State incentives for electric cars play a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of eco-friendly transportation options and fostering a sustainable automotive industry. These incentives encompass a variety of financial and non-financial benefits designed to make electric vehicles (EVs) more affordable and attractive to consumers, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting energy independence.
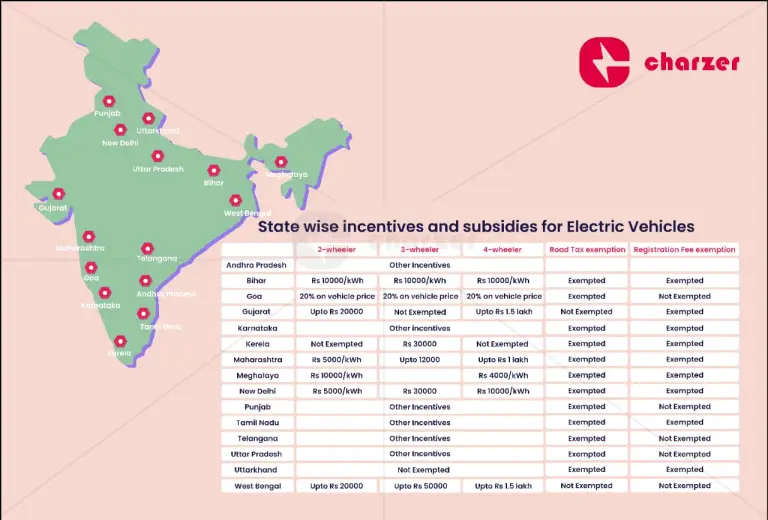
One of the most common forms of state incentives for electric cars is financial incentives, which typically include tax credits, rebates, grants, and exemptions. Tax credits provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in the amount of taxes owed by EV purchasers, effectively lowering the upfront cost of buying an electric car. These credits vary by state and can range from several hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on factors such as battery size and vehicle type. Rebates, on the other hand, provide a direct cash incentive to consumers who purchase or lease an electric vehicle, encouraging more immediate uptake of clean transportation options. States may also offer grants to support the installation of electric vehicle charging infrastructure or to incentivize fleet electrification initiatives.
In addition to financial incentives, many states offer non-financial benefits to electric car owners to enhance the overall value proposition of owning an EV. These benefits often include access to high-occupancy vehicle (HOV) lanes, reserved parking spaces in public lots, and reduced or waived fees for vehicle registration and tolls. Access to HOV lanes can significantly reduce commute times for electric car drivers, particularly in congested urban areas where traffic congestion is a common concern. Reserved parking spaces equipped with charging stations provide convenience and peace of mind to EV owners, ensuring they have access to necessary charging infrastructure when needed.
Furthermore, states may implement special programs and initiatives aimed at promoting electric vehicle adoption and infrastructure development. These programs can include partnerships with utility companies to offer discounted electricity rates for EV charging during off-peak hours, public awareness campaigns to educate consumers about the benefits of electric cars, and support for the expansion of public charging networks. By fostering a supportive ecosystem for electric vehicles, states can create a conducive environment for manufacturers, dealerships, and consumers to transition towards cleaner and more sustainable transportation solutions.
The impact of state incentives for electric cars extends beyond individual consumers to include businesses, municipalities, and public institutions. Many states offer incentives for fleet electrification, providing financial assistance and technical support to businesses and government agencies seeking to integrate electric vehicles into their vehicle fleets. These incentives help reduce operating costs, improve air quality, and demonstrate leadership in sustainable practices. Additionally, states may partner with local utilities and private sector stakeholders to develop innovative financing mechanisms and incentive programs that facilitate the deployment of electric buses, trucks, and other commercial vehicles.
However, the effectiveness of state incentives for electric cars can vary depending on several factors, including funding availability, program design, and consumer awareness. Some states may face challenges in securing adequate funding for incentive programs or may struggle to maintain consistent support due to budgetary constraints or political considerations. Moreover, the complexity of navigating different incentive programs across states can create barriers for consumers and businesses seeking to take advantage of available benefits.
Despite these challenges, state incentives for electric cars continue to play a critical role in shaping the future of transportation and advancing sustainability goals. As technology advances and costs decline, electric vehicles are becoming increasingly competitive with conventional vehicles in terms of purchase price, range, and performance. State incentives complement federal incentives, such as the federal electric vehicle tax credit, to further reduce the cost barrier and accelerate the transition to electric mobility.
In conclusion, state incentives for electric cars are essential tools for promoting the adoption of clean and energy-efficient transportation options. By offering financial incentives, non-financial benefits, and supporting infrastructure development, states can encourage consumers, businesses, and municipalities to embrace electric vehicles as viable alternatives to traditional gasoline-powered cars. As state governments continue to prioritize sustainability and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, incentives for electric cars will play a crucial role in building a greener and more resilient transportation system for future generations.


















Hmm it appears like your website ate my first comment (it was super long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I wrote and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I as well am an aspiring blog blogger but I’m still new to the whole thing. Do you have any tips and hints for beginner blog writers? I’d definitely appreciate it.
A bench is pretty versatile, because it lets you practice your entire body
with movements like single-leg lunges, incline and decline
push-ups, chest presses, and triceps dips. You can broaden your exercise options further by adjusting the angle of the bench as properly.
Chest exercises remain the identical for women and men, but the fascinating physical characteristics of female and
male our bodies are totally different. Additionally,
women and men equally benefit from exercising their chests due to the enhancements
in stability and posture. It’s important to determine private health objectives so that you simply exercise with
the suitable intensity to avoid injury or overworking your muscles.
Chest workouts are important for a well-rounded fitness routine that
builds higher body energy and tones muscle tissue.
The motion of a barbell bench press targets the chest muscle tissue,
shoulders, and triceps. The barbell bench press is
a extremely efficient train for growing upper body energy, and stimulates muscle development and strength positive aspects in the chest.
By engaging a quantity of muscle groups simultaneously,
the barbell bench press promotes the development of muscle mass
and an aesthetic physique within the higher body. The strength gained from the barbell bench press carries over to everyday actions and sports
activities that require pushing or urgent actions.
The TRX Chest Press-Flye Combo is essentially a Push-up on one aspect and a Flye on the
other. Overall, you can think of this one as an upper-inner chest train. Nice for both chest and again, the dumbbell pullover activates much of
the chest from a slightly uncommon angle, whereas preserving
arm rotation so you’re still hitting your inside chest. This variation of
the essential cable fly provides a bit more shoulder and
decrease chest, while still emphasizing the
inside chest – or in different words, the lower-inner chest.
For me, these workouts deliver higher results without the shoulder dangers that include the standard bench press.
When performing chest workout routines, you’ll be hitting every area of the chest rather than one by one.
Enhanced chest muscle tissue achieved by way of the
highest 10 isolated chest exercises can considerably contribute to improved sports activities efficiency by enhancing upper body strength and
power.
The pin press and the dead press are two similar workout routines the place you don’t place the barbell in your chest but quite on raised safeties.
The chest is made up of the pec major, pec minor, and serratus anterior.
As you decrease yourself down to the bottom of the motion you’re going
to hold a difficult isometric place. It’s this isometric position that adds to the effectiveness of this TRX chest builder.
Nevertheless, plenty of guys are responsible of following the same chest-building workout for weeks,
months, or even years at a time. Beginning position for this cable
chest train is with the cables set to a low angle, standing with toes flat
on the bottom and palms grabbing every of the handles.
Our arms will undergo a low to excessive arc, and we’re not going to
stop where we might on an Incline Bench Press.
You can perform a push-up using solely the remaining hand, then swap arms and repeat.
Transfer far enough away from the wall so you have room to decrease in course of
it. Push your higher physique off the ground while keeping your hips and thighs on the floor.
Get your form proper first, then gradually do more over time by adding reps or units.
Normally, we advocate doing a quantity of good workouts per
muscle group. But within the case of the shoulder muscular tissues, we are
basically taking a glance at three completely different muscular tissues in one.
References:
bad effects of steroids (git.smartenergi.org)
Nevertheless, the Velaasa Strakes match nice, so they’re still
a selection even if you have bigger feet. Talene Appleton is the fitness editor at
Women’s Well Being, the place she nerds out over all issues fitness, diet, and wellness.
She was previously the health and commerce editor at Men’s
Health, where she examined and reported on the newest, buzziest
fitness and wellness products to hit the market.
As a NASM-certified private coach and Precision Nutrition-certified nutrition coach, she is passionate about supporting girls at the intersections of health, food, and group.
Earlier Than coming into journalism full-time, Talene was a personal chef for
four years and nonetheless enjoys cooking for and internet hosting family and friends often.
It Is urban-environment approved, with a 4mm sole to guard your foot from whatever could additionally
be in your path and further lamination around the toe for an added buffer from
the setting. We love that the upper is constructed of eco mesh, produced from recycled plastic bottles.
Weightlifting shoes can present some advantages for newbies, however any well-fitting,
supportive sneaker will do to get began. There are a couple of things to maintain in mind in relation to choosing
the right weightlifting shoe for you. “You are going to want a shoe that has a hard sole, an elevated heel, and a few lateral assist,” says Sean Waxman, C.S.C.S., head coach and owner of Waxman’s Health Club.
The Nike Metcon eight is a versatile, sturdy, and supportive option for a wide range of weightlifting and cross-training actions.
It has a slight heel-to-toe drop, which makes it a great match for any routine in which you’re combining energy coaching with different actions, such as working.
Many weightlifting footwear today have zero.86″ heels, which makes hitting the underside positions on snatches and cleans easier.
Larger heels are additionally better when you have poor ankle mobility (you
can’t comfortably sit in a barefoot full squat). They are a method to enhance ankle mobility to optimize performance when squatting or performing olympic lifts.
The Adipower IIIs are the best weightlifting footwear for men and women who need extra support.
Their heel height is much like the Reebok Legacy Lifter II but higher than the Nike Romaleos 4.
The toe field is also extra spacious than most,
contributing to a secure expertise. With a neutral toe box and a Flexweave higher,
the Nano X3 is comfortable and suits true to size. I’m impressed with the
overall quality and love the different colorways. In my experience, the Reebok Nano X3 is
the most well-rounded shoe for CrossFit. Furthermore, Reebok’s Floatride Vitality Foam performed nicely
in my testing.
If you’re sporting the mistaken shoe for squats and deadlifts you’re
leaving the weight on the platform. With
this type of lifting, you have to have solid, stable, no-nonsense contact with
the ground and for this reason Converse Chuck
Taylor’s have been in style deadlift sneakers for therefore
lengthy. They’re great at creating most push by getting probably the most out of your lower legs.
For a long time, it was Chuck Taylors or bare ft
however that’s not the case anymore. Best shoes for lifting weights and
working must be sturdy, steady and flat but gentle on the
cushioning in order to help your ft do what 3 million years of
evolution designed them to do.
Then you probably can get away with one thing that’s slightly stiffer because
you won’t be moving a lot and don’t need that flexibility.
You may want something that’s really responsive so your feet aren’t killing
you on the finish of the day. Nike’s Metcon series is a
perpetual beast in the fitness center, and the 9 continues to improve upon the shoe’s near perfection. They’re great for basic lifting,
too, because the lace-lock system keeps everything out of the way.
Most importantly, your foot feels steady, safe, and in place,
with sturdy sturdiness to match no matter a session throws at
you—all without having to throw in some additional insoles in there.
Once you’ve found the proper size, the 2 adjustable straps
over the laces will lock you in for the journey and give
you plenty of stability to power by way of your heavy lifts.
These straps aren’t as heavy obligation and as premium because the
Adipower IIIs, but with two buckling you in, you’ll definitely be feeling safe.
The high-density TPU heel and midsole of the Adipower III offer you
incredible assist and stability on squats and cleans.
The technical shoe set-up offers you nice load bearing potential and unbelievable power switch
during your lifts. The rubber outsole offers optimal traction to promote stability and support, and the elevated heel can help you get into a great place for squats.
It’s also essential to contemplate the match of the shoe,
as a poorly becoming shoe can result in discomfort and
even injury. Look for footwear with a wide
toe field and a snug fit across the midfoot and heel. In conclusion, the
Nike Men’s Metcon 7 Coaching Shoe is a top-of-the-line weight training shoe that delivers
on its promise of stability, consolation, and performance.
Weightlifting footwear are great for squats as they provide
impressive assist and a higher range of movement so your ankles
can flex appropriately to fulfill the calls for of your squatting exercises.
Many weight lifters like squat shoes that work for deadlifts,
too, as they permit for extra versatile workouts and
effectivity within the health club, quite than needing
to focus on just one workout at a time. You can carry weights with common runners,
and loads of individuals do, but lifting sneakers
take the help and stability to the following degree, serving to you get a deeper vary of movement with out damage.
Whereas weightlifting sneakers usually are not essential for weightlifting, they are recommended because of the excessive degree
of assist and safety they provide.
References:
https://huayutianchengplus.top:2300/sherlenedejesu
http://sunnyoushop.com:7001/odessan2775051
http://shenchenyang.top:8089/willisbenn5945
https://git.epochteca.com/susannamcphers
https://syq.im:2025/hattiebrowne7
https://www.lshserver.com:3000/magdaesters487
http://git.eyesee8.com/irah4635125155
https://git.arachno.de/heribertoewing
https://git.gra.phite.ro/yasminsampson
https://git4edu.net/boycedecicco03
http://gitlab.dev.jtyjy.com/onitashifflett
http://git.huxiukeji.com/angelowalsh306
https://git.xhkjedu.com/adelegrimwade
https://git.ascarion.org/caren38m998179
https://git.9ig.com/danielaedkins
https://www.lshserver.com:3000/magdaesters487
Though the chest is the least lively muscle group in the flooring press, it
is nonetheless used as the primary mover. We will have essentially the most energetic chest
when we lower the bar, since it has a role in stabilizing the trajectory
of the bar and slowing down earlier than the elbows hit the bottom.
Also, the chest might be more active if we select to raise our elbows immediately stacked
beneath the bar as a substitute of doing a slight bend in the elbows.
As it is a multi-joint train in which we’re allowed to work with high hundreds, it will be an excellent train to realize energy.
This exercise lets you load more weight than different comparable workouts such because the bench press.
Machine chest presses are an efficient assistance movement for the chest and triceps.
Like the ground press, chest presses offer a fair quantity of control, resulting in good muscle
activation. A notable good thing about the chest press is
that you simply don’t have to fret about steadiness and all your effort goes into pressing the load.
Nonetheless, it’s essential to note that reducing the bar an excessive amount
of can cause shoulder points for some individuals, a problem that isn’t as probably during a ground
press. Another distinction is that your vary of motion is restricted
during the flooring press than on the bench press. When doing a flooring press,
you’ll have the ability to solely move the bar down until your
triceps attain the floor, limiting the quantity you presumably
can stretch your pecs.
Do reps utilizing light weights to increase muscular endurance, resting only seconds between units.
It is particularly valuable whenever you both don’t have a bench, otherwise
you need to protect your shoulder joint from a deeper range of motion. The
decline bench press emphasizes your decrease pecs, correctly referred to as the sternal head of pectoralis major.
Get all the bench press benefits with as few drawbacks and
risks as attainable by doing them correctly. Firstly, you need to bench press with a
spotter shut at hand in order that when you can not complete a rep, you won’t find yourself pinned underneath an infinite weight.
While the bench press is a protected and effective train, there are a couple of things to contemplate when doing this exercise that would have an effect on your
safety. As A Outcome Of, during this exercise, you’re on a stable, flat bench, you would possibly
be free to focus virtually exclusively on reducing and raising the
bar.
Precisely proper, the floor press is affected lots by your proportions as you said.
Some folks have the bar touching their chest whereas others have the bar positioned a
few inches above. The ROM on my floor press is only 2-3″ of my bench. Its a god raise and is an effective information to my general urgent power. The floor press is an exercise that serves as a substitute for the bench press and that, relying on our goals, we will benefit to a larger or lesser extent from it.
It’s a compound movement that targets a quantity of muscle teams, including the chest, shoulders, and triceps. It offers a unique set of advantages that might make it a more smart choice for some lifters. Each the bench press and incline bench press are effective workouts for constructing upper body energy and energy. The bench press is usually used as a benchmark for measuring upper body strength, because it allows you to carry heavier weights in comparability with the incline bench press. Nonetheless, the incline bench press can help enhance shoulder stability and general upper physique power, making it a useful addition to your exercise routine.
The bench press engages a wider vary of muscular tissues, including the pectoralis main (sternal and clavicular heads), triceps, and anterior deltoids. The bench press is a traditional upper-body carry that has been utilized by athletes and bodybuilders for close to a century. The traditional bench press is carried out on a flat bench, however you need to use an incline bench press so as to goal your upper pecs somewhat bit extra. Different common bench press variations are the dumbbell bench press, floor press, and smith-machine bench press.
The quest for a powerful, sculpted chest is a standard aim for lots of fitness enthusiasts. Two exercises that persistently prime the record for chest development are the bench press and the dumbbell press. Whereas each are efficient, understanding their nuances may help you choose the best option for maximizing hypertrophy. With a entice bar, your wrists are locked into place and stacked directly over the elbows in the course of the raise. This secure position minimizes the danger of a wrist damage even throughout more wrist-heavy variations like close-grip bench presses. The bench press supplies larger stability and assist than the seated chest press.
References:
https://voovixtv.com/@leomalemberg95?page=about
https://iflirt.app/@thanhfihelly5
https://movieby.com/@adelinea126774?page=about
https://datez.pro/@amadotuckfield
https://www.nemusic.rocks/elizareginald
https://megapersonals18.com/@staceyfortin3
https://spinvai.com/karolynmauriel
https://www.statusvideosongs.in/@fredaharkins6?page=about
https://malesandfemales.com/@darrellstoltz
https://www.propose.lk/@shawnisenberg
https://sound.digiboo.ru/tia36866085692
https://my.buzztv.co.za/@faustinolarocc?page=about
https://www.trappmasters.com/karolynbelisar
https://dzmariage.com/@franklinshiple
https://nouzwen.com/@micah977152923
https://natgeophoto.com/jenniferbalke6
Customers also recognize the components, digestion, and calorie content.
Each plant-based and animal-based proteins have their unique
advantages and may play a vital role in a balanced food plan. Your alternative should align together with your dietary preferences, well being targets,
and ethical considerations.
Blends are greatest for individuals who need to reap the benefits from having a number of sources of protein included in a single handy powder.
Whey concentrates are the most typical type of protein seen on shops cabinets.
Compared to isolates, concentrates go through fewer filtration steps with the tip product being anywhere from 25-80% pure protein and containing more fat,
carbs and lactose. This is priced proper within the normal vary for creatine supplements and
is a good value overall contemplating the quality.
I get bodywork accomplished 5 days per week, including stretching, delicate tissue work and sometimes cupping.
If you are trying to gain muscle, lose fat, or just tone up, protein is going to be
your biggest ally. As A End Result Of protein repairs and builds your muscle
tissue after each workout. Keep In Mind, it’s not about working harder—it’s
about fueling your physique smarter. With the right diet, dietary supplements, and a solid workout plan, your exhausting work will pay off.
If you’re placing within the work but not seeing outcomes, it doesn’t
mean you’re doing every thing wrong. It simply
means there are probably small adjustments that can make a massive impact.
Throughout the winter, there is not any shortage of chilly
weather activities to choose from. You would possibly go snowboarding, skating, snowshoeing,
sledding or simply take your walk or run outdoors.
A examine in the Journal of Scientific Endocrinology & Metabolismfound that chilly climate workouts may burn more energy compared to these accomplished in heat climate.
Q. Who has inspired you to maintain pursuing your ardour for sand volleyball?
Completely Different folks have impressed me at completely different points in my profession for varied causes.
This course of further provides many biologically active compounds that have direct immune and physiological advantages.
However, it does not elevate amino acidlevels in the blood to the extent whey proteins do.
Micellar casein, as opposed to caseinate, is isolated from milk by filtration quite
than by use of acid or warmth. This filtration method preserves the structural
integrity of the protein and supplies many biologically active compounds that have direct immune and physiological benefits.
This means your muscular tissues are fed with essential vitamins all through the evening, which is essential for recovery and
development. To get the most out of the finest whey protein for muscle gain and restoration, timing
and consistency are key. The finest time to eat whey protein is within half-hour after a workout, as that
is when muscular tissues are most receptive to nutrient absorption. Mixing a scoop of whey
protein with water, milk, or a smoothie provides the body with the required amino acids for optimal recovery.
One of the most important advantages of whey protein is its fast digestion price.
Not Like other protein sources that take longer to interrupt down,
whey is absorbed within 30–60 minutes, making it a perfect
post-workout supplement.
This might help to improve power ranges, scale back fatigue, and improve performance during exercises.
Muscle Feast one hundred pc Whey Protein is all pure, and doesn’t use any fillers
or artificial components in its whey protein powders.
It is sweetened with stevia and makes use of sunflower
lecithin as an emulsifier.
Muscle Feast uses a high-quality whey concentrate with a purity rate of
70-80%. Jack Cincotta is an authorized holistic health coach via AFPA
and a board-certified holistic well being practitioner by
way of AADP. He has written hundreds of articles on nutrition and supplementation. Degree in Psychology and is passionate
about researching the science behind diet.
He typically makes use of research-backed supplementation protocols for
so much of of his clients to optimize outcomes.
General, Muscle Feast one hundred pc Whey Protein has acquired constructive critiques from customers for its taste, effectiveness, value, and
high quality. Customers appreciate the low calorie content, good protein ratio, and nil bloating.
The taste just isn’t too strong and makes smoothies gentle and
fluffy. Not only will hitting your daily beneficial consumption allow
you to preserve your present state of being, it may even improve your
overall health. You’ll have to extend your water consumption if you’re exercising or residing in a
warmer region to avoid dehydration. When you’re not in tune with when it’s time to
stop consuming, you are more likely to overeat.
References:
https://git.sayndone.ru/lottielomas382
https://git.revoltsoft.ru/sanoratruman4
http://git.hjd999.com.cn/jonathanmilam
http://git.agdatatec.com/kory19h1540536
https://gitea.cattysteve.top/ojflurlene6864
http://www.hldcloud.cn:3000/guadalupedobbi
https://year2048.top:3001/nanniegrayson
https://git.aerbim.com/sherriguest414
https://git.xindongtech.com/cleo1798239470
https://www.appleradish.org/monterix154661
https://git.laser.di.unimi.it/laurenwooley06
https://git.inoe.ro/mindaulmer102
https://blog.haxeho.top/meri6136188810
https://git.hmt.im/dakotadsr47138
https://git.aerbim.com/maureenmckibbe
https://gitea.mpc-web.jp/kathydobos8588
70918248
References:
female steroids side effects (http://www.9miao.fun)