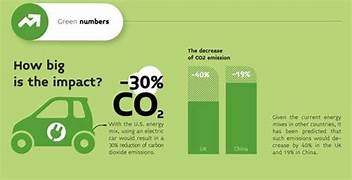
Electric cars are heralded as a transformative solution in the quest for sustainable transportation, offering substantial environmental benefits compared to conventional gasoline-powered vehicles. At the core of their appeal lies their ability to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, a critical factor in combatting climate change. Unlike internal combustion engines that burn fossil fuels and emit carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants directly into the atmosphere, electric cars operate primarily on electric motors powered by rechargeable batteries. When these batteries are charged using electricity from renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydroelectric power, the vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, effectively reducing their carbon footprint to nearly nil during operation. Even when charged from the grid, which may still rely on fossil fuels in some regions, electric cars generally emit fewer greenhouse gases over their lifetime compared to their gasoline counterparts.
Beyond CO2 emissions, electric cars contribute to improved air quality, particularly in urban areas where vehicle emissions are a significant contributor to air pollution. Traditional vehicles emit pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which have detrimental effects on human health and the environment. Electric cars produce no tailpipe emissions, thereby reducing local air pollution levels and mitigating the health risks associated with poor air quality. This reduction in emissions is especially beneficial in densely populated cities where vehicle traffic is a major source of pollution-related health issues.
In addition to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality, electric cars also play a role in reducing noise pollution. Unlike internal combustion engines, electric motors operate silently, contributing to quieter urban environments. This reduction in noise levels can enhance the quality of life for residents, especially in areas where traffic noise is a persistent issue.
Another environmental benefit of electric cars is their potential to lower overall energy consumption. Electric motors are inherently more efficient than internal combustion engines, converting a higher percentage of energy from the battery into driving force. This increased efficiency translates into lower energy consumption per mile traveled, which is beneficial for reducing overall energy demand and associated environmental impacts.
Moreover, electric cars contribute to energy security by diversifying the sources of energy used for transportation. By reducing reliance on imported oil and other fossil fuels, countries can enhance their energy independence and resilience to supply disruptions and price volatility in the global oil market. The shift towards electricity as a transportation fuel also aligns with efforts to transition to renewable energy sources, further promoting a sustainable energy future.
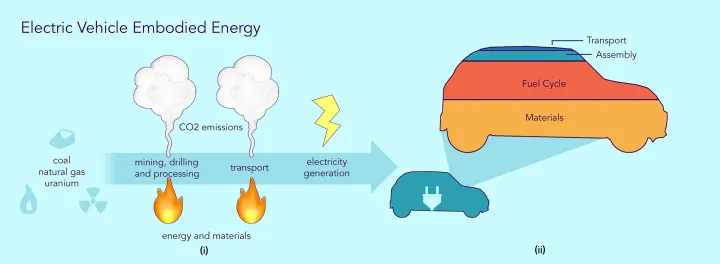
However, it’s essential to consider the full lifecycle environmental impacts of electric cars, including the manufacturing, use, and disposal phases. While electric cars produce no emissions during operation, their production process involves energy-intensive activities such as mining raw materials (e.g., lithium, cobalt) for batteries, manufacturing components, and assembling the vehicle. These activities can generate greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental impacts, depending on factors such as energy sources, production methods, and waste management practices.
Additionally, the disposal or recycling of electric vehicle batteries presents environmental challenges that require careful management. Batteries contain valuable materials that can be recycled, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, but they also pose potential environmental risks if not handled properly. Efforts are underway to develop efficient recycling technologies and sustainable battery disposal practices to minimize environmental pollution and maximize resource recovery.
Despite these challenges, ongoing advancements in technology and sustainability practices continue to improve the environmental performance of electric cars. Innovations in battery technology, such as the development of solid-state batteries and improved recycling processes, aim to enhance the efficiency, durability, and sustainability of electric vehicles. Moreover, policies and incentives that promote the adoption of electric cars and support renewable energy sources are crucial in accelerating the transition towards a low-carbon transportation system.
In conclusion, electric cars have a profound environmental impact by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving air quality, lowering energy consumption, and enhancing energy security. While challenges remain, such as the environmental impacts associated with battery production and disposal, the overall benefits of electric cars in mitigating climate change and advancing sustainable transportation solutions are significant. As technology continues to evolve and policies support the transition to cleaner vehicles, electric cars are poised to play an increasingly vital role in achieving global climate goals and creating a more sustainable and resilient transportation system for future generations.

















You have brought up a very fantastic points, thanks for the post.