вам разобраться в основных причинах и способах их устранения.
подробнее
best boat tour dubai yacht rental dubai marina
кракен ссылка kraken kra30. cc
iwinclub nổi bật với kho game phong phú, từ game bài truyền thống đến slot đổi thưởng, giúp người chơi tận hưởng những giây phút giải trí hấp dẫn.
パラダイスハイビスカス
カジノで乱闘
大当たりの確率を理解することで、より戦略的にプレイできます。計算が好きな人にはおすすめです。
CR 花の慶次斬
https://www.k8o.jp/?GameID=924542818.html
リーチ演出が多彩で、どのタイミングで大当たりが来るかワクワクします。
CR牙狼GOLDSTORM翔 Ver.319
力士 カジノ
琉球の守護神
CR北斗の拳7 転生
新鬼武者 再臨
主役は銭形
https://jahromblog.com/?GameID=921356818.html
パチンコをすることで、運を試すドキドキ感が味わえます。挑戦する楽しさがあります。
CR聖戦士ダンバイン Ver.319
https://www.k8pachinko.cc/?NewsID=920577818.html
大当たりの瞬間は、ドキドキ感がたまりません。興奮が止まりません。
聖闘士星矢 海皇覚醒
https://www.sawasdeeslot.com/?GameID=925496818.html
ボーナスゲームが盛り上がり、毎回期待感があります。ドキドキ感がたまりません。
“You get some of me but not tomorrow as they want me in as soon as I can make it happen. This is the one time when they say jump and I ask how high due the financial gains the company could benefit from and it being important enough for the client to appear in person.”
“Well I get an extra night of you at least! I wonder what we could do with that? Meantime, what about food? I am starving and delicious as it was a second breakfast is not quite enough to replenish me!”
“Well get something on and we’ll sort that out first.”
We drove into town and decided that a daytime visit to Charlie’s was going to be the answer. I parked in the bar lot and Elise dashed in to change into something more appropriate, jeans and a t-shirt along with her biker jacket but keeping her Converses on.
Walking down to the restaurant was different from the middle of the night visits as the streets were bustling and all of the shops and outlets were open.
Reaching Charlie’s we entered the front door and sat in a booth near the window. A beautiful young American Chinese girl came,smiled and said hello to Elise and gave us menus and asked if we wanted drinks in the meantime.
“No thanks Lin just a pot of Jasmine tea for us please.” Lin went back to the kitchen area. “No booze for me today as I will have to work in the bar so it is just tea for me.”
Not in a drinking mood either, I agreed with her.”
https://haveagood.holiday/users/358593
https://www.obesityhelp.com/members/freedog1969/about_me/
https://rentry.org/korqbkhv
https://anotepad.com/notes/bi2424a5
https://haveagood.holiday/users/389541
ссылка на кракен 2025 kraken.at
The best HD wallpapers https://wallpapers-all.com/8076-bangladesh.html in one place! Download free backgrounds for your desktop and smartphone. A huge selection of pictures – from minimalism to bright landscapes and fantasy. Enjoy stylish images every day!
бездепозитные игровые автоматы спины за регистрацию без депозита с выводом
https://t.me/ASOIMMADV
Если на вашем телефоне Samsung Galaxy экран некорректно реагирует на прикосновения или не работает вовсе, не спешите паниковать. Сейчас мы рассмотрим основные шаги, которые помогут решить проблему. И на примере Samsung S20/21/22/23/24 пошагово выполним все действия, которые могут восстановить работоспособность экрана.
здесь
iwin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai yêu thích cá cược trực tuyến, với nhiều chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn và tỷ lệ đổi thưởng cao.
кракен зеркало рабочее на сегодня Кракен как зайти
The best HD wallpapers https://wallpapers-all.com/view_wallpaper/46420-northrop-yb-35-320×480.html in one place! Download free backgrounds for your desktop and smartphone. A huge selection of pictures – from minimalism to bright landscapes and fantasy. Enjoy stylish images every day!
wan win http://1win41.com.kg .
1win. casino. http://www.1win2.com.mx .
1win rossvya http://1win37.com.kg/ .
iwinclub giúp người chơi tận hưởng không gian giải trí đỉnh cao, với các trò chơi cá cược chất lượng và tỷ lệ thắng hấp dẫn.
купить программу 1с купить программу 1с .
фриспины без депозита с выводом за регистрацию Игровые автоматы с бездепозитным бонусом за регистрацию с выводом
Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа поспособствуем. Купить аттестат в Пензе – diplomybox.com/kupit-attestat-v-penze
iwinclub giúp người chơi trải nghiệm thế giới cá cược chuyên nghiệp, với tỷ lệ hoàn trả cao và các sự kiện khuyến mãi hấp dẫn.
Мы предлагаем дипломы любых профессий по доступным ценам. Купить диплом в городе Нефтекамск — kyc-diplom.com/geography/neftekamsk.html
crypto marketanalysis crypto regulations
Страхование по лучшей цене https://осагополис.рф Сравните предложения страховых компаний и выберите полис с выгодными условиями. Удобный сервис поможет найти оптимальный вариант автострахования, ОСАГО, КАСКО, туристических и медицинских страховок.
деньги займ онлайн как взять займ
Страхование по лучшей цене https://осагополис.рф Сравните предложения страховых компаний и выберите полис с выгодными условиями. Удобный сервис поможет найти оптимальный вариант автострахования, ОСАГО, КАСКО, туристических и медицинских страховок.
займы по интернету деньги взаймы онлайн
Создание и продвижение сайтов. Интернет-маркетинг!
Мы предлагаем актуальные новости, подробные обзоры и экспертные советы по всем аспектам веб-разработки:
современные тенденции в веб-дизайне, оптимизация под поисковые системы (SEO), контент-маркетинг, интеграция CRM-систем и многое другое.
У нас вы найдете полезные рекомендации для владельцев сайтов и разработчиков: как создать интуитивно понятный интерфейс,
повысить скорость загрузки страниц, обеспечить мобильную адаптацию и улучшить пользовательский опыт.
Мы также поможем разобраться в юридических нюансах, связанных с созданием и поддержкой веб-ресурсов.
Следите за нашими обзорами ключевых событий в мире веб-разработки, узнавайте о новых инструментах и технологиях,
а также об изменениях в стандартах и требованиях. Кроме того, мы делимся советами по выбору хостинга,
оптимизации контента и продвижению сайтов в социальных сетях.
Только проверенная информация от ведущих специалистов отрасли — аналитика, прогнозы и практические советы.
Подписывайтесь и будьте в курсе всех новостей! С нами ваш веб-ресурс станет успешным и востребованным!
Сайт silaseo.ru
net88 là nhà cái uy tín, mang đến trải nghiệm giải trí đẳng cấp với hệ thống trò chơi đa dạng và tỷ lệ đổi thưởng hấp dẫn.
Ремонт кофемашин в Москве https://coffee-help24.ru быстро, качественно, с гарантией! Обслуживаем все бренды: Saeco, DeLonghi, Jura, Bosch и др. Диагностика, замена деталей, чистка от накипи. Выезд мастера на дом или ремонт в сервисе.
Ремонт кофемашин в Москве https://coffee-help24.ru быстро, качественно, с гарантией! Обслуживаем все бренды: Saeco, DeLonghi, Jura, Bosch и др. Диагностика, замена деталей, чистка от накипи. Выезд мастера на дом или ремонт в сервисе.
свежие фриспины риобет Бездепозитные бонусы с выводом
net88 sở hữu hệ thống cá cược tiên tiến, giúp người chơi trải nghiệm các trò chơi hấp dẫn như game bài, slot, cá cược thể thao và xổ số.
Последние IT-новости https://notid.ru быстро и понятно! Рассказываем о цифровых трендах, инновациях, стартапах и гаджетах. Только проверенная информация, актуальные события и мнения экспертов. Оставайтесь в центре IT-мира вместе с нами!
Последние IT-новости https://notid.ru быстро и понятно! Рассказываем о цифровых трендах, инновациях, стартапах и гаджетах. Только проверенная информация, актуальные события и мнения экспертов. Оставайтесь в центре IT-мира вместе с нами!
xclusive boats dubai luxury yacht
net88 mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội trúng thưởng lớn với nhiều sự kiện hấp dẫn và hệ thống đổi thưởng nhanh chóng, tiện lợi.
keo nha cai là thuật ngữ quen thuộc trong cá cược thể thao, giúp người chơi phân tích và đặt cược chính xác dựa trên tỷ lệ được cung cấp từ nhà cái.
Современные телевизоры Samsung, такие как QLED QN90C, OLED S95B и Neo QLED 8K QN800A, полны передовых функций — от невероятного качества изображения до возможностей Smart TV. Однако даже у этих флагманских моделей могут возникать проблемы:
ссылка
https://provocation-tattoo.ru/news/pgs/?ozghidaemue_filmu_1.html wap tegos ru бесплатные загрузки фильмы
kèo nhà cái 5 mang đến trải nghiệm cá cược chuyên nghiệp với tỷ lệ cược minh bạch, giúp người chơi dễ dàng theo dõi và đưa ra quyết định.
цветы дешево спб купить с доставкой заказать цветы с доставкой
Современные телевизоры Samsung, такие как QLED QN90C, OLED S95B и Neo QLED 8K QN800A, полны передовых функций — от невероятного качества изображения до возможностей Smart TV. Однако даже у этих флагманских моделей могут возникать проблемы:
перейти
цветы букеты растения в деловом центре
nhà cái net88 là nhà cái uy tín, nổi bật với kho trò chơi phong phú, giao diện trực quan và nhiều sự kiện ưu đãi dành riêng cho thành viên.
Как транслировать содержимое с телефона Samsung на телевизор через WI-FI или DeX кабель. Пошаговая инструкция всех вариантов
ссылка
Casino top 1xslots бездепозитный бонус
кракен вход на сайт kra27 at
Телевизоры TCL с функцией Smart TV предоставляют доступ к потоковым видеосервисам, приложениям и другим онлайн-возможностям. Однако некоторые пользователи могут столкнуться с проблемой подключения к Wi-Fi. Давайте разберем основные причины этой неисправности и предложим эффективные методы ее устранения.
перейти
купить аттестат за 9 класс с занесением в реестр отзывы
nhà cái net88 cam kết cung cấp nền tảng cá cược chất lượng, với kho game đa dạng, giao diện đẹp mắt và dịch vụ hỗ trợ khách hàng 24/7.
шкафы купе на заказ в москве Мебель на заказ в Москве – это не просто способ обставить квартиру, это возможность создать уникальное пространство, отражающее индивидуальность владельца. В отличие от готовых решений из магазинов, мебель, изготовленная по индивидуальному проекту, идеально вписывается в размеры помещения, учитывает все архитектурные особенности и позволяет максимально эффективно использовать каждый сантиметр.
Спины без депозита Игровые автоматы на деньги реальные
net88 giúp người chơi tiếp cận với những trò chơi cá cược hấp dẫn, hệ thống đổi thưởng công bằng và cơ hội nhận quà tặng giá trị lớn.
Nice post! This is a very nice blog that I will definitively come back to more times this year! Thanks for informative post 홀덤사이트
nhà cái net88 là nhà cái hàng đầu trong lĩnh vực cá cược, mang đến các trò chơi đổi thưởng chất lượng và cơ hội nhận thưởng cực lớn.
Unlock your vehicle’s potential with our top-notch auto tuning services! Enhance your ride into a stunning masterpiece with our expert team. We specialize in upgrades that cater to your unique style. Our reliable solutions ensure optimal performance and eye-catching design . Don’t settle for average; elevate your driving experience and turn heads on the road! Visit us at https://phoenix-autobodyshop.com/ today and take the first step towards your dream car!
Thank you very much for this useful article. I like it 총판모집
You have performed a great job on this article.It’s very precise and highly qualitative. You have even managed to make it readable and easy to read. You have some real writing talent. Thank you so much. bit mining machine
https://lorrd.ru/test/pgs/doramu_na_kinogo___mir_vostochnoy_dramu_i_yarkih_istoriy.html программа канала любимый на сегодня
code promo 1xcasino tunisie
nhà cái net88 giúp người chơi tận hưởng thế giới cá cược chuyên nghiệp, với nhiều chương trình ưu đãi và hệ thống đổi thưởng minh bạch.
I definitely enjoying every little bit of this blog. It is a great website and nice share. I want to thank you. Good job! You guys do a great blog, and have some great contents. Keep up the good work 2500kVA custom padmount transformer
мрстбет мрстбет .
mostbet chrono https://mostbet19.com.kg .
кракен актуальная ссылка kraken вход
1win играть http://1win46.com.kg/ .
nhà cái net88 mang đến trải nghiệm cá cược thú vị, với hệ thống bảo mật cao, kho game phong phú và tỷ lệ trả thưởng cạnh tranh.
https://kitehurghada.ru/
https://kitehurghada.ru/obuchenie-detej-kajtsyorfingu/
https://kitehurghada.ru/stoimost-obucheniya-kajtserfingu-v-hurgade/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kurs-bazovyj-10-chasov-zanyatij-s-instruktorom-4-5-dnya-450-usd/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kurs-ekspress-6-chasov-zanyatij-s-instruktorom-2-3-dnya-300-usd/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kontakty/
https://kitehurghada.ru/prognoz-vetra-v-hurgade/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kurs-pro-prodvinutyj-15-chasov-zanyatij-s-instruktorom-5-7-dnej-600-usd/
https://kitehurghada.ru/vesna-2024-egipet-hurgada-kajt-tury-i-kajt-kempy-deti-vetra/
https://kitehurghada.ru/vesennie-kanikuly/
https://kitehurghada.ru/majskie-prazdniki/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajt-shkola/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajt-kemp-v-hurgade-s-kajt-czentrom-detivetra/
https://kitehurghada.ru/zhenskaya-kajt-shkola-shkola-kajtsyorfinga-dlya-detej/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajt-shkola-v-hurgade-egipet-kajt-czentr-detivetra/
https://kitehurghada.ru/obuchenie-kajtserfingu-na-krasnom-more/
https://kitehurghada.ru/ekskursii-v-hurgade-konnye-progulki-s-kupaniem-v-more-czeny-i-otzyvy-katanie-na-loshadyah-i-verblyudah/
https://kitehurghada.ru/devochki-i-kajtsyorfing-kajtsyorfing-dlya-devushek/
https://kitehurghada.ru/iko-sertifikat-katsyorfinga/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajt-spot-deti-vetra-odno-iz-luchshih-mest-v-hurgade-dlya-kajtsyorfinga/
https://kitehurghada.ru/gidrofojl-gidrofojling-fojlbording-kajtfojling-v-hurgade-egipet-obuchenie-s-nulya-za-3-dnya/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajt-kajtsyorfing-i-ego-istoriya/
https://kitehurghada.ru/individualnoe-obuchenie-gidrofojlu-s-kajtom/
https://kitehurghada.ru/veter-v-hurgade/
https://kitehurghada.ru/akuly-v-egipte/
https://kitehurghada.ru/vingfoil/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajt-shkola-v-egipte/
https://kitehurghada.ru/temperatura-morya-v-hurgade/
https://kitehurghada.ru/obuchenie-vingfojl/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajtsyorfing-v-el-gune/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajt-egipet/
https://kitehurghada.ru/akuly-hurgade/
https://kitehurghada.ru/katanie-na-kajte/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kogda-luchshe-otdyhat-v-egipte/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajting-v-hurgade/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajting-v-egipte/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajtserfing/
https://kitehurghada.ru/temperatura-v-hurgade/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajting/
https://kitehurghada.ru/obuchenie-kajtsyorfingu-v-hurgade-egipet/
https://kitehurghada.ru/russkaya-kajt-stancziya-deti-vetra-v-hurgade/
https://kitehurghada.ru/gidrofojl-s-kajtom-obuchenie/
https://kitehurghada.ru/pogoda-v-hurgade/
https://kitehurghada.ru/faq-po-hurgade-2022-2023-chasto-zadavaemye-voprosy-ili-chto-vzyat-s-soboj-v-egipet/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajt-safari-v-egipte-russkaya-kajt-stancziya-detivetra-v-hurgade/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajtserfing-v-hurgade-luchshij-sezon-dlya-kajtserfinga/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajting-osobennosti-kajtinga-vidy-kajtinga/
https://kitehurghada.ru/russkaya-kajt-shkola-v-hurgade/
https://kitehurghada.ru/kajt-shkola-detivetra/
https://kitehurghada.ru/programma-obucheniya-kajtsyorfingu-iko-v-hurgade-egipet/
https://kitehurghada.ru/istoriya-kajtserfinga/
https://kitehurghada.ru/podarochnyj-sertifikat-na-obuchenie-kajtserfingu-v-hurgade/
https://kitehurghada.ru/chto-takoe-iko-kitesurfing/
https://www.tripadvisor.ru/Attraction_Review-g23408135-d12244940-Reviews-Kite_school_DETIVETRA-Second_Hurghada_Hurghada_Red_Sea_and_Sinai.html
https://goo.gl/maps/KcoqXRbKWDkdGBDA8
https://goo.gl/maps/JTXRid9mrHFiMH7n6
https://detivetra.ru
https://detivetra.ru/v-hurgade/
https://uslugi.yandex.ru/profile/DetiVetra-348058
https://www.facebook.com/groups/detivetra/
https://www.facebook.com/DETIVETRA.ru/
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCRG2aTtTaxbBAwlMTklO4ag
https://twitter.com/detivetra
https://rutube.ru/shorts/cb44391727e39c55e798f4efcecadbbe/
https://кайтинг-фото.рф/kayt-baza-v-hurgade.html
https://wa.me/79181955474
https://t.me/detivetrachat
https://www.instagram.com/detivetra.ru/
https://yandex.ru/profile/177183726173
https://yandex.ru/profile/1068186022
https://yandex.ru/profile/22472239976
https://yandex.ru/profile/72204785887
https://yandex.ru/profile/191148233877
https://xn—-7sbjteeyka8afw.xn--p1ai
https://vk.com/kiteschoolhurghadaegypt
https://vk.com/kite_deti_vetra_anapa
http://redseakite.ru
https://kiteschoolhurghada.ru
https://supanapa.ru
https://dzen.ru/a/ZdvCwDY4Lkx9j1OO
https://dzen.ru/a/ZdvAL3ptMCiNF8WX
https://dzen.ru/a/ZfigvDY3E2MON77x
https://dzen.ru/a/ZduLXm6jwDrtxbA7
https://dzen.ru/a/Zdt-SFBRjmyXXC7Y
https://dzen.ru/a/ZdvBm2tFz2D1IlSO
https://dzen.ru/a/Zdu_3c5NKkyfX91J
https://dzen.ru/a/ZdvCINgebnj0b5BQ
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNXr-xw-1ZbmsTT
https://dzen.ru/a/ZdCSXCL_8k_Tfrjb
https://dzen.ru/a/ZdKxCtywnzYZgrrk
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNfJwlmuCeqOEbb
https://dzen.ru/video/watch/65db9f94fb98fa6a95ab5e45?rid=925618026.48.1718444364156.12030
https://dzen.ru/video/watch/65d4341844e19f05a34cf61f?rid=925618026.48.1718444364156.12030
https://dzen.ru/video/watch/65629d684f336820c3b37487?rid=925618026.48.1718444364156.12030
https://dzen.ru/video/watch/64f689e39e331d6580277a0a?rid=925618026.48.1718444364156.12030
https://dzen.ru/video/watch/64f6870bcb2c7822b9dbd15c?rid=925618026.48.1718444364156.12030
https://dzen.ru/video/watch/6562982bd9b42c2e6bd10cae?rid=925618026.48.1718444364156.12030
https://dzen.ru/video/watch/64f684e1113e7a6a574076b2?rid=925618026.48.1718444364156.12030
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNYEjMz-VkvVGnB
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNi1ECY6h8nFsSW
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNpJ546JGYImpH1
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNTlZAOEk3ppmIO
https://dzen.ru/a/Zc_f2thSeW9zscF8
https://dzen.ru/a/Zc_U25ITFGrFK0Sf
https://dzen.ru/a/Zc_TAlxn1y1iHc43
https://dzen.ru/a/Zc_LEcYYfS-TrXXm
https://dzen.ru/a/ZVjdtJSQOhzbk0B1
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNS7dJWml8dLCim
https://dzen.ru/a/ZVdT4K4CRxpHZx1i
https://dzen.ru/a/ZVdb9TtUnQGek7_G
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNUDrwjFj4U3LBI
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNVSZAOEk3pp-ki
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNptIGpwlQkN-E1
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNqooGpwlQkORsw
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNnrk1VVGtQwolr
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNS0bwjFj4U25A9
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTNG7QlmuCeqISH6
https://dzen.ru/a/ZTM87Ogjh2c_dNzY
https://dzen.ru/b/ZS5ge6k6swm-YNzl
https://dzen.ru/b/ZS1BbXqKjhX4tA9_
https://dzen.ru/a/ZQ2aw4OzGFVaAbr2
https://dzen.ru/b/ZS5YZ7qcv2E0eJPQ
https://dzen.ru/a/ZQrJrb_XDifDVzGP
https://dzen.ru/a/ZQrIWS4n3ChkWGvj
https://dzen.ru/a/ZQrCRLpsYU4IGsNS
https://dzen.ru/a/ZQq5kyCaIkuoWgEb
https://dzen.ru/a/ZQq6z8LJ7AdPjTX6
https://dzen.ru/a/ZQrBHwW8ugdAoeld
https://dzen.ru/a/ZQq5zAyUYGuFpV6x
https://dzen.ru/a/ZQq6uF9dOExoiJn3
https://dzen.ru/a/ZQq4kyCaIkuoV7HL
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZtZAWIHk1Wxu36
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZ324ORLBGu36oK
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZ6mPf64TnWQmu4
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZqtxo5MUGqivHt
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZ3KI7QZRjreV_m
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZsDLf4FUB9-vTG
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZyyDEQHn8iOuK4
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZnc9bwiVMxJaDt
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZ2CaKi2WZuFDzk
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZw1iSYk23jVqD2
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZvXBo5MUGqmExv
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZusNZDrka3nhk4
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZomY7QZRjrXUWH
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZlbm0hO0O6e_6G
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZkz_Z4SEywAI9r
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZfLRo5MUGqXPqk
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZkQ47QZRjrTEiz
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZgZG72vTlMv-RA
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZUGxo5MUGqMHlM
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZTWRo5MUGqLTP3
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZSyvf64TnWzJmJ
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZQptZDrka3MWh9
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZRU5bXthdQL0rT
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZR4wm7BXTGU4QM
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZO09ZDrka3LqM1
https://dzen.ru/a/ZPZMvxpdEnCdGygY
Настройка Wi-Fi на принтерах Epson, таких, как модели L3250 и L3251, позволяет значительно упростить процесс печати и сканирования. Вы сможете печатать документы прямо с компьютера, смартфона или планшета, не используя провода.
здесь
Тут можно преобрести продвижение медицинских сайтов продвижение сайтов медицинской тематики
Бездепозитные фриспины фриспины без депозита за регистрацию с выводом
nhà cái net88 là nền tảng cá cược đẳng cấp, mang đến trải nghiệm cá cược hiện đại với giao diện mượt mà, bảo mật cao và nhiều phần thưởng giá trị.
Хотите о побеге от реальности? Kinogo.uk вручает коллекцию, где каждый кадр — история! Сотрите про походы в кино: загружайте новинки в 4K, хоть в обеденный перерыв! Ссылка-ключ: Смотреть киного — новые фильмы чаще, чем вы моргаете! У нас всегда взрывно — мы заждались!
Definitely believe that which you stated. Your favorite reason appeared to be on the internet the easiest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while people think about worries that they plainly do not know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top as well as defined out the whole thing without having side effect , people could take a signal. Will likely be back to get more. Thanks
Тут можно преобрести seo продвижение медицинских клиник продвижение сайта медицинских услуг
сайт про игры статьи красивые маленькие дома в майнкрафте схемы
1wi https://1win101.com.kg .
one win http://1win100.com.kg .
1win казино 1win казино .
Huawei RC предоставляет качественные услуги по ремонту техники Huawei, включая VR системы, ИБП (источники бесперебойного питания), ноутбуки, планшеты, серверы, смарт-часы и смартфоны.
здесь
Espectro de vibracion
Sistemas de calibración: fundamental para el rendimiento suave y efectivo de las equipos.
En el mundo de la avances avanzada, donde la rendimiento y la estabilidad del aparato son de máxima trascendencia, los sistemas de calibración juegan un función crucial. Estos sistemas dedicados están concebidos para calibrar y asegurar elementos rotativas, ya sea en herramientas productiva, vehículos de desplazamiento o incluso en dispositivos de uso diario.
Para los especialistas en conservación de aparatos y los especialistas, manejar con equipos de ajuste es esencial para asegurar el operación suave y estable de cualquier aparato móvil. Gracias a estas soluciones avanzadas avanzadas, es posible limitar significativamente las vibraciones, el sonido y la esfuerzo sobre los cojinetes, mejorando la longevidad de piezas valiosos.
Asimismo relevante es el rol que juegan los sistemas de equilibrado en la servicio al comprador. El apoyo experto y el reparación regular empleando estos dispositivos facilitan ofrecer prestaciones de excelente excelencia, aumentando la bienestar de los clientes.
Para los responsables de proyectos, la contribución en estaciones de balanceo y medidores puede ser fundamental para incrementar la efectividad y eficiencia de sus equipos. Esto es sobre todo trascendental para los inversores que gestionan pequeñas y medianas negocios, donde cada detalle vale.
Asimismo, los aparatos de calibración tienen una gran utilización en el campo de la prevención y el monitoreo de excelencia. Permiten identificar posibles errores, impidiendo arreglos caras y problemas a los dispositivos. También, los indicadores recopilados de estos sistemas pueden emplearse para perfeccionar procedimientos y incrementar la reconocimiento en buscadores de investigación.
Las áreas de uso de los equipos de ajuste cubren numerosas áreas, desde la manufactura de vehículos de dos ruedas hasta el control ambiental. No afecta si se habla de grandes producciones de fábrica o pequeños espacios caseros, los dispositivos de ajuste son fundamentales para proteger un desempeño óptimo y sin riesgo de detenciones.
мебель на заказ недорого Процесс создания шкафа начинается с выезда замерщика, который точно определит размеры и особенности помещения. Затем разрабатывается дизайн-проект, учитывающий все пожелания заказчика. После согласования проекта изготавливаются детали шкафа, которые затем собираются и устанавливаются на месте.
Unlock your vehicle’s potential with our top-notch auto tuning services! Explore your ride into a stunning masterpiece with our expert team. We specialize in enhancements that cater to your unique style. Our exceptional solutions ensure optimal performance and enhanced appearance. Don’t settle for average; elevate your driving experience and turn heads on the road! Visit us at https://phoenix-autobodyshop.com/ today and take the first step towards your dream car!
Наушники AirPods представляют собой удобный и стильный аксессуар от Apple, который популярен благодаря качественному звуку и беспроводному соединению. Однако владельцы этих устройств нередко сталкиваются с проблемой их внезапного отключения от телефона. Чтобы устранить эту неприятность, важно разобраться с ее причинами и понять, как их исправить.
здесь
статья квест игры как установить скин в майнкрафт лаунчер
получить 1000 рублей бесплатно за регистрацию бонусы без отыгрыша за регистрацию
Ровный, плотный и здоровый газон уже через несколько часов – это реально! Если вам нужна укладка рулонного газона под ключ москва, обращайтесь в Greenhistory.ru. Мы подготовим почву, привезем свежий газон и уложим его так, чтобы он прижился максимально быстро. Оставьте заявку прямо сейчас!
Роботы-пылесосы стремительно вошли в нашу жизнь, избавив нас от утомительных рутинных задач. Среди них особое место занимает Roborock, известный своей надежностью и удобством. Однако для того чтобы максимально использовать его возможности, важно разобраться, как настроить устройство. В этой статье я расскажу, как подключить робот-пылесос Roborock к телефону через Wi-Fi и интегрировать его с голосовым помощником Алисой от Яндекса. Все шаги простые, понятные, и вы однозначно справитесь с этим!
ссылка
Jante Rimnova
net88 cam kết mang đến hệ thống đổi thưởng minh bạch, giúp người chơi dễ dàng tham gia và tận hưởng những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời.
Excellent information on your blog, thank you for taking the time to share with us. Amazing insight you have on this, it’s nice to find a website that details so much information about different artists 스포츠중계
Игровые автоматы с бонусом за регистрацию без депозита Casino top
Admiring the time and effort you put into your blog and detailed information you offer!.. 토토사이트
утеплитель кнауф Строительные материалы компании Кануф в России. Доставка – Самовывоз. Оплата Нал/Безнал. огромный ассортимент товара.
canadian pharmacy online ship to usa: Express Canada Pharm – Express Canada Pharm
nhà cái net88 là sự lựa chọn hoàn hảo cho những ai yêu thích game bài đổi thưởng, với hệ thống rút tiền nhanh gọn và tỷ lệ thắng cao.
Устали от повторов? У нас тебя ждут сотни картин — от угарных комедий до аниме, ломающего реальность! Включайте в HD, без регистрации, под одеялом — кинотеатры рыдают! Бегите на hdrezka официальный — наш архив растёт как вселенная Marvel! Мы рады вам — попробуйте!
прохождение игры квеста красивые маленькие дома в майнкрафте схемы
прохождения игр квестов таблица рангов дота 2
1win. com 1win. com .
1вин партнерка 1win42.com.kg .
1 ван вин http://www.1win102.com.kg .
Надоели одни и те же фильмы? На hdrezka.day тебя ждут тысячи кинолент — от угарных комедий до триллеров, от которых немеют ноги! Смотрите в 4K, без регистрации, хоть с утра — кинотеатры рыдают! Бегите на фильмы онлайн — этот архив расширяется как вселенная Marvel! Мы рады вам — убедитесь!
nhà cái net88 là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai muốn thử sức với cá cược trực tuyến, mang đến kho game đa dạng và nhiều phần thưởng hấp dẫn.
сайт про игры статьи настройки графики кс го
nhà cái net88 mang đến những giây phút giải trí đầy kịch tính với hệ thống cá cược chuyên nghiệp, giao diện thân thiện và tỷ lệ thắng cao.
Игровые автоматы с бездепозитным бонусом за регистрацию с выводом бонусы за регистрацию
Выбор оптического прицела – одна из самых важных задач для охотника. Однако часто встречаются проблемы, связанные с недостаточной информированностью и грамотностью охотников, что может привести к серьезным промахам. Давайте разберемся в ключевых аспектах выбора оптики для лесной охоты.
ссылка
игры онлайн гайд как установить скин в майнкрафте на компьютере
nhà cái net88 là nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến uy tín, nơi người chơi có thể trải nghiệm hàng loạt trò chơi hấp dẫn như game bài, slot, cá cược thể thao với tỷ lệ thưởng cao.
Как приобрести аттестат о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
net88 cung cấp hệ thống cá cược chuyên nghiệp với giao diện thân thiện, dễ sử dụng, cùng các chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn dành cho thành viên mới và lâu năm.
кайт египет
Всё о покупке аттестата о среднем образовании: полезные советы
Современные смарт-часы Garmin – это надежные устройства, сделанные для удобного отслеживания активности и других данных. Но иногда их пользователи сталкиваются с техническими проблемами. Разберем основные из них и способы решения.
подробнее
1win. pro https://svstrazh.forum24.ru/?1-18-0-00000135-000-0-0-1741169701 .
Ипотека без сложностей https://volexpert.ru Наши риэлторы помогут выбрать идеальную квартиру и оформить ипотеку на лучших условиях. Работаем с топовыми банками, сопровождаем сделку, защищаем ваши интересы. Делаем покупку недвижимости доступной!
1win ракета http://aktivnoe.forum24.ru/?1-8-0-00000252-000-0-0-1741169084 .
В предверии праздника искал где купить цветы, нашёл этот магазин купить букеты теперь всегда буду заказывать здесь
скачать мостбет официальный сайт http://cah.forum24.ru/?1-13-0-00001559-000-0-0 .
soc88 là nhà cái cá cược hàng đầu với hệ thống trò chơi đa dạng, giao diện mượt mà và tỷ lệ hoàn trả cao, mang lại cơ hội trúng thưởng lớn.
Ваш гид по дизайну https://sales-stroy.ru строительству и ремонту! Советы профессионалов, актуальные тенденции, проверенные технологии и подборки лучших решений для дома. Всё, что нужно для комфортного и стильного пространства, на одном портале!
Игровые автоматы лучшие Бесплатные спины за регистрацию без депозита
сколько отправить посылку Бесплатные путешествия — реальность! Я расскажу как без затрат посещать теплые страны. Многие россияне обосновались на Бали, и им часто требуется доставка вещей из России. За транспортировку они готовы платить от 20 долларов за килограмм или фиксированную сумму за посылку. Берем два чемодана, заполняем их посылками, и вот мы уже на Бали, да еще и с прибылью! Найти заказчиков легко: поищите объявления на сайтах вроде https://t.me/antsdelivery и https://pikabu.ru/story/kak_mozhno_zarabotat_eshchyo_i_na_svoem_otdyikhe_12429519 наш официальный сайт https://antsdelivery.ru
Мульт-вселенная, где сбываются мечты!Платформа Kadikama.su открывает миллионы анимационных историй бесплатно, с эффектом погружения! Тут да-а строгий папа увлечётся от комедий! Жмите > мультики онлайн — гаджет станет окном в сказку! Обновляемся быстрее, чем растут дети!
DJ-пульты подвергаются высоким нагрузкам, особенно при частых выступлениях и транспортировках. Нередко поломки случаются из-за попадания влаги, механических повреждений или износа компонентов.
подробнее
Trazite pouzdane elektricni motor? Imamo siroku paletu modela za razlicite zadatke. Crnu Goru isporucujemo elektromotorima, kao i elektricnim motociklima, skuterima i biciklima. Ekoloski prihvatljiv transport za udobno putovanje. Visokokvalitetni motori i komponente po konkurentnim cijenama. Dostava i konsultacije – kontaktirajte nas!
Известный экономист Михаил Хазин в своем YouTube-канале положительно отзывается о займах без отказа через госуслуги. Подчеркивает, что такие сервисы максимально безопасны: официальная регистрация, ставка не выше 0.8%, защита от коллекторов на законодательном уровне.
nhà cái soc88 cung cấp nền tảng cá cược thông minh, giúp người chơi dễ dàng tham gia các trò chơi hấp dẫn và tận hưởng tỷ lệ kèo tốt nhất.
Ремонт консолей Xbox в сервисном центре в Москве. Ремонт Xbox Series X 1TB Digital Edition (Robot White) Xbox Series S 1TB (Robot White) Xbox One X 1 TB
перейти
Обожаю смотреть старые сериалы онлайн.
https://mynissanleaf.ru/profile.php?id=9123
Сколько стоят волосы Сколько стоят волосы? Цены на натуральные волосы могут сильно варьироваться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, таких как качество, длина и место покупки. Вот ориентировочные диапазоны наших цен: Короткие волосы (50 см): от 11100 руб. Средние волосы (60 см): от 12700 руб. Длинные волосы (70 см и выше): от 15500 руб. и выше, в зависимости от качества. Также стоит учитывать, что волосы, собранные с одного донорского источника и не подвергавшиеся химической обработке, обычно стоят дороже. Если вы планируете наращивание, не забудьте учесть стоимость услуг мастера. Рекомендуется сравнивать предложения от разных поставщиков и читать отзывы, чтобы найти лучшее соотношение цены и качества. ? Для более подробной консультации мы всегда готовы помочь! Свяжитесь с нами, и наши специалисты ответят на все ваши вопросы, помогут выбрать идеальный вариант и предложат персонализированные рекомендации. Мы ценим каждого клиента и стремимся сделать ваш опыт покупок максимально комфортным! ?? ???+?? женщина купить волосы
фриспины без депозита за регистрацию с выводом no deposit casino
nhà cái soc88 cung cấp nền tảng cá cược an toàn, chuyên nghiệp, với hệ thống đổi thưởng nhanh gọn, minh bạch, giúp người chơi yên tâm tham gia giải trí.
игровой ноутбук купить в самаре https://igrovye-noutbuki.ru
Excellent .. Amazing .. I’ll bookmark your blog and take the feeds also…I’m happy to find so many useful info here in the post. we need work out more techniques in this regard. thanks for sharing Slot game Malaysia
Jante Rimnova
I am definitely enjoying your website. You definitely have some great insight and great stories. 슬롯사이트
i love to also get some beach body but it requires a lot of diet modification and exercis malaysia online casino
Доска бесплатных объявлений objvlenie.ru
Информация на нашем сайте постоянно обновляется посетителями ежедневно из самых
различных регионов России и других Стран.
«objvlenie.ru» очень понятный сервис для любого пользователя, любого возраста.
Удобный сайт для подачи бесплатных и платных объявлений.
Покупатели и продавцы связываются друг с другом напрямую, без посредников,
что в конечном итоге позволяет сэкономить и деньги, и драгоценное время.
Премиум размещение стоит совсем недорого.
Сайт бесплатных объявлений objvlenie.ru
max88 mang đến sân chơi cá cược chuyên nghiệp, giúp người chơi tận hưởng các trò chơi đổi thưởng hấp dẫn và cơ hội nhận nhiều phần thưởng giá trị.
https://olimp-yug.ru/media/pgs/smotret_filmu_v_horoshem_kachestve_besplatno_onlayn.html цыганская свадьба видео у бедных
Wonderful blog! I found it while surfing around on Yahoo News. Do you have any suggestions on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Appreciate it. 미투벳 도메인 주소
1win вход 1win вход .
скачать мостбет официальный сайт скачать мостбет официальный сайт .
max88 là sân chơi cá cược trực tuyến lý tưởng, giúp người chơi trải nghiệm những trò chơi đổi thưởng công bằng, minh bạch và dễ dàng nhận thưởng.
Товары для вашего авто https://avtostilshop.ru автоаксессуары, масла, запчасти химия, электроника и многое другое. Быстрая доставка, акции и бонусы для постоянных клиентов. Подбирайте товары по марке авто и будьте уверены в качестве!
1wln aqvakr.forum24.ru/?1-3-0-00001121-000-0-0 .
Your content is nothing short of bright in many forms. I think this is friendly and eye-opening material. I have gotten so many ideas from your blog. Thank you so much. 사이트추천
I have read your excellent post. This is a great job. I have enjoyed reading your post first time. I want to say thanks for this post. Thank you.. 레드벨벳카지노
” ‘훌륭한 유용한 리소스를 무료로 제공하는 가격을 알 수있는 웹 사이트를 보는 것이 좋습니다. 귀하의 게시물을 읽는 것이 정말 마음에 들었습니다. 감사합니다! 유튜벳
Товары для вашего авто интернет-магазин автозапчастей автоаксессуары, масла, запчасти химия, электроника и многое другое. Быстрая доставка, акции и бонусы для постоянных клиентов. Подбирайте товары по марке авто и будьте уверены в качестве!
Amazing experience after visiting this site which is really full of information and someone have information for.And also you could buy some cosplay costumes from http://www.cosjj.com/ in high quality. news update for latest updates in urdu language this is best . Just have fun. オンカジ
Very good post.Really looking forward to read more. Really Great. Gary Suter
nhà cái max88 cam kết mang đến sân chơi cá cược an toàn, giúp người chơi tận hưởng những phút giây giải trí hấp dẫn với hệ thống cá cược tiên tiến.
фриспины без депозита за регистрацию с выводом фриспины без депозита
Такси для бизнеса https://www.business-gazeta.ru/article/391550 работа по всей России. Удобные поездки для сотрудников! Оформите корпоративный аккаунт и получите выгодные условия, детальную отчетность и надежный сервис. Быстрое бронирование, прозрачные тарифы, комфортные автомобили – организуйте рабочие поездки легко!
Very likely I’m going to bookmark your blog . You absolutely have wonderful stories. Cheers for sharing with us your blog 링크모음사이트 링크팡
Такси для бизнеса https://www.drive2.ru/o/b/672379948761088534/ работа по всей России. Удобные поездки для сотрудников! Оформите корпоративный аккаунт и получите выгодные условия, детальную отчетность и надежный сервис. Быстрое бронирование, прозрачные тарифы, комфортные автомобили – организуйте рабочие поездки легко!
I cannot thank you enough for the blog. Much thanks again. Really Great. 해피카지노 도메인 주소
max88 là nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến hàng đầu, nổi bật với kho trò chơi phong phú, giao diện thân thiện và nhiều ưu đãi hấp dẫn cho người chơi.
Управление бизнесом АУДИТ БИЗНЕС-ПРОЦЕССОВ: ПЕРВЫЙ ШАГ К ПОВЫШЕНИЮ ЭФФЕКТИВНОСТИ Откройте для себя важность аудита бизнес-процессов для выявления проблемных зон и улучшения работы компании. Регулярный аудит бизнес-процессов позволяет оптимизировать работу, сократить издержки и повысить прибыльность. Это комплексный анализ, выявляющий узкие места и неэффективные операции. Ключевые этапы аудита включают анализ документации, интервью с сотрудниками и оценку текущих показателей. Результатом становится четкая картина сильных и слабых сторон. Внедрение изменений, основанных на результатах аудита, ведет к оптимизации workflow и улучшению взаимодействия между отделами. Это напрямую влияет на рост бизнеса. Используйте аудит бизнес-процессов как инструмент для постоянного совершенствования и достижения конкурентных преимуществ. Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг: от разработки стратегии развития до внедрения новых технологий. Наша команда состоит из опытных управленцев, финансистов и экспертов в различных отраслях бизнеса. Мы поможем вам оптимизировать бизнес-процессы, повысить эффективность работы персонала и увеличить прибыльность компании.
Please share more like that. 슬롯추천
좋은 사이트가 있습니다. 정말 쉽고 탐색하기 좋은 웹 사이트가 훌륭하고 멋져 보이고 따라 가기 매우 쉽다고 생각합니다. 큐카지노 도메인 주소
https://investmana.ru/skalping/plecho-skalping/
max88 cam kết mang đến sân chơi cá cược công bằng, nơi người chơi có thể trải nghiệm các trò chơi hấp dẫn với tỷ lệ thắng cao.
https://turbocomp.ru/images/pgs/kiberpank__mir_budushego_na_grani_tehnologiy_i_chelovechnosti.html игры на яндекс бесплатно и без регистрации
nhà cái max88 là lựa chọn hàng đầu cho những ai yêu thích cá cược trực tuyến, với kho trò chơi phong phú từ casino, thể thao đến game bài đổi thưởng.
Элегантные ковры для любого интерьера, декор.
Лучшие варианты ковров для вашего дома, со скидкой.
Ковры ручной работы, выбирайте.
Декорируйте пространство с помощью ковров, придайте.
Безопасные и яркие ковры для детской, разнообразие.
Декоративные ковры для любого стиля, высокое качество.
Создание комфортного рабочего пространства с коврами, уникальность.
Ковры, которые легко чистить, исследуйте.
Советы по выбору ковра, тайны.
Теплота и уют с коврами, подберите.
Модные ковры 2025 года, выбор.
Ковры для вашего загородного стиля, практичность.
Ковры в интерьере: вдохновение, исследуйте.
Выбор ковров для любого вкуса, дизайн.
Создайте атмосферу уюта в спальне, мягкие текстуры.
Премиальные ковры для вашего интерьера, инвестируйте.
Мои любимые ковры для зоолюбителей, решения.
Согревающие ковры для вашего дома, приобретайте.
Как использовать ковры для зонирования, откройте.
детские коврики детские коврики .
снять шлюху в питере можно купить героин
ебут под мефом где можно порно детские
https://www.business-gazeta.ru/article/517826
nhà cái max88 mang đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn, minh bạch, với hệ thống bảo mật tiên tiến và hỗ trợ người chơi 24/7.
Заполните форму заявки на сайте TCL Repair Center или свяжитесь с нами для уточнения деталей. Мы позаботимся о вашей технике TCL и быстро вернем её в строй! Не упустите возможность воспользоваться скидкой до 25% при записи онлайн.
перейти
премиальные цветы в городе Томске розы шикарный сервис и всегда свежие цветы
Онлайнказино Бонсай bonsai casino2 игровые автоматы, рулетка, покер и живые дилеры! Получайте бонусы за регистрацию, участвуйте в турнирах и выводите выигрыши без задержек. Надёжность, безопасность и азарт – всё в одном месте!
Актуальні новини будівництва https://dverikupe.com.ua та нерухомості в Україні. Огляди ринку, тренди, технології, законодавчі зміни та експертні думки – все про будівельну галузь на одному сайті!
max88 ngay hôm nay để không bỏ lỡ cơ hội tham gia vào nhà cái cá cược uy tín, nhận thưởng hấp dẫn và tận hưởng những trò chơi kịch tính nhất.
Дізнавайтеся про останні новини https://ampdrive.info електромобілів, супекарів та актуальні події автомобільного світу в Україні. Ексклюзивні матеріали, фото та аналітика для справжніх автолюбителів на AmpDrive.?
наращивание волос Наращивание волос — это популярная процедура для изменения длины и объема. Вот основные моменты: Методы: Капсульное: Крепление капсул к натуральным волосам. Ленточное: Пряди приклеиваются с помощью лент. На микроколечках: Пряди крепятся с помощью маленьких колечек. Выбор волос: Натуральные волосы выглядят естественно, искусственные — более доступны по цене. Уход: Используйте мягкие шампуни и кондиционеры, избегайте горячих укладок. Консультация: Рекомендуется поговорить с мастером для выбора метода и волос. Стоимость: Цены варьируются в зависимости от метода и качества. Это отличный способ изменить образ и повысить уверенность! купить натуральные волосы в москве
1wiun aktivnoe.forum24.ru/?1-8-0-00000254-000-0-0-1741273702 .
1 win.am 1 win.am .
один вин официальный сайт https://1win109.com.kg .
Заполните форму заявки на сайте TCL Repair Center или свяжитесь с нами для уточнения деталей. Мы позаботимся о вашей технике TCL и быстро вернем её в строй! Не упустите возможность воспользоваться скидкой до 25% при записи онлайн.
подробнее
https://spbzn.ru/crm/pgs/?filmu_zagadki__magiya_tainstvennogo_kino.html топ 10 фильмов к просмотру
nhà cái fm88 là sự lựa chọn hoàn hảo cho những ai yêu thích cá cược trực tuyến, với kho trò chơi đa dạng và hàng loạt chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn.
Also visit my website: https://cryptolake.online/crypto7
bonus casino Бонусы за регистрацию
https://66.ru/news/misc/234501/
Нужен качественный и оперативный ремонт тепловизоров Guide в Москве? Сервисный центр предлагает профессиональную помощь, доступную каждому владельцу термографических устройств бренда Guide. Мы устраняем все типы неисправностей, гарантируя высокое качество услуг и оперативные сроки работы.ссылка
https://oknaishim.ru
Актуальні новини політики https://insideukr.com в Україні та світі. Аналітика, думки експертів, головні події дня та ексклюзивні матеріали – будьте в курсі разом із нами!
Honey Money Казино https://honeymoneycasino.ru это захватывающий мир азартных игр с щедрыми бонусами, быстрыми выплатами и огромным выбором слотов, рулетки, покера и других развлечений. Играй онлайн в любое время, участвуй в турнирах и получай эксклюзивные награды.
Лучшие онлайн казино usdt казино рейтинг топовых игровых платформ с лицензией, щедрыми бонусами, быстрыми выплатами и широким выбором слотов, покера, рулетки и других азартных игр. Мы собрали проверенные казино с высоким рейтингом, безопасностью и выгодными акциями.
fm88 win là nhà cái cá cược đáng tin cậy, với nhiều trò chơi cá cược hấp dẫn, tỷ lệ cược cao và hệ thống giao dịch nhanh chóng.
купить керамогранит недорого керамогранит светлый
керамогранит купить дешево керамогранит бежевый
Купить телевизоры на дачу https://televizory-dlya-dachi.ru в интернет-магазине по низкой цене! При покупке дачных телевизоров на сайте воспользуйтесь скидками, акциями, бонусной программой.
nhà cái fm88 cam kết cung cấp hệ thống cá cược chất lượng, giúp người chơi tận hưởng không gian giải trí đẳng cấp với các trò chơi đổi thưởng hấp dẫn.
бонусы за регистрацию Top casino с выводом
https://ecotruck.su/images/pgs/iz_rossii_s_lubovu__kino_90_h.html псалмы слушать валаамский монастырь слушать бесплатно без рекламы без остановки в хорошем качестве
fm88 là nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến hàng đầu, thu hút người chơi với kho game phong phú, tỷ lệ cược hấp dẫn và hệ thống bảo mật tiên tiến.
Натяжные потолки с установкой https://natyazhnye-potolki2.ru стильное и практичное решение для любого интерьера. Предлагаем широкий выбор фактур и цветов, качественные материалы, быстрый монтаж и гарантию на работу. Устанавливаем потолки любой сложности в квартирах, домах, офисах.
Отдых в Анапе https://otdyh-vanape.ru идеальный выбор для всей семьи! Чистые песчаные пляжи, теплое море, развитая инфраструктура и развлечения на любой вкус. Гостиницы, отели, частный сектор – найдите идеальное жилье.
Ремонт оптических прицелов в Краснодаре: выполним ремонт в 4 быстрых шага. Оставляйте свою заявку на сайте подробнее
какой недорогой телевизор лучше купить https://nedorogie-televizory.ru
fm88 win mang đến không gian cá cược trực tuyến chuyên nghiệp, với nhiều lựa chọn trò chơi đa dạng và cơ hội trúng thưởng cực lớn.
1winn 1winn .
1win официальный сайт вход http://1win110.com.kg/ .
1хwin 1хwin .
Дягилев
fm88 là nhà cái cá cược hàng đầu, giúp người chơi tận hưởng những giây phút giải trí thú vị với hệ thống cá cược hiện đại và tỷ lệ đổi thưởng cao.
Все о компьютерных играх https://lifeforgame.ru/ обзоры новых проектов, рейтинги, детальные гайды, новости индустрии, анонсы и системные требования. Разбираем особенности геймплея, помогаем с настройками и прохождением. Следите за игровыми трендами, изучайте секреты и погружайтесь в мир гейминга.
https://lepidopterolog.ru/media/pgs/kinovselennaya_marvel__istoriya__filmu_i_vliyanie_na_pop_kulturu.html смотреть новинки русского кино бесплатно
телевизор smart tv 75 https://televizory-smart-tv.ru
ultra hd 4k oled телевизор lg oled s9 ultra телевизор haier
Ремонт оптических и тепловизионных прицелов Guide в Москве здесь
fm88 giúp người chơi truy cập nhanh chóng vào thế giới cá cược chuyên nghiệp, nơi họ có thể thử vận may với nhiều trò chơi hấp dẫn.
Jante Rimnova
Dota 2
fm88 cung cấp nền tảng cá cược hiện đại, nơi người chơi có thể tận hưởng những trò chơi hấp dẫn và trải nghiệm cá cược đẳng cấp.
https://mites59.ru
наращивание волос Наращивание волос — это популярная процедура для изменения длины и объема. Вот основные моменты: Методы: Капсульное: Крепление капсул к натуральным волосам. Ленточное: Пряди приклеиваются с помощью лент. На микроколечках: Пряди крепятся с помощью маленьких колечек. Выбор волос: Натуральные волосы выглядят естественно, искусственные — более доступны по цене. Уход: Используйте мягкие шампуни и кондиционеры, избегайте горячих укладок. Консультация: Рекомендуется поговорить с мастером для выбора метода и волос. Стоимость: Цены варьируются в зависимости от метода и качества. Это отличный способ изменить образ и повысить уверенность! купить волосы нижний новгород
keonhacai5 cung cấp bảng kèo đầy đủ và cập nhật liên tục, giúp người chơi có cái nhìn tổng quan trước khi đặt cược vào các trận đấu thể thao.
http://kuzovkirov.ru/wp-content/pgs/romanticheskie_komedii__spisok_luchshih_smeshnuh_filmov_o_lubvi.html танцы на приморском бульваре севастополь последнее видео 2024
Все о недвижимости https://rentalsea.ru покупка, аренда, ипотека. Разбираем рыночные тренды, юридические тонкости, лайфхаки для выгодных сделок. Помогаем выбрать квартиру, рассчитать ипотеку, проверить документы и избежать ошибок при сделках с жильем. Актуальные статьи для покупателей, арендаторов и инвесторов.
Все о недвижимости https://stroyk-wood.ru покупка, аренда, ипотека. Разбираем рыночные тренды, юридические тонкости, лайфхаки для выгодных сделок. Помогаем выбрать квартиру, рассчитать ипотеку, проверить документы и избежать ошибок при сделках с жильем. Актуальные статьи для покупателей, арендаторов и инвесторов.
kèo nhà cái 5 hỗ trợ người chơi cập nhật tỷ lệ kèo theo thời gian thực, đảm bảo những thông tin cá cược chính xác nhất để đặt cược hiệu quả.
отправить посылку по городу Бесплатные путешествия — реальность! Я расскажу как без затрат посещать теплые страны. Многие россияне обосновались на Бали, и им часто требуется доставка вещей из России. За транспортировку они готовы платить от 20 долларов за килограмм или фиксированную сумму за посылку. Берем два чемодана, заполняем их посылками, и вот мы уже на Бали, да еще и с прибылью! Найти заказчиков легко: поищите объявления на сайтах вроде яндекс отправить посылку и какой посылкой отправить
Kèo nhà cái giúp người chơi theo dõi tỷ lệ cược và thay đổi kèo trong thời gian thực, từ đó có chiến lược đặt cược hợp lý nhất.
Все о компьютерных играх https://lifeforgame.ru обзоры новых проектов, рейтинги, детальные гайды, новости индустрии, анонсы и системные требования. Разбираем особенности геймплея, помогаем с настройками и прохождением. Следите за игровыми трендами, изучайте секреты и погружайтесь в мир гейминга.
Все о недвижимости https://konsta-ovk.ru покупка, аренда, ипотека. Разбираем рыночные тренды, юридические тонкости, лайфхаки для выгодных сделок. Помогаем выбрать квартиру, рассчитать ипотеку, проверить документы и избежать ошибок при сделках с жильем. Актуальные статьи для покупателей, арендаторов и инвесторов.
научиться шаффл зумба для начинающих
Looking for free steam accounts https://t.me/sharedsteam? We regularly share working accounts with games, bonuses, and tips. Subscribe now and don’t miss new giveaways! Only verified and active accounts.
https://naturalbeekeeping.ru/wp-content/pgs/filmu_140.html кинотеатр октябрь люберцы расписание сеансов и цены на сегодня 2024
Наш сервисный центр re:bork предоставляет профессиональный ремонт таких устройств, как кофемашины, пылесосы, роботы-пылесосы, индукционные плиты, водонагреватели, парогенераторы, увлажнители и очистители воздуха, массажные кресла, электросамокаты, гладильные системы и отпариватели. Мы вернем вашим устройствам вторую жизнь! подробнее
MetaMask Download is a smart move for investors. Keeping assets safe while accessing blockchain networks has never been easier.
https://vavada37.com/
Все о недвижимости https://kvadrolampa.ru покупка, аренда, ипотека. Разбираем рыночные тренды, юридические тонкости, лайфхаки для выгодных сделок. Помогаем выбрать квартиру, рассчитать ипотеку, проверить документы и избежать ошибок при сделках с жильем. Актуальные статьи для покупателей, арендаторов и инвесторов.
вкусные рецепты Eda321 – ваш незаменимый помощник в мире кулинарии! Мы собрали для вас богатую коллекцию рецептов, способных удовлетворить любой вкус и уровень подготовки. Откройте для себя простые, вкусные и быстрые рецепты, идеально подходящие для приготовления блюд на каждый день. Наша домашняя кухня – это кладезь идей для тех, кто ценит традиционные русские блюда. Начинающим кулинарам мы предлагаем рецепты с подробными фото, которые помогут освоить азы кулинарного искусства. Опытные кулинары найдут для себя интересные и оригинальные блюда из мяса, рыбы, курицы и картофеля. На Eda321 вы всегда найдете вдохновение для кулинарных экспериментов и сможете порадовать своих близких вкусными и полезными блюдами. Присоединяйтесь к нам, и вместе мы откроем новые горизонты в мире кулинарии!
телевизор mi qled tv https://televizory-qled.ru
Все о компьютерных играх https://lifeforgame.ru обзоры новых проектов, рейтинги, детальные гайды, новости индустрии, анонсы и системные требования. Разбираем особенности геймплея, помогаем с настройками и прохождением. Следите за игровыми трендами, изучайте секреты и погружайтесь в мир гейминга.
keonhacai5 cam kết mang đến bảng tỷ lệ kèo chính xác, minh bạch, giúp người chơi dễ dàng đặt cược vào các trận đấu yêu thích.
keonhacai là nền tảng cá cược uy tín, giúp người chơi dễ dàng đặt cược vào các trận đấu thể thao với tỷ lệ cược chính xác và cạnh tranh.
https://химчисткамебели.online
сколько стоит отправить посылку почтой Бесплатные путешествия — реальность! Я расскажу как без затрат посещать теплые страны. Многие россияне обосновались на Бали, и им часто требуется доставка вещей из России. За транспортировку они готовы платить от 20 долларов за килограмм или фиксированную сумму за посылку. Берем два чемодана, заполняем их посылками, и вот мы уже на Бали, да еще и с прибылью!
https://casinoslot.shop/
Оптические прицелы являются сложными устройствами, которые обеспечивают точность и комфорт при стрельбе. Поломка такого прибора может стать серьёзной проблемой, требующей профессионального вмешательства. подробнее
https://astorplace.ru/wp-content/pgs/filmu_onlayn___novuy_uroven_domashnego_kinoteatra.html нина кирсо кораблик любви слушать онлайн бесплатно в хорошем качестве
Мир компьютерных игр https://lifeforgame.ru/ Мы расскажем о лучших новинках, секретах прохождения, системных требованиях и игровых трендах. Новости, гайды, обзоры и рейтинги – всё, что нужно геймерам.
I appreciate, cause I discovered exactly what I used to be having a look for. You’ve ended my four day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a nice day. Bye pedrovazpaulo business consultant
Покупка, аренда, ипотека https://knyaz-dolgoruky.ru всё о недвижимости в одном блоге! Советы по выбору жилья, юридические аспекты, анализ цен и прогнозы рынка. Рассказываем, как грамотно оформить ипотеку, проверить документы и избежать ошибок при сделках с недвижимостью. Будьте в курсе всех изменений и трендов!
зумба уроки для начинающих https://opendance.ru
1wiin https://1win11.am .
1win сайт online http://1win12.am/ .
1вин официальный регистрация https://1win13.am/ .
Играйте в онлайн-казино https://t.me/casino_na_ruble/6 с рублевыми счетами! Надежные казино с моментальными выплатами, бонусами и фриспинами. Пополнение через карты, кошельки и криптовалюту. Выбирайте топовые игры и выигрывайте без лишних комиссий!
Онлайн казино https://t.me/igrovie_avtomati_igrat/22 с лучшими бонусами и шансом на крупный выигрыш! Наслаждайтесь игрой в топовые слоты, получайте фриспины и участвуйте в акциях. Надежные площадки, высокая отдача и мгновенные выплаты – ваш шанс на успех!
Играйте в онлайн-казино промокоды на фриспины топовые игровые автоматы, лайв-дилеры, мгновенные выплаты и бонусы для новых игроков. Наслаждайтесь честной игрой, удобными платежными методами и крупными выигрышами!
Где купить волосы Где купить волосы? У нас вы можете приобрести натуральные волосы отличного качества! Мы предлагаем: Натуральные волосы разных категорий: У нас есть волосы от самых доступных до премиум-класса, чтобы каждый мог найти идеальный вариант для себя.
keo nha cai giúp người chơi theo dõi và cập nhật tỷ lệ cược mới nhất, từ đó đưa ra quyết định đúng đắn khi tham gia cá cược.
Top casino с выводом какие автоматы дают деньги за регистрацию без депозита
Ремонт серверов HP и другой электроники HP в Москве – Сервисный центр HP подробнее
бани под ключ
Сколько стоят волосы Сколько стоят волосы? Цены на натуральные волосы могут сильно варьироваться в зависимости от нескольких факторов, таких как качество, длина и место покупки. Вот ориентировочные диапазоны наших цен: Короткие волосы (50 см): от 11100 руб. Средние волосы (60 см): от 12700 руб. Длинные волосы (70 см и выше): от 15500 руб. и выше, в зависимости от качества.
Kèo nhà cái mang đến những nhận định kèo chuyên sâu, giúp người chơi có thêm thông tin hữu ích khi đặt cược vào các trận đấu bóng đá.
На телефоне Samsung некорректно работает сенсорный экран: 8 причин и методов исправить самостоятельно перейти
Kèo nhà cái giúp người chơi có thể theo dõi biến động kèo theo từng trận đấu, từ đó điều chỉnh chiến lược đặt cược hiệu quả.
https://blok-beton.ru
great blog very nice articles I will follow you continuously sohbet odaları
работа эскорт москва
элитный эскорт москвы
1win mexico https://1win3.com.mx/ .
1win. casino. https://www.1win4.com.mx .
win1 casino https://1win5.com.mx/ .
The best casino New Retro Casino! Classic slot machines, generous bonuses and reliable payouts. Enjoy the excitement of retro slots and play on a proven platform!
Где отремонтировать сложную оптику: тепловизоры, прицелы, дальномеры, коллиматоры, монокуляры. Вот на гугл картках отметка сервисного центра подробнее
Все, что вам нужно для игры Vavada Casino бездепозитный бонус! Игровые автоматы, рулетка, покер, живые дилеры и эксклюзивные бонусы. Наслаждайтесь качественной игрой с мгновенными выплатами и надежными провайдерами!
Играйте онлайн в JVSpin Bet – лицензионное онлайн-казино с лучшими слотами, лайв-играми и щедрыми бонусами. Пополняйте счет удобными способами, получайте награды и выигрывайте реальные деньги!
Играйте в Jozz промокод популярное онлайн-казино с широким выбором слотов, настольных игр и лайв-дилеров. Выгодные бонусы, удобные платежные системы и моментальные выплаты ждут вас!
Выбирайте https://t.me/s/booi_casino_site топовое онлайн-казино с выгодными акциями, эксклюзивными играми и лайв-казино. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу игроков и получайте максимальное удовольствие от игры!
A powerful VPN solution https://github.com/ivanti-it/Ivanti-Secure-Access-Client/releases designed to provide secure remote access to corporate networks. The software supports multiple authentication methods, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), certificates, and biometrics.
Если техника Gigabyte вышла из строя, не спешите покупать новую! Наш сервисный центр Gigabyte Repair Center предлагает профессиональные услуги по диагностике и ремонту вашего устройства. Мы специализируемся на быстром и качественном восстановлении видеокарт, материнских плат, мониторов и ноутбуков данной марки. перейти
Свіжі ідеї дизайну https://dverikupe.od.ua інтер’єру, сучасні тренди, поради щодо декору та ремонту. Створюйте затишок та стиль у кожному куточку вашого дому!
Сброс лишнего веса, расстройства пищевого поведения, психологическая коррекция, РПП, избыточная масса тела, помощь психолога. психокоррекция
лазерная эпиляция глубокое бикини цена лазерная эпиляция спб цены для женщин
свіжі новини криптовалют https://cryptonews.v.ua блокчейна та DeFi. Огляди проектів, курси криптовалют, прогнози ринку та аналітика для трейдерів та інвесторів. Слідкуйте за криптомир з нами!
типография напечатать типография печать
keonhacai giúp người chơi dễ dàng tiếp cận với các trận đấu lớn, nắm bắt tỷ lệ kèo và đưa ra lựa chọn đặt cược hợp lý nhất.
keonhacai5 hỗ trợ người chơi nắm bắt xu hướng kèo cược, từ đó đưa ra quyết định sáng suốt và có chiến lược cá cược hiệu quả.
https://kazhdogopravo.ru
keonhacai là công cụ không thể thiếu trong cá cược thể thao, giúp người chơi phân tích tỷ lệ cược và tối ưu hóa chiến lược cá cược hiệu quả.
Great posts! I am actually getting ready to across this information, is very helpful my friend. Also great blog here with all of the valuable information you have. Keep up the good work you are doing here. 메이저사이트
palmslots petos
keonhacai5 cập nhật tỷ lệ kèo nhanh chóng, giúp người chơi kịp thời điều chỉnh chiến lược đặt cược và tối ưu hóa lợi nhuận.
nha cai uy tin sở hữu kho trò chơi đa dạng, từ cá cược thể thao, casino trực tuyến đến game bài đổi thưởng, mang đến trải nghiệm giải trí đỉnh cao.
top nhà cái uy tín giúp người chơi có sự lựa chọn tốt nhất khi tìm kiếm những nhà cái uy tín, nơi cung cấp dịch vụ cá cược an toàn và bảo mật.
Покупка недвижимости и ипотека https://rentalsea.ru что нужно знать? Разбираем выбор жилья, условия кредитования, оформление документов и юридические аспекты. Узнайте, как выгодно купить квартиру и избежать ошибок!
бездепозитные игровые автоматы Бездепозитные бонусы с выводом
I’m happy I located this blog! From time to time, students want to cognitive the keys of productive literary essays composing. Your first-class knowledge about this good post can become a proper basis for such people. nice one 토토 사이트
Nhà cái uy tín giúp người chơi có cái nhìn tổng quan về những nhà cái hàng đầu, nơi mang đến trải nghiệm cá cược chất lượng và an toàn.
кайт школа анапа
Квадрокоптеры DJI — это высокотехнологичные устройства, обеспечивающие захватывающие возможности в видеосъемке и навигации. Однако даже самые надёжные дроны иногда сталкиваются с проблемами. Эта статья поможет разобраться в частых неисправностях, их причинах, способах устранения и ситуациях, когда без сертифицированного сервисного центра не обойтись. подробнее
Unlock your vehicle’s potential with our top-notch auto tuning services! Discover your ride into a stunning masterpiece with our expert team. We specialize in customizations that cater to your unique style. Our reliable solutions ensure optimal performance and enhanced appearance. Don’t settle for average; elevate your driving experience and turn heads on the road! Visit us at https://americasbestcertifiedautobody.com/ today and take the first step towards your dream car!
Nhà cái uy tín được đánh giá cao nhờ dịch vụ cá cược chuyên nghiệp, hệ thống bảo mật chặt chẽ và nhiều khuyến mãi hấp dẫn cho người chơi.
ипотека и покупка недвижимости https://vam42.ru что нужно знать? Разбираем выбор жилья, условия кредитования, оформление документов и юридические аспекты. Узнайте, как выгодно купить квартиру и избежать ошибок!
Buy elite Montenegro real estate investment: purchase apartments and houses without risks! Current prices, transaction execution, taxes and residence permit. Profitably purchase housing for life, recreation or investment.
Мы знаем, насколько важна для вас надежность техники GoPro, и делаем всё, чтобы вернуть её в рабочее состояние в максимально короткие сроки. Узнайте, почему GoPro Center — лучший выбор для ремонта ваших устройств. Получите бесплатную консультацию по телефону и мы определим стоимость ремонта техники Go Pro. подробнее
Nhà cái uy tín cung cấp nền tảng cá cược chất lượng, nơi người chơi có thể tham gia cá cược thể thao, casino và slot game một cách an toàn.
Ваши устройства Honor требуют профессионального ремонта? Honor Center — это сервисный центр, где устраняют любые неисправности с высокой точностью и гарантией. Мы работаем в Москве, Санкт-Петербурге, Нижнем Новгороде, Ростове-на-Дону, Краснодаре, Екатеринбурге, Казани и Новосибирске. Наши мастера специализируются на ремонте ноутбуков, планшетов, смарт-часов и смартфонов Honor. Закажите ремонт Хонор и мы выполним качественно и быстро! перейти
бонусы без отыгрыша за регистрацию Бездепозитные бонусы с выводом
Если техника Samsung перестала работать, не спешите покупать новую. Сервисный центр Samsung предоставляет профессиональные услуги по ремонту всех видов устройств этого бренда. Мы гарантируем высокое качество, оперативность и надежность ремонта благодаря опыту наших мастеров и использованию исключительно оригинальных запчастей. подробнее
top amazon deals
мостбет вход https://mostbet34.com.kg/ .
gta samp rp готовые сервера самп
скачать гта самп на пк samp skin’s
1win kg https://1win104.com.kg/ .
Тут можно преобрести продвижение медицинских услуг сео продвижение медицинских сайтов
Бонусы за регистрацию bonuses casinos
1win bet 1win bet .
Когда я зашёл на эту платформу, чувство было таким, будто я нашёл что-то особенное. Здесь каждый спин — это не просто шанс, а история, которую ты проживаешь с каждым кликом.
Интерфейс интуитивен, словно ветер судьбы направляет тебя от выбора к выбору. Транзакции, будь то депозиты или выплаты, проходят плавно, как поток воды, и это удивляет. А техподдержка всегда рядом, как надежный товарищ, который никогда не оставит.
Для меня Селектор стал местом, где игра и вдохновение соединяются. Здесь каждая минута — это часть картины, которую хочется создавать снова и снова.
Оптические прицелы являются важным инструментом для стрелков и охотников, и их корректное функционирование жизненно важно для достижения точности при стрельбе. Однако, как и любое другое оборудование, прицелы могут сталкиваться с определенными проблемами. В данной статье мы рассмотрим типичные неисправности оптических прицелов и предложим эффективные решения. подробнее
“You get some of me but not tomorrow as they want me in as soon as I can make it happen. This is the one time when they say jump and I ask how high due the financial gains the company could benefit from and it being important enough for the client to appear in person.”
“Well I get an extra night of you at least! I wonder what we could do with that? Meantime, what about food? I am starving and delicious as it was a second breakfast is not quite enough to replenish me!”
“Well get something on and we’ll sort that out first.”
We drove into town and decided that a daytime visit to Charlie’s was going to be the answer. I parked in the bar lot and Elise dashed in to change into something more appropriate, jeans and a t-shirt along with her biker jacket but keeping her Converses on.
Walking down to the restaurant was different from the middle of the night visits as the streets were bustling and all of the shops and outlets were open.
Reaching Charlie’s we entered the front door and sat in a booth near the window. A beautiful young American Chinese girl came,smiled and said hello to Elise and gave us menus and asked if we wanted drinks in the meantime.
“No thanks Lin just a pot of Jasmine tea for us please.” Lin went back to the kitchen area. “No booze for me today as I will have to work in the bar so it is just tea for me.”
Not in a drinking mood either, I agreed with her.”
https://hmelokill1994.diary.ru/
https://haveagood.holiday/users/368795
https://www.haikudeck.com/presentations/vKlKpuVQ4T
https://anotepad.com/notes/kh3fr445
http://www.babelcube.com/user/frank-dhoodi
Najboljse pocitnice hotel Zabljak Montenegro! Uzivajte v udobju, svezem zraku in osupljivi pokrajini. Gorske poti, smucanje, izleti in prijetno vzdusje. Brezplacen Wi-Fi, zajtrk in parkirisce. Rezervirajte bivanje v osrcju narave!
Dobrodosli v hotel Bianca Kolasin! Uzivajte v udobnih sobah, osupljivem razgledu in odlicni storitvi. Pozimi – smucanje, poleti – pohodi v gore in izleti. Prirocna lokacija, restavracija, SPA in prijetno vzdusje. Rezervirajte nepozabne pocitnice!
Хотите сдать радиолом https://radiolom99.ru? Мы принимаем микросхемы, платы, процессоры и прочие радиоэлементы по выгодным ценам. Быстрая оценка, честные цены и удобные способы приема. Узнайте, сколько стоят ваши детали прямо сейчас!
Игровые автоматы на деньги реальные фриспины без депозита с выводом за регистрацию
Ремонт роботов-пылесосов iRobot в Москве: Ремонт блока питания, Замена комплекта щеток, Восстановление колеса, Ремонт гидросистемы, Калибровка, Замена датчиков, Очистка датчиков, Замена аккумулятора перейти
Купите теплицу https://tepl1.ru/catalog с доставкой по выгодной цене! Широкий выбор моделей: поликарбонатные, стеклянные, пленочные. Быстрая доставка, прочные конструкции, удобный монтаж. Идеально для дачи, сада и фермерства. Заказывайте качественные теплицы с доставкой прямо сейчас!
Бездепозитные фриспины игровые автоматы слоты с бонусами
mostbet casino mostbet1009.com.kg .
1win kg скачать http://1win105.com.kg/ .
娛樂城大解析
娛樂城,通常指的是一個線上賭博平台,提供各種娛樂遊戲,如賭場遊戲、體育博彩、電子遊戲等。這些平台讓玩家可以在網路上進行賭博,而不需要親自前往實體賭場。娛樂城通常包含了各式各樣的遊戲選項,例如百家樂、輪盤、老虎機、撲克等,並且透過即時娛樂、直播等技術,提升了玩家的沉浸感和互動性。現今的娛樂城大多數已經支援手機和桌面端的多平台操作,讓玩家可以隨時隨地參與遊戲,這樣的便利性使得它們受到全球玩家的青睞。此外,娛樂城也會推出不同的優惠活動、註冊獎金和忠誠計劃,吸引新用戶並保持老用戶的活躍度。然而,娛樂城的風險也不可忽視。由於賭博本身具有高度的娛樂性,但也存在可能的成癮問題。多數國家對於線上賭博有著嚴格的法律規範,玩家在選擇娛樂城平台時,應該格外留意平台的合法性和安全性,以避免陷入詐騙或遭遇其他法律風險。因此,理性投注並了解相關法律是每位玩家應該保持的基本態度。
Подробнее в материале перейти
Бездепозитные фриспины Игровые автоматы на деньги реальные
1win site http://1win10.com.ng/ .
Тут можно преобрести продвижение медицинских услуг продвижение сайта медицинских услуг
mostbet chrono http://mostbet1000.com.kg .
Подробнее в материале здесь
Когда я увидел эту платформу, впечатление было таким, будто я отправился в путешествие. Здесь каждая ставка — это не просто волнение, а история, которую ты проживаешь с каждым кликом.
Оформление удобен, словно невидимый проводник направляет тебя от момента к моменту. Операции, будь то пополнения или вывод средств, проходят плавно, как поток воды, и это удивляет. А служба помощи всегда отвечает мгновенно, как верный помощник, который никогда не разочарует.
Для меня Казино селектор стал миром, где удовольствие и смысл сплетаются. Здесь каждая игра — это часть пути, которую хочется создавать снова и снова.
신용카드 현금화
1 вин вход http://1win106.com.kg/ .
Бонусы без отыгрыша за регистрацию Бонус за регистрацию игровые автоматы без депозита
Подробнее в материале ссылка
Sans?n?z? Sweet Bonanza’da sweet-bonanza-casino.site deneyin – parlak ve karl? bir slot! Ucretsiz donusler, kazanc carpanlar?, kademeli kombinasyonlar ve buyuk odemeler. Ucretsiz veya parayla cevrimici oynay?n ve tatl? oduller kazan?n!
Glory Casino’da glory-casino-guncel-giris.online oynayn – en iyi oyunlar, yuksek odemeler ve 7/24 destek! Populer slotlar?, kart oyunlar?n? ve ruleti secin, bonuslar kazan ve gercek para kazan?n!
Diego Armando Maradona diego-maradona es una leyenda del futbol mundial! Campeon del Mundo de 1986, autor de “La Mano de Dios” y “El Gol del Siglo”. Un gran jugador argentino que inspiro a generaciones. ?Su tecnica, su regate y su pasion por el juego lo convirtieron en un icono del futbol!
СРОЧНЫЙ РЕМОНТ! Ваш iPhone 12 требует внимания? Профессиональный ремонт iphone 12 выполняется за 30 минут. Бесплатная диагностика, гарантия до года и круглосуточная поддержка – ваши преимущества при обращении к нам!
Mobile-Worker – это команда профессионалов с опытом от 7 лет, которые относятся к каждому устройству как к своему собственному. Мы работаем со всеми популярными брендами: iPhone, Samsung, Xiaomi и другими. Наш адрес: проспект Андропова, 17к1, работаем ежедневно с 10:00 до 20:00.
мостбет http://mostbet1010.com.kg .
Fansite de Mike Tyson http://mike-tyson.com.mx donde podras conocer su historia, peleas, noticias y todo lo relacionado a su legado boxistico. Sigue sus proyectos y conoce mas sobre esta leyenda.
Sitio de fans de Michael Phelps http://michael-phelps.com.mx Un lugar donde los fanaticos pueden encontrar toda la informacion sobre su carrera, sus records y su vida. Noticias, logros y contenido exclusivo.
Sitio de fans de Muhammad Ali https://muhammad-ali.com.mx La historia de una leyenda del boxeo, sus victorias, su lucha por sus derechos y su legado que inspiro al mundo.
Бездепозитные фриспины Бездепозитные фриспины
Sitio fan de George Foreman https://george-foreman.com.mx dedicado a su carrera, victorias, derrotas y legado en el boxeo. Historias inspiradoras y el estilo unico de una leyenda del deporte.
bonus casino бонусы без отыгрыша за регистрацию
Подробнее в материале в блоге об обзорах электронной техники ссылка
прокат авто недорого аренда авто в оздере
Играйте в Big Bamboo big-bamboo-slot.online слот с захватывающим геймплеем, фриспинами и множителями! Ощутите атмосферу восточной удачи, собирайте бонусные символы и выигрывайте по-крупному.
Join Glory Casino glory-casino-bd.online and get maximum bonuses! Top slot machines, table games, jackpots and exclusive promotions. Play online and win comfortably!
служба поддержки мостбет номер телефона mostbet1001.com.kg .
Взрослый вебкам бесплатно https://hotcams.one Тысячи моделей, приватные шоу, видео в высоком качестве и горячие трансляции. Общайтесь в чате и наслаждайтесь без ограничений!
Купить права
скачать 1win с официального сайта 1win107.com.kg .
Подробнее в материале в блоге об обзорах электронной техники здесь
“You get some of me but not tomorrow as they want me in as soon as I can make it happen. This is the one time when they say jump and I ask how high due the financial gains the company could benefit from and it being important enough for the client to appear in person.”
“Well I get an extra night of you at least! I wonder what we could do with that? Meantime, what about food? I am starving and delicious as it was a second breakfast is not quite enough to replenish me!”
“Well get something on and we’ll sort that out first.”
We drove into town and decided that a daytime visit to Charlie’s was going to be the answer. I parked in the bar lot and Elise dashed in to change into something more appropriate, jeans and a t-shirt along with her biker jacket but keeping her Converses on.
Walking down to the restaurant was different from the middle of the night visits as the streets were bustling and all of the shops and outlets were open.
Reaching Charlie’s we entered the front door and sat in a booth near the window. A beautiful young American Chinese girl came,smiled and said hello to Elise and gave us menus and asked if we wanted drinks in the meantime.
“No thanks Lin just a pot of Jasmine tea for us please.” Lin went back to the kitchen area. “No booze for me today as I will have to work in the bar so it is just tea for me.”
Not in a drinking mood either, I agreed with her.”
http://www.babelcube.com/user/christina-fox
https://rentry.org/zow9imhu
https://cannabis.net/user/158108
https://tubeteencam.com/user/leksa21963/profile
https://cannabis.net/mycannabis/p-basic-info/submit
https://www.llanelliherald.com/
Подробнее в материале в блоге об обзорах электронной техники перейти
взять микрозайм на карту срочно без отказа – нужен срочный способ получить деньги? Этот список МФО предлагает моментальные займы. Деньги на карту до 50 000 рублей без отказов, доступно круглосуточно.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу Casino top
Купить права Москва
pariuri sportive moldova http://www.1win5000.ru .
娛樂城大解析
娛樂城,通常指的是一個線上賭博平台,提供各種娛樂遊戲,如賭場遊戲、體育博彩、電子遊戲等。這些平台讓玩家可以在網路上進行賭博,而不需要親自前往實體賭場。娛樂城通常包含了各式各樣的遊戲選項,例如百家樂、輪盤、老虎機、撲克等,並且透過即時娛樂、直播等技術,提升了玩家的沉浸感和互動性。現今的娛樂城大多數已經支援手機和桌面端的多平台操作,讓玩家可以隨時隨地參與遊戲,這樣的便利性使得它們受到全球玩家的青睞。此外,娛樂城也會推出不同的優惠活動、註冊獎金和忠誠計劃,吸引新用戶並保持老用戶的活躍度。然而,娛樂城的風險也不可忽視。由於賭博本身具有高度的娛樂性,但也存在可能的成癮問題。多數國家對於線上賭博有著嚴格的法律規範,玩家在選擇娛樂城平台時,應該格外留意平台的合法性和安全性,以避免陷入詐騙或遭遇其他法律風險。因此,理性投注並了解相關法律是每位玩家應該保持的基本態度。
MetaMask Download made easy! Setting up a wallet takes minutes, and it’s perfect for managing Ethereum and NFTs effortlessly.
сео продвижение сайта компании москва сео продвижение сайта компании москва .
бонусы за регистрацию Бесплатные спины за регистрацию без депозита
прокат белых авто симферополь аренда авто
https://imcongroup.ru
aplicația 1win http://www.1win5001.ru .
Подробнее в материале в блоге об обзорах электронной техники диджитал гаджет ссылка
мостбет зеркало http://mostbet1003.com.kg .
mostbet kg скачать https://mostbet1002.com.kg .
Подробнее в обозревательном журнале чек-ноутбук ссылка
Casino bonus Игровые автоматы на деньги лучшие
Займы без отказа без проверки займ онлайн на карту без отказа без проверки мгновенно
Деньги займ онлайн быстрый онлайн займ
каталог автозапчастей https://avtoplastics.ru
Подробнее в обозревательном журнале new digital tech перейти
prirodni biser Montenegro Durmitor national park Jedinstveni planinski pejzazi, bistra jezera, kanjoni i guste sume. Idealno mjesto za planinarenje, rafting, skijanje i rekreaciju na otvorenom. Otkrijte nacionalni park pod zastitom UNESCO-a!
giros gratis en betmaster nuevoscasinosonlineespana
# Harvard University: A Legacy of Excellence and Innovation
## A Brief History of Harvard University
Founded in 1636, **Harvard University** is the oldest and one of the most prestigious higher education institutions in the United States. Located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard has built a global reputation for academic excellence, groundbreaking research, and influential alumni. From its humble beginnings as a small college established to educate clergy, it has evolved into a world-leading university that shapes the future across various disciplines.
## Harvard’s Impact on Education and Research
Harvard is synonymous with **innovation and intellectual leadership**. The university boasts:
– **12 degree-granting schools**, including the renowned **Harvard Business School**, **Harvard Law School**, and **Harvard Medical School**.
– **A faculty of world-class scholars**, many of whom are Nobel laureates, Pulitzer Prize winners, and pioneers in their fields.
– **Cutting-edge research**, with Harvard leading initiatives in artificial intelligence, public health, climate change, and more.
Harvard’s contribution to research is immense, with billions of dollars allocated to scientific discoveries and technological advancements each year.
## Notable Alumni: The Leaders of Today and Tomorrow
Harvard has produced some of the **most influential figures** in history, spanning politics, business, entertainment, and science. Among them are:
– **Barack Obama & John F. Kennedy** – Former U.S. Presidents
– **Mark Zuckerberg & Bill Gates** – Tech visionaries (though Gates did not graduate)
– **Natalie Portman & Matt Damon** – Hollywood icons
– **Malala Yousafzai** – Nobel Prize-winning activist
The university continues to cultivate future leaders who shape industries and drive global progress.
## Harvard’s Stunning Campus and Iconic Library
Harvard’s campus is a blend of **historical charm and modern innovation**. With over **200 buildings**, it features:
– The **Harvard Yard**, home to the iconic **John Harvard Statue** (and the famous “three lies” legend).
– The **Widener Library**, one of the largest university libraries in the world, housing **over 20 million volumes**.
– State-of-the-art research centers, museums, and performing arts venues.
## Harvard Traditions and Student Life
Harvard offers a **rich student experience**, blending academics with vibrant traditions, including:
– **Housing system:** Students live in one of 12 residential houses, fostering a strong sense of community.
– **Annual Primal Scream:** A unique tradition where students de-stress by running through Harvard Yard before finals!
– **The Harvard-Yale Game:** A historic football rivalry that unites alumni and students.
With over **450 student organizations**, Harvard students engage in a diverse range of extracurricular activities, from entrepreneurship to performing arts.
## Harvard’s Global Influence
Beyond academics, Harvard drives change in **global policy, economics, and technology**. The university’s research impacts healthcare, sustainability, and artificial intelligence, with partnerships across industries worldwide. **Harvard’s endowment**, the largest of any university, allows it to fund scholarships, research, and public initiatives, ensuring a legacy of impact for generations.
## Conclusion
Harvard University is more than just a school—it’s a **symbol of excellence, innovation, and leadership**. Its **centuries-old traditions, groundbreaking discoveries, and transformative education** make it one of the most influential institutions in the world. Whether through its distinguished alumni, pioneering research, or vibrant student life, Harvard continues to shape the future in profound ways.
Would you like to join the ranks of Harvard’s legendary scholars? The journey starts with a dream—and an application!
https://www.harvard.edu/
1вин rossvya https://cah.forum24.ru/?1-19-0-00000716-000-0-0-1741702224 .
скачать mostbet на телефон https://dubna.myqip.ru/?1-18-0-00000145-000-0-0-1741708632 .
Подробнее в обозревательном журнале proektorOFF здесь
1win казино aktivnoe.forum24.ru/?1-2-0-00000100-000-0-0-1741701286 .
Бонусы без отыгрыша за регистрацию Спины без депозита
everything about the world t.me/ufc_ar/ of UFC in Arabic! Latest news, tournament schedules, fighter ratings and exclusive analytical materials. Follow the best fights and stay up to date with all the events in the world of mixed martial arts!
mosbet mosbet .
Сертификат происхождения СТ-1 подтверждает, что товар был произведен в определенной стране, что важно для таможенного оформления и применения тарифных преференций. Протокол испытания, в свою очередь, документирует результаты лабораторных исследований продукции, подтверждая соответствие определенным стандартам качества и безопасности. Сертификат соответствия на продукцию удостоверяет, что товар соответствует требованиям технических регламентов или национальных стандартов. Свидетельство о государственной регистрации продукции требуется для товаров, подлежащих санитарно-эпидемиологическому надзору, и подтверждает их безопасность для здоровья человека. Декларация ТР ТС – это документ, которым производитель или импортер подтверждает соответствие продукции требованиям технических регламентов Таможенного союза. Нотификация ФСБ требуется для ввоза или вывоза продукции, содержащей шифровальные (криптографические) средства. Декларация Минсвязи, в свою очередь, необходима для оборудования связи, подтверждая его соответствие установленным требованиям в сфере связи и телекоммуникаций. Все эти документы играют важную роль в обеспечении качества, безопасности и законности продукции, обращающейся на рынке. Нотификация ФСБ
1 vin aktivnoe.forum24.ru/?1-8-0-00000259-000-0-0-1741701621 .
аренда авто в чанаккале аренда авто в аланье
mostbet официальный сайт cah.forum24.ru/?1-19-0-00000715-000-0-0-1741702061 .
бездепозитные игровые автоматы какие автоматы дают деньги за регистрацию без депозита
Эффективное продвижение сайтов, лучшие стратегии.
Как добиться успеха в SEO, проводите.
Узнайте, как продвигать сайт, трафик.
Инновационные методы продвижения сайтов, которые изменят ваш бизнес.
Понимание основ SEO, которые вы должны знать.
Что важно для онлайн-продвижения, которые принесут плоды.
Лучшие агентства по SEO, которые заслуживают внимания.
14 ошибок при продвижении сайтов, которые можно исправить.
Как продвинуть сайт без бюджета, узнайте.
Самые популярные инструменты для продвижения сайтов, которые станут вашими помощниками.
Показатели успешного SEO, которые нельзя игнорировать.
Как контент влияет на трафик, не забывайте.
Успех в локальном SEO, методы для вашего региона.
Психология пользователей и SEO, основа успешного продвижения.
Мобильное SEO: продвигайте сайт на устройствах, учитывайте это в стратегиях.
Сравнение стратегий для вашего сайта, определите свою цель.
Значение ссылочного продвижения, учтите это в стратегии.
Что нового в SEO в этом году, изучите подробнее.
Сила SMM в SEO, создавайте интересный контент.
Как правильно оптимизировать, необходимые для успеха.
seo google seo google .
Follow UFC fights with https://t.me/s/ufc_ar full tournament schedule, fight results, fighter ratings and analytics. Exclusive news, reviews and interviews with top MMA athletes – all in one place!
Рейтинг казино играть на деньги Рейтинг лучших новых казино
Бонус за регистрацию игровые автоматы без депозита Спины без депозита
Играйте в Mostbet Casino http://mostbet.spas-extreme.ru лицензированное онлайн-казино с огромным выбором игр! Получайте бонусы, выигрывайте в лучших слотах и наслаждайтесь быстрыми выплатами. Удобные способы пополнения счета!
Выбираем недвижимость в Киеве https://automat.kiev.ua как оценить район, новостройки и вторичный рынок? Анализ цен, проверка застройщика, юридическая безопасность сделки. Полезные советы для покупки квартиры без ошибок и переплат!
Строительный онлайн журнал https://kero.com.ua ваш источник актуальной информации о строительстве и ремонте! Советы, обзоры материалов, технологии, тренды и новости отрасли. Узнайте о современных методах строительства, инженерных решениях и дизайне интерьера!
Аркада казино, или казино аркада, – это относительно новое направление в индустрии азартных игр, которое стремится сочетать элементы классических аркадных игр с традиционными казино-играми. Этот гибридный формат нацелен на привлечение более молодой аудитории, выросшей на видеоиграх, и тех, кто ищет более интерактивный и захватывающий опыт, нежели стандартные слоты и настольные игры.
казино аркада
Все про остекление и ремонт балконов — новости, советы и услуги в одном месте!
Хотите преобразить свой балкон или лоджию?
Мы предлагаем свежие идеи, актуальные обзоры и экспертные мнения
по всем ключевым вопросам: современные тенденции в остеклении,
варианты дизайна и материалы для отделки.
Полезные рекомендации для тех, кто планирует обновление балкона:
как выбрать подходящий тип остекления — тёплое или холодное,
какие материалы использовать для утепления и отделки, а также
как избежать распространённых ошибок при монтаже.
Мы поможем вам разобраться в юридических аспектах согласования
перепланировок и остекления.
Следите за нашими обзорами новых технологий и материалов,
узнавайте о лучших предложениях на рынке, а также получайте советы
по уходу за окнами и балконными конструкциями.
Мы делимся рекомендациями по выбору надёжных подрядчиков,
рассказываем о преимуществах различных систем остекления и
предлагаем идеи по функциональному использованию пространства балкона.
Только актуальная информация от ведущих специалистов отрасли — проверенные факты,
практические советы и вдохновляющие примеры.
Подписывайтесь и оставайтесь в курсе последних тенденций!
С нами ваш балкон станет уютным и функциональным пространством,
радующим вас каждый день!
Сайт balconyokna.ru
1вин https://www.1win112.com.kg .
официальный сайт 1win http://1win113.com.kg .
wan win http://www.1win713.ru .
фриспины за регистрацию Бонус с выводом без депозита
Всё для мужчин https://kompanion.com.ua в одном месте! Спорт, мода, авто, гаджеты, здоровье и лайфхаки. Читай полезные советы, следи за трендами и будь лучшей версией себя.
Новости шоу-бизнеса https://mediateam.com.ua мода, красота и афиша – всё в одном месте! Узнавайте о главных событиях, свежих трендах и топовых мероприятиях. Будьте в курсе всего, что происходит в мире стиля и развлечений!
заказ продвижения сайта заказ продвижения сайта .
Все автомобильные новости https://nmiu.org.ua в одном месте! Новые модели, обзоры, сравнения, тест-драйвы, технологии и автоиндустрия. Следите за тенденциями и оставайтесь в курсе событий автопрома!
Актуальные новости бизнеса https://rentwell.in.ua экономики и недвижимости! Аналитика, тренды, инвестиции, рынок недвижимости и финансовые прогнозы. Будьте в курсе главных событий и принимайте взвешенные решения!
Лучший женский портал https://rosetti.com.ua Стиль, красота, здоровье, семья, карьера и саморазвитие. Узнавайте о новых трендах, читайте полезные советы и вдохновляйтесь идеями для счастливой жизни!
Выбор недвижимости в Киеве https://odinden.com.ua на что обратить внимание? Анализ районов, проверка застройщиков, сравнение цен на новостройки и вторичное жилье.
Бесплатные спины за регистрацию без депозита с выводом Спины без депозита
Современный женский портал https://womanlife.kyiv.ua мода, стиль, красота, здоровье, отношения и карьера. Читайте актуальные статьи, находите полезные советы и вдохновляйтесь на новые достижения!
мостбет кг https://www.mostbet1011.com.kg .
мостбет кыргызстан мостбет кыргызстан .
Все для женщин https://timelady.kyiv.ua в одном месте! Новости моды, бьюти-советы, отношения, карьера, психология и лайфхаки. Читайте статьи, находите вдохновение и будьте уверены в себе каждый день!
Детский портал о здоровье https://run.org.ua полезная информация для заботливых родителей! Советы педиатров, питание, развитие, вакцинация, профилактика болезней и здоровый образ жизни. Всё, что нужно знать о здоровье вашего ребенка!
1win bet http://www.1win11.com.ng .
https://ramregion.ru
The cryptocurrency market remains a whirlwind of activity, with Bitcoin price predictions oscillating wildly amidst global economic uncertainty. Ethereum’s market analysis reveals a struggle to maintain momentum, weighed down by network congestion and scaling challenges, even as the Merge’s long-term potential remains undeniable. Investors are keenly eyeing top altcoins, searching for the next breakout star, while bracing themselves for potential market corrections. Crypto market crash or pump
commercial movers toronto best office movers toronto
Всё для женщин https://allwoman.kyiv.ua в одном месте! Советы по стилю, уходу за собой, психологии, семье, карьере и саморазвитию. Узнавайте о новинках моды, секретах успешных женщин и будьте на шаг впереди!
Современный женский сайт https://dama.kyiv.ua красота, стиль, здоровье, семья и карьера. Читайте актуальные статьи, находите полезные советы и вдохновляйтесь на новые достижения!
Женский онлайн-журнал https://krasotka.kyiv.ua мода, красота, здоровье, семья и карьера. Полезные статьи, тренды, лайфхаки и вдохновение для современной женщины. Читайте, развивайтесь и наслаждайтесь жизнью!
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://otnoshenia.net которые стремятся к лучшему! Советы по стилю и макияжу, секреты счастливых отношений, здоровое питание, психология и идеи для отдыха.
Лучший сайт для женщин https://model.kyiv.ua секреты красоты, стильные образы, отношения, карьера, лайфхаки и вдохновение. Оставайтесь в курсе трендов, читайте экспертные советы и развивайтесь вместе с нами!
Сайт для современных женщин https://princess.kyiv.ua Все о последних трендах в мире моды и красоты, секреты здоровья, психология, советы по саморазвитию, карьере и личным отношениям.
Портал для женщин https://woman365.kyiv.ua которые ценят красоту и уверенность! Новинки моды, макияж, секреты счастья, психология, карьера и вдохновение. Узнавайте полезные советы и воплощайте мечты в реальность!
Женский онлайн-клуб https://womanclub.kyiv.ua для тех, кто ценит стиль, здоровье и успех! Узнайте секреты красоты, тренды моды, советы по отношениям и карьере. Читайте вдохновляющие истории, пробуйте новые лайфхаки и развивайтесь каждый день!
https://construct-metall.ru
CS:GO/CS2 skins https://wiki.vpesports.com catalog with full description! Check out rare, legendary and popular skins, their cost, collections and features. Find the perfect skin for your inventory!
The best online marketplace https://www.reddit.com/user/theonlineforyou/comments/1j6t11i/simplify_social_media_marketing_with_facebook/! Buy and sell game, social, business and other accounts. Convenient filtering system, transaction security and current offers. All popular services and games in one place!
Buy verified accounts account marketplace with ease! Gaming, business, and social media accounts available at competitive prices. Fast transactions, trusted sellers, and secure payments. Get the best deals now!
1win бк http://www.1win715.ru .
1 win казино 1win114.com.kg .
1wiin 1win708.ru .
свежие фриспины риобет Спины без депозита
Единственный знак зодиака, который имеет особую связь с Богом https://www.pinterest.com/pin/957366833290360277
Лучший автомобильный портал https://kia-sportage.in.ua Обзоры автомобилей, сравнения, новинки, тест-драйвы, лайфхаки для водителей и советы по выбору авто. Всё, что нужно автолюбителям и профессионалам!
Сайт для женщин https://womanexpert.kyiv.ua которые хотят быть успешными и счастливыми! Советы по красоте, здоровью, воспитанию детей, карьере и личностному росту. Актуальные тренды, лайфхаки и вдохновение для современных женщин!
Портал для автолюбителей https://lada.kharkiv.ua всё об автомобилях! Автообзоры, рейтинг лучших моделей, новинки, цены, советы по уходу и эксплуатации. Узнайте, какие авто заслуживают вашего внимания!
какие автоматы дают деньги за регистрацию без депозита Бонусы за регистрацию
pinco casino pinco casino .
Выявлен фрукт, который является природным эликсиром молодости https://www.pinterest.com/pin/957366833290370789
спарк Казино всегда манили азартом и возможностью быстро разбогатеть. С появлением интернета эта индустрия перешла в онлайн, предлагая игрокам доступ к любимым играм в любое время и из любой точки мира. Онлайн казино стали невероятно популярными благодаря удобству, широкому выбору игр и щедрым бонусам.
Which Zodiac signs should be careful – a dangerous period begins tomorrow! https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1901169237206397369
Сайт для женщин https://womanportal.kyiv.ua всё о моде, красоте, здоровье, отношениях и саморазвитии! Полезные советы, тренды, лайфхаки и вдохновение для современной женщины. Будьте стильной, уверенной и успешной!
Автомобильный сайт https://newsgood.com.ua для водителей и автолюбителей! Узнавайте актуальные новости, читайте обзоры новых моделей, изучайте советы по обслуживанию и вождению.
Авто портал для всех https://rupsbigbear.com кто любит автомобили! Новости, тест-драйвы, характеристики, тюнинг, страхование, покупка и продажа авто. Следите за последними тенденциями и выбирайте лучшее для себя!
раскрутка сайтов в москве раскрутка сайтов в москве .
Which Zodiac signs should be careful – a dangerous period begins tomorrow!
https://www.pinterest.com/pin/957366833290379120
Проститутки курск
Лучший женский онлайн-журнал https://sweetheart.kyiv.ua Всё о моде, красоте, здоровье, отношениях и успехе. Экспертные советы, лайфхаки и мотивация для уверенных в себе женщин.
Женский журнал онлайн https://sunshadow.com.ua стиль, уход, секреты красоты, семья, карьера и саморазвитие. Будьте в курсе трендов, находите полезные лайфхаки и вдохновляйтесь на новые достижения!
Ваш гид в мире красоты https://wonderwoman.kyiv.ua моды и саморазвития! Экспертные статьи о здоровье, отношениях, карьере, психологии и лайфхаках для повседневной жизни. Оставайтесь в курсе трендов и открывайте новые возможности!
мостбет скачать на андроид https://mostbet1005.com.kg/ .
1 win.pro 1 win.pro .
баланс 1win https://1win709.ru/ .
Discover the expertise of auto tuning at Saratoga Auto Body, where your vehicle’s ability is fully unleashed . Our skilled team offers bespoke tuning services designed to enhance your car’s look and efficiency . Experience our satisfied clientele and drive a vehicle that truly represents your distinct taste. Visit https://saratogaautobody.com/ and start your car’s journey today!
фриспины за регистрацию получить 1000 рублей бесплатно за регистрацию
азартные игры Криптовалюта стремительно меняет ландшафт азартных игр. Анонимность, быстрые транзакции и отсутствие посредников привлекают как операторов, так и игроков. Биткоин, Эфириум и другие цифровые активы становятся все более популярным способом пополнения счетов и вывода выигрышей.
Женский мир https://vsegladko.net без границ! Узнайте всё о моде, уходе за собой, фитнесе, психологии, карьере и хобби. Читайте актуальные статьи, следите за новыми тенденциями и наполняйте жизнь яркими моментами!
Автомобильный онлайн-журнал https://svobodomislie.com всё о мире авто! Свежие новости, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, автоспорт, технологии и лайфхаки для водителей. Следите за трендами и будьте в курсе последних событий автопрома!
Онлайн-журнал о машинах https://sw.org.ua всё, что нужно знать об автомобилях! Премьеры новых моделей, сравнение авто, автострахование, технологии, электрокары и советы для владельцев.
Энвато Envato, Adobe Stock, iStock, Depositphotos, Dreamstime – это лишь верхушка айсберга в мире стоковых платформ, предлагающих фотографии, видео, графику и другие креативные ресурсы. Каждая из них имеет свои сильные стороны и особенности ценообразования, поэтому выбор оптимальной площадки зависит от конкретных потребностей пользователя.
Сайт о красоте и здоровье https://beautytips.kyiv.ua полезные советы, тренды ухода, секреты молодости, правильное питание и фитнес. Узнавайте, как оставаться красивой, здоровой и энергичной в любом возрасте!
Мода, красота и здоровье https://fashiontop.com.ua всё в одном месте! Советы по стилю, уходу за волосами и кожей, диеты, тренировки и wellness-тренды. Узнайте, как выглядеть и чувствовать себя на 100%!
Современный женский https://adviceskin.com журнал для тех, кто хочет быть стильной, уверенной и успешной! Секреты красоты, модные тенденции, здоровье, карьера, психология и лайфхаки для повседневной жизни.
Когда состоится встреча Путина и Трампа? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QaQAFGjNvyM
Идеальный баланс стиля https://feromonia.com.ua красоты и здоровья! Читайте о модных тенденциях, косметике, правильном питании, спорте и психологическом комфорте. Найдите вдохновение для гармоничной жизни!
Секреты идеального стиля https://ladyone.kyiv.ua молодости и здоровья! Советы по моде, косметике, уходу за кожей и волосами, фитнесу и сбалансированному питанию. Узнайте, как создать гармоничный образ и чувствовать себя великолепно!
Мода, красота и здоровье https://gryada.org.ua ваш путь к идеальному образу! Последние тренды, советы по уходу, секреты стройности и здорового образа жизни. Создавайте гармонию в своём стиле и самочувствии!
Почему Нимесил запрещён в некоторых странах? https://x.com/DeyanetKrmv/status/1901394421708452176
фриспины без депозита за регистрацию с выводом Бонусы за регистрацию
Bu burcl?r pula daha meyillidir https://www.pinterest.com/pin/957366833290413195
Секреты красоты и здоровья https://magiclady.kyiv.ua в одном месте! Полезные советы по уходу, тренды моды, спорт, правильное питание и психология уверенности. Узнайте, как выглядеть и чувствовать себя великолепно!
Ваш гид по стилю https://magictech.com.ua красоте и жизни! Женский журнал о модных трендах, секретах молодости, психологии, карьере и личных отношениях.
Лучший женский журнал https://modam.com.ua онлайн! Мода, стиль, уход за собой, фитнес, кулинария, саморазвитие и лайфхаки. Полезные советы и вдохновение для современной женщины, которая стремится к лучшему!
Top casino с выводом Игровые автоматы лучшие
1вин кг http://1win717.ru/ .
1вин официальный сайт вход https://1win818.ru .
1win,com https://1win819.ru/ .
Современный женский онлайн https://viplady.kyiv.ua журнал для тех, кто хочет большего! Всё о моде, косметике, фитнесе, питании, психологии, карьере и отношениях. Узнавайте новое, вдохновляйтесь и воплощайте мечты в реальность!
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://one-lady.com которые хотят быть стильными и успешными! Последние тренды, секреты красоты, уход за собой, здоровье, психология и карьера. Будьте в курсе новинок и наслаждайтесь жизнью!
Ваш женский путеводитель https://topwoman.kyiv.ua по красоте, стилю и саморазвитию! Полезные советы, модные тенденции, лайфхаки по уходу за собой, психология, отношения и вдохновение.
Выявлен единственный напиток, который спасает волосы https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1901556598939468146
Подробнее в обозревательном журнале компьютерный эксперт здесь
цена бетона минск цена бетона минск .
Автомобильный портал https://kakavto.com всё, что нужно знать о машинах! Новинки автопрома, технологии, электрокары, автоспорт, автострахование и советы по ремонту. Следите за трендами автоиндустрии!
Портал для родителей https://rodkom.org.ua всё о воспитании, развитии и здоровье детей! Полезные советы, лайфхаки, педиатрические рекомендации, семейная психология и идеи для досуга. Растите счастливых и здоровых детей вместе с нами!
Советы для родителей https://agusha.com.ua в одном месте! Развитие ребёнка, воспитание, здоровье, питание, семейные отношения и идеи для досуга. Полезные статьи, лайфхаки и экспертные мнения помогут вам в заботе о малыше!
Актуальные новости Украины https://vesti.in.ua политика, экономика, спорт, культура и общество! Оперативная информация, эксклюзивные материалы, репортажи и аналитика. Следите за событиями в режиме реального времени!
Главные новости дня https://mostmedia.com.ua политика, экономика, общество, спорт и культура! Оперативные события, аналитика, мнения экспертов и репортажи. Читайте актуальные новости Украины и мира в одном месте!
Медицинский онлайн-журнал https://medicalanswers.com.ua ваш личный консультант по здоровью! Полезные статьи, советы врачей, профилактика, диагностика, лечение и здоровый образ жизни.
Предсказания Ванги на 2025 год: правда или миф?
https://x.com/Ruslansavalv/status/1901612556772409580
спины за регистрацию без депозита с выводом бонусы без отыгрыша за регистрацию
Сайт для женщин https://bbb.dp.ua всё о моде, красоте, здоровье, отношениях и саморазвитии! Читайте полезные советы, следите за трендами, вдохновляйтесь и наслаждайтесь гармоничной жизнью!
Juega sin limites! apuestas deportivas sin registro ofrecen altas cuotas, pagos rapidos y anonimato. ?Compara casas de apuestas populares, elige metodos de apuestas convenientes y disfruta de la emocion!
Apuestas deportivas casas de apuestas deportivas internacionales plataformas con licencia, cuotas favorables, variedad de deportes y pagos rapidos. ?Consulta la valoracion de las mejores casas de apuestas y elige la tuya!
Are you searching for a top-tier online casino involvement in Colombia? Look no above than Casino Wplay, a greatest principles that has bewitched the Colombian gaming market near storm. Whether you’re a trained player or a beginner exploring the area of online gambling, Wplay offers an rousing, steady, and accommodating atmosphere tailored to your needs. In this sweeping handle, we’ll plunge into all you call to skilled in about Casino Wplay, from its victim offerings and bonuses to its juridical ongoing and tips for the treatment of maximizing your experience.
What is Casino Wplay?
Casino Wplay is inseparable of Colombia’s main online gambling platforms, operated not later than Aquila Wide-ranging League S.A.S. Launched in 2017, it holds the distinction of being the principal online casino to inherit a entitle from Coljuegos, the hinterlands’s formal gambling regulator. This milestone not solely solidified Wplay’s credibility but also fix a benchmark payment permitted online gaming in Colombia. Today, Wplay is synonymous with quality pleasure, sacrifice a measureless selection of casino games, sports betting options, and restricted promotions.
With a heart on delivering a localized episode, Wplay caters specifically to Colombian players, supporting payments in Colombian Pesos (COP) and providing client bolster in Spanish. Whether you’re spinning the reels on slots or placing bets on your favorite sports rig, Wplay ensures a seamless and enjoyable experience.
Why Determine Casino Wplay https://wplay-co1.krw0.com/ ?
When it comes to online casinos, players acquire heaps of options. So, what makes Casino Wplay withstand out? Here are some opener reasons why it’s a top choice recompense Colombian gamers:
1. Juridical and Regulated Gaming
Casino Wplay operates comprised in a license from Coljuegos, ensuring full compliance with Colombian gambling laws. This means you can stage play with peace of reprimand, knowing your funds and disparaging news are secure.
2. Distinct Unflinching Piece
Wplay boasts an awe-inspiring library of games, including:
– Slots: From classic fruit machines to modern video slots with immersive graphics.
– Board Games: Blackjack, roulette, baccarat, and poker variants.
– Palpable Casino: Real-time gaming with businesslike dealers owing an authentic casino vibe.
– Sports Betting: Wager on football, basketball, tennis, and more, with competitive odds.
3. Closed Bonuses and Promotions
New players can kickstart their trip with a philanthropic salutation tip, while regulars utilize relentless promotions like free spins, cashback offers, and devotion rewards. Agree to an contemplate on Wplay’s promotions page to overstress your winnings.
4. Mobile-Friendly Platform
Whether you’re at domestic or on the open to, Wplay’s mobile-optimized orientation and dedicated app ensure you not at any time slip a moment of the action. Compatible with both Android and iOS devices, it delivers slippery gameplay and peacefully navigation.
5. State Payment Options
Wplay supports a variety of payment methods tailored to Colombian users, including:
– Bancolombia
– Efecty
– Visa/Mastercard
– PSE (Pagos Seguros en Linea)
Deposits and withdrawals are expeditious, unimperilled, and hassle-free.
How to Take Started with Casino Wplay
Ready to enlist in the fun? Signing up with Casino Wplay is expert and straightforward. Dog these steps:
1. Visit the Authentic Website: Headmaster to the Wplay homepage (wplay.co).
2. Calendar an Account: Click “Mark Up” and top up in your details, including your name, email, and phone number.
3. Verify Your Individuality: As a regulated platform, Wplay requires accord verification to comply with Coljuegos standards.
4. Lay down Funds: Select your preferred payment method and add change to your account.
5. Claim Your Extra: Arouse the welcome sell and start playing!
Crop Games to Take part in at Casino Wplay
Casino Wplay offers something for everyone. Here are some universal picks to make an effort:
Best Slots at Wplay
– Book of Insensitive: An Egyptian-themed adventure with high payout potential.
– Starburst: A vibrant, fast-paced hollow whole for beginners.
– Gonzo’s For: Ally the quest for secret treasures with cascading reels.
Alight Casino Favorites
– Actual Roulette: Lay on your providential numbers with real dealers.
– Last Blackjack: Check your skills against the bordello in real time.
– Loony Time: A thrilling meeting show-style experience with burly gain a victory in opportunities.
Sports Betting Highlights
Football reigns transcendent in Colombia, and Wplay delivers with commodious betting markets on Liga BetPlay, ecumenical leagues, and notable tournaments like the Copa America.
Tips for the benefit of Fetching at Casino Wplay
While gambling is by helter-skelter luck, a few strategies can augment your be familiar with and shove your chances of sensation:
1. Situate a Budget: Take how much you’re docile to splash out and cane to it.
2. Leverage Bonuses: Speak meet offers and free spins to continue your playtime without extra cost.
3. Learn the Games: Rule uncontrolled versions of slots or flatland games to apprehend the rules preceding betting real money.
4. Bet Smart on Sports: Analysis teams, stats, and odds previously placing your wagers.
5. Play Responsibly: Contain breaks and keep off chasing losses to keep the gaiety alive.
Is Casino Wplay Non-toxic and Legit?
Absolutely. As a Coljuegos-licensed practitioner, Wplay adheres to punctilious regulations to protect unblemished play and actor protection. The plank uses SSL encryption to safeguard your matter and offers forthright terms and conditions. Additionally, Wplay promotes dependable gambling with tools like sediment limits and self-exclusion options.
Wplay vs. Other Colombian Online Casinos
How does Wplay stack up against competitors like Stake365 or Rushbet? While all bid quality gaming, Wplay’s crawl lies in its:
– Localized Experience: Designed specifically repayment for Colombian players.
– First-Mover Advantage: As the trend-setter of proper online gaming in Colombia, it has built a tireless reputation.
– Sports Betting Blurred: A standout feature for sports enthusiasts.
Decisive Thoughts on Casino Wplay
Casino Wplay is more than right-minded an online casino—it’s a gateway to премиум fun as a service to Colombian players. With its admissible help, mixed games, and player-centric features, it’s no in the act that Wplay remains a favorite in the market. Whether you’re spinning slots, playing actual blackjack, or betting on your favorite rig, Wplay delivers a rousing and trustworthy experience.
Fit out to plunge in? By wplay.co today, rights your welcome perquisite, and determine why Casino Wplay is the go-to choice for online gaming in Colombia!
—
SEO Optimization Notes
– Predominant Keyword: “Casino Wplay” – Not unexpectedly integrated into the title, headings, and from the beginning to the end of the content.
– Imitated Keywords: “online casino Colombia,” “Wplay games,” “Coljuegos licensed casino” – Adapted to contextually to boost relevance.
– Character: H1, H2, and H3 headings emend readability and keyword placement.
– Information Number: ~700 words, imaginary to save ranking without overwhelming readers.
– Internal Linking Opportunity: Links to speculative tournament guides or bonus pages could be added if business of a larger site.
– Order to Vim: Encourages visits to the sanctioned neighbourhood, aligning with alcohol intent.
This article is designed to order poetically as far as something searches related to “Casino Wplay” while providing valuable intelligence to readers. Acquit me positive if you’d like adjustments!
прием бетона с миксера цена прием бетона с миксера цена .
Dobite a preskumajte https://www.bobotov-kuk.com a pocitite majestatnost hor! Najvyssi vrch Ciernej Hory (2523 m) ponuka ohromujuce panoramy, vzrusujuce trasy a nezabudnutelne emocie. Zistite najlepsie lezecke cesty a tipy na bezpecny vylet!
Otkrijte most https://www.durdevica-tara-bridge.com – jedan od najlepsih mostova u Evropi! Jedinstvena gradevina iznad kanjona Tare zadivljuje svojom razmjerom i panoramskim pogledom. Najbolje rute, izleti i savjeti za putnike!
Kaufen Sie investitionen in montenegro – Ihr Zuhause am Meer oder in den Bergen! Tolle Angebote, Villen, Wohnungen und Apartments. Informieren Sie sich uber die besten Lagen, Preise, rechtlichen Feinheiten und Investitionsmoglichkeiten!
Подробнее в блоге обзоров прицелов и другой оптической техники ссылка
Sakupon an Salog Tara rafting canyon Tara an pinakamarahay na pag-rafting sa Montenegro! Pag-raft sa saro sa pinakahararom na mga kanyon sa Europa, an pinakadalisay na tubig asin naturalesa kan Durmitor. An perpektong pakikipagsapalaran para sa mga mahilig sa luwas!
Enjoy fun at Tara extreme rafting, kayaking, boating and camping in picturesque places. The perfect place for active recreation and immersion in wild nature!
бонусы без отыгрыша за регистрацию Игровые автоматы играть на деньги
Хотите списать долги? банкротство в самаре помощь в сложных финансовых ситуациях. Освободитесь от кредитов, штрафов и задолженностей. Узнайте, как начать процедуру прямо сейчас!
Цветы выглядят потрясающе, очень свежие и ароматные.
цветы
1win официальный https://www.1win820.ru .
1-win 1-win .
https://ceramodecol.ru
1win онлайн https://www.1win808.ru .
Неожиданный способ есть финики превращает их в природное лекарство
https://x.com/SebiBilalova/status/1901774516755309011
химчистка мебели
химчистка мебели
Top casino с выводом Бездепозитные фриспины
цена бетона за 1 куб с доставкой цена бетона за 1 куб с доставкой .
downtown toronto movers movers toronto
игры Steam со скидкой
Эти четыре знака Зодиака накроет волна счастья уже на этой неделе
https://www.pinterest.com/pin/957366833290452816/
Статьи о ремонте и строительстве https://tvin270584.livejournal.com советы, инструкции и лайфхаки! Узнайте, как выбрать материалы, спланировать бюджет, сделать ремонт своими руками и избежать ошибок при строительстве.
Ремонт и сантехника https://santekhnik-moskva.blogspot.com пошаговые инструкции, выбор материалов, монтаж систем водоснабжения и отопления, устранение протечек и установка сантехнических приборов. Советы экспертов для качественного ремонта!
Los logros de George Foreman lo colocan entre los mejores boxeadores de la historia | Los fanáticos del boxeo siguen recordando las grandes peleas de George Foreman | El poder de golpe de George Foreman fue temido por sus rivales | El nombre de George Foreman es sinónimo de poder y determinación Todo sobre George Foreman.
Нужна машина в прокат? аренда авто турция стамбул быстро, выгодно и без лишних забот! Машины всех классов, удобные условия аренды, страховка и гибкие тарифы. Забронируйте авто в несколько кликов!
мостбет войти https://www.mostbet1006.com.kg .
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу 1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу
мостбет кыргызстан мостбет кыргызстан .
heroin esports heroin
мотбет http://www.mostbet1008.com.kg .
Ready-made custom works https://buying-papers-online.com fast, high-quality and inexpensive! We will help with abstracts, term papers, diplomas, essays and other academic assignments. Guaranteed originality, deadlines and 24/7 support!
2 знака зодиака, от которых практически невозможно что-либо скрыть
https://pin.it/1l95y2WeH
Нужен качественный бетон? https://beton-moscvich.ru/tovarnii-beton/ быстро, надёжно и по выгодной цене! Прямые поставки от производителя, различные марки, точное соблюдение сроков. Оперативная доставка на стройплощадки, заказ онлайн или по телефону!
где открывать кейсы кс го https://cs-go.ru
1Win Brasil 1winbr.com apostas esportivas e cassino online! Altas odds, bonus generosos e ampla variedade de jogos. Aposte em esportes, jogue no cassino e aproveite as melhores promocoes agora mesmo!
Когда ушёл муж, думала не справлюсь. Городская ритуальная служба взяла все заботы на себя. Приехали сразу, всё объяснили. ул. Сибирский Тракт, 31А, г. Казань
Prostat x?rc?ngin? qars? hans? qidalar istifad? edilm?lidir? https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1902037337590108612
фриспины без депозита за регистрацию с выводом bezdep
Sports betting with 1xbetapp-br! Huge selection of matches, live bets, generous bonuses and lightning-fast payouts. Play casino, eSports and win at any time!
Welcome to Winbet Casino winbetaz.biz/ a place where luck is on your side! Huge selection of games, bonuses for new players and instant payouts. Try your luck right now!
дренаж участка спб дренаж участка спб .
Что допустим важные финансовые новости проходят мимо вас? На Оформление займов: как не попасть в долговую яму стоит обратить внимание, чтобы всегда быть в курсе актуальных аналитических данных, стоимости валют и тенденций кредитования. Мы публикуем только проверенную информацию: какие микрозаймы выгоднее, где взять займ на выгодных ставках, что происходит с инфляцией и какие оценки специалистов.
Не упускайте ключевые новости! На нашем портале Что делать, если курс валют резко изменился? обновляются ежедневно, а экспертные обзоры объясняется понятными словами. Следите за тенденциями, читайте прогнозы экспертов и принимайте решения осознанно. В мире, где финансовые рынки нестабильны, важно быть в числе первых.
скачать автомат crazy monkey https crazymonkeygame com
maximum winnings with https://onewinwin.in! Bet on sports, play in the casino, participate in promotions and tournaments. Convenient payments, fast payouts and a welcome bonus for beginners. Join 1win and collect your winnings!
戰神賽特
「戰神賽特」— 2025年最火爆的老虎機,等你來挑戰!
如果你正在尋找一款高賠率、刺激又充滿神秘感的老虎機遊戲,那麼「戰神賽特」絕對是你的最佳選擇!這款由RG電子精心打造的遊戲,以古埃及戰神賽特為主題,結合精美畫面與震撼音效,帶你進入神秘的沙漠世界,感受無與倫比的刺激體驗。
為何玩家瘋狂愛上戰神賽特?
超狂賠率 51,000 倍:一轉瞬間,財富翻倍不是夢
高RTP達96.89%:更高勝率,更多機會贏得大獎
獨特遊戲機制:掉落消除+獎金購買,玩法多樣更刺激
極致視聽享受:古埃及風格設計+震撼音效,讓你完全沉浸其中
無論你是老虎機高手還是新手玩家,「戰神賽特」都能帶給你前所未有的遊戲體驗!快來挑戰戰神,贏取屬於你的豐厚獎勵!
Цветы свежие, красивые, упаковка стильная.
букет цветов томск
скачать mostbet http://www.mostbet787.ru .
мостбет казино mostbet788.ru .
1win.kg http://1win809.ru .
gambling without limits one 1win wide selection of games, high odds, fast payouts and exclusive bonuses. Try your luck in the casino and on bets. Play, win and earn with 1win!
your game, your rules https://winbkaz.biz Sports, eSports, casino, poker and slots – choose and win! Convenient account replenishment, instant withdrawals and cool promotions for new players. Join now!
Kingmaker Kingmaker, Kingmaker Casino, Kingmaker greece Casino
обучение по пожарной безопасности Переподготовка и повышение квалификации: инвестиции в профессиональный рост. В современном динамичном мире потребность в непрерывном обучении становится ключевым фактором успеха. Профессиональная переподготовка и курсы повышения квалификации – это эффективные инструменты для адаптации к меняющимся требованиям рынка труда и расширения профессиональных горизонтов. Если вы стремитесь к карьерному росту, желаете освоить новую специальность или углубить свои знания в уже имеющейся, курсы переподготовки предоставят вам необходимые компетенции. В ряде случаев возникает необходимость подтверждения квалификации. В таких ситуациях возможно купить удостоверение, соответствующее пройденному обучению. Особое внимание уделяется обучению в сферах, требующих повышенной безопасности. Обучение работе на высоте и безопасным работам на высоте, а также обучение по пожарной безопасности являются критически важными для обеспечения безопасности на рабочем месте. Для тех, кто ценит свое время и предпочитает гибкий график, курсы повышения квалификации дистанционно предоставляют возможность обучения в удобном формате. Обучение по профессиям охватывает широкий спектр специальностей, позволяя каждому найти подходящую программу.
Хотите получить https://10eurosgratissindepositocasinoespana.com начни игру без риска – Открой для себя захватывающие слоты, живое казино и эксклюзивные бонусы. Играй с комфортом, наслаждайся топовыми играми и выигрывай!
Возможно ли получать тысячи манатов в месяц в соцсетях в Азербайджане?
https://pin.it/1OLQiA9c2
бездепозитные игровые автоматы спины за регистрацию без депозита с выводом
Mostbet Uzbekistan http://mostbetuzbekistan-apk.com offers you profitable bets, top odds and instant payouts. Make sports predictions, play online casino and enjoy the excitement with registration bonuses!
В нотариальной конторе юрист рекомендовал правильные выражения соболезнования. Ритуальные услуги оказаны на высоком уровне. Спасибо за понимание ситуации.
Ищете надежных исполнителей в столице? В статье ремонт квартир в Москве представлены проверенные компании, которые помогут воплотить ваши дизайнерские задумки в реальность с соблюдением всех стандартов качества.
мастбет https://www.mymoscow.forum24.ru/?1-2-0-00000718-000-0-0-1742357638 .
кайтсёрфинг в анапе
1вин кг https://mymoscow.forum24.ru/?1-2-0-00000717-000-0-0-1742357431 .
1win pro 1win pro .
Магазин печей и каминов https://pech.pro широкий выбор дровяных, газовых и электрических моделей. Стильные решения для дома, дачи и бани. Быстрая доставка, установка и гарантия качества!
terrorist attack ufc heroin
шубы со скидками в Москве Мех как искусство: от норки до каракульчи, преображение и вдохновение Мир моды изменчив, но любовь к роскошному меху остается неизменной. Норка, каракульча – каждое полотно обладает своей неповторимой красотой и историей. Выбор шубы – это не просто приобретение теплой одежды, это инвестиция в элегантность и уверенность. В Москве и Санкт-Петербурге, в витринах бутиков и на распродажах, можно найти шубу своей мечты. Важно помнить, что скидки – это отличная возможность приобрести качественное изделие по выгодной цене. Но что делать, если в шкафу уже висит шуба, вышедшая из моды? Не спешите с ней прощаться! Авторский канал дизайнера предлагает вдохновляющие решения по перешиву и преображению меховых изделий. Дизайнер делится секретами, как вдохнуть новую жизнь в старую шубу, превратив ее в современный и стильный предмет гардероба. Кроме того, канал предлагает цитаты дня, мотивирующие на перемены и помогающие женщинам старше 60 лет почувствовать себя красивыми и уверенными в себе. Мех – это не просто материал, это способ выразить свою индивидуальность и подчеркнуть свой неповторимый стиль.
Mostbet oferuje bezpieczne płatności i profesjonalne wsparcie techniczne | Mostbet bonus bez depozytu to świetny sposób na start w kasynie online | Czy wiesz, że Mostbet posiada dedykowaną aplikację mobilną? | Czy warto grać w Mostbet? Opinie użytkowników potwierdzają wysoką jakość usług Mostbet rejestracja – krok po kroku.
Chicken Road offers a casino adventure like no other. Dive bonus crab into its chaotic yet thrilling world, combining humor, strategy, and huge jackpots that guarantee endless entertainment with every spin.
септик под ключ цены спб установка септика цена
porn esports terrorist attack
Новый BMW X6: стиль и мощь, модельный ряд.
BMW X6: динамика и комфорт, безусловно.
дизайн.
Брутальный внешний вид BMW X6, ценителей.
BMW X6: мощь на каждый день, исследуйте.
BMW X6: лучшее сочетание цены и качества, в удобство и комфорт.
Комфортабельный интерьер BMW X6, выражают.
BMW X6: идеальный автомобиль для путешествий, безопасность.
Причины популярности BMW X6, в нашем анализе.
Спортивный характер BMW X6, всех.
Обеспечьте свою безопасность с BMW X6, в приоритете.
Почему BMW X6 – это лучшее решение, выдвигает.
Инновации в BMW X6, ваш опыт.
Как будет ощущаться поездка на BMW X6, узнайте.
Что дает вам BMW X6?, в нашем анализе.
BMW X6: стиль, который невозможно не заметить, выразит вашу индивидуальность.
Как BMW X6 выглядит на фоне конкурентов, в нашем отчете.
Изучите отзывы владельцев BMW X6, в нашем обзоре.
Новые технологии безопасности в BMW X6, гарантируют вашу безопасность.
Итоги: BMW X6, как лучший выбор, обобщаем мнение.
bmw x6 m50 https://bmw-x6.biz.ua/ .
gay esports terrorist attack
1winmd https://1win705.ru/ .
Исследуйте разнообразие модельного ряда BMW, которые порадуют.
Узнайте о лучших моделях BMW, которые впечатляют.
Проверьте последние достижения BMW, особенно.
Каждый найдет свою идеальную BMW, впечатляюще широк.
Погрузитесь в мир премиальных автомобилей BMW, лучшие технологии.
Почему стоит выбрать BMW, узнайте.
Каждая модель BMW — это шедевр, разработанный для.
Лучшие автомобили в модельном ряду BMW, которые завоюют ваше сердце.
Как BMW отвечает на вызовы времени, узнайте.
Разнообразие моделей BMW: для каждого, подходящие для городской жизни.
BMW — это больше, чем просто автомобиль, это образ жизни.
Исключительное качество: выбор BMW, который покоряет сердца.
Переосмысленный комфорт и элегантность BMW, энтузиастов.
Почему BMW — это ваш идеальный выбор, от комфорта до инноваций.
Автомобили BMW: вдохновение на каждом километре, с передовыми технологиями.
Наслаждайтесь разнообразием автомобилей BMW, для любых приключений.
Модельный ряд BMW: сочетание стиля и технических решений, для истинных ценителей.
Модельный ряд BMW: ваше новое путешествие начинается, с удовольствием от вождения.
Изучите мир BMW с новой перспективы, для любого владельца.
bmw x6 2015 https://model-series-bmw.biz.ua/ .
мос бет http://www.mostbet780.ru .
поддержка мостбет поддержка мостбет .
porn esports heroin
heroin esports terrorist attack
Are you searching to a top-tier online casino savoir vivre in Colombia? Look no depth than Casino Wplay, a important principles that has bewitched the Colombian gaming demand near storm. Whether you’re a experienced participant or a beginner exploring the exactly of online gambling, Wplay offers an inspiring, steady, and practicable setting tailored to your needs. In this complete handle, we’ll submerge into everything you call to skilled in with reference to Casino Wplay, from its meeting offerings and bonuses to its legal continued and tips payment maximizing your experience.
What is Casino Wplay?
Casino Wplay is inseparable of Colombia’s main online gambling platforms, operated nearby Aquila International Group S.A.S. Launched in 2017, it holds the division of being the principal online casino to inherit a permit from Coljuegos, the hinterlands’s endorsed gambling regulator. This milestone not only solidified Wplay’s credibility but also set a benchmark after legal online gaming in Colombia. Today, Wplay is synonymous with eminence pastime, offering a unlimited option of casino games, sports betting options, and exclusive promotions.
With a convergence on delivering a localized knowledge, Wplay caters specifically to Colombian players, supporting payments in Colombian Pesos (COP) and providing customer brace in Spanish. Whether you’re spinning the reels on slots or placing bets on your favorite sports get, Wplay ensures a seamless and enjoyable experience.
Why Prefer Casino Wplay https://wplay-co1.krw0.com/ ?
When it comes to online casinos, players acquire heaps of options. So, what makes Casino Wplay stay out? Here are some humour reasons why it’s a meridian election pro Colombian gamers:
1. Juridical and Regulated Gaming
Casino Wplay operates supervised a license from Coljuegos, ensuring blinding compliance with Colombian gambling laws. This means you can portray with peace of reprimand, perceptive your funds and private news are secure.
2. Mixed Contest Number
Wplay boasts an stimulating library of games, including:
– Slots: From time-honoured fruit machines to in vogue video slots with immersive graphics.
– Board Games: Blackjack, roulette, baccarat, and poker variants.
– Flaming Casino: Real-time gaming with maven dealers for an authentic casino vibe.
– Sports Betting: Wager on football, basketball, tennis, and more, with competitive odds.
3. Limited Bonuses and Promotions
Late players can kickstart their gallivant with a kindly welcome tip, while regulars utilize ongoing promotions like unregulated rid of spins, cashback offers, and dependability rewards. Agree to an watch on Wplay’s promotions page to overstress your winnings.
4. Mobile-Friendly Rostrum
Whether you’re at home or on the go, Wplay’s mobile-optimized site and dedicated app insure you never long for a half a second of the action. Compatible with both Android and iOS devices, it delivers smooth gameplay and carefree navigation.
5. State Payment Options
Wplay supports a assortment of payment methods tailored to Colombian users, including:
– Bancolombia
– Efecty
– Visa/Mastercard
– PSE (Pagos Seguros en Linea)
Deposits and withdrawals are irresponsibly, snug, and hassle-free.
How to Absorb Started with Casino Wplay
Happy to unite the fun? Signing up with Casino Wplay is expert and straightforward. Dog these steps:
1. Upon the Lawful Website: Headmaster to the Wplay homepage (wplay.co).
2. Ledger an Account: Click “Foreshadowing Up” and fill in your details, including your style, email, and phone number.
3. Verify Your Indistinguishability: As a regulated party line, Wplay requires sameness verification to concur with Coljuegos standards.
4. Alluvium Funds: Choose your preferred payment method and tote up money to your account.
5. Title Your Bonus: Prompt the welcome propose and start playing!
Cap Games to Philander at Casino Wplay
Casino Wplay offers something payment everyone. Here are some popular picks to try:
Best Slots at Wplay
– Hard-cover of Dead: An Egyptian-themed adventure with elevated payout potential.
– Starburst: A vibrant, fast-paced slot perfect as a service to beginners.
– Gonzo’s Quest: Enter the hunt seek after fit recondite treasures with cascading reels.
Physical Casino Favorites
– Stay Roulette: Bet on your fortuitous numbers with existent dealers.
– Dynamic Blackjack: Exam your skills against the bordello in verified time.
– Loony Leisure: A exciting design show-style experience with beefy achieve first place in opportunities.
Sports Betting Highlights
Football reigns supreme in Colombia, and Wplay delivers with extensive betting markets on Liga BetPlay, international leagues, and chief tournaments like the Copa America.
Tips in compensation Charming at Casino Wplay
While gambling is in great measure about fortunes, a few strategies can augment your participation and raise your chances of celebrity:
1. Plump a Budget: Take how much you’re willing to splash out and jab to it.
2. Leverage Bonuses: Use acceptable offers and let off spins to extend your playtime without ancillary cost.
3. Learn the Games: Exercise uncontrolled versions of slots or chart games to apprehend the rules preceding betting real money.
4. Risk Smart on Sports: Examination teams, stats, and odds before placing your wagers.
5. Drama Responsibly: Hold breaks and keep off chasing losses to provision the gaiety alive.
Is Casino Wplay Non-toxic and Legit?
Absolutely. As a Coljuegos-licensed operator, Wplay adheres to strict regulations to protect light-complexioned contend with and performer protection. The stand uses SSL encryption to keep your data and offers transparent terms and conditions. Additionally, Wplay promotes dependable gambling with tools like set aside limits and self-exclusion options.
Wplay vs. Other Colombian Online Casinos
How does Wplay bundle up against competitors like Wager365 or Rushbet? While all offer standing gaming, Wplay’s acuteness lies in its:
– Localized Experience: Designed specifically in search Colombian players.
– First-Mover Usefulness: As the pioneer of legal online gaming in Colombia, it has built a tireless reputation.
– Sports Betting Blurred: A standout have a role in the interest sports enthusiasts.
Last Thoughts on Casino Wplay
Casino Wplay is more than just an online casino—it’s a gateway to premium diversion object of Colombian players. With its legal approval, mixed games, and player-centric features, it’s no catch red-handed that Wplay remains a favorite in the market. Whether you’re spinning slots, playing live out blackjack, or betting on your favorite duo, Wplay delivers a arousing and faithful experience.
Timely to dive in? Drop in on wplay.co today, command your accepted bonus, and discover why Casino Wplay is the go-to choice representing online gaming in Colombia!
—
SEO Optimization Notes
– Primary Keyword: “Casino Wplay” – Not unexpectedly integrated into the caption, headings, and all over the content.
– Unoriginal Keywords: “online casino Colombia,” “Wplay games,” “Coljuegos licensed casino” – Adapted to contextually to lift relevance.
– Structure: H1, H2, and H3 headings correct readability and keyword placement.
– Information Count: ~700 words, epitome to save ranking without bewildering readers.
– Internal Linking Chance: Links to speculative strategy guides or remuneration pages could be added if part of a larger site.
– Order to Activity: Encourages visits to the formal placement, aligning with user intent.
This article is designed to distinguished poetically for searches tied up to “Casino Wplay” while providing valuable low-down to readers. Let slip me positive if you’d like adjustments!
terrorist attack esports whores
gay esports porn
кайт анапа
мостбет кг http://agility.forum24.ru/?1-0-0-00000756-000-0-0-1742360323/ .
1вин официальный сайт http://agility.forum24.ru/?1-0-0-00000755-000-0-0-1742359870/ .
cazinouri online moldova http://1win5002.ru/ .
кайт египет
кайтсерфинг в египте
cocaine esports whores
cocaine esports porn
Odwiedzilem strone ?? z nadzieja, ze znajde dobra strone, ale to po prostu rozczarowanie! Design nieaktualny, menu nieintuicyjne, a gry dzialaja niestabilnie. Wszedzie wyskakujace okna, strony laduja sie wolno, a obsluga techniczna nie odpowiada na wiadomosci. Dane na portalu sa bez ladu i bezuzyteczne. Wydaje sie, ze portal od dawna nie jest aktualizowany. Zdecydowanie warto zainwestowac uwage na naprawde wiarygodne platformy!
Миру могут угрожать вспышки неизвестных ранее болезней https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1902696858473910276
Free steam accounts https://t.me/s/freesteamaccountc
Transform your car into a remarkable creation with Eurshall’s Auto Body’s elite tuning services . Our experienced team dedicates itself to refining each vehicle to unleash its full performance. Whether you’re aiming for rapidity or chic, our bespoke solutions ensure comprehensive results. Visit https://eurshallsautobody.com/ today to experience the transformation and maneuver a vehicle that truly expresses your character .
Тут можно преобрести сейф пожаровзломостойкие купить сейф взломостойкий цена
Преподаватель колледжа посоветовал ознакомиться с народными верованиями. Организация похорон прошла по всем канонам. Персонал работает от души.
купить дубликат водительских прав
Piano sheet music free piano sheet music
Noten zum ausdrucken klavier klavier noten pdf kostenlos
Noten von klavier noten auf dem klavier
согласование перепланировки согласование перепланировки .
Piano notes free sheet music
1wiun http://www.belbeer.borda.ru/?1-6-0-00001555-000-0-0-1742473542 .
1 win.pro http://www.taksafonchik.borda.ru/?1-14-0-00002041-000-0-0 .
Хотите списать долги? списание долгов физ лицам законное освобождение от кредитных обязательств. Работаем с физлицами и бизнесом. Бесплатная консультация!
Site-ul https://betsysrealfood.com este o resursa cu diverse articole in limba romana, acoperind subiecte precum sanatatea, nutri?ia, moda ?i stilul de via?a. Titlurile articolelor includ teme precum „?tiri de sanatate”, „?tiri pentru bebelu?i”, „?tiri de Medicina Alternativa” ?i „?tiri de via?a”. Site-ul este destinat publicului vorbitor de romana, interesat de un stil de via?a sanatos ?i re?ete de casa.
mostbet kg ongame.forum24.ru/?1-18-0-00001219-000-0-0-1742360461 .
Быстрая продажа и покупка profis.com.ua размещайте объявления о продаже товаров, поиске услуг, аренде недвижимости и работе. Простой интерфейс, удобный поиск, бесплатные публикации!
Mostbet to jedno z najlepszych kasyn online w Polsce | Mostbet bonus bez depozytu to świetny sposób na start w kasynie online | Wypłaty w Mostbet są błyskawiczne i bezpieczne | Mostbet to jedna z najczęściej wybieranych platform hazardowych w Polsce Mostbet kasyno online.
Grając w Mostbet, możesz liczyć na szybkie wypłaty wygranych | Z Mostbet masz dostęp do zakładów sportowych na żywo | Jeśli szukasz legalnego kasyna online, Mostbet to doskonały wybór | Nie wiesz, jak wypłacić wygraną z Mostbet? Sprawdź instrukcję na stronie Najlepsze promocje w Mostbet Polska.
led вывески стенд для школы
Розыгрыш сертификатов OZON и WB – участвуй бесплатно!
Хотите получить подарочный сертификат Ozon или подарочный сертификат Wildberries совершенно бесплатно? Тогда подписывайтесь на наш Telegram-канал @lawka_hop и участвуйте в розыгрышах!
В нашем канале регулярно разыгрываются сертификаты Ozon и Wildberries номиналом от 500 до 5000 рублей. Получить их можно легко:
1.Подписывайтесь на канал @lawka_hop
2.Участвуйте в розыгрышах, выбирая билеты
3. Ожидайте результаты – победители определяются случайным образом!
Подарочные карты Ozon и Wildberries – это удобный способ оплатить любые покупки на популярных маркетплейсах. Участвуйте в розыгрышах и выигрывайте!
Присоединяйтесь прямо сейчас: @lawka_hop Розыгрыш сертификатов OZON WB
изготовление всех видов рекламы замена вывесок
где можно купить медицинскую справку получить медицинскую справку 003 в у
Все о недвижимости в России и мире — новости, аналитика, советы экспертов в одном месте!
Хотите быть в курсе последних событий на рынке недвижимости? Мы предлагаем свежие новости, актуальные обзоры и экспертные мнения по всем ключевым вопросам: изменения в законодательстве, тренды в сфере жилья и коммерческой недвижимости, а также прогнозы цен на ближайшее будущее.
У нас вы найдете полезные рекомендации для инвесторов и владельцев недвижимости: как выгодно вложить средства в жилье, защитить свои инвестиции, выбрать надежного застройщика и избежать ошибок при заключении сделок. Мы также поможем разобраться в юридических тонкостях покупки, аренды и оформления прав собственности.
Следите за обзорами крупнейших событий на рынке недвижимости, узнавайте о новых проектах, возможностях для инвестиций и изменениях в инфраструктуре городов. Кроме того, мы делимся советами по обустройству жилья, лайфхаками для ремонта и рекомендациями по выбору материалов и услуг — от поиска профессиональных подрядчиков до экономии без потери качества.
Только актуальная информация от ведущих экспертов отрасли — проверенные факты, аналитика и прогнозы.
Подписывайтесь и оставайтесь в центре событий! С нами вы всегда будете на шаг впереди — ведь ваш дом и инвестиции заслуживают самого лучшего!
Сайт sis69.ru
1win online http://www.1win822.ru .
карнизы для штор с электроприводом карнизы для штор с электроприводом .
mostbet скачать http://mostbet782.ru/ .
Play Casino Games http://nomini-casino.ru
1win. 1win. .
Зимой населённый пункт погружается в снегу, создавая неудобства для автомобилей и пешеходов. Мы решаем эту сложность! Компания «Снегоплав» – эксперт в сфере утилизации снега, предлагающий эффективные решения для предприятий. Наши технологии помогают в кратчайшие сроки и качественно устранять снежные завалы, экономя затраты и гарантируя комфорт на дорогах. Каждая снегоплавильная установка яндекс маркет от «Снегоплав» – это оптимальное сочетание прочности, мощности и удобства эксплуатации.
Мы производим оборудование, способное утилизирует снег в воду прямо на месте. Это безопасный и рациональный способ очистки улиц, избавляющий от затрат транспортировки снежных отложений. В нашем ассортименте – переносные и стационарные решения, созданные под различные условия эксплуатации. Если вам нужна эффективная снегоплавильная установка спу 3 мы поможем найти рациональное решение для разных объёма работ – для частных нужд до областных центров.
Обратившись к нам, вы получаете инновационные технологии, надёжную продукцию и техническую поддержку. Наши разработки – выбор коммунальных служб, строительных компаний и промышленных предприятий. Звоните: +7 (495) 123-45-67 или приезжайте к нам: г. Москва, ул. Примерная, д. 10.
1vin kg 1win823.ru .
Mostbet to zaufana platforma dla miłośników zakładów sportowych | Sprawdź logowanie do kasyna Mostbet i graj bez ograniczeń | Mostbet opinie potwierdzają wysoką jakość obsługi klienta most bet Polska
кайтсёрфинг хургада
Хотите перекусить вкусно? купить Хлеб для сэндвичей питу, шаверму, донер, гирос и тортилью. Ароматная свежая выпечка, мясо на гриле и фирменные соусы. Отличный выбор для перекуса, обеда или вечеринки.
Каждый после регистрации на сайте Estul.ru получает на баланс аккаунта 100? для возможности бесплатного размещения ваших объявлений, + рандомно еще 100? за размещение первого объявления. На сайте есть все от товаров до услуг их продажа и покупка Доска объявлений
Не забываем про группу Авторынок РФ – https://vk.com/club227724491
Telegram chanel- https://t.me/estulrus
Каждый после регистрации на сайте Estul.ru получает на баланс аккаунта 100? для возможности бесплатного размещения ваших объявлений, + рандомно еще 100? за размещение первого объявления. На сайте есть все от товаров до услуг их продажа и покупка https://estul.ru/blog
Не забываем про группу Авторынок РФ – Товары и услуги
Telegram chanel- https://t.me/estulrus
кайтинг в анапе
Zakłady sportowe i gry w jednym miejscu? Tylko w Mostbet | Sprawdź logowanie do kasyna Mostbet i graj bez ograniczeń | Mostbet rejestracja to pierwszy krok do emocjonującej rozgrywki http://www.mostbet.com
типография спб дешево https://tipografiya-price.ru
цифровая типография спб типография спб дешево рядом
Тут можно преобрести сейф банковский взломостойкий купить взломостойкие сейфы
Dzięki Mostbet możesz obstawiać i wygrywać każdego dnia | Sprawdź logowanie do kasyna Mostbet i graj bez ograniczeń | Grając w Mostbet masz dostęp do wsparcia technicznego 24/7 mostbet.com
Розыгрыш сертификатов OZON и WB – участвуй бесплатно!
Хотите получить подарочный сертификат Ozon или подарочный сертификат Wildberries совершенно бесплатно? Тогда подписывайтесь на наш Telegram-канал и участвуйте в розыгрышах!
В нашем канале регулярно разыгрываются сертификаты Ozon и Wildberries номиналом от 500 до 5000 рублей. Получить их можно легко:
1.Подписывайтесь на канал
2.Участвуйте в розыгрышах, выбирая билеты
3. Ожидайте результаты – победители определяются случайным образом!
Подарочные карты Ozon и Wildberries – это удобный способ оплатить любые покупки на популярных маркетплейсах. Участвуйте в розыгрышах и выигрывайте!
Присоединяйтесь прямо сейчас: Подарочный сертификат Вайлдберриз
1win официальный сайт https://1win810.ru .
мрстбет мрстбет .
кайт школа анапа
скачать mostbet на телефон http://mostbet784.ru/ .
Mostbet kasyno online przyciąga atrakcyjnymi promocjami | Mostbet pl to legalna strona z certyfikatem i ochroną danych | Grając w Mostbet masz dostęp do wsparcia technicznego 24/7 Mostbet login Polska
1win rossvya 1win rossvya .
служба поддержки мостбет номер телефона mostbet783.ru .
mostbet kg отзывы https://mostbet784.ru/ .
Kasyno Mostbet oferuje setki automatów i gier na żywo | Mostbet kasyno to nowoczesna platforma z grami od topowych dostawców | Mostbet rejestracja to pierwszy krok do emocjonującej rozgrywki Rejestracja Mostbet
Ищете идеальный детейлинг? Nord-West детейлинг в Великом Новгороде выполняет все виды работ для восстановления автомобиля. После обработки в нашей студии ваш авто будет выглядеть как новый, а вы будете сиять на дорогах.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Kasyno Mostbet oferuje setki automatów i gier na żywo | Mostbet online daje dostęp do gier 24/7 z każdego urządzenia | Mostbet rejestracja to pierwszy krok do emocjonującej rozgrywki kasyno mostbet online
Logowanie do Mostbet jest szybkie i bezpieczne | Mostbet online daje dostęp do gier 24/7 z każdego urządzenia | Dzięki Mostbet logowanie możesz grać w swoje ulubione gry w kilka sekund mostbet online pl
Dzięki Mostbet możesz obstawiać i wygrywać każdego dnia | Dzięki bonusowi powitalnemu w Mostbet zaczniesz grę z przewagą | Mostbet kasyno oferuje darmowe spiny i turnieje z nagrodami mostbet-kasyno-strona-pl.com
Dzięki Mostbet możesz obstawiać i wygrywać każdego dnia | Mostbet pl to legalna strona z certyfikatem i ochroną danych | Mostbet opinie potwierdzają wysoką jakość obsługi klienta mostbet com login
Logowanie do Mostbet jest szybkie i bezpieczne | Mostbet pl to legalna strona z certyfikatem i ochroną danych | Dzięki Mostbet logowanie możesz grać w swoje ulubione gry w kilka sekund Kasyno i zakłady Mostbet
Названы доказательства пребывания на Земле более высоких цивилизаций https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1903334968513745235
Rejestracja w Mostbet zajmuje tylko chwilę, a bonusy czekają od razu | Dzięki bonusowi powitalnemu w Mostbet zaczniesz grę z przewagą | Dzięki Mostbet logowanie możesz grać w swoje ulubione gry w kilka sekund mostbet com login
круизы В мире, где горизонты становятся ближе, а мечты о приключениях — осязаемыми, наше агентство открывает двери в мир безграничных возможностей. Мы – ваш надежный компас в океане туризма, предлагая не просто путешествия, а мастер-туры, сотканные из ваших желаний и нашей экспертизы. Солнечная Турция, роскошные ОАЭ, загадочный Египет – мы подберем идеальное направление, соответствующее вашему вкусу. Оформление виз, организация трансфера, бронирование отелей и авиабилетов – все это мы берем на себя, чтобы вы могли полностью расслабиться и наслаждаться каждым моментом. Мечтаете о морском круизе или отдыхе в живописной Черногории? Хотите исследовать бескрайние просторы России? Мы поможем воплотить в жизнь самые смелые планы. Наша цель – сделать ваше путешествие незабываемым, комфортным и безопасным. Доверьтесь профессионалам, и ваш отпуск станет настоящим шедевром!
уф печать буклетов печать листовок буклетов
уф печать наклеек https://pechat-nakleek-spb.ru
печать на сувенирах спб сувениры с печатью на заказ
мостбет скачать бесплатно http://eisberg.forum24.ru/?1-0-0-00000327-000-0-0-1742579529 .
mostbet kg http://www.taksafonchik.borda.ru/?1-14-0-00002042-000-0-0-1742473173 .
Mostbet to zaufana platforma dla miłośników zakładów sportowych | Z Mostbet możesz zagrać na automatach, ruletce i w pokera | Mostbet opinie potwierdzają wysoką jakość obsługi klienta Rejestracja Mostbet
1winn https://fanfiction.borda.ru/?1-3-0-00000125-000-0-0-1742475251 .
Пицца Теплый ключ Жаждете сочного итальянского наслаждения, не покидая Кемерово? Добро пожаловать в мир аппетитной пиццы, где каждый кусочек – это маленький праздник. Наша пицца на тонком, хрустящем итальянском тесте – это симфония вкусов, созданная из свежайших ингредиентов. Живете в Теплом ключе? Мы доставим ваш заказ прямо к вашей двери, быстро и аккуратно. А для тех, кто предпочитает забрать заказ самостоятельно, предусмотрена удобная опция самовывоза. Но это еще не все! Наша пиццерия предлагает не только восхитительную пиццу, но и сытные осетинские пироги, приготовленные по традиционным рецептам. Это идеальный выбор для тех, кто хочет попробовать что-то новое и аутентичное. Ищете идеальное место для празднования дня рождения? Мы дарим подарки именинникам, делая ваш особенный день еще более радостным и запоминающимся. Закажите пиццу прямо сейчас на нашем сайте и насладитесь непревзойденным вкусом!
mostbest https://www.eisberg.forum24.ru/?1-0-0-00000327-000-0-0-1742579529 .
mostbet https://taksafonchik.borda.ru/?1-14-0-00002042-000-0-0-1742473173 .
1win кыргызстан https://fanfiction.borda.ru/?1-3-0-00000125-000-0-0-1742475251/ .
кайт школа егтпет
https://zarcasinorank.online/
упаковка изготовление печать печать упаковки типография
заказать печать на холсте holst-pechat-spb.ru
срочная печать блокнотов печать блокнотов с логотипом
кайт хургада
До конца марта эти 4 знака Зодиака обретут личное счастье https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1903525881395507337
https://imgtube.ru/
1win на телефон http://1win824.ru/ .
1win. pro 1win. pro .
1win kg https://1win811.ru .
1 win.pro https://1win824.ru/ .
1 win.pro https://1win825.ru/ .
1win online 1win online .
Названа дата, когда привычная всем жизнь на Земле станет невозможной https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1903674512593359008
https://shvejnye.ru/
Промокод Фонбет – это кодовые слова, например: MAX777, ввод которых при регистрации в БК Фонбет или в личном кабинете позволяет получить фрибеты, страховки ставок и другие специальные бонусы. Промокодом в беттинге называется комбинация букв и цифр, при вводе которых активируется бонус. Новым клиентам Фонбет предлагает приветственные фрибеты на сумму от 100 до 15 000 рублей.
Фонбет промокод: MAX777, используйте его при регистрации аккаунта. Новые пользователи могут активировать бонус и получить бездепозитный фрибет до 15 000 рублей. Воспользоваться бесплатно промокодами «Фонбет» для получения подарочной ставки или другого бонуса можно во время создания аккаунта на официальном сайте букмекерской конторы, а также после активации личного кабинета. Действующие промокоды могут давать зачисление кэшбэка на депозит, бесплатное пари и т.п.
pari промокод без депозита
mostbet apk скачать http://www.mostbet785.ru .
1 вин вход в личный кабинет http://www.1win826.ru .
1win ru https://1win812.ru .
Here is my homepage; https://cryptolake.online/crypto2
кайт египет
мрстбет http://mostbet785.ru/ .
1vin pro https://1win826.ru/ .
https://voenoboz.ru/
1 win http://1win812.ru/ .
Transform your vehicle with high-quality tuning solutions. Release its whole capability and delight in upgraded effectiveness. Our master team excels in modifying individual aspect of your auto to fit your taste and expectations. See our website https://autobodywilson.com/ to know further, and adopt a fresh vehicle venture today.
https://my-caffe.ru/
быстрая продажа аккаунтов продать аккаунты соц сетей
купить аккаунты в соц сетях https://akkaunt-marketplace.ru
куплю продажа аккаунтов маркетплейсы для покупки аккаунта
1win вход в личный кабинет http://1win827.ru .
pariuri sportive moldova http://www.1win5003.ru .
mostbet apk скачать http://mostbet786.ru .
pariuri sportive moldova 1win5003.ru .
pdacenter.ru – сервис по ремонту бытовой техники
Ремонт МФУ в Москве в официальном сервисном центре PDACENTER.
Наши инженеры выполняют ремонт любой сложности по дотупным ценам!
Назван простой напиток, который спасает от повышения сахара в крови https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1904006505147629966
1вин сайт http://www.1win827.ru .
mostbet официальный сайт http://mostbet786.ru/ .
банкротство
кайт школа хургада
https://kaizen-tmz.ru/
Прочные и удобные зип пакет опт и розница, разные размеры, надежная застежка. Для хранения, фасовки и перевозки. Оформите заказ онлайн с быстрой доставкой!
Discover Montenegro crystal clear sea, mountain landscapes, ancient cities and delicious cuisine. We organize a turnkey trip: flight, accommodation, excursions.
Новая кухня? Только Эталон Кухни! Замеры, проект, установка – всё четко и профессионально. https://yandex.ru/maps/org/etalon_kukhni/1146748982/ Казань, пр. Альберта Камалеева
Эскорт Екатеринбург Индивидуалки Екб ,Индивидуалки Екатеринбурга ,Индивидуалки Екатеринбург ,Проститутки Екб ,Проститутки Екатеринбурга ,Эскорт Екатеринбург ,Дешевые проститутки Екатеринбурга ,Дешевые проститутки Екб ,Шлюхи Екатеринбург ,Путаны Екатеринбург
iphone phone apple iphone 16
В Баку найдена одна из трех пропавших без вести несовершеннолетних подруг https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1904141438733979773
Kasyno online z licencją w Polsce? Tutaj znajdziesz najlepsze opcje | Legalne kasyna i bukmacherzy z licencją, polecam sprawdzić | Dobry wybór kasyn z darmowymi spinami | Nowe promocje aktualizowane na bieżąco | Serwis idealny dla nowych i doświadczonych graczy | Wszystko zgodne z polskim prawem – legalne opcje | Bezpieczne zakłady bukmacherskie bez depozytu | Przydatne informacje dla każdego gracza | Bezpieczne metody płatności – szybkie wypłaty mostbet pl.
https://artcet.ru/
Jeśli szukasz sprawdzonych bukmacherów, warto sprawdzić to zestawienie | Dobry opis funkcjonalności serwisów kasynowych | Szybki dostęp do logowania i promocji | Nowe promocje aktualizowane na bieżąco | Bardzo dobre porównanie kodów promocyjnych | Duża baza wiedzy o rynku gier w Polsce | Legalne kasyno z wysokim bonusem powitalnym | Kasyno online z najlepszymi ocenami – wszystko jasne | Dostępność wsparcia technicznego i FAQ online kasyno polska.
1win сайт вход http://www.1win6011.ru .
скачать 1win с официального сайта 1win813.ru .
мос бет https://www.mostbet794.ru .
Jeśli szukasz sprawdzonych bukmacherów, warto sprawdzić to zestawienie | Ranking kasyn online naprawdę ułatwia orientację na rynku | Świetne opisy promocji i ofert dla nowych graczy | Rzetelne recenzje i wskazówki dla każdego gracza | Lista legalnych kasyn w Polsce z dokładnymi opisami | Funkcjonalna wyszukiwarka kodów promocyjnych | Legalne kasyno z wysokim bonusem powitalnym | Fajne porady dla graczy początkujących i zaawansowanych | Kasyno polecane przez graczy z Polski online kasyno polska.
Planning a vacation? hotel Podgorica is a warm sea, picturesque beaches, cozy cities and affordable prices. A great option for a couple, family or solo traveler.
Holidays in Budva are European comfort at an affordable price. Transparent sea, clean beaches, historical cities and warm climate all year round.
Rejestracja szybka i intuicyjna – zyskałem bonus bez depozytu | Pomocna porównywarka legalnych bukmacherów | Przydatne porady jak wypłacić pieniądze z konta | Wszystko opisane prostym językiem, bez zbędnego żargonu | Lista legalnych kasyn w Polsce z dokładnymi opisami | Duża baza wiedzy o rynku gier w Polsce | Bardzo przystępna nawigacja po serwisie | Łatwo znaleźć idealne kasyno dzięki filtrom | Najwyższy poziom bezpieczeństwa i szyfrowania bukmacher online bonus na start.
1 vin официальный сайт http://1win6011.ru .
1win вход https://www.1win813.ru .
1-win http://www.pboarders.borda.ru/?1-11-0-00000929-000-0-0-1742818701 .
mostbet.kg mostbet.kg .
mostbet промокод https://shorts.borda.ru/?1-18-0-00000397-000-0-0 .
Fajne zestawienie kasyn z płatnościami BLIK i przelewy24 | Sprawdzona strona dla graczy online w Polsce | Wszystkie informacje są aktualne i dobrze przedstawione | Opcja filtrowania kasyn według metod płatności – super | Bardzo dobre porównanie kodów promocyjnych | Najlepsze kasyno z szybką rejestracją i płatnościami BLIK | Legalne kasyno z wysokim bonusem powitalnym | Przydatne informacje dla każdego gracza | Najwyższy poziom bezpieczeństwa i szyfrowania legalni bukmacherzy online w polsce.
профильные трубы металлические proftruba-moscow.ru с доставкой по области. собственный автопарк для оперативной отгрузки.
Портал для любознательных https://kbe-online.ru/unikalnye-vozmozhnosti-anglijskie-posloviczy-i-pogovorki-dlya-detej-s-transkripcziej-i-perevodom/ Полезная информация, тренды, обзоры, советы и много вдохновляющего контента. Каждый день — повод зайти снова!
1 вин 1 вин .
Новруз может быть объявлен официальным праздником в Турции https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1904268540363915402
mostbet.kg https://shorts.borda.ru/?1-18-0-00000397-000-0-0 .
кайтинг в анапе
Fajne zestawienie kasyn z płatnościami BLIK i przelewy24 | Doskonałe źródło wiedzy o legalnych grach w Polsce | Dobry wybór kasyn z darmowymi spinami | Opcja filtrowania kasyn według metod płatności – super | Legalne zakłady esportowe w jednym miejscu | Najlepsze kasyno z szybką rejestracją i płatnościami BLIK | Bardzo przystępna nawigacja po serwisie | Kasyno online z najlepszymi ocenami – wszystko jasne | Najciekawsze opcje gier dostępne w kasynach bukmacherzy z cashbackiem.
Najlepsze kasyna w Polsce w jednym miejscu – wszystko jasno opisane | Pomocna porównywarka legalnych bukmacherów | Strona rzetelna, bezpieczna i przyjazna graczom | Rzetelne recenzje i wskazówki dla każdego gracza | Darmowe spiny bez depozytu – warto zajrzeć | Najlepsze kasyno z szybką rejestracją i płatnościami BLIK | Oferty kasyn z rejestracją w kilka kliknięć | Możliwość rejestracji bez ryzyka – bonus bez depozytu | Oferty bez haczyków – wszystko transparentne zakłady bukmacherskie cashback.
Najlepsze kasyna w Polsce w jednym miejscu – wszystko jasno opisane | Świetny poradnik jak odebrać bonus bez depozytu krok po kroku | Dobry wybór kasyn z darmowymi spinami | Przyjazny interfejs i łatwość poruszania się po stronie | Kasyna dostępne na urządzeniach mobilnych – to duży plus | Świetne kasyna z darmową rejestracją i bonusem | Legalne kasyno z wysokim bonusem powitalnym | Legalność serwisów szczegółowo wyjaśniona | Oferty bez haczyków – wszystko transparentne legalni bukmacherzy online w polsce.
сайт для покупки аккаунтов официальный магазин аккаунтов
продать аккаунты моментально маркетплейсы для покупки аккаунта
Kasyno online z licencją w Polsce? Tutaj znajdziesz najlepsze opcje | Strona pomaga wybrać najlepsze zakłady bukmacherskie w Polsce | Znalazłem tu ciekawe kasyna z bonusem za rejestrację | Rzetelne recenzje i wskazówki dla każdego gracza | Darmowe spiny bez depozytu – warto zajrzeć | Wszystko zgodne z polskim prawem – legalne opcje | Zestawienie kasyn online z szybkimi wypłatami | Łatwo znaleźć idealne kasyno dzięki filtrom | Kasyno polecane przez graczy z Polski vulkan vegas bonusy.
Rejestracja szybka i intuicyjna – zyskałem bonus bez depozytu | Doskonałe źródło wiedzy o legalnych grach w Polsce | Strona rzetelna, bezpieczna i przyjazna graczom | Wszystko opisane prostym językiem, bez zbędnego żargonu | Legalne zakłady esportowe w jednym miejscu | Najlepsze kasyno z szybką rejestracją i płatnościami BLIK | Często aktualizowane bonusy i promocje | Kasyna i bukmacherzy dopasowani do polskich graczy | Kasyno polecane przez graczy z Polski zakłady lol.
Rejestracja szybka i intuicyjna – zyskałem bonus bez depozytu | Legalne kasyna i bukmacherzy z licencją, polecam sprawdzić | Rejestracja w kasynie online jeszcze nigdy nie była tak prosta | Opcja filtrowania kasyn według metod płatności – super | Legalne zakłady esportowe w jednym miejscu | Świetna selekcja zakładów bukmacherskich esportowych | Szeroka oferta bukmacherów z cashbackiem i promocjami | Łatwo znaleźć idealne kasyno dzięki filtrom | Bezpieczne metody płatności – szybkie wypłaty kasyno vulkan vegas.
Rejestracja szybka i intuicyjna – zyskałem bonus bez depozytu | Sprawdzona strona dla graczy online w Polsce | Szybki dostęp do logowania i promocji | Rzetelne recenzje i wskazówki dla każdego gracza | Strona wspiera wybór najlepszych bonusów bukmacherskich | Ranking kasyn ze szczegółowymi opiniami graczy | Legalne kasyno z wysokim bonusem powitalnym | Zestawienie top kasyn w Polsce z recenzjami | Najciekawsze opcje gier dostępne w kasynach zakłady bukmacherskie cashback.
кайтсерфинг в египте
1win win http://boardwars.forum24.ru/?1-10-0-00000406-000-0-0 .
1-win 1win6012.ru .
1win скачать последнюю версию http://www.1win814.ru .
казино онлайн kg http://www.tagilshops.forum24.ru/?1-4-0-00000205-000-0-0 .
Mostbet oferuje szeroki wybór gier kasynowych i zakładów sportowych. | Zarejestruj się w Mostbet i skorzystaj z bonusu powitalnego. | Mostbet posiada licencję gwarantującą uczciwość gier. | Dołącz do społeczności graczy Mostbet i dziel się doświadczeniami. mostbet pl
скачат мостбет http://www.mostbet795.ru/ .
1win кейсы https://boardwars.forum24.ru/?1-10-0-00000406-000-0-0/ .
riobet рабочее зеркало риобет зеркало на сегодня
покупка аккаунтов покупка продажа аккаунтов
Dołącz do Mostbet i ciesz się ekscytującymi grami kasynowymi. | Mostbet regularnie aktualizuje ofertę promocyjną dla stałych klientów. | Mostbet oferuje wysokie kursy na zakłady sportowe. | Mostbet dba o odpowiedzialną grę i oferuje narzędzia samowykluczenia. mostbet casino
1win http://www.1win814.ru .
мрстбет мрстбет .
Mostbet oferuje zakłady na żywo z atrakcyjnymi kursami. | Mostbet zapewnia profesjonalną obsługę klienta 24/7. | Dołącz do turniejów i wyzwań organizowanych przez Mostbet. | Mostbet oferuje szeroki wybór metod depozytu dostosowanych do polskich graczy. mostbet-online-casino-polska.com
поддержка мостбет http://mostbet795.ru/ .
Enhance your vehicle’s efficiency and appearance with our remarkable tuning options. Discover the true promise of your vehicle through customized modifications. Our team of technicians ensures incomparable standard and ingenuity. See our site https://precisionautobodyfrederick.com/ to learn additional, and start your quest towards auto perfection today.
Бетономешалки в Омске Аренда и услуги спецтехники в Омске – Мы предоставляем услуги по аренде и эксплуатации спецтехники для различных сфер деятельности, включая строительство, дорожные работы и транспортировку грузов. Наши услуги охватывают аренду автокранов, экскаваторов, самосвалов и других машин для больших и малых предприятий, а также для частных клиентов. Спецтехника для вашего бизнеса с гарантией надежности и эффективности — это наш приоритет. https://avtosturman.ru
Platforma Mostbet zapewnia atrakcyjne bonusy dla nowych graczy. | Bezpieczeństwo i prywatność są priorytetem w Mostbet. | Dołącz do turniejów i wyzwań organizowanych przez Mostbet. | Mostbet oferuje zakłady na e-sporty i wydarzenia specjalne. mostbet
Ремонт помещений https://msksfera.ru/remont-skladov/ под ключ: офисы, отели, склады. Полный комплекс строительно-отделочных работ, от черновой отделки до финишного дизайна.
Zalogowalem sie na strone edessa i bylem rozczarowany! Gry regularnie nie dzialaja, interfejs jest koszmarnie niewygodny, a wyskakujace okna sa wszedzie. Odczuwa sie, jakby strona byla nieaktualizowana od lat – kompletna ignorancja obslugi klienta, usterki na kazdym kroku, a dzialanie jest przerazajaco powolne. Przydatnych materialow prawie nie ma, a sa one nieaktualne. Jesli szukasz wygodnie uczestniczyc w partiach, poszukaj inne platformy – ta strona to strata czasu!
Platforma Mostbet zapewnia atrakcyjne bonusy dla nowych graczy. | Graj odpowiedzialnie i korzystaj z narzędzi kontroli w Mostbet. | Mostbet posiada licencję gwarantującą uczciwość gier. | Mostbet dba o odpowiedzialną grę i oferuje narzędzia samowykluczenia. mostbet online
оценка дома сбербанк ocenka-zagorod.ru
типография спб официальный сайт услуги типографии цена
цифровая типография спб заказ бланков в типографии
Зеркало Ретро Казино https://newretromirror.ru .
Mostbet umożliwia szybkie i bezpieczne transakcje finansowe. | Mostbet wspiera różne metody płatności, w tym karty i e-portfele. | Sprawdź aktualne promocje i bonusy dostępne w Mostbet. | Mostbet zapewnia szybkie wypłaty wygranych na Twoje konto. mostbet
Dzięki Mostbet możesz obstawiać ulubione dyscypliny sportowe w Polsce. | Doświadczeni gracze docenią zaawansowane funkcje Mostbet. | Mostbet oferuje wysokie kursy na zakłady sportowe. | Korzystaj z promocji cashback dostępnych w Mostbet. most bet
Odkryj bogatą ofertę slotów w kasynie Mostbet. | Bezpieczeństwo i prywatność są priorytetem w Mostbet. | Mostbet posiada licencję gwarantującą uczciwość gier. | Mostbet oferuje szeroki wybór metod depozytu dostosowanych do polskich graczy. http://mostbet-online-casino-polska.com
грузоперевозки услуги грузчиков https://priozersk.standart-express.ru
грузчики услуга https://toguchin.standart-express.ru
грузчики заказать https://isilkul.standart-express.ru
Школьные парты и стулья для школы
Школьные парты и стулья для школы
Mostbet oferuje szeroki wybór gier kasynowych i zakładów sportowych. | Doświadczeni gracze docenią zaawansowane funkcje Mostbet. | Dołącz do turniejów i wyzwań organizowanych przez Mostbet. | Skorzystaj z opcji cash-out dostępnej w Mostbet. mostbet com
Dzięki Mostbet możesz obstawiać ulubione dyscypliny sportowe w Polsce. | Bezpieczeństwo i prywatność są priorytetem w Mostbet. | Mostbet oferuje gry od renomowanych dostawców oprogramowania. | Mostbet zapewnia szybkie wypłaty wygranych na Twoje konto. mostbet opinie
1 win казино http://www.1win815.ru .
1вин онлайн http://www.1win6014.ru .
мосбет https://kharkovbynight.forum24.ru/?1-15-0-00003047-000-0-0-1742814422 .
1win ваучер http://yamama.forum24.ru/?1-11-0-00000459-000-0-0-1742818616/ .
Mostbet to legalne kasyno online dostępne dla graczy z Polski. | Mostbet regularnie aktualizuje ofertę promocyjną dla stałych klientów. | Korzystaj z programu lojalnościowego Mostbet i zbieraj punkty. | Dołącz do społeczności graczy Mostbet i dziel się doświadczeniami. mostbet opinie
служба поддержки мостбет номер телефона mostbet6001.ru .
Mostbet to legalne kasyno online dostępne dla graczy z Polski. | Doświadczeni gracze docenią zaawansowane funkcje Mostbet. | Mostbet oferuje gry od renomowanych dostawców oprogramowania. | Mostbet dba o odpowiedzialną grę i oferuje narzędzia samowykluczenia. mostbet casino login
Строительные бытовки
Вагончики и передвижные помещения: практичное способ для личных задач
Бытовки и блок-контейнеры помогают оборудовать рабочее пространство, склад или временный домик. Мы гарантируем объекты, которые отвечают качественным критериям качества и удобства.
Параметры
Стойкость. Каждая модули изготовлены из материалов, прочных к воздействию и погодным условиям.
Моментальная доставка. Конструкция перевозится в пределах 1–2 календарных дней после подписания договора.
Настройка под запросы. Доступна добавление защиты от холода, электрооборудования или вентиляции.
Где применяются
На строительных площадках для хранения инструментов или оборудования места для персонала.
Во время событий для оборудования пункта контроля или хранилища техники.
В качестве офисных модулей или пунктов управления.
Преимущества
Оптимизация времени. Не требуется создавать временные конструкции.
Удобство. Атмосфера, которые усиливают эффективность работы сотрудников.
Гибкость. Решение краткосрочного пользования или приобретения под индивидуальные нужды и ресурсы.
Практический пример
Строительная компания использовала блок-контейнер для накопления материалов и зоны отдыха. Объект была доставлена на место за один день, с специальным утеплением. Заказчик подчеркнул на улучшение условий работы и сокращение простоя.
Как начать сотрудничество
Для заключения договора достаточно связаться с нами. Предоставим подробную информацию, окажем помощь определить идеальный выбор и проведём поставку.
1 win 1 win .
1win rossvya 1win rossvya .
мосбет http://kharkovbynight.forum24.ru/?1-15-0-00003047-000-0-0-1742814422 .
ваучер 1win http://www.yamama.forum24.ru/?1-11-0-00000459-000-0-0-1742818616 .
mostbet mostbet6001.ru .
Единственный знак зодиака, который является магнитом для несчастий и проблем https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1904737515858174078
онлайн казино спарк ру Мир азартных игр в интернете непрерывно эволюционирует, и портал Спарк.ру остается надежным источником актуальных новостей и аналитики в этой сфере. Казино онлайн переживают период бурного роста, привлекая все больше пользователей благодаря удобству, разнообразию игр и привлекательным бонусам.
покупка продажа аккаунтов http://akkaunt-market.ru
Продажа путёвок camp-centr.com. Спортивные, творческие и тематические смены. Весёлый и безопасный отдых под присмотром педагогов и аниматоров. Бронируйте онлайн!
печать визиток а4 печать визиток спб
Всё о строительстве, дизайне и ремонте в своём доме.
Добро пожаловать на «Свой Угол» – ваш партнер в мире строительства, дизайна и ремонта для вашего дома!
Наш блог создан для того, чтобы предоставить вам всю необходимую информацию, которая сделает ваш дом еще уютнее, красивее и функциональнее.
Мы – эксперты в следующих сферах:
Строительство
Мы поделимся с вами советами о выборе материалов, поиске надежных строителей в Беларуси и планировке стройплощадки.
Если у вас возникают вопросы о строительстве своего дома с нуля или о расширении уже существующего пространства, мы предоставим вам экспертные советы.
Дизайн интерьера
У нас есть идеи и решения для каждой комнаты в вашем доме.
Мы расскажем о последних трендах в дизайне, поделимся советами по выбору цветовой палитры, мебели и аксессуаров, чтобы создать уникальное пространство, отражающее ваш стиль и вкус.
Ремонт
От простых косметических обновлений до капитального ремонта – у нас есть идеи и рекомендации для каждого случая.
Мы поддержим вас на каждом этапе, начиная от планирования и заканчивая последним штрихом.
Что вы найдете на нашем сайте
Экспертные советы
Статьи разработаны профессионалами в области строительства, дизайна и ремонта.
Полезные ресурсы
Ссылки на проверенные магазины, услуги и материалы, которые помогут вам в ваших проектах.
Модные тренды
Мы следим за последними тенденциями и новинками в мире строительства и дизайна.
«Свой Угол» – ваш проводник в мире уюта и стиля в вашем доме. Погружайтесь в наши статьи, найдите вдохновение, задавайте вопросы и делитесь своим опытом.
Создайте свой угол вместе с нами!
Информационный портал «Свой Угол»
Проектирование улиц и дорог Услуги по аренде техники и строительству с логотипом компании – На протяжении многих лет компания “ТрансАвто№7” предоставляет в аренду дорожно-строительную технику, а также выполняет широкий спектр строительных и земляных работ. Мы работаем как с крупными корпорациями, так и с малым и средним бизнесом, обеспечивая высокое качество услуг по строительству дорог, благоустройству территорий и прокладке инженерных сетей.
1win казино http://www.1win816.ru .
1вин официальный http://www.1win6015.ru .
мостбет скачать бесплатно https://maksipolinovtsu.forum24.ru/?1-1-0-00000194-000-0-0-1742815870 .
кайтсерфинг в египте
1вин кыргызстан https://mymoscow.forum24.ru/?1-6-0-00026928-000-0-0/ .
https://avtosturman.ru/ Аренда и услуги спецтехники в Омске – Мы предоставляем услуги по аренде и эксплуатации спецтехники для различных сфер деятельности, включая строительство, дорожные работы и транспортировку грузов. Наши услуги охватывают аренду автокранов, экскаваторов, самосвалов и других машин для больших и малых предприятий, а также для частных клиентов. Спецтехника для вашего бизнеса с гарантией надежности и эффективности — это наш приоритет.
мостбет зеркало http://mostbet6002.ru .
https://mercedes-avtoservise.ru/ Ремонт и обслуживание автомобилей Mercedes-Benz – Мы уже много лет предоставляем профессиональные услуги по ремонту и техническому обслуживанию автомобилей Mercedes-Benz как для крупных автопарков, так и для владельцев автомобилей малого и среднего бизнеса. Наши специалисты предлагают диагностику, кузовной ремонт, замену масла и другие услуги с использованием только оригинальных запчастей и современного оборудования.
Zajrzalem na witryne isoaiti i przezylem szok. Interfejs wyglada tak, jakby nie byl aktualizowany od lat, strony laduja sie wolno, a pozytecznych informacji jest minimum. Niektore sekcje sa puste, pelno martwych linkow, a administratorzy milcza. Bledy na kazdym kroku, nie da sie tu nic znalezc! Jesli zalezy ci na wiarygodnych danych o trasach, lepiej poszukaj alternatywnych stron – ten strona jest calkowicie bezwartosciowy.
1win онлайн http://www.1win816.ru .
мостбет вход http://www.maksipolinovtsu.forum24.ru/?1-1-0-00000194-000-0-0-1742815870 .
1.вин http://1win6015.ru/ .
1вин про http://www.mymoscow.forum24.ru/?1-6-0-00026928-000-0-0 .
Betika Aviator (https://betika-aviator.readme.io/) – a trending hit is a high-stakes arcade-style game where quick reflexes pay off.
The rules are easy to follow: a plane rises higher and higher, and as it flies, the winning odds rise.
Hit “Withdraw” before the flight ends
Hesitate — you lose it all.
That’s why success depends on your instincts and timing.
With Betika, you get:
– a user-friendly interface
– fast withdrawals
– live chat at any time
– full mobile access
Launch Aviator day or night — at home, at work, or on the go.
Log in to the site and make your first takeoff.
Nerve, speed, and cash — all in one game!
Dużo informacji o legalnych bukmacherach. | Szeroki wybór gier wideo. | Ciekawe zestawienia automatów hazardowych. | Regularnie aktualizowane wiadomości sportowe. | Dobre źródło dla graczy konsolowych i PC | sloty bez depozytu | Pomocne informacje o płatnościach. | Nowoczesna grafika i responsywny design. | valve gry wideo | Wszystkie gry i promocje w jednym miejscu. | Sloty klasyczne i nowoczesne w jednym miejscu direct sport polska sklepy
Натко фарма официальный сайта Natco Pharma Limited, широко известная как Натко фарма, зарекомендовала себя как один из лидеров индийской фармацевтической индустрии. Компания, представленная на своем официальном сайте natcopharma.co.in, специализируется на разработке, производстве и маркетинге широкого спектра фармацевтических препаратов, охватывающих различные терапевтические области.
мос бет мос бет .
Thanks for another informative web site. The place else may I get that kind of info written in such an ideal approach? I have a venture that I’m just now working on, and I’ve been at the glance out for such information.
вход lee bet
Dużo informacji o legalnych bukmacherach. | Kasyna online dobrze porównane. | Kompleksowe informacje o grach studia Rockstar. | Regularnie aktualizowane wiadomości sportowe. | Strona przejrzysta i merytoryczna. | darmowe gry kasyno sloty | Bezpieczne i sprawdzone źródło informacji. | Polecane przez wielu użytkowników. | techland gry wideo | Bezpieczne kasyna opisane w szczegółach. | Portal tworzony przez ekspertów. https://newsports.pl
Выполняем качественное https://energopto.ru под ключ. Энергоэффективные решения для домов, офисов, промышленных объектов. Гарантия, соблюдение СНиП и точные сроки!
изготовление печати бланков печать бланков заказа
печать папок для документов а4 pechat-papok.ru
Wszystko, co musisz wiedzieć o grach hazardowych. | Wszystko o sportach i transmisjach. | Ciekawe zestawienia automatów hazardowych. | Regularnie aktualizowane wiadomości sportowe. | Solidna baza wiedzy dla każdego gracza. | sloty bez depozytu | Pełna baza wiedzy o grach sportowych. | Najlepsze gry i kasyna 2025 roku. | polskie studio gier | Wybór slotów z różnych kategorii. | Strona działa szybko i bez błędów. sport w polsce
Hi, yes this post is genuinely good and I have learned lot of things from it concerning blogging. thanks.
https://indiatours.ru/
казино В мире азартных игр онлайн казино заняли прочное место, предлагая игрокам широкий выбор развлечений и возможность испытать удачу, не выходя из дома. От классических слотов до настольных игр с живыми дилерами – разнообразие поражает воображение. Стратегии в казино играют важную роль, позволяя игрокам повысить свои шансы на успех. Однако стоит помнить, что казино – это прежде всего игра случая, и никакая стратегия не гарантирует выигрыш.
Świetne miejsce dla fanów gier. | Wszystko o sportach i transmisjach. | Kompleksowe informacje o grach studia Rockstar. | Idealna dla początkujących i zaawansowanych. | Legalne kasyna i wszystko o rejestracji. | darmowe sloty | Zawsze świeże wiadomości o branży hazardowej. | Kasyna przyjazne dla polskich graczy. | valve gry wideo | Przydatne wskazówki dla nowych graczy. | Wygodne porównanie ofert promocyjnych. polsat sport polska
печать на холсте с натяжкой на подрамник печать на холсте с натяжкой
dtf печать на заказ uf dtf печать
широкоформатная уф печать широкоформатная печать плакатов
Техосмотр категория Б Москва – мегаполис, где техосмотр (ТО) является обязательной процедурой для большинства транспортных средств. Найти аккредитованный пункт техосмотра в Москве несложно, достаточно воспользоваться онлайн-картами или поисковыми системами. Важно помнить, что приобретение техосмотра без фактического осмотра автомобиля – незаконно. Стоимость прохождения ТО зависит от категории транспортного средства. Проверить легитимность диагностической карты ТО можно по базе ЕАИСТО (Единая автоматизированная информационная система техосмотра). Это позволяет убедиться, что данные внесены в официальную базу и соответствуют требованиям. Вопрос о необходимости техосмотра для конкретного типа транспорта регламентируется законодательством, и его отсутствие может повлечь штраф.
Polecam, bardzo dobrze opisane kasyna. | Podoba mi się przystępny język strony. | Strona działa płynnie na telefonie. | Znajdziesz tutaj przydatne porównania bukmacherów. | Strona przejrzysta i merytoryczna. | darmowe sloty | Wszystkie popularne automaty w jednym miejscu. | Profesjonalne podejście do tematyki bukmacherskiej. | ubisoft gry wideo | Świetna platforma dla fanów hazardu. | Sloty klasyczne i nowoczesne w jednym miejscu tvp sport mecz polska
1block casino
1Block Casino: Full Platform Overview
1Block Casino is a modern gaming platform that offers a wide range of gambling entertainment for players worldwide. From classic slots to unique games like Plinko, the service provides everything needed for gambling enthusiasts. Let’s take a closer look at the main features of the platform, game categories, and key advantages.
Game Categories
1Block Casino boasts an extensive collection of games divided into several categories:
Originals
This section features exclusive games developed specifically for the platform. It’s a great choice for those seeking a unique gaming experience.
Slots
Classic and modern slots with various themes, bonuses, and mechanics are available here. Whether you prefer traditional fruit machines or innovative video slots, there’s something for everyone.
Live Games
Immerse yourself in the atmosphere of a real casino with live dealer games. These games are streamed in real-time, offering an authentic experience with professional dealers.
Fishing Games
A unique category that combines gambling with interactive gameplay. Fishing games are gaining popularity due to their engaging mechanics and potential for big wins.
Poker
Test your skills against other players in various poker formats. The platform offers both traditional and fast-paced poker games.
Esports Betting
Bet on your favorite esports teams and tournaments. This section caters to fans of competitive gaming who want to add excitement to their matches.
Lucky Bets and High Rollers
1Block Casino caters to all types of players, from casual gamers to high rollers. The Lucky Bets section highlights random wins, while the High Rollers section showcases impressive payouts from large bets. Whether you’re betting small or large amounts, the platform ensures fair play and exciting opportunities.
Our Community and Partnerships
1Block Casino values its community and collaborates with trusted partners to enhance the gaming experience. The platform proudly works with leading providers, ensuring top-quality games and services for its users.
Legal Information
1Block Casino is owned and operated by JogoMaster Limited, a company registered under number 15748. The company’s registered address is located in Hamchako, Mutsamudu, Autonomous Island of Anjouan, Union of Comoros.
The platform is licensed and regulated by the Gaming Board of Anjouan (License No. ALSI-152406032-FI3). 1Block has passed all regulatory compliance checks and is legally authorized to conduct gaming operations for all games of chance and wagering.
Why Choose 1Block Casino?
Diverse Game Selection : From slots to live games, there’s something for every type of player.
Transparency : All bets and payouts are clearly displayed, ensuring trust and fairness.
Crypto-Friendly : The platform supports cryptocurrency transactions, making it convenient for modern players.
Licensed and Regulated : With a valid license from the Gaming Board of Anjouan, players can enjoy a secure and legal gaming experience.
Whether you’re a fan of classic casino games or looking to explore unique options like Plinko, 1Block Casino offers a comprehensive and enjoyable platform for all gambling enthusiasts.
лак для огнезащиты паркетных покрытий В мире современных интерьеров, где дерево занимает почетное место, особое внимание уделяется безопасности. Огнезащитный лак для деревянного паркета становится не просто декоративным элементом, а жизненно важным средством защиты. Лак КМ1, специально разработанный для огнезащиты паркетных полов, обеспечивает надежный барьер против распространения огня. Этот лак для паркетных покрытий с огнезащитой создает на поверхности древесины слой, способный замедлить или предотвратить возгорание. Огнезащитное покрытие для паркетных досок, такое как паркетный лак КМ1 с огнезащитными свойствами, позволяет не только сохранить эстетику натурального дерева, но и повысить пожарную безопасность помещения. Лак для паркета КМ1 – это гарантия спокойствия и уверенности в защите вашего дома.
заключить контракт на службу Процесс поступления на военную службу по контракту начинается с изъявления гражданином желания заключить соответствующий контракт. Это может быть как первичное поступление на службу, так и перезаключение контракта после окончания предыдущего. Основным документом, регулирующим данный процесс, является Федеральный закон “О воинской обязанности и военной службе”. Для заключения контракта необходимо обратиться в военный комиссариат по месту жительства или в пункт отбора на военную службу по контракту. Там гражданин получит подробную консультацию о требованиях, предъявляемых к кандидатам, и перечне необходимых документов. Важно учитывать, что к кандидатам предъявляются определенные требования по возрасту, образованию, состоянию здоровья и физической подготовке.
Najlepsze bonusy bez depozytu w jednym miejscu. | Wszystko o sportach i transmisjach. | Lista bukmacherów z cashbackiem bardzo przydatna. | Regularnie aktualizowane wiadomości sportowe. | Solidna baza wiedzy dla każdego gracza. | sloty polska | Szczegółowe opisy promocji i kodów bonusowych. | Polecane przez wielu użytkowników. | polskie studio gier | Przydatne wskazówki dla nowych graczy. | Dostępne są recenzje gier i kasyn. polsat sport polska
что делать с бонусным балансом на 1win 1win817.ru .
1win rossvya 1win rossvya .
aviator mostbet http://corgan.borda.ru/?1-0-0-00000265-000-0-0/ .
Wszystko jasno i przejrzyście. | Szybki dostęp do najnowszych informacji o grach. | Kompleksowe informacje o grach studia Rockstar. | Interesujące artykuły o zakładach online. | Ciekawe artykuły o historii gier. | automaty kasyno sloty | Ranking najlepszych gier i slotów. | Najlepsze gry i kasyna 2025 roku. | gry dla dorosłych pl | Ciekawy blog z poradami i recenzjami. | Sloty klasyczne i nowoczesne w jednym miejscu https://newsports.pl/
Portal godny zaufania dla graczy z Polski. | Sloty w euro i złotówkach opisane dokładnie. | Strona działa płynnie na telefonie. | Znajdziesz tutaj przydatne porównania bukmacherów. | Legalne kasyna i wszystko o rejestracji. | darmowe sloty | Bezpieczne i sprawdzone źródło informacji. | Polecam każdemu zainteresowanemu zakładami. | valve gry wideo | Wszystkie gry i promocje w jednym miejscu. | Strona działa szybko i bez błędów. newsports.pl
скачать mostbet http://www.mostbet6003.ru .
Wszystko, co musisz wiedzieć o grach hazardowych. | Szeroki wybór gier wideo. | Strona działa płynnie na telefonie. | Znajdziesz tutaj przydatne porównania bukmacherów. | Ciekawe artykuły o historii gier. | https://slots-play.pl/ | Kasyna online dobrze sklasyfikowane. | Polecane przez wielu użytkowników. | gry przygodowe polska | Świetna platforma dla fanów hazardu. | Kompleksowe informacje o legalnym hazardzie. http://www.newsports.pl
1вин официальный сайт мобильная http://1win817.ru .
1win официальный сайт регистрация http://dogzz.forum24.ru/?1-10-0-00000155-000-0-0-1742818537/ .
скачать mostbet на телефон скачать mostbet на телефон .
Wszystko jasno i przejrzyście. | Szybki dostęp do najnowszych informacji o grach. | Strona działa płynnie na telefonie. | Regularnie aktualizowane wiadomości sportowe. | Obszerny katalog polskich bukmacherów. | sloty za darmo bez logowania | Szczegółowe opisy promocji i kodów bonusowych. | Kasyna przyjazne dla polskich graczy. | gry przygodowe polska | Ciekawy blog z poradami i recenzjami. | Wygodne porównanie ofert promocyjnych. m sport polska
Wszystko jasno i przejrzyście. | Rejestracja i logowanie opisane krok po kroku. | Znajdziesz tu aktualności sportowe z całej Polski. | Interesujące artykuły o zakładach online. | Dobre źródło dla graczy konsolowych i PC | sloty z największym rtp | Kasyna online dobrze sklasyfikowane. | Dobre miejsce do znalezienia kodów promocyjnych. | cd projekt gry wideo | Ciekawy blog z poradami i recenzjami. | Strona działa szybko i bez błędów. https://newsports.pl
Четыре знака Зодиака ждет переломный момент на этих выходных https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1905095937828978718
мостбет скачать казино https://www.mostbet6003.ru .
Świetne miejsce dla fanów gier. | Szeroki wybór gier wideo. | Kasyna online działające w Polsce. | Wszystkie informacje o bonusach w jednym miejscu. | Szybka rejestracja i łatwy dostęp do gier. | http://www.slots-play.pl | Wszystkie popularne automaty w jednym miejscu. | Polecane przez wielu użytkowników. | http://www.gamesplays.pl | Rzetelne recenzje i opinie graczy. | Portal tworzony przez ekspertów. m sport polska
Наш сервисный центр предлагает надежный сервисный центр по ремонту ноутбуков адреса любых брендов и моделей. Мы понимаем, насколько значимы для вас ваши ноутбуки, и готовы предложить сервис высочайшего уровня. Наши квалифицированные специалисты проводят ремонтные работы с высокой скоростью и точностью, используя только оригинальные запчасти, что обеспечивает долговечность и надежность выполненных работ.
Наиболее общие проблемы, с которыми сталкиваются владельцы ноутбуков, включают поломку жесткого диска, неисправности экрана, неисправности программного обеспечения, неработающие разъемы и проблемы с охлаждением. Для устранения этих поломок наши профессиональные техники выполняют ремонт жестких дисков, экранов, ПО, разъемов и систем охлаждения. Обращаясь в наш сервисный центр, вы обеспечиваете себе надежный и долговечный сервисный центр по ремонту ноутбука.
Подробная информация представлена на нашем сайте: https://remont-noutbukov-first.ru
1win кейсы http://1win6016.ru .
бюстгальтер Caitline с поддержкой для больших грудей Ищете идеальный бюстгальтер? Обратите внимание на Caitline! Отзывы покупательниц подтверждают: это сочетание комфорта и элегантности. Широкий размерный ряд, включая модели для больших размеров, позволяет каждой женщине найти подходящий вариант. В интернет-магазине Caitline вас ждет разнообразие моделей: с эффектом пуш-ап, для повседневной носки, с кружевом, для спорта и даже для особых случаев, таких как свадьба или вечерний выход.
most bet http://www.mostbet789.ru .
водка казино водка казино .
Списание долгов по 127-ФЗ лучшее решение, когда у вас начались просрочки и уже нечем платить за кредиты https://bankrotstvo-v-moskve123.ru .
мостбет скачать http://ashapiter0.forum24.ru/?1-19-0-00001444-000-0-0-1742819001 .
1win kg скачать http://www.zdorovie.forum24.ru/?1-7-0-00000231-000-0-0-1742818050 .
1 win 1win6016.ru .
Откройте для себя мир ставок с 1xbet, советуем.
Добро пожаловать в мир ставок с 1xbet, в индустрии.
1xbet предлагает щедрые бонусы, акции.
Скорее ставьте на свои любимые команды с 1xbet, от процесса.
Лайв-ставки с 1xbet – это захватывающе, сделайте каждую секунду важной.
1xbet – это огромное количество спортивных событий, свои стратегии.
На 1xbet найдётся ставку для каждого, от футбола до тенниса.
1xbet – живые трансляции ваших любимых матчей, сделайте вашу ставку.
1xbet – получите свои выигрыши мгновенно, открывайте возможности.
1xbet – аналитика ставок для вас, поможем вам оставаться в курсе.
Ставьте с уверенностью на 1xbet, мы ценим вашу конфиденциальность.
Скидки и бонусы только для вас с 1xbet, максимизируйте свой выигрыш.
Выигрывайте и наслаждайтесь с 1xbet, выберите 1xbet для своей игры.
Получите помощь в любое время на 1xbet, мы рядом, чтобы помочь.
Участвуйте в конкурсах и выигрывайте с 1xbet, воспользуйтесь шансом.
1xbet в вашем кармане, удобно и быстро.
Ставьте на основе данных с 1xbet, это умная игра.
Простая регистрация на 1xbet, приступайте к ставкам.
Откройте новый уровень азартных игр с 1xbet, начните выигрывать.
Не упустите уникальные возможности на 1xbet, развивайте свои навыки.
????? ???? 1xbet https://1xbet-login-egypt.com/ .
Odwiedzilem portal hengittaa i nie polecam. wyglad wyglada staro, korzystanie jest niewygodne, a danych jest minimum. ciagle awarie, strony laduja sie wolno, banery przeszkadzaja w przegladanie. Widac, ze serwis nikt o nia nie dba, poniewaz administracja nic nie robi. Support ignoruje, URL-e nie dzialaja. Jesli potrzebujesz wartosciowego serwisu, szukaj gdzie indziej!
mostbet промокод https://mostbet789.ru .
мостбет скачать мостбет скачать .
1vin 1vin .
1win казино https://1win6017.ru/ .
https://firelak.ru В современном строительстве и отделке, где дерево занимает важное место, обеспечение пожарной безопасности становится приоритетной задачей. Огнезащитный лак – это эффективное решение для защиты деревянных конструкций и элементов интерьера от возгорания и распространения пламени.
Najlepsze bonusy bez depozytu w jednym miejscu. | Szeroki wybór gier wideo. | Nowości o grach i studiach developerskich. | Dobrze opisane warunki promocji. | Obszerny katalog polskich bukmacherów. | polskie sloty bez depozytu | Pełna baza wiedzy o grach sportowych. | Zakłady sportowe przedstawione jasno. | techland gry wideo | Wartość merytoryczna na wysokim poziomie. | Portal tworzony przez ekspertów. jd sport polska
seo продвижение стоимость продвижение сайтов в месяц
seo оптимизация стоимость сео продвижение сайтов
1win вход на сайт 1win вход на сайт .
Aviator is a fast-paced online game where results depend on your strategic timing.
Gameplay is straightforward: a plane starts flying, and with every second, the coefficient rises.
Your goal is to press “Stop” before the plane disappears. If you’re fast enough — you collect your prize. Wait too long — and the winnings disappear.
That’s why this game is not just about luck.
Visit https://9323fb.com/how-to-deposit-money-to-aviator-2024-fast-safe-beginner-friendly/ to learn how to make fast, safe, and beginner-friendly deposits for Aviator.
Play with ease thanks to:
– smooth UX
– quick withdrawals
– live chat help
– mobile-friendly interface
Start the flight now and test your timing!
Виза в Китай для бизнеса Планируете поездку в Китай? Наш визовый центр предоставляет полный спектр услуг по оформлению виз в Китай для различных целей: туризм, бизнес, учеба. Мы оказываем профессиональные консультации по всем вопросам, связанным с визовым режимом Китая и подготовкой необходимых документов. Мы поможем вам оформить туристическую визу, бизнес-визу, а также визу для студентов. Наши специалисты подробно проконсультируют вас о необходимых документах, сроках получения визы и ответят на все ваши вопросы. Мы также предлагаем услуги экспресс-визы для тех, кому требуется срочное оформление.
Dużo informacji o legalnych bukmacherach. | Rejestracja i logowanie opisane krok po kroku. | Kasyna online działające w Polsce. | Interesujące artykuły o zakładach online. | Dobre źródło dla graczy konsolowych i PC | polskie sloty bez depozytu | Pomocne informacje o płatnościach. | Polecam każdemu zainteresowanemu zakładami. | cd projekt gry wideo | Szczegółowe analizy i rankingi slotów. | Portal tworzony przez ekspertów. sporty w Polsce
pegas Компания пегас является одним из лидеров рынка и работает в сфере международного туризма, предлагая выгодные туры в Таиланд, Турцию, Египет и другие страны мира. Подбор тура и заказ осуществляется в удобном личном кабинете, где можно забронировать отель, купить билеты и оформить путевку без переплат онлайн. Турфирма Pegas работает с проверенными отелями и предлагает широкий выбор направлений и услуг, включая авиабилеты, круизы, трансферы, путевки и подбор лучших отелей для проживания.
Wszystko, co musisz wiedzieć o grach hazardowych. | Wszystko o sportach i transmisjach. | Znajdziesz tu aktualności sportowe z całej Polski. | Dobrze opisane warunki promocji. | Szybka rejestracja i łatwy dostęp do gier. | sloty polska | Najważniejsze aktualizacje sportowe. | Polecam każdemu zainteresowanemu zakładami. | videogames Polska | Wszystkie gry i promocje w jednym miejscu. | Można znaleźć tutaj najlepsze RTP. http://www.newsports.pl
услуги сео оптимизации https://seokontekstnayareklama.ru
Планируете каникулы? купить https://camp-centr.com! Интересные программы, безопасность, забота и яркие эмоции. Бронируйте заранее — количество мест ограничено!
Świetne miejsce dla fanów gier. | Szybki dostęp do najnowszych informacji o grach. | Nowości o grach i studiach developerskich. | Dobrze opisane warunki promocji. | Szybka rejestracja i łatwy dostęp do gier. | https://slots-play.pl/ | Ranking najlepszych gier i slotów. | Polecam każdemu zainteresowanemu zakładami. | http://www.gamesplays.pl | Wybór slotów z różnych kategorii. | Portal tworzony przez ekspertów. tvp sport polska transmisja
win 1 http://www.1win6013.ru .
1вин официальный мобильная https://knowledge.forum24.ru/?1-0-0-00000101-000-0-0-1742817704 .
1 вин вход 1 вин вход .
most bet most bet .
Polecam, bardzo dobrze opisane kasyna. | Dobre źródło wiedzy o e-sporcie i zakładach. | Lista bukmacherów z cashbackiem bardzo przydatna. | Dobrze opisane warunki promocji. | Obszerny katalog polskich bukmacherów. | polskie sloty bez depozytu | Bezpieczne i sprawdzone źródło informacji. | Polecam każdemu zainteresowanemu zakładami. | gamesplays.pl | Świetna platforma dla fanów hazardu. | Strona działa szybko i bez błędów. jd sport polska
1win. https://1win6013.ru .
1 win.pro 1 win.pro .
1wi https://1win9109.ru .
mosbet mostbet6004.ru .
https://bet-riot.fr
Enhance your vehicle with our unique tuning services. Alter your machine into a distinctive masterpiece. Our team of experts is dedicated to offering superior results that exceed your anticipations. Whether you’re looking to augment performance, refresh aesthetics, or add new features, we have the knowledge to deliver your vision to life. Visit our website at https://timbrellosautobody.com/ to explore our services and schedule a consultation today.Let us assist you build the auto of your dreams.
Ciekawy wybór slotów online. | Podoba mi się przystępny język strony. | Ciekawe zestawienia automatów hazardowych. | Wszystkie informacje o bonusach w jednym miejscu. | Dobre omówienie zakładów esportowych. | sloty bez depozytu | Ranking najlepszych gier i slotów. | Kasyna przyjazne dla polskich graczy. | gry z fabułą | Przydatne wskazówki dla nowych graczy. | Miejsce, gdzie znajdziesz wszystko o grach online. http://www.newsports.pl
Znalazłem tu pomocne porady dla graczy. | Rejestracja i logowanie opisane krok po kroku. | Strona działa płynnie na telefonie. | Znajdziesz tutaj przydatne porównania bukmacherów. | Strona przejrzysta i merytoryczna. | sloty za darmo bez logowania | Kasyna online dobrze sklasyfikowane. | Opisane turnieje i wydarzenia e-sportowe. | polskie studio gier | Wartość merytoryczna na wysokim poziomie. | Miejsce, gdzie znajdziesz wszystko o grach online. polska siatkówka sport
Portal godny zaufania dla graczy z Polski. | Znalazłem wiele darmowych spinów. | Ciekawe zestawienia automatów hazardowych. | Idealna dla początkujących i zaawansowanych. | Dobre źródło dla graczy konsolowych i PC | sloty 777 online | Ranking najlepszych gier i slotów. | Polecam każdemu zainteresowanemu zakładami. | gry z fabułą | Ciekawy blog z poradami i recenzjami. | Portal tworzony przez ekspertów. newsports.pl
Wszystko jasno i przejrzyście. | Szybki dostęp do najnowszych informacji o grach. | Kompleksowe informacje o grach studia Rockstar. | Interesujące artykuły o zakładach online. | Dobre źródło dla graczy konsolowych i PC | darmowe sloty owocowe | Kasyna online dobrze sklasyfikowane. | Dobre miejsce do znalezienia kodów promocyjnych. | cd projekt gry wideo | Wybór slotów z różnych kategorii. | Wygodne porównanie ofert promocyjnych. tvp sport polska
bet-riot.fr best casino
Najlepsze bonusy bez depozytu w jednym miejscu. | Podoba mi się przystępny język strony. | Znajdziesz tu aktualności sportowe z całej Polski. | Kasyna z darmowymi spinami bez depozytu. | Legalne kasyna i wszystko o rejestracji. | sloty bez depozytu | Kasyna online dobrze sklasyfikowane. | Kasyna przyjazne dla polskich graczy. | best video games pl | Przydatne wskazówki dla nowych graczy. | Wygodne porównanie ofert promocyjnych. https://newsports.pl/
На берегу моря нашли русалку https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1905487137991958614
MetaMask Chrome simplifies NFT purchases. Connecting to OpenSea and other marketplaces is seamless and secure.
Ciekawy wybór slotów online. | Szybki dostęp do najnowszych informacji o grach. | Znajdziesz tu aktualności sportowe z całej Polski. | Dobrze opisane warunki promocji. | Legalne kasyna i wszystko o rejestracji. | darmowe sloty owocowe | Zawsze świeże wiadomości o branży hazardowej. | Opisane turnieje i wydarzenia e-sportowe. | ubisoft gry wideo | Ciekawy blog z poradami i recenzjami. | Sloty klasyczne i nowoczesne w jednym miejscu https://newsports.pl
Ciekawy wybór slotów online. | Szeroki wybór gier wideo. | Znajdziesz tu aktualności sportowe z całej Polski. | Wszystkie informacje o bonusach w jednym miejscu. | Strona przejrzysta i merytoryczna. | polskie sloty z bonusem | Zawsze świeże wiadomości o branży hazardowej. | Najlepsze gry i kasyna 2025 roku. | gry przygodowe polska | Wartość merytoryczna na wysokim poziomie. | Można znaleźć tutaj najlepsze RTP. m sport polska
На берегу моря нашли русалку https://x.com/Fariz418740/status/1905487137991958614
настольные игры Table Mania – магазины настольных игр, в котором представлен широчайший ассортимент настольных игр. У нас широко представлены как семейные, детские и вечериночные, так и сложные стратегические, коллекционно-карточные и тактические игры с миниатюрами.
1 вин вход http://belbeer.borda.ru/?1-6-0-00001583-000-0-0 .
mostbet kg отзывы https://www.girikms.forum24.ru/?1-1-0-00000361-000-0-0-1742819287 .
1 win pro http://1win6018.ru .
mostber kharkovbynight.forum24.ru/?1-15-0-00003047-000-0-0 .
vahentaa to prawdziwa katastrofa! Dane dawno nie byly odswiezane, a czasami calkowicie bledne. Poszukiwalem zdobyc kluczowe informacje medyczne, ale znalazlem na ogromna ilosc niescislosci i jawnych nonsensow. Mozna pomyslec, ze artykuly zamieszczane przez zespol bez wiedzy! To moze byc szkodliwe dla uzytkownikow, ktorzy polegaja na tymi informacjami. Moderatorzy nie odpowiadaja niedociagniec, a oceny sa wyraznie podrobione.
play now click
1вин https://belbeer.borda.ru/?1-6-0-00001583-000-0-0 .
riobet casino riobet casino
mostbet kg скачать mostbet kg скачать .
1вин онлайн https://www.1win6018.ru .
most bet http://kharkovbynight.forum24.ru/?1-15-0-00003047-000-0-0 .
Подробнее в блоге обзоров прицелов и другой оптической техники на сайте obzor-pricelov.ru на сайте
Mostbet je spolehlivá platforma pro sázení i kasino | Mostbet online hry jsou zábavné a rozmanité | Mostbet se českými hráči opravdu počítá https://mostbet-casino-register-cz.com.
buy steroids with cryptocurrency https://anabolshop.org
где можно купить анализы купить анализы без прохождения
Семейный доктор рекомендовал молитвенные тексты для поминовения. Ритуальные услуги помогли нам в трудную минуту. Всё организовано с уважением.
Zkuste štěstí na Mostbet online je to snadné | Mostbet nabízí kasino s živými dealery | Mostbet představuje novou úroveň online hraní mostbet account.
Доставка продуктов и готовой еды на дом – EdaDostavkoy.ru на сайте
трансформатор масляный трансформатор масляный .
1с бухгалтерия 8.3 цена 1с бухгалтерия 8.3 цена .
Mostbet casino přináší kvalitní zábavu online | Nejlepší automaty najdete v Mostbet casino cz | Většina hráčů doporučuje Mostbet mostbet casino cz.
купить готовый диплом казань
Registrace na Mostbet je jednoduchá a rychlá | Užijte si sportovní sázky na Mostbet cz | Vyzkoušejte sázení na Mostbet a uvidíte rozdíl mostbet login.
Привет!
Без университета сложно было продвинуться по карьере. В последние годы этот документ не дает абсолютно никаких гарантий, что получится получить высокооплачиваемую работу. Намного более важны профессиональные навыки специалиста и его опыт. Именно из-за этого решение о покупке диплома стоит считать мудрым и рациональным. Купить диплом об образовании mir.4admins.ru/posting.php?mode=post&f=10&sid=8316a8a1206612d0f50f47f834ddc5a2
Экскурсии в Геленджике и Архипо-Осиповке: контакты, жмякай перейти
Mostbet je spolehlivá platforma pro sázení i kasino | Mostbet com přináší top kvalitu mezi online kasiny | Mostbet představuje novou úroveň online hraní mostbet games.
Need to top up real money in the game Aviator?
Super quick!
First, sign in, then go to the balance area.
After that, choose your favorite payment method:
Skrill.
Enter the deposit size you want to send — as much as you want.
Submit the payment and you’re good to go!
For more info, visit https://cajnews.co.ke/ — no redirects.
Fast processing — enjoy the game!
купить мед анализы купить анализ яйца глистов
Топ сайтов кейсов CS2 http://ggdrop.cs2-case.org проверенные сервисы с высоким шансом дропа, промокодами и моментальными выводами. Только актуальные и безопасные платформы!
мостбет скачать mostbet6005.ru .
Купить диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и других профессий по доступным ценам. Вы покупаете документ в надежной и проверенной компании. : feolet.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=1080
Диплом любого ВУЗа РФ!
Без института достаточно сложно было продвинуться по карьерной лестнице. Именно из-за этого решение о покупке диплома следует считать выгодным и целесообразным. Быстро и просто приобрести диплом университета 1abakan.ru/forum/showthread-365282
Землетрясение в Бангкоке: что стало причиной?
https://x.com/SebiBilalova/status/1905743685712855518
1win букмекер obmen.forum24.ru/?1-1-0-00004428-000-0-0-1742816292 .
Привет!
Заказать диплом университета по невысокой стоимости можно, обращаясь к проверенной специализированной компании. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании: kupitediplom.ru/kupit-diplom-spetsialista-14/
1вин http://www.1win6019.ru .
мостбет официальный сайт https://hiend.borda.ru/?1-16-0-00000259-000-0-0-1743052953 .
служба поддержки мостбет номер телефона http://www.alfatraders.borda.ru/?1-0-0-00004917-000-0-0-1743053068 .
Mostbet podporuje mobilní hraní bez omezení | Mostbet com přináší top kvalitu mezi online kasiny | Výhry z Mostbet lze snadno vybrat mostbet casino cz.
мостбет https://mostbet6005.ru/ .
Mostbet je skvělou volbou pro sázení a kasino online | Nejlepší automaty najdete v Mostbet casino cz | Vyzkoušejte sázení na Mostbet a uvidíte rozdíl http://mostbet-casino-register-cz.com.
Ремонт электронники в Москве – сервисный центр, который может отремонтировать все на сайте
Zkuste štěstí na Mostbet online je to snadné | Mostbet online hry jsou zábavné a rozmanité | Mostbet představuje novou úroveň online hraní mostbet live.
1win ru http://www.obmen.forum24.ru/?1-1-0-00004428-000-0-0-1742816292 .
1win live http://1win6019.ru/ .
мостбет кыргызстан http://hiend.borda.ru/?1-16-0-00000259-000-0-0-1743052953/ .
мостбет казино войти https://alfatraders.borda.ru/?1-0-0-00004917-000-0-0-1743053068 .
купить диплом в назрани diplomys-vsem.ru .
Zkuste štěstí na Mostbet online je to snadné | Mostbet com přináší top kvalitu mezi online kasiny | Mostbet online casino nabízí jackpoty a turnaje mostbet přihlášení.
Zkuste štěstí na Mostbet online je to snadné | Mostbet má skvělou mobilní aplikaci pro České uživatele | Vyzkoušejte sázení na Mostbet a uvidíte rozdíl mostbet official website.
Mostbet je skvělou volbou pro sázení a kasino online | Mostbet má skvělou mobilní aplikaci pro České uživatele | S Mostbet máte jistotu kvalitní podpory http://mostbet-casino-register-cz.com.
Mostbet je spolehlivá platforma pro sázení i kasino | Bonus bez vkladu najdete na Mostbet casino cz | Výhry z Mostbet lze snadno vybrat mostbet official website.
На официальном сайте Волна Казино вас ждут выгодные акции, уникальные предложения и отличные условия для игры https://volna7777.casino/
MetaMask Download changed my crypto experience. Managing tokens has never been easier. A must-have for anyone in the space.
каналы для рекрутеров В современном мире HR-специалисты сталкиваются с необходимостью оперативной коммуникации и обмена опытом. HR чат становится незаменимым инструментом для решения этих задач. Разнообразие платформ предоставляет широкие возможности для HR-профессионалов: от специализированных чат-ботов до телеграм-каналов.
Приобрести документ ВУЗа вы можете у нас в столице. vuz-diplom.ru/kupit-diplom-ekonomista-2-3
elonbet casino
автоматизация бизнес-процессов
Актуальные новости и тренды из мира цифровых активов — Узнайте больше информации https://independent.academia.edu/CryptonsCryptons
мостбет скачать андроид http://severussnape.borda.ru/?1-10-0-00000023-000-0-0-1743053372/ .
mostbet скачать https://cah.forum24.ru/?1-3-0-00000096-000-0-0-1743053764 .
1winn https://fanfiction.borda.ru/?1-0-0-00029708-000-0-0-1743051664 .
mostbet http://www.assa0.myqip.ru/?1-23-0-00000149-000-0-0-1743053201 .
https://qrkoder.ru/
https://eloncola.com/
Создание QR кодов
скачать mostbet http://assa0.myqip.ru/?1-23-0-00000149-000-0-0-1743053201/ .
мостбет кыргызстан severussnape.borda.ru/?1-10-0-00000023-000-0-0-1743053372 .
скачать mostbet https://www.cah.forum24.ru/?1-3-0-00000096-000-0-0-1743053764 .
вход 1win вход 1win .
https://qrkoder.ru/
Создание QR кодов
After trying several different options, Smart Vision stands out as the best video surveillance software available. The ease of use combined with the powerful AI object detection makes it a top choice. I especially appreciate its reliability as an IP camera recorder, ensuring I never miss a crucial moment. The time-lapse recording feature is surprisingly useful and helps me quickly scan through hours of footage. For anyone looking for a dependable VMS to bolster their security, Smart Vision is an excellent choice. This video surveillance software has truly elevated my security system. smart vision vms for windows
Glory Casino app
1win.kg https://admiralshow.forum24.ru/?1-17-0-00000242-000-0-0-1742816555/ .
Best non Gamstop casino I’ve found has epic tournaments—cool!
non uk casinos not on gamstop
Лучшие сайты кейсов https://ggdrop.casecs2.com/ в CS2 – честный дроп, редкие скины и гарантии прозрачности. Сравниваем платформы, бонусы и шансы. Заходи и забирай топовые скины!
https://orgnaztech.mirtesen.ru/blog/43202871346/Gde-Kazhdyiy-Gost-Osobennyiy-Otel-Glory
1win.kg http://www.admiralshow.forum24.ru/?1-17-0-00000242-000-0-0-1742816555 .
автоматизация бизнес-процессов
This non Gamstop casino has the best slots I’ve played in ages—wow!
non gamstop uk casinos
1Block Casino: Full Platform Overview
1Block Casino is a modern gaming platform that offers a wide range of gambling entertainment for players worldwide. From classic slots to unique games like Plinko, the service provides everything needed for gambling enthusiasts. Let’s take a closer look at the main features of the platform, game categories, and key advantages.
Game Categories
1Block Casino boasts an extensive collection of games divided into several categories:
Originals
This section features exclusive games developed specifically for the platform. It’s a great choice for those seeking a unique gaming experience.
Slots
Classic and modern slots with various themes, bonuses, and mechanics are available here. Whether you prefer traditional fruit machines or innovative video slots, there’s something for everyone.
Live Games
Immerse yourself in the atmosphere of a real casino with live dealer games. These games are streamed in real-time, offering an authentic experience with professional dealers.
Fishing Games
A unique category that combines gambling with interactive gameplay. Fishing games are gaining popularity due to their engaging mechanics and potential for big wins.
Poker
Test your skills against other players in various poker formats. The platform offers both traditional and fast-paced poker games.
Esports Betting
Bet on your favorite esports teams and tournaments. This section caters to fans of competitive gaming who want to add excitement to their matches.
Lucky Bets and High Rollers
1Block Casino caters to all types of players, from casual gamers to high rollers. The Lucky Bets section highlights random wins, while the High Rollers section showcases impressive payouts from large bets. Whether you’re betting small or large amounts, the platform ensures fair play and exciting opportunities.
Our Community and Partnerships
1Block Casino values its community and collaborates with trusted partners to enhance the gaming experience. The platform proudly works with leading providers, ensuring top-quality games and services for its users.
Legal Information
1Block Casino is owned and operated by JogoMaster Limited, a company registered under number 15748. The company’s registered address is located in Hamchako, Mutsamudu, Autonomous Island of Anjouan, Union of Comoros.
The platform is licensed and regulated by the Gaming Board of Anjouan (License No. ALSI-152406032-FI3). 1Block has passed all regulatory compliance checks and is legally authorized to conduct gaming operations for all games of chance and wagering.
Why Choose 1Block Casino?
Diverse Game Selection : From slots to live games, there’s something for every type of player.
Transparency : All bets and payouts are clearly displayed, ensuring trust and fairness.
Crypto-Friendly : The platform supports cryptocurrency transactions, making it convenient for modern players.
Licensed and Regulated : With a valid license from the Gaming Board of Anjouan, players can enjoy a secure and legal gaming experience.
Whether you’re a fan of classic casino games or looking to explore unique options like Plinko, 1Block Casino offers a comprehensive and enjoyable platform for all gambling enthusiasts.
Создание QR кодов
Приобрести диплом университета!
Мы готовы предложить документы ВУЗов, которые расположены на территории всей России. Документы выпускаются на бумаге самого высшего качества: diy-tubes.ru/image/pgs/?poluchite_attestat_kolledzgha_s_nashey_pomoshu.html
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
Мы предлагаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам. Мы можем предложить документы ВУЗов, расположенных в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Вы сможете заказать качественный диплом от любого заведения, за любой год, включая документы СССР. Документы выпускаются на “правильной” бумаге высшего качества. Это позволяет делать настоящие дипломы, не отличимые от оригиналов. Они заверяются необходимыми печатями и штампами. Всегда стараемся поддерживать для заказчиков адекватную ценовую политику. Важно, чтобы документы были доступными для большинства наших граждан. diplompro.ru/kupit-diplom-2-2
1vin kg https://www.realistzoosafety.forum24.ru/?1-11-0-00001540-000-0-0-1742816894 .
1wln 1wln .
Best non Gamstop casinos keep me entertained—love them!
online casinos no gamstop
Создание QR кодов
1win. 1win. .
Рэпер Паша Техник находится в критическом состоянии в Таиланде
https://x.com/NargisEhme94100/status/1906094610788573414
1 вин скачать https://naigle.borda.ru/?1-17-0-00000329-000-0-0-1742816734/ .
Создание QR кодов
Купить диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы можем предложить документы ВУЗов, расположенных в любом регионе Российской Федерации.
diplomg-cheboksary.ru/diplom-kupit-texnikum-5
Non Gamstop casinos no deposit offers are my new favorite thing—sweet!
non gamstop casinos online
Создание QR кодов
https://orgnaztech.mirtesen.ru/blog/43202871346/Gde-Kazhdyiy-Gost-Osobennyiy-Otel-Glory
Non Gamstop casinos UK have such a wide variety of games—impressed!
non gamstop casino 2021
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным ценам. О преимуществах покупки документов в нашей компании
Вы заказываете диплом в надежной и проверенной временем компании. Это решение позволит сэкономить не только много средств, но и ваше драгоценное время.
Плюсов куда больше:
• Дипломы изготавливаются на настоящих бланках со всеми печатями;
• Предлагаем дипломы любых ВУЗов России;
• Стоимость намного меньше той, которую пришлось бы платить на очном обучении в ВУЗе;
• Максимально быстрая доставка в любые регионы РФ.
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании– http://mosvol.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=542/ – mosvol.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=542
https://qrkoder.ru/
Создание QR кодов
Non Gamstop casinos no deposit deals are a game-changer—wow!
new casino sites with no gamstop
https://orgnaztech.mirtesen.ru/blog/43202871346/Gde-Kazhdyiy-Gost-Osobennyiy-Otel-Glory
Создание QR кодов
1win online site https://1win12.com.ng/ .
1win на телефон http://www.familyclub.borda.ru/?1-6-0-00002163-000-0-0-1743051813 .
автоматизация бизнес-процессов
Создание QR кодов
Создание QR кодов
1win.pro http://familyclub.borda.ru/?1-6-0-00002163-000-0-0-1743051813/ .
мрстбет https://www.mostbet6006.ru .
бесплатный онлайн генератор QR кодов
1 win http://1win12.com.ng .
Что такое «Порту Пати» в Дубае и почему об этом говорят все
https://x.com/DeyanetKrmv/status/1906296026006220909
Где приобрести диплом специалиста?
Готовый диплом со всеми печатями и подписями целиком и полностью отвечает запросам и стандартам Министерства образования и науки России, никто не отличит его от оригинала – даже со специально предназначенным оборудованием. Не стоит откладывать личные мечты на потом, реализуйте их с нашей помощью – отправьте быструю заявку на диплом сегодня! Диплом о высшем образовании – не проблема! diplomv-v-ruki.ru/kupit-diplom-medrabotnika/
Покупка диплома через надежную фирму дарит массу преимуществ. Данное решение помогает сберечь как продолжительное время, так и значительные деньги. Тем не менее, преимуществ значительно больше.Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии. Дипломы производятся на настоящих бланках государственного образца. Доступная цена по сравнению с крупными затратами на обучение и проживание. Приобретение диплома института будет выгодным шагом.
Приобрести диплом: fastdiploms.com/diplom-moskva-kupit-2/
1win bets http://1win12.com.ng/ .
1win партнерка вход 1win партнерка вход .
web siteniz çok güzel başarılarınızın devamını dilerim. makaleler çok hoş sürekli sitenizi ziyaret edeceğim
1win личный кабинет 1win6020.ru .
Налаживание связей Управленческие консультации от Светланы Подкладышевой, серийного предпринимателя с более чем 20-летним опытом. Она обладает уникальной способностью анализировать сложные ситуации и предлагать практические решения, основанные на глубоких знаниях и реальном опыте. Светлана помогает оптимизировать бизнес-процессы, разработать индивидуальные стратегии роста, повысить конкурентоспособность. Например, оптимизация структуры компании, разработка бизнес-моделей, внедрение технологий.
1 win.pro http://1win6001.ru/ .
mosbet mostbet6006.ru .
1win скачать kg 1win6001.ru .
Your site is amazing, the articles are great, I will always come to this site and continue to read because you have very nice articles, thank you
Не хочется ждать — решение нужно сейчас? Тогда вам в рейтинг займов с моментальным одобрением. Онлайн займ на карту до 30 000 рублей доступен круглосуточно, без отказов и проверок. Деньги — за 5 минут.
1 win kg http://familyclub.borda.ru/?1-6-0-00002163-000-0-0-1743051813/ .
1вин приложение http://1win6001.ru .
web siteniz çok güzel başarılarınızın devamını dilerim. makaleler çok hoş sürekli sitenizi ziyaret edeceğim
web siteniz çok güzel başarılarınızın devamını dilerim. makaleler çok hoş sürekli sitenizi ziyaret edeceğim
web siteniz çok güzel başarılarınızın devamını dilerim. makaleler çok hoş sürekli sitenizi ziyaret edeceğim
Your site is amazing, the articles are great, I will always come to this site and continue to read because you have very nice articles, thank you
раскрутка сайта в топ http://www.seogift.ru/news/press-release/2463-geymifikaciya-v-prodvizhenii-internet-magazinov-kak-vovlekat-klientov-s-pervogo-kasaniya/ .
We offer a vast selection of trusted pharmaceutical products for different conditions.
This website guarantees quick and safe order processing to your location.
All products is supplied by licensed pharmaceutical companies for guaranteed effectiveness and reliability.
You can explore our online store and get your medicines with just a few clicks.
If you have questions, Customer service is ready to assist you at any time.
Take care of yourself with our trusted medical store!
https://www.linkcentre.com/review/shailoo.gov.kg/ru/vybory-oktyabr-2020_/regulations-organization-and-procedure-voting-and-establishment-voting-results-election-commissions-election-deputies-jogorku-kenesh-kyrgyz-republic/
Jestem niesamowicie rozczarowany witryna Suu. Tresci na niej sa nieaktualne, a support po prostu ignoruje wiadomosci. Procedura zamawiania to calkowity balagan: niekonczace sie bledy, powolne ladowanie i calkowity brak obslugi. Mam przekonanie, ze wlasciciele po prostu lekcewaza odwiedzajacych. Nie marnujcie osobistego czasu i nerwow, sa o wiele lepsze rozwiazania!
Very nice design and style and wonderful subject matter, absolutely nothing else we require : D.
Your site is amazing, the articles are great, I will always come to this site and continue to read because you have very nice articles, thank you
кайт школа анапа
мостбет mostbet6006.ru .
web siteniz çok güzel başarılarınızın devamını dilerim. makaleler çok hoş sürekli sitenizi ziyaret edeceğim
web siteniz çok güzel başarılarınızın devamını dilerim. makaleler çok hoş sürekli sitenizi ziyaret edeceğim
seo продвижение сайтов seo продвижение сайтов .
Your site is amazing, the articles are great, I will always come to this site and continue to read because you have very nice articles, thank you
ремонт стиральных в видном ремонт холодильников в москве недорого на дому
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
раскрутка сайта в топ http://seogift.ru/news/press-release/2463-geymifikaciya-v-prodvizhenii-internet-magazinov-kak-vovlekat-klientov-s-pervogo-kasaniya// .
Добро пожаловать на sofisimo.com, на нашем сайте вы откроете.
Погрузитесь в уникальный контент sofisimo.com, новые тренды.
sofisimo.com – ключ к вашему развитию, новые перспективы.
Платформа sofisimo.com для всех, что.
Позаботьтесь о своем образовании с sofisimo.com, находя новые знания.
Общайтесь, учитесь и развивайтесь на sofisimo.com, находить друзей.
sofisimo.com – это источник креативности, ценит.
Посетите sofisimo.com для открытия новых возможностей, ваши возможности.
sofisimo.com для любителей знаний, учиться.
sofisimo.com: соединение знаний и практики, где.
sofisimo.com: уникальный контент для всех, новые идеи.
Каждый день с sofisimo.com – это новая возможность, находить новые пути.
sofisimo.com – свяжитесь с единомышленниками, ценятся.
sofisimo.com – ключ к вашему успеху, где каждый.
sofisimo.com: ваш путь к знаниям, который.
Вступайте в сообщество sofisimo.com, источник вдохновения для всех.
Присоединяйтесь к нам на sofisimo.com, где.
Собирайте идеи на sofisimo.com, каждый день новые открытия.
sofisimo.com – платформа для инноваций, раскрыть свои таланты.
muebles elegantes https://sofisimo.com/ .
1 вин про 1win6049.ru .
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Методы управления бизнесом Управленческие консультации от Светланы Подкладышевой, серийного предпринимателя с более чем 20-летним опытом. Она обладает уникальной способностью анализировать сложные ситуации и предлагать практические решения, основанные на глубоких знаниях и реальном опыте. Светлана помогает оптимизировать бизнес-процессы, разработать индивидуальные стратегии роста, повысить конкурентоспособность. Например, оптимизация структуры компании, разработка бизнес-моделей, внедрение технологий.
бк 1win 1win6049.ru .
1 win. http://balashiha.myqip.ru/?1-12-0-00000437-000-0-0-1743258848 .
Our store provides a vast selection of high-quality pharmaceutical products to suit your health requirements.
Our platform guarantees fast and reliable order processing right to your door.
Each medication comes from trusted pharmaceutical companies for guaranteed safety and quality.
You can explore our catalog and get your medicines in minutes.
Need help? Pharmacy experts will guide you 24/7.
Take care of yourself with our trusted medical store!
https://bresdel.com/blogs/795068/Tadacip-Side-Effects-User-Experiences-and-How-to-Handle-Them
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
Your site is very nice, the articles are great, I wish you continued success, I love your site very much, I will visit it constantly
In Azerbaijan, the 12-day holiday vacation has ended https://pin.it/5XGTX4YRH
Электросчетчики с пультом Модифицированные электросчетчики, включая модели с дистанционным управлением, а также газовые счетчики, подвергшиеся изменениям с использованием магнитов или пленок, стали предметом обсуждения. В продаже доступны счетчики электроэнергии с пультом, а также сами пульты управления для счетчиков. Вопрос экономии электроэнергии приводит к поиску способов остановки учета потребления. Приобретение счетчика с пультом – одно из решений, рассматриваемых потребителями. Предлагаются к покупке как готовые электросчетчики с интегрированным пультом, так и устройства, предназначенные для модификации существующих счетчиков.
Быстрые онлайн займы на карту, подробнее на официальном сайте ссылка
Быстрые онлайн займы на карту, подробнее на официальном сайте перейти
Быстрые онлайн займы на карту, подробнее на официальном сайте ссылка
Счетчики Газа с магнитом Приборы учета с дистанционным управлением, электросчетчики, оснащенные пультом, устройства для измерения потребления электроэнергии с возможностью удаленного контроля, экономичные модели счетчиков, модифицированные приборы учета, разнообразные счетчики, газовые счетчики, подвергшиеся воздействию магнитом или пленкой, способы остановки работы счетчика, приобретение счетчика с пультом дистанционного управления, покупка электросчетчика с пультом.
кайт анапа
кайт школа анапа
Tremendous issues here. I’m very happy to look your post. Thanks so much and I am taking a look ahead to touch you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
https://webhitlist.com/profiles/blogs/1xbet-promo-code-bd-bonus-100-up-to-130
Hidden Link Placement in Established Content Hubs
Hey there! You’re likely here because you want to improve your site’s search engine ranking. Let’s face it — navigating SEO can be daunting, especially with so many “quick-fix” services out there vowing overnight success without real outcomes. That’s why I want to share my approach with you. It’s not just another generic solution — it’s a custom-tailored plan designed to deliver concrete improvements.
I specialize in building tiered authority systems that combine high-authority, mid-tier, and foundational links. Think of it like constructing a strong foundation for your house. Without a solid base, everything else crumbles. My goal is to drive authority straight to your money site in a way that aligns with search engine algorithms and actually works.
The Proof Is in the Results
To be straightforward: I’ve been in the search engine optimization industry for years, and I’ve experienced the full spectrum — the good, the bad, and the downright spammy. I’ve worked with clients who poured resources on services that claimed foolproof results but resulted in search engine bans. That’s why I decided to redefine the process.
I focus on high-quality, dofollow backlinks from authoritative websites. Over 80% of Tier 1 links in my strategy are dofollow because they offer maximum SEO value. And here’s the catch — you’ll get this premium service at significantly reduced rates (costing just 200–350 USD). Why pay more for less? Save your hard-earned cash ?? in something that delivers real ROI.
What Makes My Approach Different?
High Authority Guest Posts
I avoid low-quality directories. Nope. I curate only the top-tier platforms — websites Google prioritizes. These are the kinds of sites that elevate your domain’s credibility.
Unique, Handwritten Content
Let’s face it — spun or generic content sticks out like a sore thumb. It’s detrimental to your brand. That’s why every article I create is plagiarism-free, engaging, and tailored to your niche. Whether it’s for content hubs, I guarantee originality reports that blends seamlessly into your campaign. No shortcuts, no fluff — just high-quality writing that gets results.
Pyramid-Structured Backlinks
Here’s where things get powerful. My method goes beyond basics by incorporating Tier 2 and Tier 3 support links. This multi-phase strategy amplifies the power of your primary backlinks, driving long-term success for your money site. Picture compounding momentum, growing exponentially.
Diverse Link Sources
Search engines reward variety, so I incorporate diverse high-authority sources: content hubs, document shares, social signals. This isn’t about exploiting loopholes; it’s about creating enduring value.
Full Transparency
When you work with me, you’ll know exactly what you’re getting. I provide a comprehensive breakdown, including full administrative rights. Clear communication, no surprises. You’ll monitor each placement and their impact on rankings.
A Little Story from My Experience
A case study: A few years ago, I worked with a client who was struggling to gain traction despite countless strategies. They’d tried various “experts”, but progress stalled. When they came to me, I took the time to understand their goals. A personalized approach was implemented. Within a few months, their traffic doubled, and they achieved measurable sales growth. That’s the kind of success I strive to deliver with every client.
Time to transform your rankings! Let’s connect and let’s make Google work for you. ??
Espectro de vibracion
Equipos de equilibrado: esencial para el rendimiento fluido y productivo de las maquinarias.
En el ámbito de la ciencia actual, donde la rendimiento y la seguridad del aparato son de alta trascendencia, los aparatos de balanceo cumplen un rol esencial. Estos equipos específicos están desarrollados para calibrar y estabilizar partes dinámicas, ya sea en maquinaria de fábrica, medios de transporte de traslado o incluso en electrodomésticos hogareños.
Para los expertos en conservación de aparatos y los técnicos, trabajar con equipos de balanceo es fundamental para asegurar el funcionamiento uniforme y estable de cualquier sistema móvil. Gracias a estas opciones avanzadas avanzadas, es posible reducir sustancialmente las oscilaciones, el sonido y la presión sobre los cojinetes, aumentando la vida útil de partes importantes.
También relevante es el tarea que juegan los equipos de equilibrado en la servicio al consumidor. El soporte profesional y el mantenimiento constante utilizando estos aparatos permiten proporcionar servicios de óptima nivel, mejorando la agrado de los compradores.
Para los dueños de emprendimientos, la financiamiento en unidades de ajuste y detectores puede ser fundamental para aumentar la efectividad y eficiencia de sus sistemas. Esto es sobre todo relevante para los inversores que gestionan reducidas y pequeñas emprendimientos, donde cada elemento vale.
Por otro lado, los equipos de calibración tienen una gran utilización en el área de la fiabilidad y el supervisión de calidad. Permiten encontrar eventuales problemas, evitando mantenimientos onerosas y problemas a los dispositivos. Incluso, los resultados obtenidos de estos sistemas pueden aplicarse para maximizar métodos y aumentar la exposición en motores de búsqueda.
Las zonas de aplicación de los equipos de ajuste incluyen variadas sectores, desde la fabricación de bicicletas hasta el monitoreo del medio ambiente. No importa si se habla de importantes producciones manufactureras o reducidos espacios hogareños, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para asegurar un desempeño óptimo y sin paradas.