Electric vehicle cost analysis is essential for prospective buyers looking to understand the financial implications of owning an EV. While the initial purchase price of electric vehicles can be higher than that of traditional gas-powered cars, numerous factors contribute to overall savings over time. First, EVs typically have lower fueling costs; charging an electric vehicle is generally cheaper than gasoline, especially when utilizing home charging options. Additionally, maintenance costs for electric vehicles tend to be lower, as they have fewer moving parts and do not require oil changes, which can lead to significant long-term savings.
Insurance rates can also vary, but many companies offer discounts for electric vehicles due to their lower risk profiles. Furthermore, government incentives, rebates, and tax credits can substantially reduce the upfront costs of purchasing an EV. By considering these various factors, potential buyers can gain a clearer understanding of the true cost of ownership and make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.

Electric vehicle cost analysis is a critical component for anyone considering the switch from a traditional gasoline vehicle to an electric vehicle (EV). As the automotive market evolves and more consumers prioritize sustainability, understanding the financial implications of owning an electric vehicle becomes increasingly important. Initially, the purchase price of electric vehicles can be a deterrent for potential buyers, as EVs typically come with a higher upfront cost compared to their internal combustion engine counterparts. However, this electric vehicle cost analysis must take into account various factors that can lead to significant savings over time. For instance, many governments and local authorities offer incentives, rebates, and tax credits specifically designed to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles.
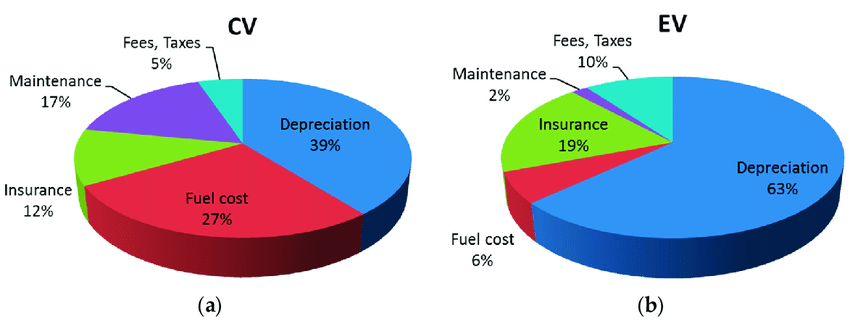
These financial incentives can substantially reduce the purchase price, making EVs more accessible to a broader audience. The potential for lower fuel costs is another significant aspect of this analysis. Charging an electric vehicle is generally much cheaper than refueling a gasoline car. On average, the cost to charge an EV at home can range from $1 to $2 for a full charge, providing a range of 200 to 300 miles depending on the vehicle model. This starkly contrasts with fluctuating gasoline prices, which can add up quickly for drivers who commute regularly. For those who can take advantage of time-of-use electricity rates, charging during off-peak hours can further lower expenses, making it even more economical to own an electric vehicle.
Maintenance costs also play a significant role in the overall electric vehicle cost analysis. Electric cars typically require less maintenance than traditional vehicles due to fewer moving parts and the absence of complex systems such as fuel injection and exhaust systems. For example, EVs do not require oil changes, fuel filters, spark plugs, or exhaust system repairs, which can save drivers a considerable amount over the lifespan of the vehicle. Instead, the primary maintenance concerns are often limited to tires, brakes, and occasional battery checks. Many manufacturers also offer warranties that cover battery performance for eight years or more, providing additional peace of mind regarding the longevity of the vehicle’s most critical component. Insurance rates can also vary when it comes to electric vehicles, adding another layer to the cost analysis.
While some insurers may initially charge higher premiums for EVs, many now offer discounts, recognizing the lower risk profile and potential for reduced claims associated with electric cars. This shift means that, depending on the model and the driver’s location, insurance costs may not be as high as some expect. Additionally, as electric vehicles become more mainstream, competition among insurers is likely to result in better rates, making EV ownership more financially viable. Another important consideration in electric vehicle cost analysis is the potential for increased property value. Homeowners who invest in electric vehicles may find that adding a Level 2 home charging station not only improves convenience but also enhances the desirability of their property.
As electric vehicle adoption grows, having charging capabilities could be an attractive feature for future buyers. The expansion of charging infrastructure across many regions further supports the practicality of owning an EV. Public charging stations are becoming more prevalent, with many cities investing in fast-charging networks to accommodate the growing number of electric vehicles on the road. This accessibility alleviates concerns about range anxiety, which has been a significant barrier to EV adoption. Many public chargers offer free or low-cost charging options, while others operate on a pay-per-use basis or offer subscription services that provide unlimited charging for a monthly fee. Understanding these costs is crucial for potential EV owners when conducting their electric vehicle cost analysis. Additionally, resale value is an essential factor to consider.
While early electric vehicle models tended to depreciate more quickly than gasoline cars, recent trends show stabilization in resale values as technology improves and the market matures. Factors such as battery condition, mileage, and brand reputation play crucial roles in determining resale value, but many electric vehicles are proving to be a sound investment over time. The overall electric vehicle cost analysis should also consider the societal benefits associated with EV ownership. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, electric vehicles contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions and improved air quality, aligning with many consumers’ values regarding sustainability.
The financial implications of owning an electric vehicle, combined with the positive environmental impact, make a compelling case for many buyers. In conclusion, electric vehicle cost analysis encompasses various elements, including purchase price, charging expenses, maintenance, insurance, and resale value. While the initial investment may seem daunting, the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance, coupled with government incentives and the evolving market landscape, present a more favorable picture. By conducting a thorough electric vehicle cost analysis, potential buyers can better understand the financial commitment involved and make informed decisions that align with their personal and financial goals. As electric vehicles continue to gain traction in the market, the cost-benefit analysis will increasingly highlight their attractiveness as a viable and sustainable transportation option, ultimately shaping the future of mobility.

















Garanti zayıflama yöntemi SEO çalışmaları sayesinde Google’da daha görünür hale geldik. http://www.royalelektrik.com/